Abstract
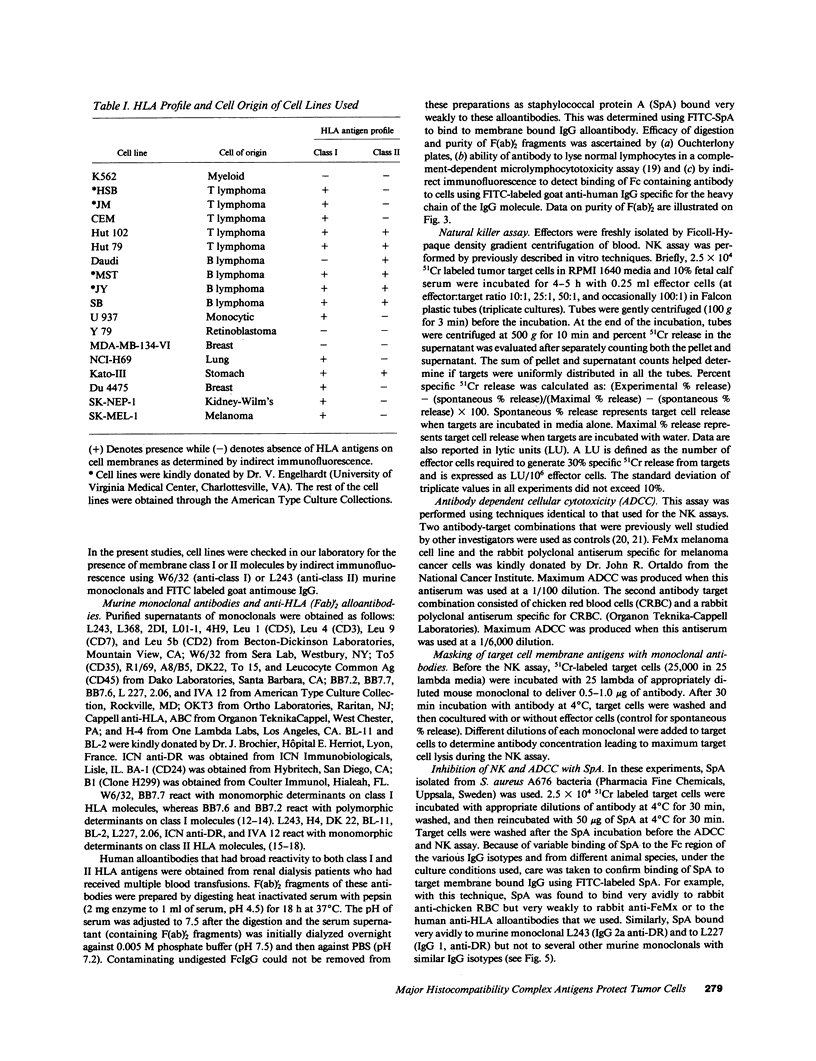
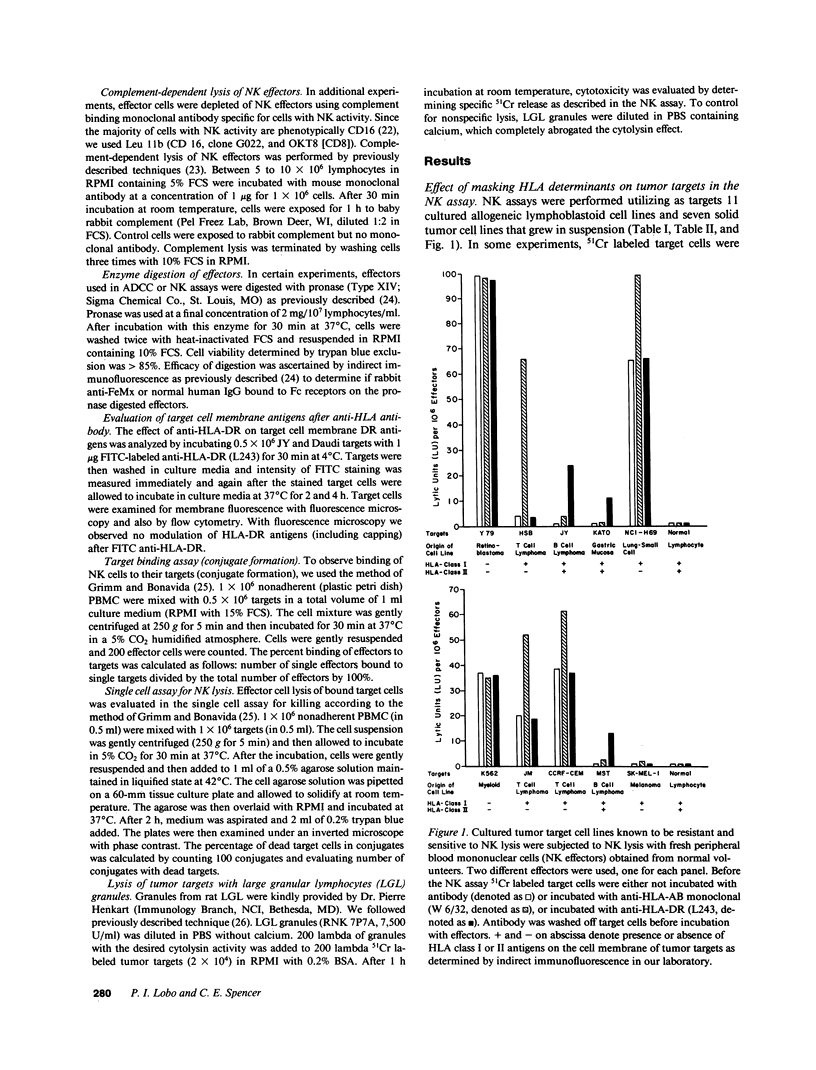
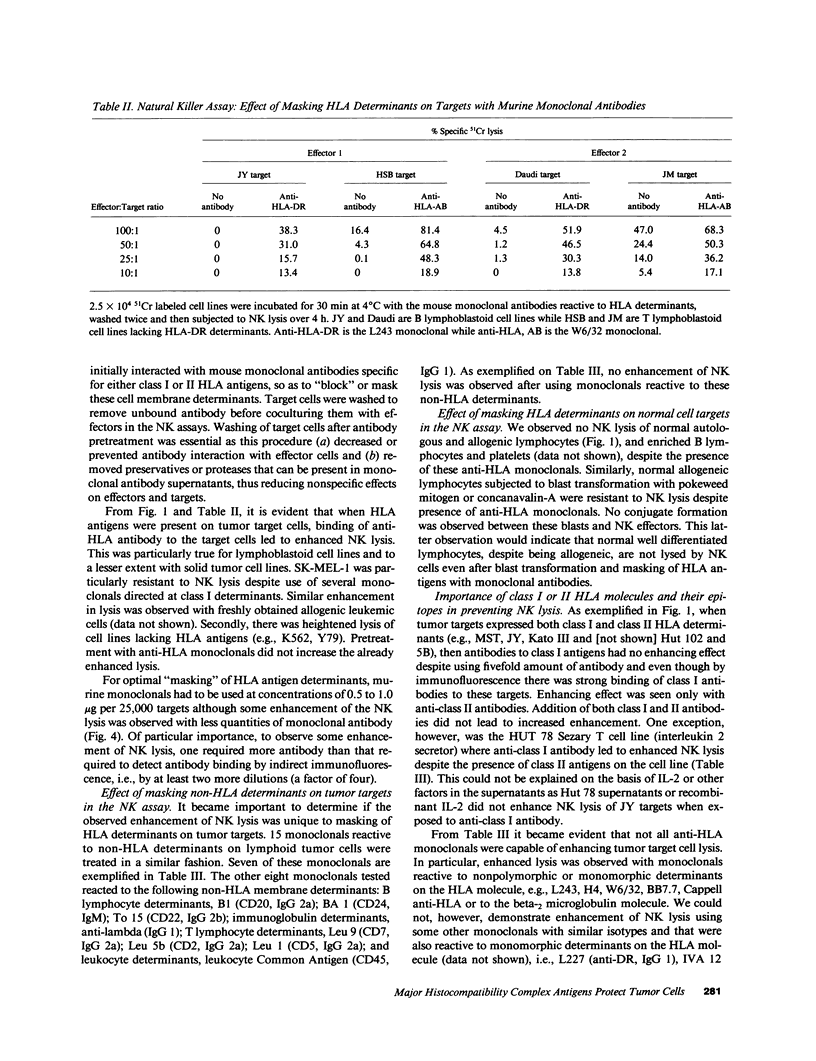
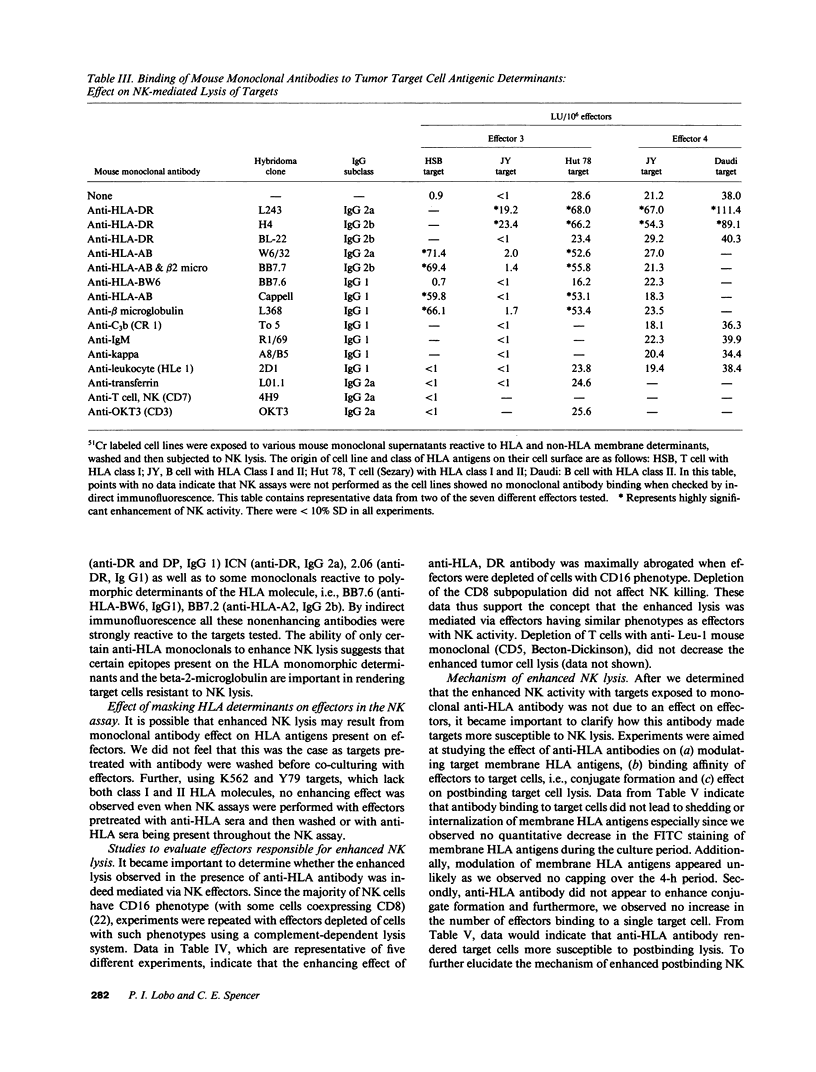
The role of major histocompatibility gene products (i.e., HLA molecules) in rendering tumor cells resistant to natural killer (NK) cell-mediated lysis was investigated by using mouse monoclonal antibodies to bind and mask HLA or non-HLA gene products on the cell membrane of human allogeneic tumor targets. Enhanced lysis of resistant lymphoid and certain other solid tumor cell lines was observed only when monoclonals used reacted to class I and II HLA molecules but not non-HLA molecules on tumor targets. Enhanced lysis was not due to antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity or due to an effect of antibody on NK effectors. Of importance, normal autologous and allogeneic human lymphocytes could not be lysed by NK cells despite blast transformation with mitogens or masking of HLA membrane determinants on blasts with monoclonal antibodies. Enhanced lysis, in the presence of antibody to HLA antigens, was not due to increased NK cell binding to tumor targets, but a consequence of enhanced postbinding lysis. Studies using granules obtained from NK cells indicated that masking of HLA antigens did not enhance the susceptibility of tumor targets to cytolysins. Such observations would suggest that HLA antigens on tumor targets inhibit the triggering of effector cells (and release of cytolysins) after recognition and binding of NK cells to target cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brodsky F. M. A matrix approach to human class II histocompatibility antigens: reactions of four monoclonal antibodies with the products of nine haplotypes. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(3):179–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00364762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Parham P., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibodies to HLA--DRw determinants. Tissue Antigens. 1980 Jul;16(1):30–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1980.tb00285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Parham P. Monomorphic anti-HLA-A,B,C monoclonal antibodies detecting molecular subunits and combinatorial determinants. