Abstract
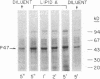
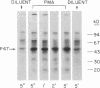
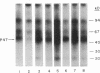
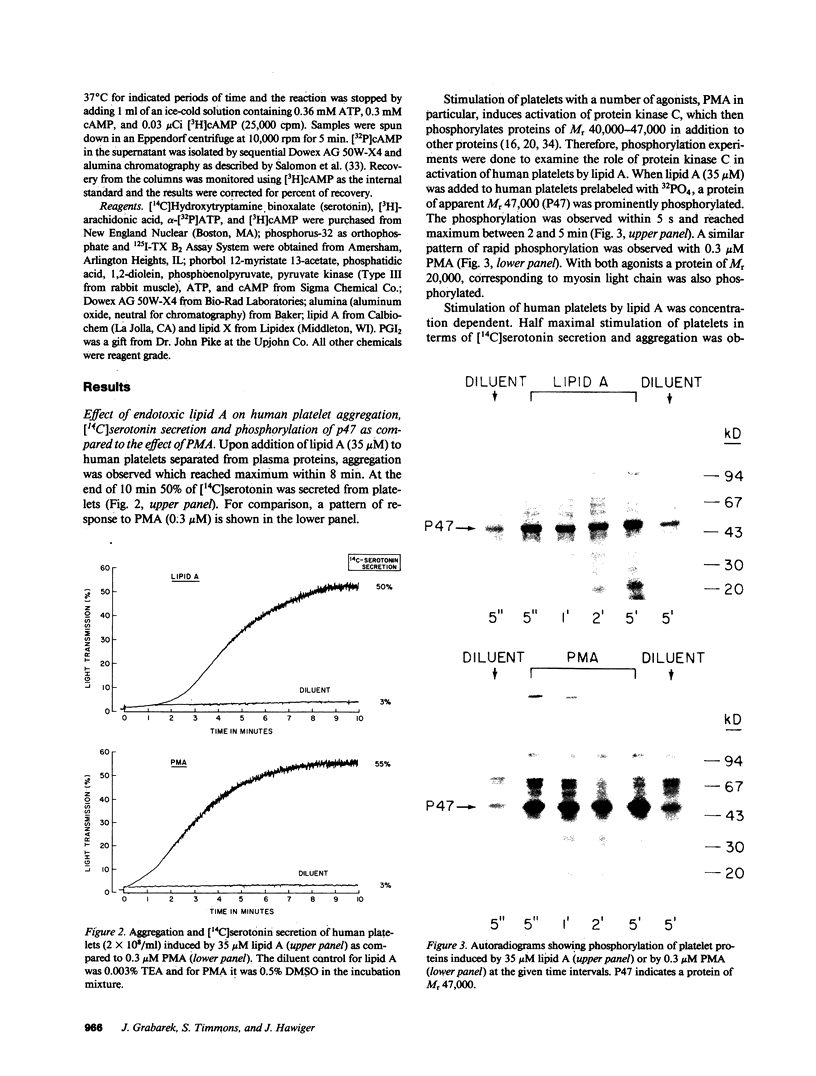
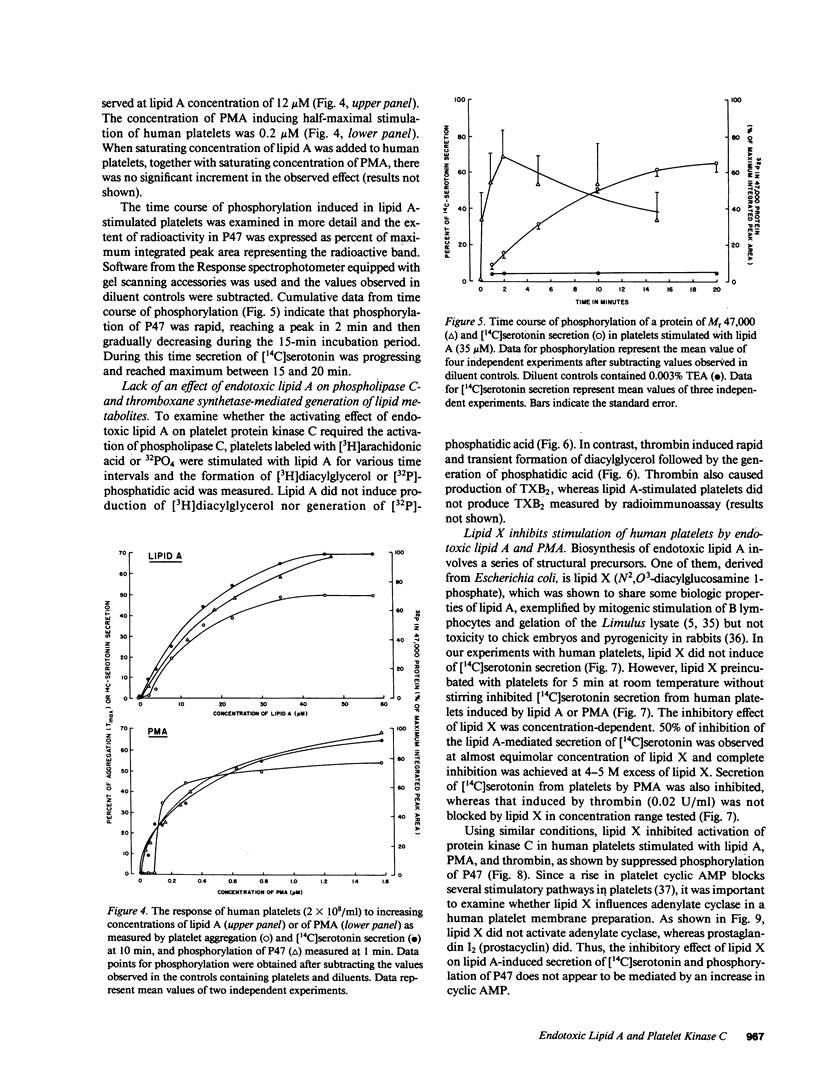
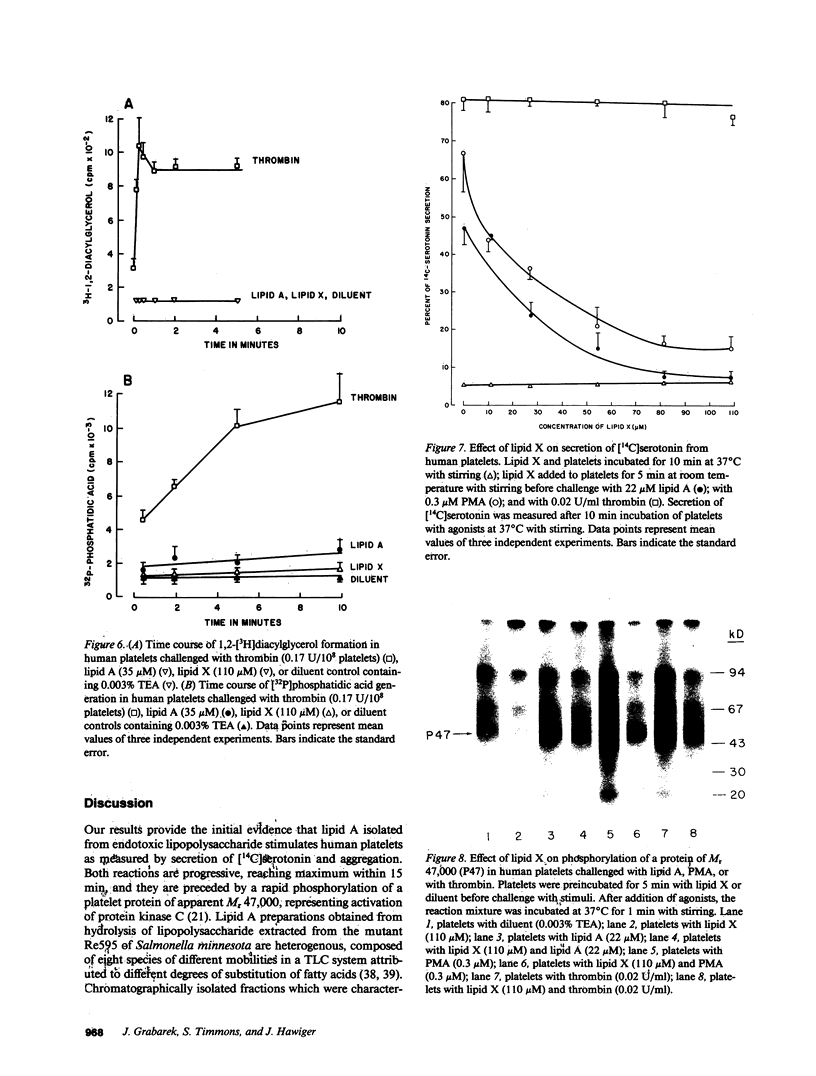
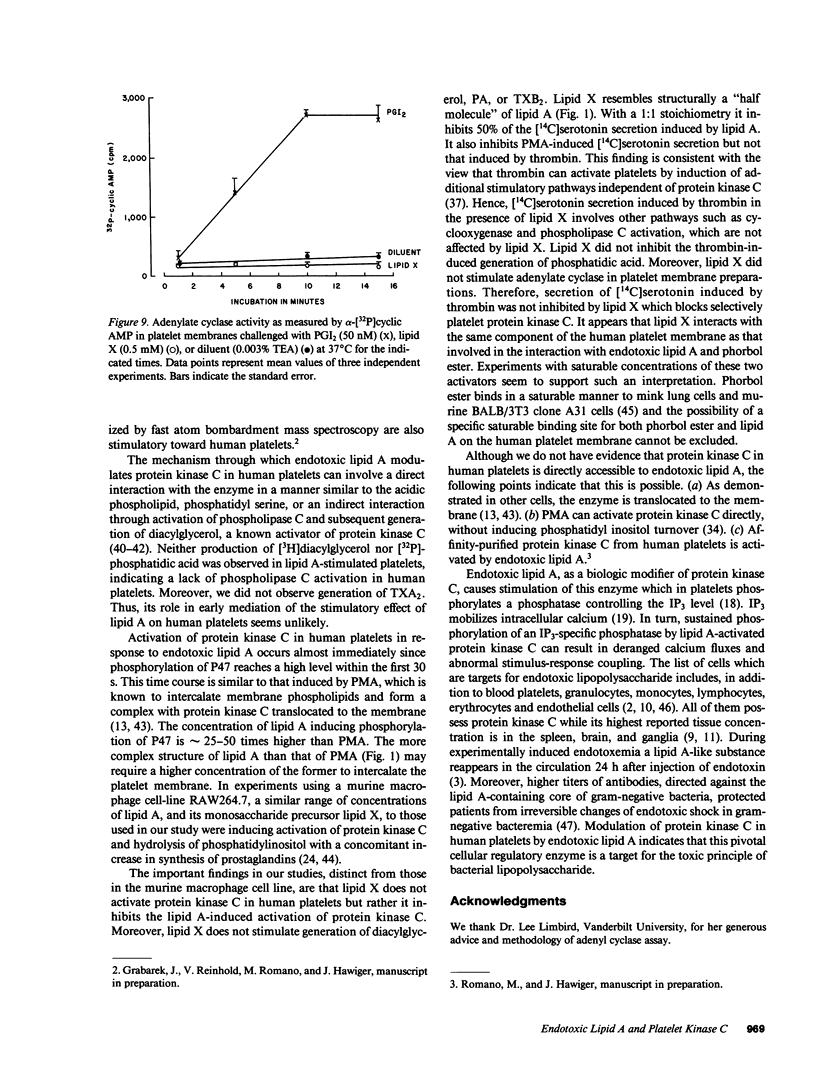
Lipid A is the toxic principle of lipopolysaccharide of gram-negative bacteria, which causes a spectrum of changes in blood cells and vascular cells. We now report that human platelets are directly stimulated by endotoxic lipid A that activates protein kinase C. Rapid phosphorylation of a human platelet protein of Mr 47,000, a marker of protein kinase C activation, accompanies secretion of [14C]serotonin and aggregation triggered by endotoxic lipid A. These events are time and concentration dependent, with phosphorylation reaching maximum in 2 min and the concentration of lipid A causing a 50% effect (EC50) between 12 and 15 microM. Phospholipase C activation in lipid A-stimulated platelets was not observed as judged by a lack of generation of [3H]diacylglycerol in [3H]arachidonic acid-labeled platelets and a lack of generation of [32P]-phosphatidic acid in 32PO4-labeled platelets. Lipid A did not induce formation of TXA2 as measured by radioimmunoassay for TXB2. The stimulation of human platelets and activation of protein kinase C by endotoxic lipid A was blocked by lipid X, a structural precursor of lipid A. Lipid X also blocked the stimulation of human platelets by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, suggesting that lipid A, lipid X and phorbol ester share reactive site(s) on the human platelet membrane. Although lipid X inhibited thrombin-induced phosphorylation of P47 it did not suppress secretion of [14C]serotonin, indicating the role of protein kinase C-independent pathways in platelet stimulation by thrombin. The inhibitory effect of lipid X did not involve generation of cyclic AMP in human platelet membrane preparations. These results indicate that human platelets are stimulated by endotoxic lipid A, a naturally occurring biologic modifier of protein kinase C. Due to the widespread presence of this enzyme in blood cells, vascular cells, and neurons, its modulation by lipid A may represent a significant mechanism underlying hematologic and circulatory derangements observed in endotoxic shock in humans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORN G. V. