Abstract
Epidermal growth factor (EGF), an endogenous mitogenic peptide, has recently been shown to be a potent vasoconstrictor of vascular smooth muscle. In view of its potential role in proliferative and inflammatory renal glomerular diseases, we examined the effects of EGF both on cultured rat mesangial cells and on in vivo glomerular hemodynamics. Mesangial cells possess specific, saturable EGF receptors of differing affinities, with Kd's of 0.1 and 1.7 nM, respectively. EGF produced a rapid increase in intracellular pH of 0.12 +/- 0.01 pH U, which was sodium dependent and amiloride inhibitable. The addition of EGF to mesangial cells cultured on either glass or dimethylpolysiloxane substratum induced reproducible cell contraction. Intrarenal EGF infusion did not affect systemic blood pressure or hematocrit but reversibly decreased GFR and renal blood flow from 4.19 +/- 0.33 to 3.33 +/- 0.26 and from 1.17 +/- 0.09 to 0.69 +/- 0.07 ml/min, respectively. Glomerular micropuncture confirmed decreases in single nephron plasma flow and in single nephron GFR (from 142 +/- 9 to 98 +/- 8 and from 51.6 +/- 11.7 to 28.5 +/- 3.5 nl/min, respectively) which were due to significant increases in both pre- and postglomerular arteriolar resistances (from 1.97 +/- 0.31 to 2.65 +/- 0.36 and from 1.19 +/- 0.11 to 2.00 +/- 0.15 10(10) dyn.s.cm-5 respectively) and to a significant decrease in the ultrafiltration coefficient, Kf, which fell from 0.100 +/- 0.019 to 0.031 +/- 0.007 nl/(s.mmHg). These studies demonstrate that mesangial cells possess specific receptors for EGF, and exposure of these cells to physiologic concentrations of EGF results in an in vitro functional response characterized by activation of Na+/H+ exchange and by resultant intracellular alkalinization, as well as by cell contraction. EGF administration in vivo significantly reduces the glomerular capillary ultrafiltration coefficient, Kf, which, in combination with EGF-induced constriction of both preglomerular and postglomerular arterioles, results in acute major reductions in the rates of glomerular filtration and perfusion.
Full text
PDF

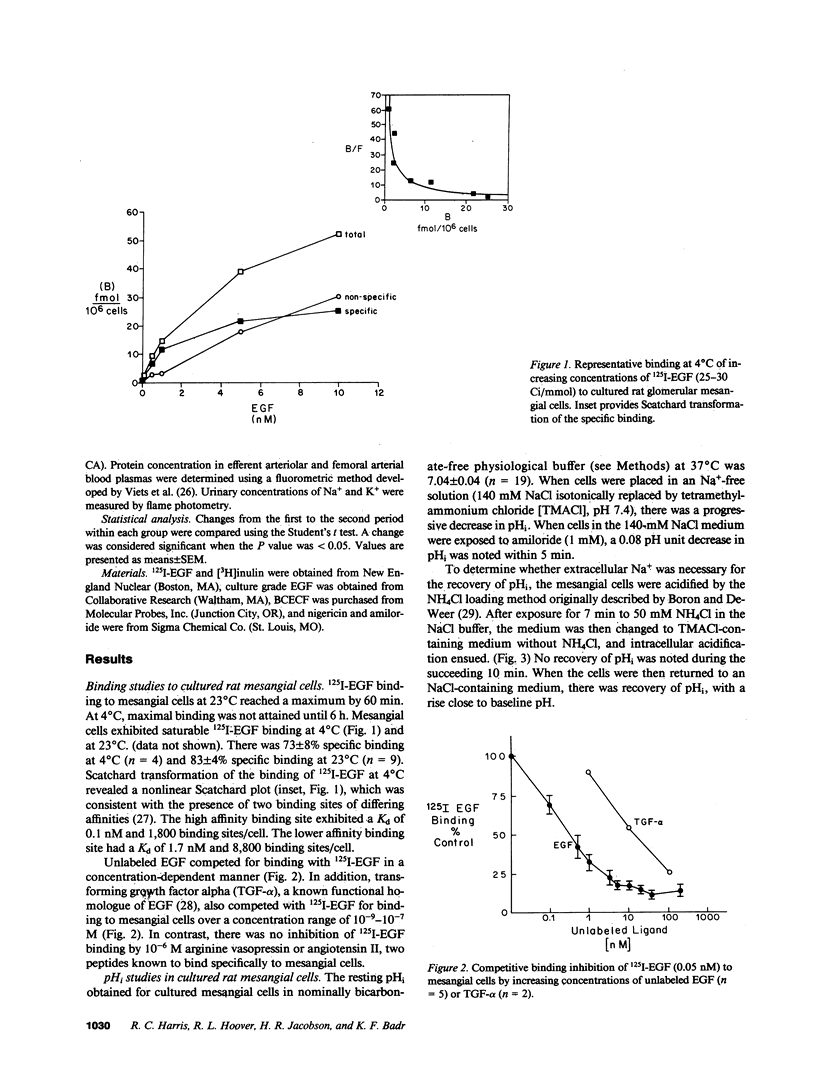
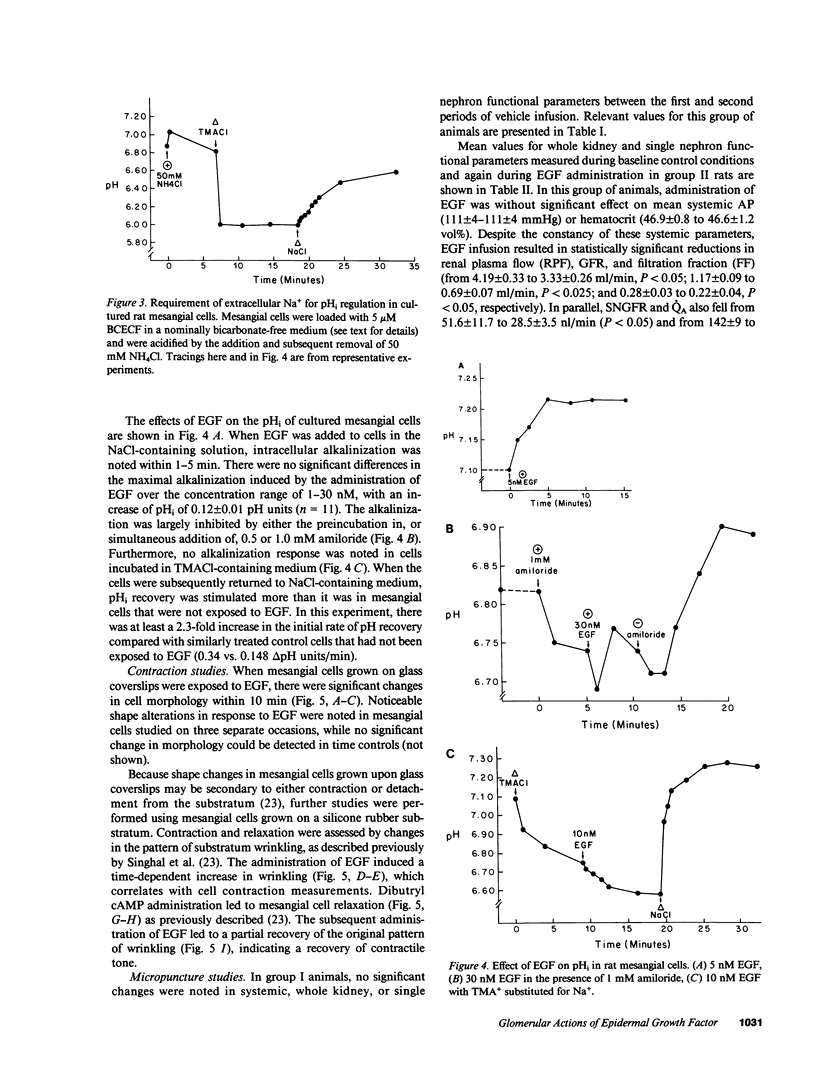

