Abstract
Diversity in 26 microsatellite loci from section Caulorrhizae germplasm was evaluated by using 33 accessions of A. pintoi Krapov. & W.C. Gregory and ten accessions of Arachis repens Handro. Twenty loci proved to be polymorphic and a total of 196 alleles were detected with an average of 9.8 alleles per locus. The variability found in those loci was greater than the variability found using morphological characters, seed storage proteins and RAPD markers previously used in this germplasm. The high potential of these markers to detect species-specific alleles and discriminate among accessions was demonstrated. The set of microsatellite primer pairs developed by our group for A. pintoi are useful molecular tools for evaluating Section Caulorrhizae germplasm, as well as that of species belonging to other Arachis sections.
Keywords: Arachis, genetic diversity, germplasm, microsatellites, molecular markers
Introduction
The genus Arachis comprises nine taxonomic sections, viz., Arachis, Caulorrhizae, Erectoides, Extranervosae, Heteranthae, Procumbentes, Rhizomatosae, Trierectoides and Triseminatae, (Krapovickas and Gregory (1994), and includes both annual and perennial species. In this genus, most secies are acceptable as versatile forage plants. Nevertheless, more recent studies have provided abundant information on the potential and effective commercial use of accessions from the sections Caulorrhizae and Rhizomatosae (Loch and Ferguson, 1999; Teguia, 2000). Section Caulorrhizae is represented by only two stoloniferous species, Arachis pintoi Krapov. & Gregory and Arachis repens Handro. Both are native of valleys of the rivers Jequitinhonha, Araçuai, São Francisco and Paranã, the latter a tributary of the Tocantins, in Central Brazil.
Arachis pintoi is assuming increasing importance in the production of forage in tropical and sub-tropical areas, whereas A. repens is used as an ornamental plant, as well as for ground-cover in substitution of several species of common grass. Most of their cultivars were based on the two original accessions, A. pintoi GK12787 and A. repens GKP10538, which apparently represent extreme morphological types, with the occurrence of intermediate forms (Valls and Simpson, 1994). The basic use of the A. pintoi GK 12787 accession has been for developing forage cultivars in Australia, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Honduras and Venezuela (Valls, 1996).
Lately, the number of accessions available in both species has increased, with the current maintenance of over 150 in the Arachis Germplasm Bank (EMBRAPA Recursos Genéticos e Biotecnologia, Brasília, DF, Brazil). Furthermore, a program for agronomic appraisal and production of intra- and inter-specific hybrids from section Caulorrhizae, as well as progenies from accessions with high forage potential, has been developed (Carvalho S, PhD Thesis, UNESP, São Paulo, 2000). The significant genetic variability in available germplasm, both in accessions and hybrids, requires conservation, investigation and economical exploitation (Gimenes et al., 2000).
Several genetic markers have been used to estimate the genetic variability in species of section Caulorrhizae, including morphological characters (Monçato L, MSc Dissertation, UNESP, São Paulo, 1995), seed storage proteins (Bertozo and Valls, 2001), isozymes (Maass et al., 1993) and RAPDs (Gimenes et al., 2000) These markers were useful for the characterization of genetic variation in both species, but they offered limited informative content since some detected low levels of polymorphism (morphological characters, isozymes and seed proteins). RAPDs, on the other hand, yielded more complex band patterns (RAPDs). Due to their limitations, these markers were incapable of providing relevant information regarding important points for the conservation and use of the species, such as an estimate of the cross-pollination rate, identification of hybrids among species, and accurate estimation of genetic variability.
Microsatellites or simple sequence repeats (SSRs), the most informative molecular markers, have not been extensively used with section Caulorrhizae species (Palmieri et al., 2002; 2005). These sequences, besides being abundant and distributed throughout eukaryotic genomes, are highly polymorphic, inherited codominantly and reproducible, with simple screening requirements (Rosseto et al., 2002). The high polymorphism in microsatellite loci is due to DNA polymerase slippage during replication, and (or) unequal crossing-over, thereby resulting in differences in the copy numbers of the core sequences (Schlötterer and Tautz, 1992). Microsatellites have been extensively used in genetic mapping and genome analysis (Brondani et al., 1998; Li et al., 2000), genotype identification, variety protection (Giancola et al., 2002), seed purity evaluation, germplasm characterization (Brown et al., 1996; Hokanson et al., 1998), diversity studies (Métais et al., 2002), marker-assisted breeding (Weissing et al., 1998), and gene and quantitative trait loci analysis (Fahima et al., 1998; Brondani et al., 2002).
From recent studies, 18 microsatellite markers from A. pintoi have been described. The utility of these markers in evaluating genetic variability in section Caulorrhizae (20 accessions of A. pintoi and five of A. repens) has been demonstrated (Palmieri et al., 2002, 2005). In the present study, we used 19 previously described microsatellite markers and seven new primer pairs to estimate genetic variation in accessions of A. pintoi and A. repens.
Material and Methods
Plant material
Thirty-three accessions of A. pintoi and ten of A. repens were analyzed (Table 1). The samples were obtained from Dr. José F.M. Valls, curator of Wild Arachis Germplasm Bank, EMBRAPA Recursos Genéticos e Biotecnologia, Brasília, DF, Brazil, and from Dr. Sandremir de Carvalho, the Fundação Faculdade de Agronomia “Luiz Meneghel”, Bandeirantes, PR, Brazil. In the ArLag (Arachis sp.) accession, collected at Botucatu, SP, Brazil, the morphological type appeared to be closer to A. repens accessions, although definitive botanical identification was not possible.
Table 1.