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., McDevitt H. O. Analysis of HLA-D region-associated molecules with monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. L., Walker T. A., Lewis A. M., Jr, Ruley H. E., Graham F. L., Pilder S. H. Expression of the adenovirus E1A oncogene during cell transformation is sufficient to induce susceptibility to lysis by host inflammatory cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6965–6969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Landon C., Lord E. M., Bahler D. W., Frelinger J. G. Lysis of a lung carcinoma by poly I:C-induced natural killer cells is independent of the expression of class I histocompatibility antigens. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2472–2475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Knowles B. B., Wettstein P. J. Immunological surveillance of tumors in the context of major histocompatibility complex restriction of T cell function. Adv Cancer Res. 1984;42:1–65. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheţie V., Moţa G., Dobre-Gheţie M. A., Laky M., Olinescu A., Dima S., Moraru I., Sjöquist J. Modulation of IgG effector functions by a monovalent fragment of staphylococcal protein A. Mol Immunol. 1986 Apr;23(4):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorelik E., Gunji Y., Herberman R. B. H-2 antigen expression and sensitivity of BL6 melanoma cells to natural killer cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):2096–2102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E., Bonavida B. Mechanism of cell-mediated cytotoxicity at the single cell level. I. Estimation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte frequency and relative lytic efficiency. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2861–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Quillet A., Marchiol C., DeMars R., Tursz T., Fradelizi D. Natural killer susceptibility of human cells may be regulated by genes in the HLA region on chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Millard P. J., Reynolds C. W., Henkart M. P. Cytolytic activity of purified cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat large granular lymphocyte tumors. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):75–93. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Djeu J., Kay H. D., Ortaldo J. R., Riccardi C., Bonnard G. D., Holden H. T., Fagnani R., Santoni A., Puccetti P. Natural killer cells: characteristics and regulation of activity. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:43–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Reynolds C. W., Ortaldo J. R. Mechanism of cytotoxicity by natural killer (NK) cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:651–680. