Abstract
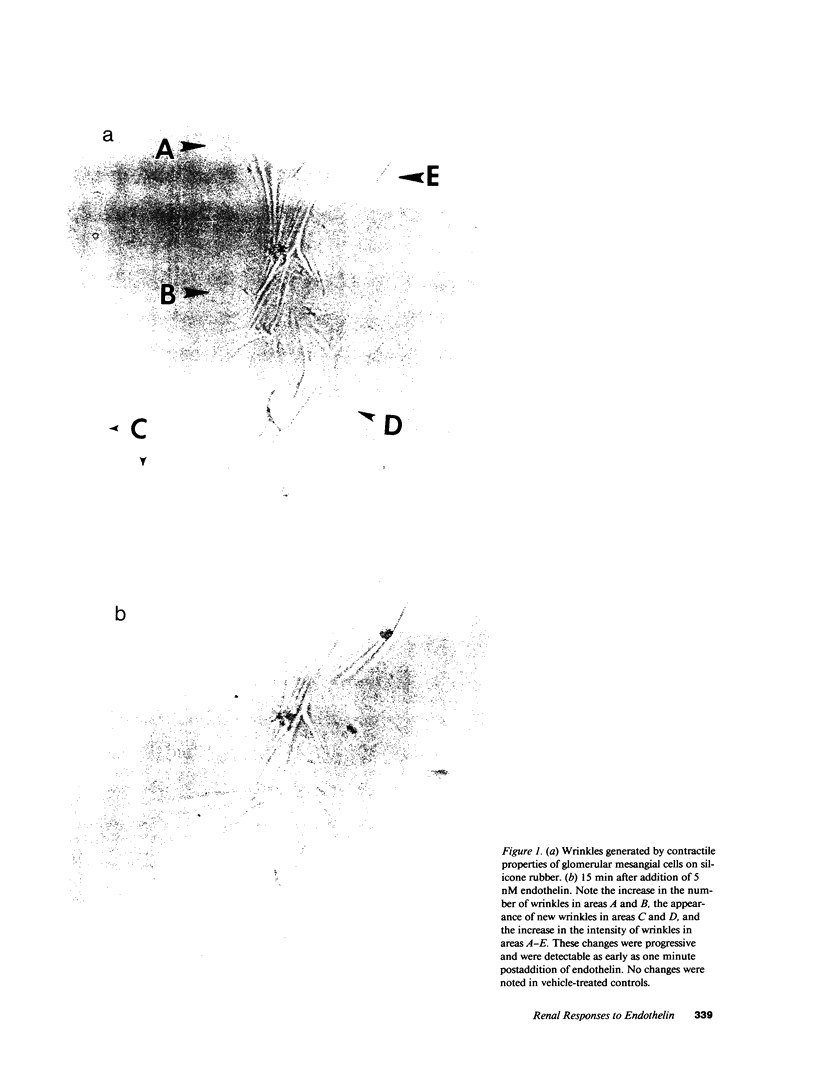
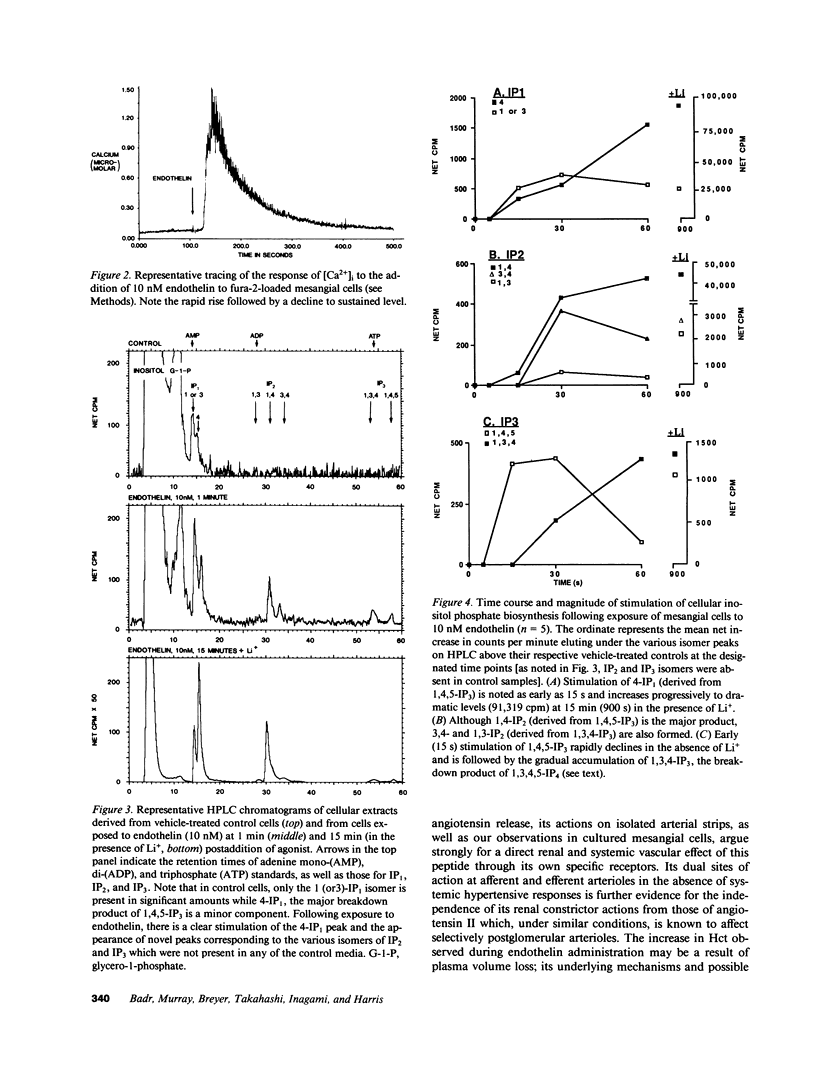
We investigated the actions of endothelin in anesthetized rats and cultured mesangial cells. Intravenous infusion of endothelin (10 pmol/min) decreased renal blood flow by 44% at 20 min without changing arterial pressure, which subsequently rose significantly from 124 +/- 3 to 133 +/- 4 mmHg over 60 min. Micropuncture during the nonhypertensive period revealed increases in afferent (65%) and efferent (82%) arteriolar resistances, thereby reducing nephron plasma flow rate. The glomerular ultrafiltration coefficient (Kf) fell from 0.097 +/- 0.035 to 0.031 +/- 0.011 nl/(s.mmHg) as did single nephron filtration rate (41 +/- 3 to 19 +/- 3 nl/min). Addition of 5 nM endothelin to mesangial cells plated on a silicone rubber substrate increased the intensity and number of tension-generated wrinkles, and caused their reappearance in forskolin prerelaxed cells. 20-30 s following exposure of fura-2 loaded mesangial cells to 10 nM endothelin, single cell intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca]i) increased from a mean baseline value of 66 +/- 11 (SE) to a peak of 684 +/- 250 nM (P less than 0.05) followed by a sustained elevation at 145 +/- 42 nM. Anion exchange HPLC revealed rapid (15 s) and dose-dependent stimulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) generation following exposure of [3H]myoinositol preloaded mesangial cells to 10-100 nM endothelin. Endothelin also led to intracellular alkalinization of 2'7'-bis(2-carboxy-ethyl)-5(and-6)carboxyfluorescein (BCECF)-loaded mesangial cells and its addition was associated with dramatic augmentation of mitogenic activity. Thus, endothelin exerts potent constrictor effects on renal arterioles which precede its systemic hypertensive action. It lowers Kf and contracts mesangial cells, likely through stimulation of IP3 generation and elevation of [Ca]i. It is a potent mesangial cell mitogen. These studies define functional responses and signal transduction pathways for endothelin in the rat kidney and propose a potential role for this peptide in the control of mesangial cell function, glomerular filtration rate, and renal vascular tone.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badr K. F., Brenner B. M., Ichikawa I. Effects of leukotriene D4 on glomerular dynamics in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 2):F239–F243. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.2.F239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Aronow M. S., Brock T. A., Cragoe E., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Angiotensin II-stimulated Na+/H+ exchange in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5057–5064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. IV. Determination of the ultrafiltration coefficient. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1500–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI107324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon S. B., Murray J. J., Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Regulation of inositol phosphate metabolism in chemoattractant-stimulated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Definition of distinct dephosphorylation pathways for IP3 isomers. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11546–11552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda Y., Hirata Y., Yoshimi H., Kojima T., Kobayashi Y., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Endothelin is a potent secretagogue for atrial natriuretic peptide in cultured rat atrial myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):167–172. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. K., Wild P., Stopak D. Silicone rubber substrata: a new wrinkle in the study of cell locomotion. Science. 1980 Apr 11;208(4440):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.6987736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C., Hoover R. L., Jacobson H. R., Badr K. F. Evidence for glomerular actions of epidermal growth factor in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1028–1039. doi: 10.1172/JCI113659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Yoshimi H., Takata S., Watanabe T. X., Kumagai S., Nakajima K., Sakakibara S. Cellular mechanism of action by a novel vasoconstrictor endothelin in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):868–875. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlondorff D., Satriano J. A., Hagege J., Perez J., Baud L. Effect of platelet-activating factor and serum-treated zymosan on prostaglandin E2 synthesis, arachidonic acid release, and contraction of cultured rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1172/JCI111309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlondorff D. The glomerular mesangial cell: an expanding role for a specialized pericyte. FASEB J. 1987 Oct;1(4):272–281. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.4.3308611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal P. C., Scharschmidt L. A., Gibbons N., Hays R. M. Contraction and relaxation of cultured mesangial cells on a silicone rubber surface. Kidney Int. 1986 Dec;30(6):862–873. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder P. M., Krause K. H., Welsh M. J. Inositol trisphosphate isomers, but not inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate, induce calcium influx in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11048–11051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomobe Y., Miyauchi T., Saito A., Yanagisawa M., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Effects of endothelin on the renal artery from spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar Kyoto rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug 2;152(3):373–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90736-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viets J. W., Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Determination of serum protein concentration in nanoliter blood samples using fluorescamine or 9-phthalaldehyde. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):513–521. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]