Germplasm of section Caulorrhizae analyzed in this study.
| Samples | Code | Collector's number a | Origin | River basin b |
| A. repens | 012114 | V 5868 | São Gabriel-RS | - |
| 014770 | VSW 6673 | Várzea da Palma-MG | SF | |
| 014788 | VSW 6674 | Várzea da Palma-MG | SF | |
| 029190 | Nc 1563 | Buenópolis-MG | SF | |
| 029203 | Nc 1577 | Vitória-ES | SF | |
| 029220 | Nc 1579 | Januaria-MG | SF | |
| 032310 | WPn 205 | Pres. de Moraes-MG | SF | |
| 032352 | WPn 215 | Buenópolis-MG | SF | |
| 032379 | WPn 217 | Buenópolis-MG | SF | |
| 032395 | WPn 219 | Bocaiúva-MG | JQ | |
| A. pintoi | 012122 | VW 5895 | Unaí-MG | SF |
| 014982 | VSW 6740 | Pres. Juscelino-MG | SF | |
| 015083 | VSW 6784 | Sta Maria da Vitória-BA | SF | |
| 015121 | V6791-CPAC | Faz. Genipapo-GO | PR | |
| 015253 | W 34 | Fco. Badaró-MG | JQ | |
| 015598 | W 47 | Brasília-DF | - | |
| 016357 | Vi 301 | Araçuaí-MG | JQ | |
| 016683 | VSa 7394 | Brasília-DF | - | |
| 020401 | VRVe 7529 | Campinas-SP | - | |
| 030261 | VFaPzSv 13099 | Araçuaí-MG | JQ | |
| 031305 | WPn 124 | Buritis-MG | SF | |
| 031321 | WPn 128 | Buritis-MG | SF | |
| 031364 | WPn 132 | Unaí-MG | SF | |
| 031461 | WPn 147 | Jaíba-MG | SF | |
| 031534 | VPzBmVaDb 13357 | Jussari-BA | JQ | |
| 032191 | WPn 189 | F.da Mata-BA | SF | |
| 032239 | WPn 193 | Sta Maria da Vitória-BA | SF | |
| 032409 | WPn 220 | Eng. Navarro-MG | SF | |
| 034100 | VPzAg 13338 | Formosa-GO | PR | |
| 034347 | VApW 13877 | Formosa-GO | PR | |
| 034355 | VApW 13888 | Buritonópolis-GO | PR | |
| N.D. | Prog. W34b – I | N.A. | - | |
| N.D. | Prog. W34b – V | N.A. | - | |
| 012122 | CIAT 18744 - cv. Porvenir | Unaí-MG | JQ | |
| 013251 | GK 12787 - Ctes | Argentina | JQ | |
| 013251 | GK 12787 - TAES | U.S.A. | JQ | |
| 013251 | CIAT 17434 - Maní Forrajero Perenne | Colombia | JQ | |
| 013251 | CIAT 17434 - Maní Mejorador | Costa Rica | JQ | |
| 013251 | GK 12787 - cv. Amarillo | Australia | JQ | |
| 037036 | NP s/nº | Rio Pardo-RS | - | |
| 037036 | cv. Alqueire | Rio Pardo-RS | - | |
| 031828 | JP s/nº - cv. Belmonte | Itabuna-BA | JQ | |
| 031895 | Ag2 (2n = 30) | San José-CRA | - | |
| A. sp. | N.D. | ArLag | Botucatu-SP | - |
aCollectors – Ap = A. Peñaloza, Bm = B. Maass, Db = M. Bechara, Fa = L. Faraco, Nc = N. Costa, NP = N. Perez, Pn = P. Pinheiro, Pz = E. Pizarro, R = V. Rao, S = C. Simpson, Sa = J. Santos, Sv = Silva, Ve = R. Veiga, Vi = J. Vieira, V = J. Valls, Va = S. Valente, W = W. Werneck.
bRiver basin – JQ = Jequitinhonha, PR = Paranã, SF = São Francisco.
Source of microsatellites primer pairs
Nineteen primer pairs had already been described by Palmieri et al. (2002, 2005) and Hoshino et al. (2006), and seven new ones are described herein (Table 2). All the microsatellites used were isolated by applying library-enrichment protocol adapted from Kijas et al. (1994). The Primer 3 (Rozen and Skaletsky, 2000) program was employed for designing all the primer pairs, according to the following criteria: Tm of 50 to 60 °C (Tm difference between each primer within a pair was maintained below 3 °C), length of PCR products ranging from 100 to 350 bp and GC-content maintained around 50%. All primer pairs were synthesized by Invitrogen, SP, Brazil. BLAST searches were performed for all microsatellite sequences using blastx program to determine whether the microsatellites were associated with conserved gene regions (Altschul et al., 1997). These searches were based on the full-length sequence from which the primer pairs were designed.
Table 2.
Primer sequences, characteristics and source of the 26 microsatellite loci used in estimating genetic variation in germplasm of section Caulorrhizae.