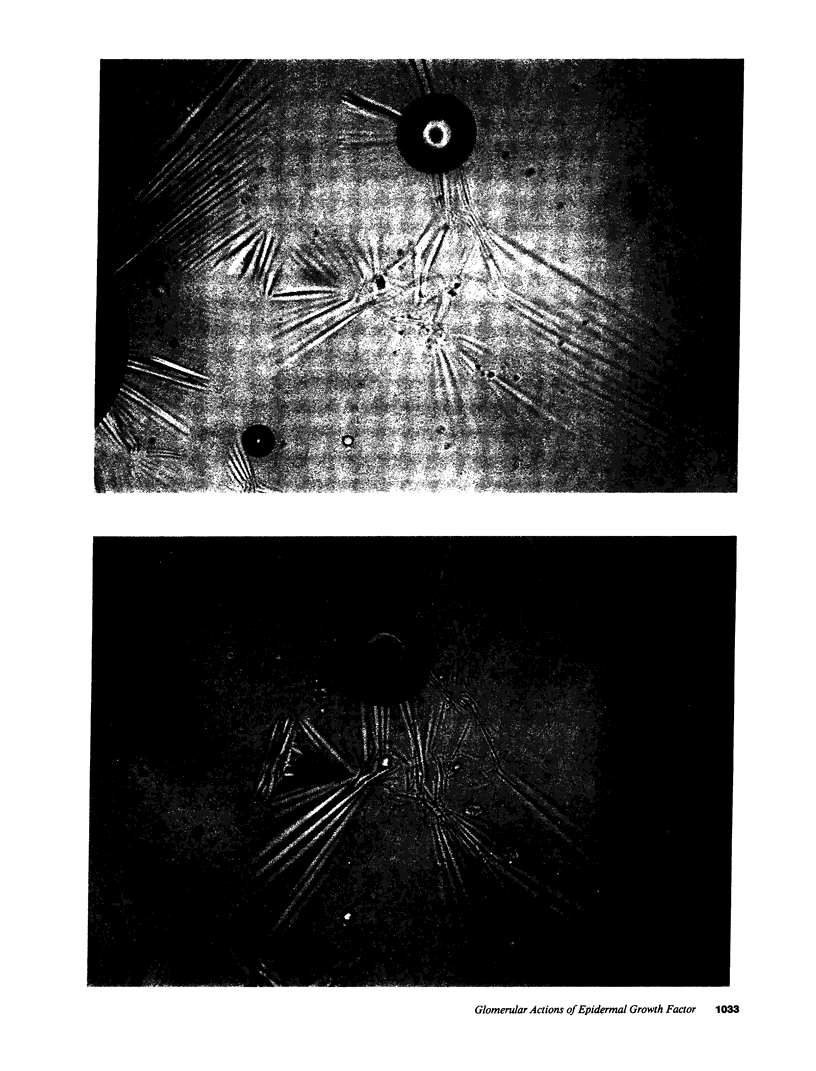
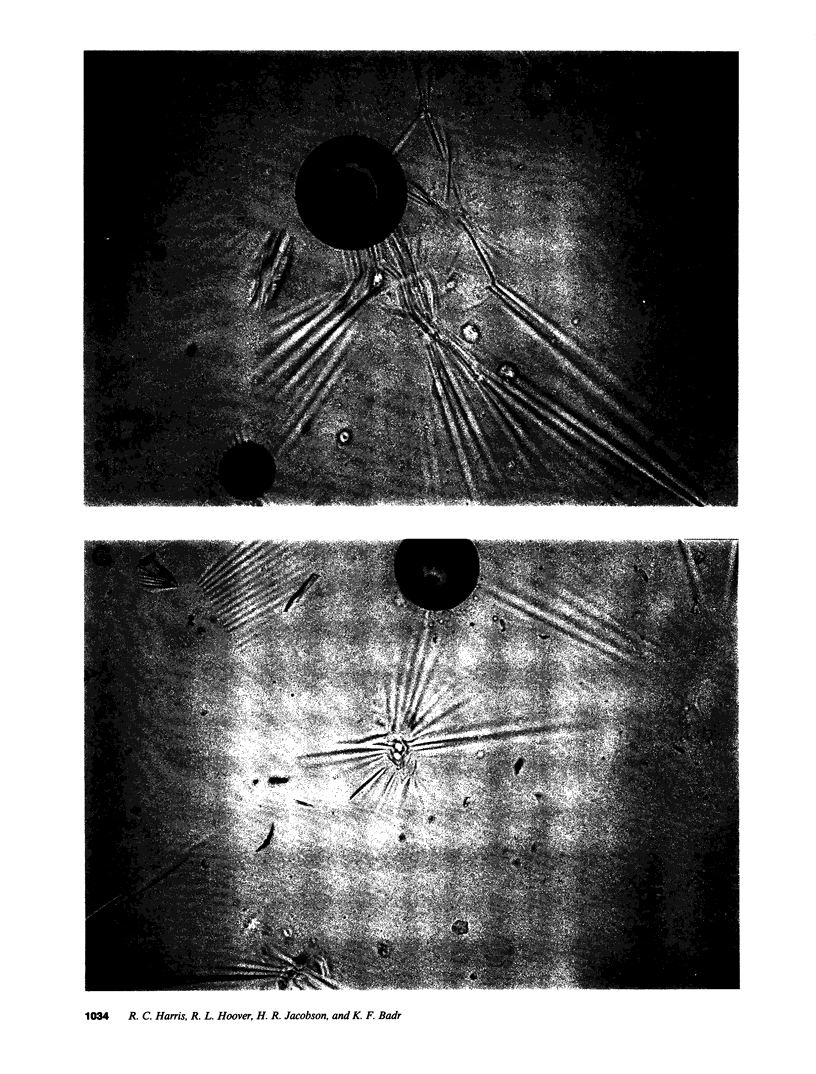



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assoian R. K., Grotendorst G. R., Miller D. M., Sporn M. B. Cellular transformation by coordinated action of three peptide growth factors from human platelets. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):804–806. doi: 10.1038/309804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausiello D. A., Kreisberg J. I., Roy C., Karnovsky M. J. Contraction of cultured rat glomerular cells of apparent mesangial origin after stimulation with angiotensin II and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):754–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI109723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Aronow M. S., Brock T. A., Cragoe E., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Angiotensin II-stimulated Na+/H+ exchange in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5057–5064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Brock T. A., Webb R. C., Taubman M. B., Atkinson W. J., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Epidermal growth factor, a vascular smooth muscle mitogen, induces rat aortic contraction. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):1083–1086. doi: 10.1172/JCI111772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava G., Rifas L., Makman M. H. Presence of epidermal growth factor receptors and influence of epidermal growth factor on proliferation and aging in cultured smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Aug;100(2):365–374. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Wilson C. B. Acute effects of antiglomerular basement membrane antibody on the process of glomerular filtration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):899–911. doi: 10.1172/JCI108543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., De Weer P. Intracellular pH transients in squid giant axons caused by CO2, NH3, and metabolic inhibitors. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jan;67(1):91–112. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1555–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. S. Platelets and glomerulonephritis. Nephron. 