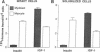Abstract
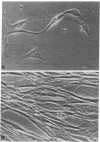
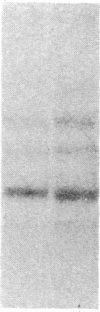
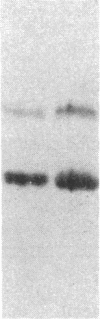
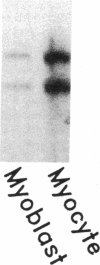
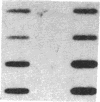
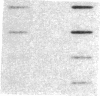
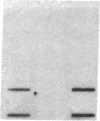
Muscle is a major tissue for insulin action. To study the effect of muscle differentiation on insulin receptors, we employed cultured mouse muscle BC3H-1 and C2 cells. In both cell lines differentiation from myoblasts to myocytes was associated with a 5-10-fold increase in specific 125I-insulin binding to intact cells. When 125I-insulin binding was carried out on solubilized myocytes and myoblasts, 125I-insulin binding to myoblasts was low. After differentiation the number of insulin receptors increased 5-10-fold. In contrast to insulin binding, insulin growth factor I receptor binding was elevated in myoblasts and was decreased by 50% in myocytes. Specific radioimmunoassay of the insulin receptor indicated that the increase in insulin binding to myocytes was due to an increase in insulin receptor content. Studies employing [35S]methionine indicated that this increase in insulin-binding sites reflected an increase in insulin receptor biosynthesis. To study insulin receptor gene expression, myoblast and myocyte mRNA was isolated and analyzed on Northern and slot blots. Differentiation from myoblasts to myocytes was accompanied by a 5-10-fold increase in insulin receptor mRNA. These studies demonstrate, therefore that differentiation in muscle cells is accompanied by increased insulin receptor biosynthesis and gene expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beguinot F., Kahn C. R., Moses A. C., Smith R. J. Distinct biologically active receptors for insulin, insulin-like growth factor I, and insulin-like growth factor II in cultured skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15892–15898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beguinot F., Kahn C. R., Moses A. C., Smith R. J. The development of insulin receptors and responsiveness is an early marker of differentiation in the muscle cell line L6. Endocrinology. 1986 Jan;118(1):446–455. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-1-446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonanno A., Merlie J. P. Transcriptional regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes during muscle development. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11452–11455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., Konda T. S., Standaert M. L., Davis J. S., Pollet R. J., Farese R. V. Insulin increases membrane and cytosolic protein kinase C activity in BC3H-1 myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3633–3639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. The nature and regulation of the insulin receptor: structure and function. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:357–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Hendler R., Felig P., Wahren J. Regulation of splanchnic and peripheral glucose uptake by insulin and hyperglycemia in man. Diabetes. 1983 Jan;32(1):35–45. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Barnes D. E., Davis J. S., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J. Effects of insulin and protein synthesis inhibitors on phospholipid metabolism, diacylglycerol levels, and pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in BC3H-1 cultured myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7094–7100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsayeth J., Maddux B., Goldfine I. D. Biosynthesis and processing of the human insulin receptor. Diabetes. 1986 Jul;35(7):837–846. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.7.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuke M., Dennis K. J., Busch H. Characterization of cloned rat ribosomal DNA fragments. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00422762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D. The insulin receptor: molecular biology and transmembrane signaling. Endocr Rev. 1987 Aug;8(3):235–255. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-3-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. J., Muller-Wieland D., Kahn C. R. Variation in insulin receptor messenger ribonucleic acid expression in human and rodent tissues. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Nov;1(11):759–766. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-11-759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings K. E., Emerson C. P., Jr cDNA clone analysis of six co-regulated mRNAs encoding skeletal muscle contractile proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1553–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor: structure and function. Endocr Rev. 1981 Summer;2(3):251–263. doi: 10.1210/edrv-2-3-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. The molecular mechanism of insulin action. Annu Rev Med. 1985;36:429–451. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.36.020185.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Heidenreich K. A., Horikoshi H. Stoichiometric translocation of adipocyte insulin receptors from the cell-surface to the cell-interior. Studies using a novel method to rapidly remove detergent and concentrate soluble receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4128–4135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. R., Maddux B. A., Okabayashi Y., Wong K. Y., Hawley D. M., Logsdon C. D., Goldfine I. D. Regulation of insulin-receptor mRNA levels by glucocorticoids. Diabetes. 1987 Jun;36(6):779–781. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.6.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medford R. M., Wydro R. M., Nguyen H. T., Nadal-Ginard B. Cytoplasmic processing of myosin heavy chain messenger RNA: evidence provided by using a recombinant DNA plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5749–5753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Caldwell K. L., Glaser L. Multiple controls for the synthesis of muscle-specific proteins in BC3H1 cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):350–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. LIlly lecture 1980. Insulin resistance and insulin action. An in vitro and in vivo perspective. Diabetes. 1981 Feb;30(2):148–162. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.2.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Caldwell K. L., Gordon J. I., Glaser L. Regulation of creatine phosphokinase expression during differentiation of BC3H1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2644–2652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Glaser L., Merlie J. P., Lindstrom J. Expression of acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit mRNA during differentiation of the BC3H1 muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3330–3336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Insulin secretion and insulin action in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: which defect is primary? Diabetes Care. 1984 May-Jun;7 (Suppl 1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. The nature and regulation of the receptors for insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:425–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Harris A. J., Devine C. E., Heinemann S. Characterization of a unique muscle cell line. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):398–413. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Bell G. I. Rsa1 polymorphism at the insulin receptor locus (INSR) on chromosome 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8661–8661. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standaert M. L., Schimmel S. D., Pollet R. J. The development of insulin receptors and responses in the differentiating nonfusing muscle cell line BC3H-1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2337–2345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch A. R., Offord J. D., Chalkley R., Rubenstein P. A. Characterization of actin mRNA levels during BC3H1 cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):849–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch A. R., Rubenstein P. A. Induction of vascular smooth muscle alpha-isoactin expression in BC3H1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3152–3159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]