| Locus | Primer Sequences (5' to 3') | Repeat motif | Annealing temp. (ºC) | Size (bp)a | Accession number | Source of primers |
| Ap10 | GAGGGAGTGAGGGGTTTAG | (AG)42 | 52 | 144 | AY540972 | This work |
| ATCCCCACCCCTTCTTT | ||||||
| Ap18 | TGCAGCCCACTGTATATTCG | (TA)36 | 52 | 200 | AY540973 | This work |
| TACACAGCGTAACAACTTATTTAGTG | ||||||
| Ap32 | ATAGGGAGAAGGCAGGGAGA | (TC)19 | 55 | 148 | AY540976 | Hoshino et al. (2006) |
| GATCATGCTCATCATCAACACC | ||||||
| Ap35 | TTAGACTACCAATCTATACGTACA | (GA)58 | 52 | 202 | AY540978 | This work |
| TCACCGATCCACTTTAAAGACA | ||||||
| Ap38 | GCGAACAAAGGAGGAAGAGA | (CT)25 | 55 | 154 | AY540979 | Hoshino et al. (2006) |
| GCTGGAAGACGTCATGGTTT | ||||||
| Ap45 | TGTGCACACTCAGACTCAACA | (TC)40 | 55 | 185 | AY540980 | This work |
| TTTAGCCTAGAGCCGAATTCAC | ||||||
| Ap164 | TGGTGGAATTGCAGAGAAC | (AG)33 | 55 | 213 | AY540985 | This work |
| GATTCAGGCTGCAGATGGAC | ||||||
| Ap177 | CCGAATTCACCGATCCACT | (CT)35 | 55 | 143 | AY540987 | This work |
| GGGCGATACTGAGCAACGTA | ||||||
| Ap190 | CTGTTTGATCGCCGCTATG | (TC)17 | 55 | 178 | AY540990 | This work |
| GTCAAGTGCTTCCTCCGATG | ||||||
| Ap40 | CTGTTTGATCGCCGCTATG | (TC)17 | 55 | 178 | AF504067 | Palmieri et al. (2002) |
| GTCAAGTGCTTCCTCCGATG | ||||||
| Ap46 | GAAATCACCGATCCCACTTT | (AG)22 | 55 | 158 | AF504068 | Palmieri et al. (2002) |
| CCATGATTTCATTCGCAAAC | ||||||
| Ap152 | AGAGGATGCAGCGGAGTAGA | (TC)24 | 50 | 277 | AF504069 | Palmieri et al. (2002) |
| CTGGCCAATTCCTATGATCG | ||||||
| Ap166 | CGGCAGTCAACGAAGCTAT | (CT)14 | 50 | 200 | AF504070 | Palmieri et al. (2002) |
| TCGCCAAAGGTTAGATTGC | ||||||
| Ap175 | CCAATAGGCTAATTCAGAAGG | (AG)22 | 50 | 177 | AF504071 | Palmieri et al. (2002) |
| GCCTTATTTTGCGACTGAGG | ||||||
| Ap176 | CCAACACAGGGCTTACCAAG | (AG)18 | 50 | 222 | AF504072 | Palmieri et al. (2002) |
| TCACCGATCCCACTTTTCC | ||||||
| Ap22 | ACTGCACGTCCTCTCTCCTC | (AG)14..(GGA)4..(GA)9 | 55 | 255 | AY540974 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| TGCATCTTCACCAGCCTACA | ||||||
| Ap23 | TGCTCCCAACTGCTACCAA | (AG)22 | 52 | 199 | AY540975 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| TGAGCAAGAAGAACGAACGA | ||||||
| Ap33 | CAGCCTAGAGCCGAAAACAC | (CT)36 | 55 | 161 | AY540977 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| GATGGCATGGCTGTCAGTAA | ||||||
| Ap48 | ACCGATCCCACTTTTCCAC | (AG)18 | 52 | 205 | AY540981 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| CCAAGAATGGCGATTGATTC | ||||||
| Ap154 | TGTCCAAATCACCTGAGACG | (CT)18 | 55 | 187 | AY540982 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| GGAACGGAGATGACAGAAGG | ||||||
| Ap158 | GTCTGCAGAGGAGCCAACAT | (AG)29 | 55 | 115 | AY540983 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| TCTTCCTCTCCTCGCGTTC | ||||||
| Ap161 | ACCGTCCTCTTCCTCTCCTC | (GT)32 | 55 | 215 | AY540984 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| CCCTCTCCAAATGGACACAT | ||||||
| Ap172 | TGCATCTTCACCAGCCTACA | (AG)14 | 55 | 255 | AY540986 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| ACTGCACGTCCTCTCTCCTC | ||||||
| Ap183 | CATCGTGTGGAGACGAAGGT | (GA)23 | 55 | 198 | AY540988 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| GAACCAACAGAGAGCGGATG | ||||||
| Ap187 | TTCGTCATCGTCGTCGTTC | (AG)24 | 55 | 179 | AY540989 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| GTGGTGATGATGACGCAGAA | ||||||
| Ap196 | CGCAAGCTCCTTCTTTCTTG | (AG)22 | 55 | 197 | AY540991 | Palmieri et al. (2005) |
| GCGACGTAAGAAGCTCCAAC |
aDetermined from cloned sequence.
DNA extraction
Genomic DNA was extracted using the protocol described by Grattapaglia and Sederoff (1994) with minor modifications as to DNA precipitation. DNA quality was checked with electrophoresis in 1% agarose gels, and concentration estimated by spectrophotometry (Spectronic, Inc., Rochester, NY, USA).
DNA amplification and electrophoresis
PCR reactions contained 15 ng of genomic DNA, 1U of Taq DNA polymerase (Amersham Biosciences), 1x PCR buffer (200 mM Tris pH 8.4, 500 mM KCl), 1.5-2.0 mM MgCl2, 200 μM of each dNTP, and 0.4 μM of each primer, in a final reaction volume of 10 μL. All PCR amplifications were carried out in a PTC100 thermocycler (MJ Research, Inc., Watertown, MA, USA). PCR conditions were 96 °C for 5 min, followed by 32 cycles of 96 °C for 30 s, X ºC for 45 s, 72 °C for 1 min, with a final extension of 10 min at 72 °C. The X value for each primer pair is shown in Table 2. PCR reactions were mixed with equal volumes of loading buffer (95% formamide, 0.01% bromophenol blue, 0.01% xylene cyanol, 0.5% NaOH 0.2 M), denatured at 95 °C for 5 min, cooled on ice and loaded onto the gel. PCR products were separated in denaturing polyacrylamide gels (6% acrylamide/bisacrylamide, 29:1, 5 M urea in TBE, pH 8.3) at 60 W for 4 h in 1x TBE buffer. DNA fragments were visualized by silver staining. The silver staining procedure consisted of 10 min in 10% ethanol/1% acetic acid solution, staining for 15 min in 0.2% (w/v) silver nitrate solution, and rinsing for 30 s in deionized water, and developing in 30 g/L of NaOH/10 mL/L of 37% formaldehyde solution for about 10 min or until bands became visible.
