Abstract
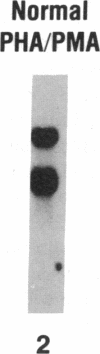
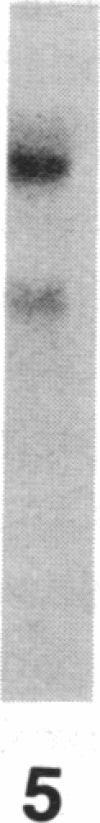
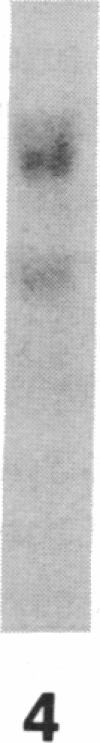
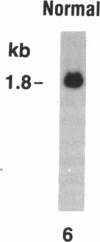
Current concepts of the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis suggest that the expanded numbers of activated T-helper/inducer cells at sites of disease activity result, at least in part, from their proliferation in the local milieu. Normal clonal proliferation of T cells involves activation and expression of the IL 2 receptor (IL 2R) gene. Thus, knowing that IL 2R mRNA transcripts are relatively long lived, we hypothesized that sarcoid blood T cells may contain IL 2R mRNA transcripts and express functional surface IL 2R, although the cells are probably activated elsewhere. Northern analysis using a 32P-labeled cDNA probe for the IL 2R p55 protein demonstrated that blood T cells of patients with active sarcoidosis, but not of normal patients, express 3.5- and 1.5-kb IL 2R mRNA transcripts, the same as those observed in normal T cells activated in vitro. Consistent with this, using flow cytometry and an MAb directed against the IL 2R p55 protein (2A3), we observed detectable levels of IL 2R surface protein on increased numbers of blood T cells of active sarcoidosis patients (4.7 +/- 0.9%) compared with blood T cells of normal patients (0.9 +/- 0.2%). Importantly, when the sarcoid blood T cells were exposed to IL 2 in vitro, they proliferated at a rate greater than that of normal blood T cells under the same conditions, suggesting that the IL 2R spontaneously expressed by sarcoid blood T cells were functionally active. In the context of the known compartmentalization of spontaneous IL 2 production and T cell proliferation at sites of disease in active pulmonary sarcoidosis, these IL 2R positive blood T cells would probably have a proliferative advantage if they trafficked to sites of active sarcoidosis, such as the lower respiratory tract.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer W., Gorny M. K., Baumann H. R., Morell A. T-lymphocyte subsets and immunoglobulin concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage of patients with sarcoidosis and high and low intensity alveolitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Nov;132(5):1060–1065. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.5.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C., Scollay R. G., Weissman I. L. Organ specificity of lymphocyte migration: mediation by highly selective lymphocyte interaction with organ-specific determinants on high endothelial venules. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jul;10(7):556–561. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. Transient expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Consequences for T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1895–1911. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin W., Hay J. B. A comparison of lymphocyte migration through intestinal lymph nodes, subcutaneous lymph nodes, and chronic inflammatory sites of sheep. Gastroenterology. 1980 Dec;79(6):1231–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costabel U., Bross K. J., Rühle K. H., Löhr G. W., Matthys H. Ia-like antigens on T-cells and their subpopulations in pulmonary sarcoidosis and in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Analysis of bronchoalveolar and blood lymphocytes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):337–342. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniele R. P., Dauber J. H., Rossman M. D. Immunologic abnormalities in sarcoidosis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Mar;92(3):406–416. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-3-406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. L., Faust J., Pessano S., Daniele R. P., Rovera G. Differentiation and activation phenotypes of lung T lymphocytes differ from those of circulating T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):60–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI111977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Krönke M., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Augmented T cell growth factor receptor expression in HTLV-1-infected human leukemic T cells. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1691–1695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Rocha B., Coutinho A. A. Lymphocyte population kinetics in the mouse. Immunol Rev. 1986 Jun;91:5–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulmer J. D., Roberts W. C., von Gal E. R., Grystal R. G. Small airways in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Comparison of morphologic and physiologic observations. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):595–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI108811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWANS J. L., KNIGHT E. J. THE ROUTE OF RE-CIRCULATION OF LYMPHOCYTES IN THE RAT. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Jan 14;159:257–282. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. A cell-surface molecule involved in organ-specific homing of lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):30–34. doi: 10.1038/304030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Andrus L., Steinman R. M. Lymphokine and nonlymphokine mRNA levels in stimulated human T cells. Kinetics, mitogen requirements, and effects of cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):922–937. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The mouse gut T lymphocyte, a novel type of T cell. Nature, origin, and traffic in mice in normal and graft-versus-host conditions. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1661–1677. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Brenner M. B., McLean J. M., Strominger J. L. Antigenic stimulation regulates the level of expression of interleukin 2 receptor on human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann F., Cannistra S. A., Levine H., Griffin J. D. Expression of interleukin 2 receptors and binding of interleukin 2 by gamma interferon-induced human leukemic and normal monocytic cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Bedell G. N., Zavala D. C., Monick M., Brady M. Role of interleukin-2 release by lung T-cells in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Oct;128(4):634–638. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.4.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Mechanisms of hypergammaglobulinemia in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Site of increased antibody production and role of T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):86–92. doi: 10.1172/JCI110036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: a disorder mediated by excess helper T-lymphocyte activity at sites of disease activity. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 20;305(8):429–434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108203050804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Young R. C., Jr, Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Maintenance of granuloma formation in pulmonary sarcoidosis by T lymphocytes within the lung. N Engl J Med. 1980 Mar 13;302(11):594–598. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198003133021102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S., Reichert R. A., Gallatin W. M., Bargatze R. F., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. Homing receptors and the control of lymphocyte migration. Immunol Rev. 1986 Jun;91:39–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S., Steere A. C., Fox R. I., Butcher E. C. A distinct endothelial cell recognition system that controls lymphocyte traffic into inflamed synovium. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):556–558. doi: 10.1126/science.3726548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Expression of cell-cycle-dependent genes in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5375–5379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataria Y. P., Padgett R. C., English L. S. Spontaneous production of interleukin-2 in the supernatants of cultured cutaneous sarcoidal granulomas. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;465:157–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb18491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. A., Hunninghake G. W., Line B. R., Crystal R. G. The alveolitis of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Evaluation of natural history and alveolitis-dependent changes in lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Aug;128(2):256–265. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.2.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. R., Kagnoff M. F. Nonspecific recruitment of cytotoxic effector cells in the intestinal mucosa of antigen-primed mice. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1931–1936. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence E. C., Berger M. B., Brousseau K. P., Rodriguez T. M., Siegel S. J., Kurman C. C., Nelson D. L. Elevated serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptors in active pulmonary sarcoidosis: relative specificity and association with hypercalcemia. Sarcoidosis. 1987 Sep;4(2):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Krönke M., Peffer N. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2 receptor gene expression in normal human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6281–6285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Line B. R., Hunninghake G. W., Keogh B. A., Jones A. E., Johnston G. S., Crystal R. G. Gallium-67 scanning to stage the alveolitis of sarcoidosis: correlation with clinical studies, pulmonary function studies, and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Apr;123(4 Pt 1):440–446. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.4.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb M. F., Lyons C. R., O'Hara R. M., Jr, Stein-Streilein J. The antigen-induced selective recruitment of specific T lymphocytes to the lung. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):111–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLoud T. C., Epler G. R., Gaensler E. A., Burke G. W., Carrington C. B. A radiographic classification for sarcoidosis: physiologic correlation. Invest Radiol. 1982 Mar-Apr;17(2):129–138. doi: 10.1097/00004424-198203000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. N., Scadding J. G. Sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Dec;110(6):774–802. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.6P1.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Meyer P. R., Sharma O. P., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. In situ demonstration of T lymphocyte subsets in granulomatous inflammation: leprosy, rhinoscleroma and sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Mar;51(3):430–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley P. L., Hemken C., Monick M., Nugent K., Hunninghake G. W. Interferon and growth factor activity for human lung fibroblasts. Release from bronchoalveolar cells from patients with active sarcoidosis. Chest. 1986 May;89(5):657–662. doi: 10.1378/chest.89.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Kehrl J. H., Longo D. L., Volkman D. J., Smith K. A., Fauci A. S. Interleukin 2 receptors on human B cells. Implications for the role of interleukin 2 in human B cell function. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):181–197. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Quernheim J., Saltini C., Sondermeyer P., Crystal R. G. Compartmentalized activation of the interleukin 2 gene by lung T lymphocytes in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3475–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIH conference. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: a disease characterized and perpetuated by activated lung T-lymphocytes. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jan;94(1):73–94. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro R. F., Jalkanen S. T., Hsu M., Søenderstrup-Hansen G., Goronzy J., Weyand C., Fathman C. G., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Butcher E. C. Human T cell clones express functional homing receptors required for normal lymphocyte trafficking. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1075–1080. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradis I. L., Rogers R. M., Rabin B. S., Dauber J. H. Lymphocyte phenotypes in bronchoalveolar lavage and lung tissue in sarcoidosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;465:148–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb18490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkston P., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous release of interleukin-2 by lung T lymphocytes in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Apr 7;308(14):793–800. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198304073081401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Alpers J. D., Nowell P. C., Hoover R. G. Sequential expression of protooncogenes during lectin-stimulated mitogenesis of normal human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. W., McLemore T. L., Crystal R. G. Gamma interferon is spontaneously released by alveolar macrophages and lung T lymphocytes in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1488–1495. doi: 10.1172/JCI111852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G. A., Sacco O., Cosulich E., Risso A., Balbi B., Ravazzoni C. Helper T-lymphocytes in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Functional analysis of a lung T-cell subpopulation in patients with active disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jun;133(6):1086–1090. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.6.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltini C., Hance A. J., Ferrans V. J., Basset F., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Accurate quantification of cells recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):650–658. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltini C., Hemler M. E., Crystal R. G. T lymphocytes compartmentalized on the epithelial surface of the lower respiratory tract express the very late activation antigen complex VLA-1. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Feb;46(2):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltini C., Spurzem J. R., Kirby M. R., Crystal R. G. Sarcoidosis is not associated with a generalized defect in T cell suppressor function. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1854–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltini C., Spurzem J. R., Lee J. J., Pinkston P., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous release of interleukin 2 by lung T lymphocytes in active pulmonary sarcoidosis is primarily from the Leu3+DR+ T cell subset. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1962–1970. doi: 10.1172/JCI112525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenzato G., Agostini C., Trentin L., Zambello R., Chilosi M., Cipriani A., Ossi E., Angi M. R., Morittu L., Pizzolo G. Evidence of cells bearing interleukin-2 receptor at sites of disease activity in sarcoid patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):331–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenzato G., Chilosi M., Ossi E., Trentin L., Pizzolo G., Cipriani A., Agostini C., Zambello R., Marcer G., Gasparotto G. Bronchoalveolar lavage and lung histology. Comparative analysis of inflammatory and immunocompetent cells in patients with sarcoidosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):400–404. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon M., Klausner R. D., Cullen B. R., Chizzonite R., Leonard W. J. Novel interleukin-2 receptor subunit detected by cross-linking under high-affinity conditions. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):859–863. doi: 10.1126/science.3095922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M., Bond M. W., Gallatin W. M., St John T., Smith H. T., Fried V. A., Weissman I. L. Cell surface molecule associated with lymphocyte homing is a ubiquitinated branched-chain glycoprotein. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):823–829. doi: 10.1126/science.3003913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J. Antigen-induced selective sequestration of T lymphocytes: role of the major histocompatibility complex. Monogr Allergy. 1980;16:233–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T., Gallatin W. M., Siegelman M., Smith H. T., Fried V. A., Weissman I. L. Expression cloning of a lymphocyte homing receptor cDNA: ubiquitin is the reactive species. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):845–850. doi: 10.1126/science.3003914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein-Streilein J., Witte P. L., Streilein J. W., Guffee J. Local cellular defenses in influenza-infected lungs. Cell Immunol. 1985 Oct 15;95(2):234–246. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90311-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teshigawara K., Wang H. M., Kato K., Smith K. A. Interleukin 2 high-affinity receptor expression requires two distinct binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):223–238. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Nelson D. L., Fleisher T. A., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. II. Expression of Tac antigen on activated cytotoxic killer T cells, suppressor cells, and on one of two types of helper T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1398–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdal D. L., March C. J., Gillis S., Larsen A., Dower S. K. Purification and chemical characterization of the receptor for interleukin 2 from activated human T lymphocytes and from a human T-cell lymphoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6481–6485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]