Abstract
A young man with a long history of abnormal bleeding was seen in January 1985. Coagulation tests showed dysfibrinogenemia and an antifibrinogen autoantibody was demonstrable in his serum. This antibody, when purified, was capable of inhibiting the polymerization of normal fibrin monomers, apparently through binding to the alpha fibrinogen chain. 6 mo later the patient was asymptomatic, coagulation tests were normal, and the antifibrinogen autoantibody was barely detectable. At this time, affinity-purified autologous and rabbit antifibrinogen antibodies were capable of absorbing an IgG kappa antibody from the patient's serum, which reacted indistinctly with both autologous and xenogeneic antifibrinogen antibodies in enzyme immunoassays. It has been concluded that the patient's dysfibrinogenemia was the result of an antifibrinogen autoantibody, and that later on an anti-idiotype antibody, which binds an interspecies cross-reactive idiotype expressed on anti-human fibrinogen antibodies, inhibited the production of the antifibrinogen autoantibody which led to the remission of the disorder.
Full text
PDF


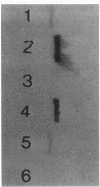
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Wall H., Lindsley H. B., Halsey J. F., Suzuki T. Network theory in autoimmunity. In vitro suppression of serum anti-DNA antibody binding to DNA by anti-idiotypic antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1297–1304. doi: 10.1172/JCI110158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Johnson A. M. Immunofixation electrophoresis: a technique for the study of protein polymorphism. Vox Sang. 1969 Nov;17(5):445–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1969.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Hessel B., Iwanaga S., Reuterby J., Blombäck M. Primary structure of human fibrinogen and fibrin. I. Clevage of fibrinogen with cyanogen bromide. Isolation and characterization of NH 2 -terminal fragments of the ("A") chain. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1496–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crum E. D., Shainoff J. R., Graham R. C., Ratnoff O. D. Fibrinogen Cleveland II. An abnormal fibrinogen with defective release of fibrinopeptide A. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1308–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI107678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Comunale M. Regulation of immunoglobulin E antibody synthesis in man by antiidiotypic antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):46–54. doi: 10.1172/JCI110750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S. Presence of auto-anti-idiotypic antibody during the normal human immune response to tetanus toxoid antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geltner D., Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Antiidiotypic activity in the IgM fractions of mixed cryoglobulins. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1530–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gårdlund B., Hessel B., Marguerie G., Murano G., Blombäck B. Primary structure of human fibrinogen. Characterization of disulfide-containing cyanogen-bromide fragments. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 1;77(3):595–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henschen A., Kehl M., Southan C. Genetically abnormal fibrinogens--strategies for structure elucidation, including fibrinopeptide analysis. Curr Probl Clin Biochem. 1984;14:273–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. L., Penner J. A., Shafer J. A. Fibrinogen Petoskey: identification of a new dysfibrinogenemia characterized by altered release of fibrinopeptide A. Thromb Res. 1981 Sep 15;23(6):491–504. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoots W. K., Carrell N. A., Wagner R. H., Cooper H. A., McDonagh J. A naturally occurring antibody that inhibits fibrin polymerization. N Engl J Med. 1981 Apr 9;304(15):857–861. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198104093041501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JIM R. T. A study of the plasma thrombin time. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jul;50(1):45–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehl M., Lottspeich F., Henschen A. Analysis of human fibrinopeptides by high-performance liquid chromatography. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Dec;362(12):1661–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mammen E. F., Schmidt K. P., Barnhart M. I. Thrombophlebitis migrans associated with circulating antibodies against Fibrinogen. A case report. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Dec 31;18(3-4):605–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Stage D. E. Antibody-agarose immunoadsorbents: complete removal of classes of immunoglobulins from serum. J Immunol. 1971 Jun;106(6):1670–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak E., Greenwood M. F. Acquired coagulation inhibitor delaying fibrinopeptide release. Blood. 1979 Jan;53(1):81–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. C., Jr, Rossen R. D., Twomey J. J. Naturally occurring circulating immune complexes: normal human serum contains idiotype-anti-idiotype complexes dissociable by certain IgG antiglobulins. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1672–1680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., MARKUS G., WISSLER F. C. Separation of univalent fragments of rabbit antibody by reduction of a single, labile disulphide bond. Nature. 1961 Jan 28;189:293–295. doi: 10.1038/189293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquali J. L., Urlacher A., Storck D. Idiotypic network: possible explanation of seronegativity in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):281–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posnett D. N., Wisniewolski R., Pernis B., Kunkel H. G. Dissection of the human antigammaglobulin idiotype system with monoclonal antibodies. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Feb;23(2):169–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Colman R. W., Lorand L. A new haemorrhagic disorder with defective fibrin stabilization and cryofibrinogenaemia. Br J Haematol. 1974 Feb;26(2):269–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Arguelles A., Perez-Romano B. Sensitive and rapid measurement of fibrin polymerisation by laser nephelometry. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Feb;39(2):227–229. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.2.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruíz-Reyes G., Landero de Ruíz N., Armenta-Olvera T. Immunoelectrocataphoresis: an immunoelectrophoresis variant to detect fibrinogen electrophoretic abnormalities. Rev Invest Clin. 1978 Oct-Dec;30(4):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultan Y., Kazatchkine M. D., Maisonneuve P., Nydegger U. E. Anti-idiotypic suppression of autoantibodies to factor VIII (antihaemophilic factor) by high-dose intravenous gammaglobulin. Lancet. 1984 Oct 6;2(8406):765–768. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90701-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Hosono O., Koide J., Homma M., Abe T. Suppression of rheumatoid factor synthesis by antiidiotypic antibody in rheumatoid arthritis patients with cross-reactive idiotypes. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Aug;28(8):873–881. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N. Autoimmunity and the immunologic network. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Sep-Oct;21(7):853–861. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbain J., Collignon C., Franssen J. D., Mariamé B., Léo O., Urbain-Vansanten G., Van de Walle P., Wikler M., Wuilmart C. Idiotypic networks and self-recognition in the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1979 Mar-Apr;130(2):281–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D., Huldt G., Engvall E. A microplate method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and its application to malaria. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51(2):209–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]