Data collection and analysis
Fragment sizes were estimated by comparison with a 10-bp DNA ladder (Life Technologies) using Gene Profiler 4.03 for Windows software, evaluation edition (Scanalytics, Inc., Fairfax, VA, USA). Bands with the same mobility were considered identical. Assuming the absence of null alleles, the presence of only one fragment of a given microsatellite indicated homozygosis. The Ap172 primer pair amplified a putative duplicate locus, and for this reason the amplification of two independent loci for this marker was considered. PopGene software (version 1.31; Yeh et al., 1999) was used to estimate genetic diversity based on the following indexes: polymorphic information content, allele number (observed and effective) per locus, allelic frequencies, observed (HO) and expected (HE) heterozygosities. Allelic polymorphic information content (PIC) was calculated for each microsatellite locus using the formula:
 , where pi and pj are the frequencies of the ith and jth alleles in the population (Weber, 1990). PIC values provided an estimate of the discriminatory power of a marker by taking into account, not only the number of alleles at a locus, but also their relative frequencies in the population under study. Markers with a large number of alleles occurring at equal frequencies will always have the highest PIC values (Senior et al., 1998). Effective alleles per locus (ne) were calculated according to Weir (1989) with the formula 1/(1 - HE). HE, the expected heterozygosity per locus, is equal to
, where pi and pj are the frequencies of the ith and jth alleles in the population (Weber, 1990). PIC values provided an estimate of the discriminatory power of a marker by taking into account, not only the number of alleles at a locus, but also their relative frequencies in the population under study. Markers with a large number of alleles occurring at equal frequencies will always have the highest PIC values (Senior et al., 1998). Effective alleles per locus (ne) were calculated according to Weir (1989) with the formula 1/(1 - HE). HE, the expected heterozygosity per locus, is equal to
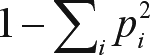 , where pi is the frequency of the ith allele at the locus. The Unweighted Pair-Group Method was applied for cluster analysis, using Arithmetic Averages (UPGMA) based on unbiased genetic distance measures (Nei, 1978).
, where pi is the frequency of the ith allele at the locus. The Unweighted Pair-Group Method was applied for cluster analysis, using Arithmetic Averages (UPGMA) based on unbiased genetic distance measures (Nei, 1978).
Results and Discussion
Twenty six microsatellite primer pairs were tested. Nineteen pairs (73%; Ap18, Ap22, Ap23, Ap33, Ap40, Ap45, Ap48, Ap152, Ap154, Ap158, Ap161, Ap166, Ap172, Ap175, Ap176, Ap183, Ap187, Ap190 and Ap196) allowed the detection of polymorphism while seven did not (27%; Ap10, Ap32, Ap35, Ap38, Ap46, Ap164 and Ap177) when all samples of the two species were considered. Sequences of Ap10, Ap18, Ap35, Ap45, Ap164, Ap177 and Ap190 are being presented for the first time. Locus Ap45 was mono-morphic only in A. pintoi,whereas Ap48 was monomorphic only in A. repens accessions (Table 2). Polymorphism in Ap40 (17 repeats) and Ap176 (18 repeats) had already been revealed in previous studies on Arachis genetic variability (Bravo et al., 2006; Hoshino et al., 2006; Angelici et al., 2008), as well as in the present study.
The number of monomorphic loci was high by accounting that each primer pair that did not allow detection of polymorphism was adjacent to regions containing a high number of repeats, these ranging from 19 (Ap32) to 58 (Ap35) repeats. Among the ones that did not detect any polymorphism four are described in this paper and two (Ap32 and Ap38) were previously used in three studies on genetic variability in Arachis (Bravo et al., 2006; Hoshino et al., 2006; Angelici et al., 2008), all with similar results. We tested the latter two primer pairs because Hoshino et al. (2006) studied only one accession of each species of section Caulorrhizae, whereas Bravo et al. (2006) and Angelici et al. (2008) used these two primers in other sections of genus Arachis. Thus, we expected additional information from these primers by using samples of the species from which they had been isolated. It may be that the areas targeted by the two primer pairs are within conserved regions of the genome. There was no similarity between the sequences used to design primers for these six microsatellites and any nucleotide or protein sequence in GenBank.
The Ap172 primer pair amplified a putative duplicated locus. At first, the double-band pattern was interpreted as a technical artifact, but after several attempts to optimize the amplification reaction, the band pattern still remained, thereby implying locus duplication. Amplification of duplicated loci has been observed in several species, such as Glycine max (L.) Merr. (Powell et al., 1996; Peakall et al., 1998), Zea mays L. (Senior et al., 1998), Vigna radiata (Kumar et al. 2002) and Cicer arietinum L. (Sethy et al., 2003). In rice and sunflowers, the amplification of double-band patterns has also been attributed to the occurrence of a duplication process within the genome itself, as well as to the evolution of families of repetitive sequences (Akagi et al., 1998; Paniego et al., 2002). In the amphidiploid A. hypogaea, amplification of duplicated loci was reported by Hopkins et al. (1999), and duplication at several genomic regions by Burow et al. (2001). Despite A. pintoi and A. repens being diploid species, gene duplication is not rare in the genus Arachis, and it could have happened to Ap172.
In this study, only Ap172 and Ap176 sequences showed similarity at the amino acid level to seryl-tRNA synthetase (57% identity, 76% similarity) and lipoxygenase (41% identity, 47% similarity) of plants, respectively. These stretches of similarity are localized adjacent to microsatellite sequences (data not shown). A like occurrence was reported by Peakall et al. (1998) in soybean. These authors found a similarity of 96% at the amino acid level between a microsatellite sequence and a seryl-tRNA synthetase of Arabidopsis thaliana. These data seem to be in agreement with observations from several authors (Tóth et al., 2000; Li et al., 2002; Morgante et al., 2002), in the sense that microsatellite sequences are present both in coding and non-coding regions of nuclear and organellar genomes.