1977;18(5):253–258. doi: 10.1159/000180841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Properties of the receptor for epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):357–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., McKanna J. A., Cohen S. Rapid induction of morphological changes in human carcinoma cells A-431 by epidermal growth factors. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):260–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. IV. Determination of the ultrafiltration coefficient. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1500–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI107324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembinski A. B., Johnson L. R. Effect of epidermal growth factor on the development of rat gastric mucosa. Endocrinology. 1985 Jan;116(1):90–94. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-1-90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: structure and biological activities. J Cell Biochem. 1986;32(4):293–304. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240320406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01869680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. A., Robinson J. M., Hoover R. L., Wright T. C., Karnovsky M. J. Improved methods for culturing rat glomerular cells. Kidney Int. 1984 Dec;26(6):875–880. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. K., Wild P., Stopak D. Silicone rubber substrata: a new wrinkle in the study of cell locomotion. Science. 1980 Apr 11;208(4440):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.6987736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatori N., Fine B. P., Nakamura A., Cragoe E., Jr, Aviv A. Angiotensin II effect on cytosolic pH in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5073–5078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Miele J. F., Brenner B. M. Reversal of renal cortical actions of angiotensin II by verapamil and manganese. Kidney Int. 1979 Aug;16(2):137–147. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasselberg A. G., Orth D. N., Gray M. E., Stahlman M. T. Immunocytochemical localization of human epidermal growth factor/urogastrone in several human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Apr;33(4):315–322. doi: 10.1177/33.4.3884705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Cuatrecasas P. Resolution of high and low affinity epidermal growth factor receptors. Inhibition of high affinity component by low temperature, cycloheximide, and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3053–3060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Amiloride inhibition of the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F374–F379. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Karnovsky M. J. Glomerular cells in culture. Kidney Int. 1983 Mar;23(3):439–447. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Hassid A. Epidermal growth factor stimulates prostaglandin biosynthesis by canine kidney (MDCK) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 20;76(4):1181–1187. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90980-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G. Activation of 45Ca2+ influx and 22Na+/H+ exchange by epidermal growth factor and vanadate in A431 cells is independent of phosphatidylinositol turnover and is inhibited by phorbol ester and diacylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9321–9327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Yarden Y., de Laat S. W., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces electrically silent Na+ influx in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8502–8506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Hollenberg M. D., Lederis K. Vascular actions of epidermal growth factor-urogastrone: possible relationship to prostaglandin production. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;63(8):994–999. doi: 10.1139/y85-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Orth D. N. Human plasma epidermal growth factor/beta-urogastrone is associated with blood platelets. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):249–259. doi: 10.1172/JCI110964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R. M., Kim C. S., Grove R. I. Role of glucocorticoids and epidermal growth factor in normal and abnormal palatal development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1984;19:81–101. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60396-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Scott J., Bell G. I., Crawford R. J., Penschow J. D., Niall H. D., Coghlan J. P. Mouse prepro-epidermal growth factor synthesis by the kidney and other tissues. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):228–231. doi: 10.1038/313228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. A., Tam J. P., Finke U., Saunders M., Bernanke J., Silen W., Murphy R. A. Transforming growth factor alpha inhibits secretion of gastric acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3844–3846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. A., O'Keefe E. J., Earp H. S. Alteration of epidermal growth factor-dependent phosphorylation during rat liver regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):776–780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. Allosteric regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2067–2072. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal P. C., Scharschmidt L. A., Gibbons N., Hays R. M. Contraction and relaxation of cultured mesangial cells on a silicone rubber surface. Kidney Int. 1986 Dec;30(6):862–873. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Voelkel E. F., Lloyd W., Derynck R., Winkler M. E., Levine L. Actions of growth factors on plasma calcium. Epidermal growth factor and human transforming growth factor-alpha cause elevation of plasma calcium in mice. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1405–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI112728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan-Jones R. D., Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J. Effects of changes of intracellular pH on contraction in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jun;89(6):1015–1032. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.6.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viets J. W., Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Determination of serum protein concentration in nanoliter blood samples using fluorescamine or 9-phthalaldehyde. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):513–521. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]