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:927–929. doi: 10.1038/194927b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1790–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block L. H., Jaksche H., Erne P., Bolli P., Bühler F. R. (-)-Adrenaline-induced, calcium-dependent phosphorylation of proteins in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1600–1607. doi: 10.1172/JCI111866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Balconi G., Lorenzet R., Pietra A., Locati D., Donati M. B., Semeraro N. Cultured human endothelial cells generate tissue factor in response to endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1893–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI110945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Biology of endotoxin. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:127–141. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.27.020176.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Steckley S., Hammond D., Cheng C., Timmons S., Glick A. D., Des Prez R. M. Staphylococci-induced human platelet injury mediated by protein A and immunoglobulin G Fc fragment receptor. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):931–937. doi: 10.1172/JCI109559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Setkowsky Dangelmaier C. A. Adenine nucleotide metabolism of blood platelets. X. Formaldehyde stops centrifugation-induced secretion after A23187-stimulation and causes breakdown of metabolic ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):46–61. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasa Y., Takai Y., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Phosphorylation of calf thymus H1 histone by calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):180–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajikawa N., Kishimoto A., Shiota M., Nishizuka Y. Ca2+ -dependent neutral protease and proteolytic activation of Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;102:279–290. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)02028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Tanaka Y., Miyake R., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C as a possible receptor protein of tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11442–11445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Andersson R. G., Wise B. C., Mackerlova L., Salomonsson I., Brackett N. L., Katoh N., Shoji M., Wrenn R. W. Calcium-dependent protein kinase: widespread occurrence