A total of 196 putative alleles were detected at 20 polymorphic loci. It was assumed that fragments of different lengths were different alleles. The number of alleles ranged from two at Ap45 to 23 at Ap18 (a mean of 9.8 alleles/locus) (Table 3). The effective number of alleles ranged from 1.07 at Ap45 to 16.7 at Ap18 (Table 4). In A. pintoi, 174 alleles were detected distributed among the 19 polymorphic loci (mean of 9.2 alleles/locus), their fragment sizes ranging from 140 bp (Ap161) to 306 bp (Ap152). In A. repens accessions, 99 alleles, with fragment sizes ranging from 140 bp (Ap161) to 304 bp (Ap33), were detected among 19 polymorphic loci (mean 5,2 alleles/locus) (Table 3). Ninety-nine alleles (49%) were exclusively present in A. pintoi and twenty-one alleles (10.7%) were found in A. repens accessions only. Seventy-ninealleles (40.3%) were shared between the two species (data not shown). On using RAPDs, Gimenes et al. (2000) obtained lower values for exclusive fragments for these two species (22% in A. pintoi and 5% in A. repens) and a higher value for shared fragments (73%). Based on these results, they discussed the difficulty in justifying the separation into two species. Our data could reinforce a separation of these species into two taxa, as the higher values observed were due to the codominance and informativeness of microsatellite markers, thereby allowing us to distinguish and better estimate the genetic diversity within the analyzed germplasm.
Table 3.
E xpected size (bp) and total number of alleles of the 26 microsatellite loci in the section Caulorrhizae. The size-range and number of alleles from A. pintoi and A. repens accessions are presented. Numbers between parentheses represent mean numbers of alleles/locus.
| Locus name | Length (bp) | Total alleles | A. pintoi
|
A. repens |
|||
| Size range | No. alleles | Size range | No. alleles | ||||
| Ap10 | 114 | 1 | 114 | 1 | 114 | 1 | |
| Ap18 | 160-234 | 23 | 160-234 | 20 | 166-234 | 11 | |
| Ap22 | 168-178 | 3 | 174-178 | 3 | 168-178 | 3 | |
| Ap23 | 228-240 | 6 | 228-240 | 5 | 232-236 | 4 | |
| Ap32 | 150 | 1 | 150 | 1 | 150 | 1 | |
| Ap33 | 296-304 | 4 | 296-300 | 3 | 298-304 | 3 | |
| Ap35 | 192 | 1 | 192 | 1 | 192 | 1 | |
| Ap38 | 152 | 1 | 152 | 1 | 152 | 1 | |
| Ap40 | 156-192 | 7 | 156-192 | 6 | 168-188 | 3 | |
| Ap45 | 180-184 | 2 | 180 | 1 | 180-184 | 2 | |
| Ap46 | 148 | 1 | 148 | 1 | 148 | 1 | |
| Ap48 | 186-190 | 3 | 186-190 | 3 | 186 | 1 | |
| Ap152 | 262-306 | 14 | 268-306 | 10 | 278-302 | 7 | |
| Ap154 | 166-176 | 5 | 166-176 | 5 | 166-172 | 5 | |
| Ap158 | 206-224 | 5 | 296-224 | 4 | 210-216 | 5 | |
| Ap161 | 140-180 | 12 | 140-180 | 10 | 140-180 | 5 | |
| Ap164 | 206 | 1 | 206 | 1 | 206 | 1 | |
| Ap166 | 160-232 | 22 | 160-218 | 22 | 166-208 | 5 | |
| Ap172a | 242-252 | 4 | 244-252 | 4 | 242-252 | 2 | |
| Ap172b | 174-180 | 3 | 174-180 | 2 | 174-178 | 3 | |
| Ap175 | 160-206 | 15 | 160-204 | 15 | 176-206 | 5 | |
| Ap176 | 202-264 | 15 | 202-264 | 11 | 212-224 | 9 | |
| Ap177 | 138 | 1 | 138 | 1 | 138 | 1 | |
| Ap183 | 190-228 | 16 | 190-228 | 16 | 192-210 | 8 | |
| Ap187 | 152-194 | 18 | 152-192 | 17 | 156-194 | 7 | |
| Ap190 | 152-182 | 15 | 152-182 | 14 | 158-172 | 9 | |
| Ap196 | 186-194 | 4 | 186-194 | 4 | 186-192 | 3 | |
| Total | 114-306 | 203 (7.5) | 114-306 | 182 (6.7) | 114-304 | 107 (4.0) | |
| Polymorphic loci | 140-306 | 196 (9.8) | 140-306 | 174 (9.2) | 140-304 | 99 (5.2) | |
Table 4.
Characterization of the 20 polymorphic microsatellite loci in the section Caulorrhizae. Polymorphic information content (PIC), effective number of alleles, and observed (HO) and expected (HE) heterozygosities obtained per locus.
