Abstract
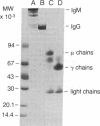
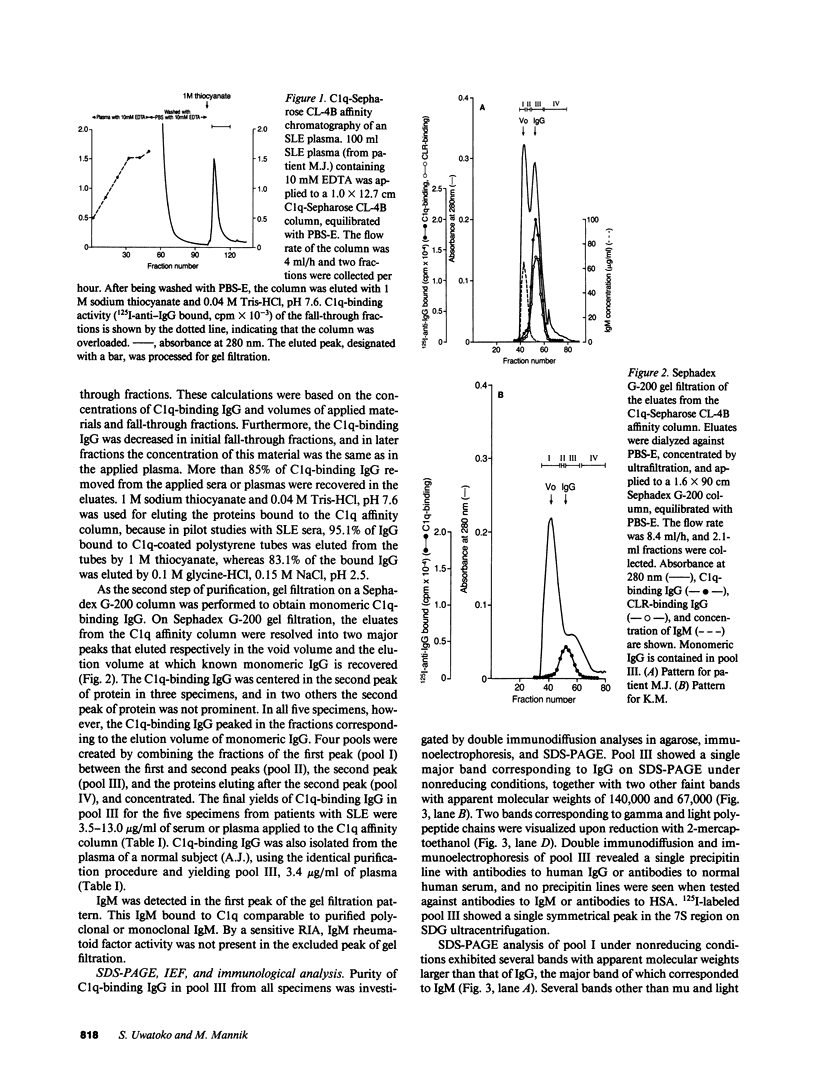
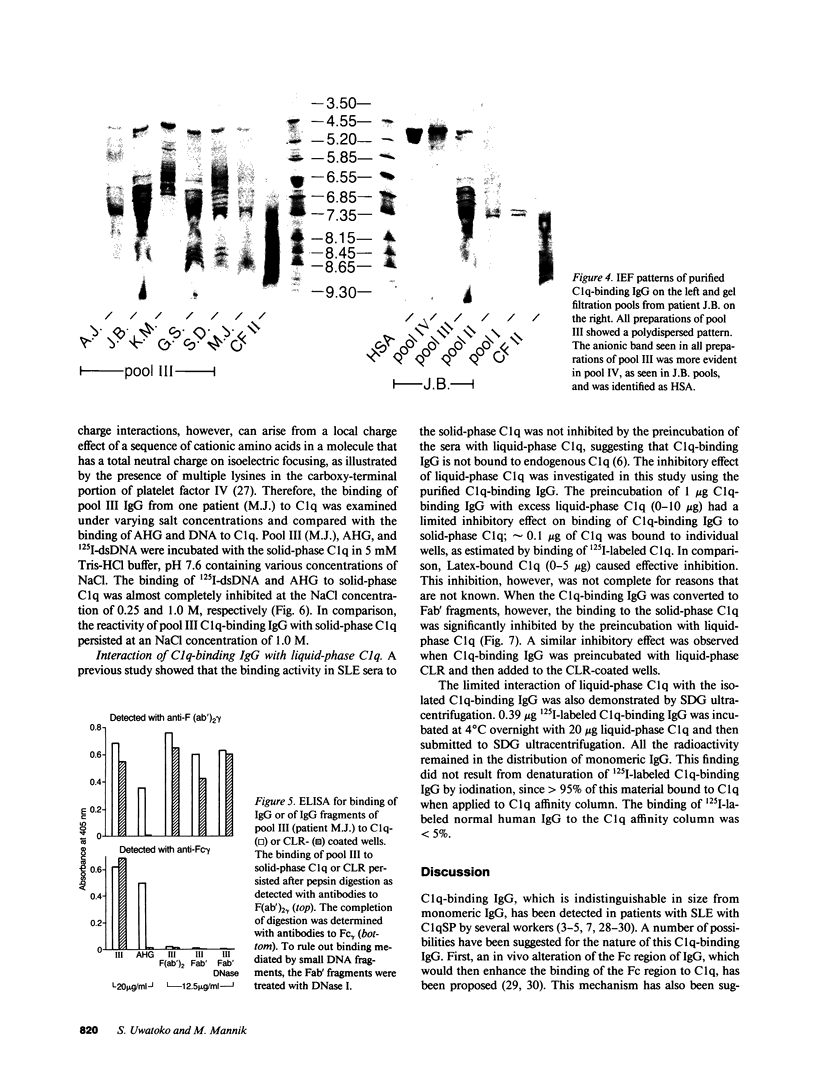
The majority of C1q-binding IgG in sera of some patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) cosediments with monomeric IgG. This study was undertaken to provide definitive proof that the low-molecular weight C1q-binding IgG consists of autoantibodies to C1q. Monomeric C1q-binding IgG was isolated from five SLE plasmas by C1q affinity chromatography and gel filtration. All C1q-binding IgG preparations and their F(ab')2 fragments bound to both C1q and the collagen-like region of C1q by an ELISA. To rule out the possibility that small DNA-antiDNA immune complexes caused this binding activity, Fab' fragments of the C1q-binding IgG preparations were digested with DNase I to degrade any DNA. The Fab' fragments continued to bind to C1q and its collagen-like region after this treatment. C1q-binding IgG was heterogenous on isoelectric focusing. Interaction of C1q-binding IgG with solid-phase C1q was retained in 1 M NaCl, whereas the binding of DNA or heat-aggregated IgG to solid-phase C1q was abrogated or markedly diminished. The association constant of C1q-binding IgG with solid-phase C1q was 2.7 X 10(7) M-1. We conclude that low-molecular weight C1q-binding IgG in the studied patients with SLE consists of autoantibodies to the collagen-like region of C1q.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrass C. K., Nies K. M., Louie J. S., Border W. A., Glassock R. J. Correlation and predictive accuracy of circulating immune complexes with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Mar;23(3):273–282. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnello V., Koffler D., Eisenberg J. W., Winchester R. J., Kundel H. G. C1g precipitins in the sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other hypocomplementemic states: characterization of high and low molecular weight types. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):228s–241s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnello V., Mitamura T. Evidence for detection of low molecular weight DNA--anti-DNA complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jul;25(7):788–792. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emlen W., Ansari R., Burdick G. DNA-anti-DNA immune complexes. Antibody protection of a discrete DNA fragment from DNase digestion in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):185–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI111400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier V. J., Mannik M., Striker G. E. Effect of cationized antibodies in performed immune complexes on deposition and persistence in renal glomeruli. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):766–777. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisman S. G., Redecha P. B., Kimberly R. P., Christian C. L. Differences among immune complexes: association of C1q in SLE immune complexes with renal disease. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):739–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMKAMP R. W., GOODLAND R. L., BALE W. F., SPAR I. L., MUTSCHLER L. E. High specific activity iodination of gamma-globulin with iodine-131 monochloride. Cancer Res. 1960 Nov;20:1495–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Belmer A. J. The IgG detected in the C1q solid-phase immune-complex assay is not always of immune-complex nature. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jan;38(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handin R. I., Cohen H. J. Purification and binding properties of human platelet factor four. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4273–4282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M. Routine assay for the detection of immune complexes of known immunoglobulin class using solid phase C1q. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):396–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusser C., Boesman M., Nordin J. H., Isliker H. Effect of chemical and enzymatic radioiodination on in vitro human Clq activities. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):820–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennette J. C., Hipp C. G. Immunohistopathologic evaluation of C1q in 800 renal biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Apr;83(4):415–420. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Kolb L. M., Podack E. R. C1q: isolation from human serum in high yield by affinity chromatography and development of a highly sensitive hemolytic assay. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):2103–2111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Busch G. J., Schur P. H. Gamma G globulin subgroup composition of the glomerular deposits in human renal diseases. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1103–1113. doi: 10.1172/JCI106326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Arend M. P., Hall A. P., Gilliland B. C. Studies on antigen-antibody complexes. I. Elimination of soluble complexes from rabbit circulation. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):713–739. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M. Binding of albumin to gamma-A-myeloma proteins and Waldenström macroglobulins by disulfide bonds. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):899–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder R. J., Burch F. X., Schmid F. R., Zeiss C. R., Gewurz H. Low molecular weight C1q-precipitins in hypocomplementemic vasculitis-urticaria syndrome: partial purification and characterization as immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):613–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder R. J., Potempa L. A., Jones J. V., Toriumi D., Schmid F. R., Gewurz H. Assay, purification and further characterization of 7S C1q-precipitins (C1q-p) in hypocomplementemic vasculitis urticaria syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand Suppl. 1984;284:25–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natori Y., Hayakawa I., Shibata S. Passive Heymann nephritis with acute and severe proteinuria induced by heterologous antibody against renal tubular brush border glycoprotein gp108. Lab Invest. 1986 Jul;55(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. L., Nardella F. A., Mannik M. Competition between antigen and anti-idiotypes for rheumatoid factors. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2357–2361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSTERLAND C. K., HARBOE M., KUNKEL H. G. Anti-gamma-globulin factors in human sera revealed by enzymatic splitting of anti-Rh antibodies. Vox Sang. 1963 Mar-Apr;8:133–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1963.tb03290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppliger I. R., Nardella F. A., Stone G. C., Mannik M. Human rheumatoid factors bear the internal image of the Fc binding region of staphylococcal protein A. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):702–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Isolation, by partial pepsin digestion, of the three collagen-like regions present in subcomponent Clq of the first component of human complement. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):5–17. doi: 10.1042/bj1550005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Lowe D. M., Porter R. R. Isolation and characterization of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, from human and rabbit sera. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):749–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1300749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart M. P., Malamud D. Protein transfer from isoelectric focusing Gels: the native blot. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. F., Roberts J. L., Jones J. V., Lewis E. J. Circulating immune complex assays in patients with lupus and membranous glomerulonephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Nov;14(3):348–360. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel R. C., Schumaker V. N. Measurement of the association constants of the complexes formed between intact C1q or pepsin-treated C1q stalks and the unactivated or activated C1r2C1s2 tetramers. Mol Immunol. 1983 Jan;20(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sledge C. R., Bing D. H. Binding properties of the human complement protein Clq. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2818–2823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. The biology and detection of immune complexes. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:89–220. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung K. S., DeHoratius R. J., Williams R. C. Study of circulating immune complex size in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):615–625. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uwatoko S., Aotsuka S., Okawa M., Egusa Y., Yokohari R., Aizawa C., Suzuki K. C1q solid-phase radioimmunoassay: binding properties of solid-phase C1q and evidence that C1q-binding IgG complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus are not bound to endogenous C1q. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Oct 12;73(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uwatoko S., Aotsuka S., Okawa M., Egusa Y., Yokohari R., Aizawa C., Suzuki K. C1q solid-phase radioimmunoassay: evidence for detection of antibody directed against the collagen-like region of C1q in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jul;69(1):98–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uwatoko S., Aotsuka S., Okawa M., Egusa Y., Yokohari R., Aizawa C., Suzuki K. Characterization of C1q-binding IgG complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Jan;30(1):104–116. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schravendijk M. R., Dwek R. A. Interaction of C1q with DNA. Mol Immunol. 1982 Sep;19(9):1179–1187. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wener M. H., Mannik M., Schwartz M. M., Lewis E. J. Relationship between renal pathology and the size of circulating immune complexes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1987 Mar;66(2):85–97. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198703000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wener M. H., Mannik M. Selective losses of large immune complexes during density gradient ultracentrifugation and an approach for prevention of these losses. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 28;84(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90409-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernick R., LoSpalluto J. J., Fink C. W., Ziff M. Serum IgG and IgM rheumatoid factors by solid phase radioimmunoassay. A comparison between adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Dec;24(12):1501–1511. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]