in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom and comparison of effects of phospholipid, calmodulin, and trifluoperazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced protein phosphorylation in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):924–936. doi: 10.1172/JCI108172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsby-Baltzer I., Gemski P., Alving C. R. Heterogeneity of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):444–448. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Kreger B. E., Johns M. Type-specific and cross-reactive antibodies in gram-negative bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 10;287(6):261–267. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208102870601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi N., Mascagni P., Ribi E., Takayama K. Monophosphoryl lipid A obtained from lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella minnesota R595. Purification of the dimethyl derivative by high performance liquid chromatography and complete structural determination. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5271–5278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R., Purcell S., Takayama K. Molecular requirements for B-lymphocyte activation by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4624–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Wollenweber H. W., Russa R., Brade H., Zähringer U. Concepts of the chemical structure of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):432–438. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E. Human platelets contain phospholipase C that hydrolyzes polyphosphoinositides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5417–5420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Takai Y., Yamanishi J., Nishizuka Y. A role of calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in human platelet activation. Comparison of thrombin and collagen actions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2010–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., Todaro G. J. Specific high affinity cell membrane receptors for biologically active phorbol and ingenol esters. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):451–455. doi: 10.1038/288451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Smolowe A. F., Sullivan R. C., Barclay M. Separation of lipid classes by thin-layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 4;106(2):386–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Mascagni P., Nashed M. A., Anderson L., Raetz C. R. Fatty acyl derivatives of glucosamine 1-phosphate in Escherichia coli and their relation to lipid A. Complete structure of A diacyl GlcN-1-P found in a phosphatidylglycerol-deficient mutant. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7379–7385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Ribi E., Cantrell J. L. Separation and characterization of toxic and nontoxic forms of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):439–443. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons S., Hawiger J. Separation of human platelets from plasma proteins including factor VIII VWF by a combined albumin gradient-gel filtration method using HEPES buffer. Thromb Res. 1978 Feb;12(2):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons S., Huzoor-Akbar, Grabarek J., Kloczewiak M., Hawiger J. Mechanism of human platelet activation by endotoxic glycolipid-bearing mutant Re595 of Salmonella minnesota. Blood. 1986 Nov;68(5):1015–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal O. Bacterial endotoxins. The second Carl Prausnitz Memorial Lecture. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(1-2):1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Rao G. H., Estensen R. D. Investigation of the release reaction in platelets exposed to phorbol myristate acetate. Am J Pathol. 1974 May;75(2):301–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wightman P. D., Raetz C. R. The activation of protein kinase C by biologically active lipid moieties of lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10048–10052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. M., Bennett J. V. Editorial: Gram-negative-rod bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 3;291(14):733–734. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410032911411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoeller R. A., Wightman P. D., Anderson M. S., Raetz C. R. Accumulation of lysophosphatidylinositol in RAW 264.7 macrophage tumor cells stimulated by lipid A precursors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17212–17220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Troll W., Belman S. The tumor-promoter phorbol ester (12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate), a potent aggregating agent for blood platelets. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):325–336. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]