| Locus | PIC | Overall sample
|
A. pintoi |
A. repens |
||||||
| ne1 | H0 | HE * | H0 | HE * | H0 | HE * | ||||
| Ap18 | 0.9369 | 16.7 | 0.8077 | 0.9401 | 0.9444 | 0.9383 | 0.5714 | 0.8571 | ||
| Ap22 | 0.4076 | 2.09 | 0.9767 | 0.5214 | 0.9688 | 0.5142 | 1.0000 | 0.5450 | ||
| Ap23 | 0.7223 | 4.17 | 1.0000 | 0.7604 | 1.0000 | 0.7812 | 1.0000 | 0.5938 | ||
| Ap33 | 0.4476 | 1.93 | 0.0227 | 0.4832 | 0.0303 | 0.4844 | 0.0000 | 0.4600 | ||
| Ap40 | 0.7432 | 4.45 | 0.3077 | 0.7751 | 0.3000 | 0.7750 | 0.0000 | 0.5000 | ||
| Ap45 | 0.0651 | 1.07 | 0.0233 | 0.0673 | - | - | 0.1000 | 0.0950 | ||
| Ap48 | 0.1624 | 1.21 | 0.0270 | 0.1735 | 0.0385 | 0.2374 | - | - | ||
| Ap152 | 0.8682 | 8.18 | 0.8667 | 0.8778 | 0.8000 | 0.8750 | 1.0000 | 0.7800 | ||
| Ap154 | 0.6594 | 3.43 | 0.9667 | 0.7083 | 0.9565 | 0.6720 | 1.0000 | 0.7361 | ||
| Ap158 | 0.4646 | 1.98 | 0.1724 | 0.4941 | 0.1739 | 0.3677 | 0.2000 | 0.7800 | ||
| Ap161 | 0.8358 | 6.63 | 0.1923 | 0.8491 | 0.2000 | 0.8350 | 0.2000 | 0.6600 | ||
| Ap166 | 0.9188 | 13.1 | 0.5714 | 0.9235 | 0.5909 | 0.9308 | 0.4000 | 0.3400 | ||
| Ap172a | 0.4086 | 2.09 | 1.0000 | 0.5227 | 1.0000 | 0.5303 | 1.0000 | 0.5000 | ||
| Ap172b | 0.4097 | 2.10 | 0.9756 | 0.5235 | 1.0000 | 0.5000 | 1.0000 | 0.5000 | ||
| Ap175 | 0.8465 | 7.07 | 0.3448 | 0.8585 | 0.3913 | 0.8251 | 0.2000 | 0.5800 | ||
| Ap176 | 0.8896 | 9.80 | 0.6667 | 0.8980 | 0.6250 | 0.8711 | 0.7500 | 0.8438 | ||
| Ap183 | 0.8632 | 7.93 | 0.6897 | 0.8740 | 0.6667 | 0.8526 | 0.7143 | 0.7959 | ||
| Ap187 | 0.9170 | 12.8 | 0.9643 | 0.9222 | 0.9545 | 0.9215 | 1.0000 | 0.8000 | ||
| Ap190 | 0.8692 | 8.36 | 1.0000 | 0.8803 | 1.0000 | 0.8769 | 1.0000 | 0.8250 | ||
| Ap196 | 0.4103 | 1.83 | 0.0000 | 0.4537 | 0.0000 | 0.3182 | 0.0000 | 0.5926 | ||
| Mean | 0.6423 | 4.59 | 0.5788 | 0.6753 | 0.5820 | 0.6553 | 0.5861 | 0.6202 | ||
| St.Dev. | 0.3975 | 0.2572 | 0.3988 | 0.2705 | 0.4192 | 0.1985 | ||||
1Effective number of alleles (Kimura and Crow, 1964).
*Nei (1973) expected heterozygosity.
Data on allelic polymorphic information content (PIC), and observed (HO) and expected (HE) heterozygosities per locus are presented in Table 4. PIC values ranged from 0.0651 at Ap45 to 0.9369 at Ap18, with an average value of 0.6423 when considering 20 polymorphic loci (Table 4). Average observed heterozygosities at 20 loci for the whole A. pintoi and A. repens sample were 0.5788, 0.5820 and 0.5861, respectively (Table 4), and average expected heterozigosities for the whole sample, A. pintoi and A. repens accessions were 0.6753, 0.6553 and 0.6202, respectively (Table 4). Mean values of observed heterozygosity (HO) were lower than the HE values estimated from allele frequencies. At some loci, HO values were higher than HE (Ap22, Ap23, Ap154, Ap172a, Ap172b, Ap187, and Ap190). The variability observed in A. pintoi could be the consequence of crosses between different accessions that had been vegetatively maintained at experimental plots. Thus, the high observed heterozygosity at some loci could be attributed to the presence of parentals carrying different alleles, thereafter being sustained through the vegetative propagation methods used in conserving accessions.
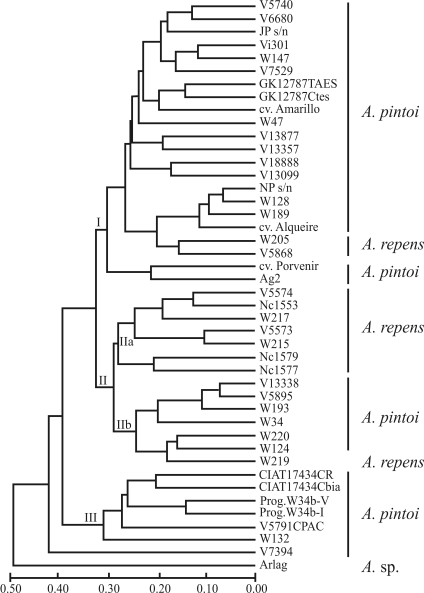
The dendrogram showing the relationships among A. pintoi and A. repens accessions is presented in Figure 1. Cluster analysis allowed the discrimination of all individuals from the two species. Such differentiation was also obtained using RAPD markers (Gimenes et al., 2000). However, microsatellites should be the marker of choice because they are much more effective and have higher reproducibility since longer primer pairs are used instead of unique short primers that allows multiple loci amplification, which makes the analysis difficult.
Figure 1.
UPGMA dendrogram of 33 accessions of A. pintoi and ten of A. repens. The distance matrix was estimated by the Nei (1978) coefficient using 27 microsatellite loci. Clades were defined by roman numerals at the nodes. Individual accessions and species are listed to the right of the dendrogram.
Three major groups (I, II and III) were formed in the tree. In general, A. pintoi accessions were positioned in all the three major groups, with a mean genetic distance among them of 0.295, ranging from 0.064 (between NP s/nº and WPn 128) to 0.566 (between W 34 and CIAT 17434 – Maní Mejorador). Group I was formed by 20 A. pintoi accessions and only two A. repens (WPn 205 and V 5868). Two subgroups were observed in Group II. Subgroup IIa was formed by seven out of ten A. repens accessions with a mean genetic distance of 0.232. Six of these were collected in Minas Gerais State, Brazil. Subgroup IIb was represented by six A. pintoi accessions (VPzAg 13338, VW 5895, WPn 193, W 34, WPn 220 and WPn 124) and only one A. repens (WPn 219). Group III was formed solely by A. pintoi accessions.