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Lobo P. I. Characterizaiton of two populations of human lymphocytes bearing easily detectable surface immunoglobulin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1464–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI108227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., West W. H., Herberman R. B. A functional comparison of human Fc-receptor-bearing lymphocytes active in natural cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2058–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth J., Spear B., Raab S. S., Wilson D. B. Evidence for the role of class I and class II HLA antigens in the lytic function of a cloned line of human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):728–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kärre K., Ljunggren H. G., Piontek G., Kiessling R. Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):675–678. doi: 10.1038/319675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamoyi E., Nisonoff A. Preparation of F(ab')2 fragments from mouse IgG of various subclasses. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jan 28;56(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90415-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Levy R. Two populations of Ia-like molecules on a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Phillips J. H., Hackett J., Jr, Tutt M., Kumar V. Natural killer cells: definition of a cell type rather than a function. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2735–2739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren H. G., Kärre K. Host resistance directed selectively against H-2-deficient lymphoma variants. Analysis of the mechanism. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1745–1759. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo P. I., Spencer C., Gorman J., Pirsch G. Critical appraisal of complement dependent microlymphocytotoxicity assay for detecting donor-specific alloantibody pretransplant--importance of indirect immunofluorescence as a superior alternative. Hum Immunol. 1981 Feb;2(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo P. I., Winfield J. B., Craig A., Westervelt F. B., Jr Utility of protease-digested human peripheral blood lymphocytes for the detection of lymphocyte-reactive alloantibodies by indirect immunofluorescence. Transplantation. 1977 Jan;23(1):16–21. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197701000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Herzenberg L. A. Localization of murine Ig-1b and Ig-1a (IgG 2a) allotypic determinants detected with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1979 Dec;16(12):1005–1017. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Woodhouse C., Morgan A. C., Herberman R. B., Cheresh D. A., Reisfeld R. Analysis of effector cells in human antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity with murine monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3566–3572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P. On the fragmentation of monoclonal IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b from BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2895–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Induction and inhibition by humoral antibody and nature of effector cells. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:91–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., Zeltzer P. M., Portaro J., Seeger R. C. Inhibition of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity by protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):981–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Föhring B., Shenk T. E., Raska K., Jr Tumorigenicity of adenovirus-transformed cells: region E1A of adenovirus 12 confers resistance to natural killer cells. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Ziegler A., DeMars R. Specificity of monoclonal antibodies directed against human and murine class II histocompatibility antigens as analyzed by binding to HLA-deletion mutant cell lines. Hum Immunol. 1985 Apr;12(4):191–211. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(85)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Howell D. N., Salter R. D., Dawson J. R., Cresswell P. NK susceptibility varies inversely with target cell class I HLA antigen expression. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1657–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Isselbacher K. J., Khoury G., Jay G. Reversal of oncogenesis by the expression of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):26–30. doi: 10.1126/science.3975631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Bulbuc N., Hämmerling G. J., Katzav S., Segal S., Feldman M. Abrogation of metastatic properties of tumour cells by de novo expression of H-2K antigens following H-2 gene transfection. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):301–305. doi: 10.1038/315301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