The longest genetic distance (0.582) was obtained between the accessions CIAT 17434 – Maní Mejorador (A. pintoi) and WPn 215 (A. repens), whereas the shortest (0.064) was between two A. pintoi accessions (NP s/nº and WPn 128). The VSa 7394 (A. pintoi) accession, the most diverse, was positioned outside the three major groups (Figure 1). Tree analysis showed that the species could not be characterized based on polymorphism detected by using 20 microsatellite loci, since accessions of each species were not entirely grouped together. Likewise, Bravo et al. (2006) and Hoshino et al. (2006) did not resort to microsatellites when characterizing Arachis species. They pointed out that this was probably due to: 1 – high microsatellite-detected polymorphism, requiring larger samples for adequate representation of species variability; and 2 – the existence of homoplasies (fragments of the same size but from different loci that have no common origin). These same factors could possibly have affected the results obtained in this study. However, we believe the main reason is that crossability in A. pintoi and A. repens is high (86.7%, Krapovickas and Gregory, 1994), these being considered by some authors as a single species (Gimenes et al., 2000). As mentioned above, differentiation between A. repens and A. pintoi, as observed in the present study, was greater than that observed by Gimenes et al. (2000). We consider this to be a relevant result, because it shows that the primary gene pool of these species probably has a wider base than was detected by the RAPD data.
It has been demonstrated that the set of microsatellite markers previously described and used here provides a powerful tool for germplasm characterization analysis of A. pintoi and A. repens species. Among the primer pairs presented in this study, 21 are readily available. These primers could be useful in all the steps from conservation to the use of germplasm. The existence of duplicates, mislabeling and loss of integrity due to physical contamination, cross-pollination or genetic drift are realities, so these markers could be used as an aid in evaluating these events in the germplasm collection. Furthermore, they could also be used in identifying accessions and cultivars and for selecting parents for hybridization.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo). The participation of D.A.P. and C.R.L. was sponsored by a CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento do Pessoal de Nível Superior) fellowship and a CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico-Tecnológico) research fellowship, respectively.
Footnotes
Associate Editor: Márcio de Castro Silva Filho
References
- Akagi H., Yokzeki Y., Inagaki A., Fujimura T. Origin and evolution of twin microsatellites in the genus Oryza. Heredity. 1998;81:187–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S.F., Madden T.L., Schäffer A.A., Zhang J., Zhang Z., Miller W., Lipman D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:3389–3402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelici C.M.L.C.D., Gimenes M.A., Hoshino A.A., Lopes C.R., Palmieri D.A., Valls J.F.M., Nobile P.M. Genetic diversity in species of section Rhizomatosae, genus Arachis (Leguminosae), using microsatellite markers. Genet Mol Biol. 2008;31:79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Bertozo M.R., Valls J.F.M. Seed storage protein electrophoresis in Arachis pintoi and A. repens (Leguminosae) for evaluating genetics diversity. Genet Resour Crop Evol. 2001;48:121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo J.P., Hoshino A.A., Angelici C.M.L.C.D., Lopes C.R., Gimenes M.A. Transferability and use of microsatellite markers for the genetic analysis of the germplasm of some Arachis section species of the genus Arachis. Genet Mol Biol. 2006;29:516–524. [Google Scholar]
- Brondani C., Rangel P.H.N., Brondani R.P.V., Ferreira M.E. QTL mapping and introgression of yield-related traits from Oryza glumaepatula to cultivated rice (Oryzasativa) using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet. 2002;104:1192–1203. doi: 10.1007/s00122-002-0869-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brondani R.P.V., Brondani C., Tarchini R., Grattapaglia D. Development, characterization and mapping of microsatellite markers in Eucalyptus grandis and E. urophylla. Theor Appl Genet. 1998;97:816–827. [Google Scholar]
- Brown S.M., Hopkins M.S., Mitchell S.E., Senior M.L., Wang T.Y., Duncan R.R., Gonzalez-Candelas F., Kresovich S. Multiple methods for the identification of polymorphic simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L. ) Moench] Theor Appl Genet. 1996;93:190–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00225745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burow M.D., Simpson C.E., Starr J.L., Paterson A.H. Transmission genetics of chromatin from a synthetic amphidiploid to cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L. ): Broadening the gene pool of a monophyletic polyploidy species. Genetics. 2001;159:823–837. doi: 10.1093/genetics/159.2.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahima T., Röder M.S., Grma A., Nevo E. Microsatellite DNA polymorphism divergence in Triticum dicoccoides accessions highly resistant to yellow rust. Theor Appl Genet. 1998;96:187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Giancola S., Marcucci Poltri S., Lacaze P., Hopp H.E. Feasibility of integration of molecular markers and morphological descriptors in a real case study of a plant variety protection system for soybean. Euphytica. 2002;127:95–113. [Google Scholar]
- Gimenes M.A., Lopes C.R., Galgaro M.L., Valls J.F.M., Kochert G. Genetic variation and phylogenetic relationships based on RAPD analysis in section Caulorrhizae, genus Arachis (Leguminosae) Euphytica. 2000;116:187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Grattapaglia D., Sederoff R.R. Genetic linkage maps of Eucalyptus grandis and Eucalyptus urophilla using a pseudo-testcross mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics. 1994;137:1121–1137. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokanson S.C., Szewc-Fadden A.K., Lamboy W.F., Mcferson J.R. Microsatellite (SSR) markers reveal genetic identities, genetic diversity and relationship in Malus x domestica Borkh. core subset collection. Theor Appl Genet. 1998;97:671–683. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins M.S., Casa A.M., Wang T., Mitchell S.E., Dean R.E., Kochert G.D., Kresovich S. Discovery and characterization of polymorphic simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in peanut. Crop Sci. 1999;39:1243–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino A.A., Bravo J.P., Angelici C.M.L.C.D., Barbosa A.V.G., Lopes C.R., Gimenes M.A. Heterologous microsatellite primer pairs informative for the whole genus Arachis. Genet Mol Biol. 2006;29:665–675. [Google Scholar]
- Kijas J.M.H., Fowler J.C.S., Garbett C.A., Thomas M.R. Enrichment of microsatellites from the Citrus genome using biotinylated oligonucleotide sequences bound to streptavidin-coated magnetic particles. BioTechniques. 1994;16:657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Crow J.F. The number of alleles that can be maintained in a finite population. Genetics. 1964;49:725–738. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapovickas A., Gregory W.C. Taxonomía del género Arachis (Leguminosae) Bonplandia. 1994;8:1–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S.V., Tan S.G., Quah S.C., Yusoff K. Isolation of microsatellite markers in mungbean, Vigna radiata. Mol Ecol Notes. 2002;2:96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Li C.D., Rossnagel B.G., Scoles G.J. The development of oat microsatellite markers and their use in identifying Avena species and oat cultivars. Theor Appl Genet. 2000;101:1259–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Li Y.C., Korol A.B., Fahima T., Beiles A., Nevo E. Microsatellites: Genomic distribution, putative functions and mutational mechanisms: A review. Mol Ecol. 2002;11:2453–2465. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294x.2002.01643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loch D.S., Ferguson J.E. Tropical and subtropical forage seed production: An overview. In: Loch D.S., Ferguson J.E., editors. Forage Seed Production. 2. Tropical and Subtropical Species. New York: CABI Publishing; 1999. pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Maass B.L., Torres A.M., Ocampo C.H. Morphological and isozyme characterization of Arachis pintoi Krap. & Greg. nom. nud. germplasm. Euphytica. 1993;70:43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Métais I., Hamon B., Jalouzot R., Peltier D. Structure and level of genetic diversity in various bean types evidenced with microsatellite markers isolated from a genomic enriched library. Theor Appl Genet. 2002;104:1346–1352. doi: 10.1007/s00122-002-0901-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgante M., Hanafey M., Powell W. Microsatellites are preferentially associated with nonrepetitive DNA in plant genomes. Nat Genet. 2002;30:194–200. doi: 10.1038/ng822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1973;70:3321–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics. 1978;89:583–590. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri D.A., Hoshino A.A., Bravo J.P., Lopes C.R., Gimenes M.A. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci from the forage species Arachis pintoi (Genus Arachis) Mol Ecol Notes. 2002;2:551–553. [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri D.A., Bechara M.D., Curi R.A., Gimenes M.A., Lopes C.R. Novel polymorphic microsatellite markers in section Caulorrhizae (Arachis, Fabaceae) Mol Ecol Notes. 2005;5:77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Paniego N., Echaide M., Muñoz M., Fernández L., Torales S., Faccio P., Fuxan I., Carrera M., Zandomeni R., Suárez E.Y., et al. Microsatellite isolation and characterization in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L. ) Genome. 2002;45:34–43. doi: 10.1139/g01-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peakall R., Gilmore S., Keys W., Morgante M., Rafalski A. Cross-species amplification of soybean (Glycine max) simple sequence repeats (SSRs) within the genus and other legume genera: Implication for the transferability of SSRs in plants. Mol Biol Evol. 1998;15:1275–1287. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W., Morgante M., Doyle J.J., McNicol J.W., Tingey S.V., Rafalski A.J. Genepool variation in genus Glycine subgenus Soja revealed by polymorphic nuclear and chloroplast microsatellites. Genetics. 1996;144:793–803. doi: 10.1093/genetics/144.2.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosseto M., Mcnally J., Henry R.J. Evaluating the potential of SSR flanking regions for examining taxonomic relationships in the Vitaceae. Theor Appl Genet. 2002;104:61–66. doi: 10.1007/s001220200007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen S., Skaletsky H.J. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S., Misener S., editors. Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols: Methods in Molecular Biology. New Jersey: Humana Press; 2000. pp. 365–386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlötterer C., Tautz D. Slippage synthesis of simple sequence DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992;20:211–215. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior M.L., Murphy J.P., Goodman M.M., Stuber C.W. Utility of SSR for determining genetic similarities and relationships in maize using an agarose gel system. Crop Sci. 1998;38:1088–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Sethy N.K., Shokeen B., Bhatia S. Isolation and characterization of sequence-tagged microsatellite sites markers in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L. ) Mol Ecol Notes. 2003;3:428–430. [Google Scholar]
- Teguia A. A note on the effect of feeding local forages to commercial layers on egg production and yolk colour. J Anim Feed Sci. 2000;9:391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth G., Gáspari Z., Jurka J. Microsatellites in different eukaryotic genomes: Survey and analysis. Genome Res. 2000;10:967–981. doi: 10.1101/gr.10.7.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valls J.F.M., Simpson C.E. Taxonomy, natural distribution, and attributes of Arachis. In: Kerridge P.C., Hardy B., editors. Biology and Agronomy of Forage Arachis. Cali: CIAT; 1994. pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Valls J.F.M. Variability in the genus Arachis and potential forage uses. In: Springer T.L., Pittman R.N., editors. Identifying Germplasm for Successful Forage Legume-Grass Interactions. Proceedings of a Symposium of the Crop Science Society of America; Washington: USDA; 1996. pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Weber J.L. Informativeness of human (dC – dA)n (dG – dT)n polymorphisms. Genomics. 1990;7:524–530. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90195-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir B.S. Sampling properties of gene diversity. In: Brown A.H.D., Clegg M.T., Kahler H.L., Weir B.S., editors. Plant Population Genetics, Breeding and Genetic Resources. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates; 1989. pp. 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Weissing K.P., Winter P., Huttel B., Kahl G. Microsatellite markers for molecular breeding. J Crop Prod. 1998;1:113–143. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh F.C., Yang R.C., Boiley T., Ye Z.H., Mao J.X. PopGene, the user-friendly shareware for population genetic analysis. University of Alberta: Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Center; 1999. [Google Scholar]