Abstract
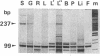
Different forms of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) have been described in different tissues. Moreover, the directly determined amino acid sequence amino end of the red cell enzyme does not exactly match the sequence deduced from cDNA isolated from HeLa cells or lymphoblasts. We have therefore investigated the sequence of cDNA from sperm, granulocytes, reticulocytes, brain, placenta, liver, lymphoblastoid cells, and cultured fibroblasts. A novel human cDNA, which has extra 138 bases coding 46 amino acids, was isolated from a lymphoblastoid cell library. Sequencing of genomic DNA amplified by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) revealed that the extra sequence was derived from the 3'-end of intron 7 by alternative splicing. This longer form of mRNA was also detected in sperm and granulocytes. Sequence analysis using PCR-amplified cDNA revealed that the 5'-end of the coding sequence of G6PD mRNA in reticulocytes is identical to those in other tissues.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., West C., Blume K. G. The removal of leukocytes and platelets from whole blood. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Aug;88(2):328–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehab F. F., Doherty M., Cai S. P., Kan Y. W., Cooper S., Rubin E. M. Detection of sickle cell anaemia and thalassaemias. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):293–294. doi: 10.1038/329293b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirono A., Beutler E. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA for human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variant A(-). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3951–3954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirono A., Forman L., Beutler E. Enzymatic diagnosis in non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia. Medicine (Baltimore) 1988 Mar;67(2):110–117. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198803000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A., Bertrand O., Cottreau D., Boivin P., Dreyfus J. C. Evidence for structural differences between human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase purified from leukocytes and erythrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A., Boivin P., Vibert M., Cottreau D., Dreyfus J. C. Post-translational modifications of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochimie. 1974;56(10):1395–1407. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan S. C., Doherty M., Gitschier J. An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. Application to hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):985–990. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapeyre B., Amalric F. A powerful method for the preparation of cDNA libraries: isolation of cDNA encoding a 100-kDal nucleolar protein. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini G., Toniolo D., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., Dono R., Viglietto G., Paonessa G., D'Urso M., Persico M. G. Structural analysis of the X-linked gene encoding human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1849–1855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Nishimura S., Seela F. Improvement of the dideoxy chain termination method of DNA sequencing by use of deoxy-7-deazaguanosine triphosphate in place of dGTP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Viglietto G., Martini G., Toniolo D., Paonessa G., Moscatelli C., Dono R., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., D'Urso M. Isolation of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) cDNA clones: primary structure of the protein and unusual 5' non-coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2511–2522. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegawa S., Fujii H., Miwa S. Change of pyruvate kinase isozymes from M2- to L-type during development of the red cell. Br J Haematol. 1983 Jul;54(3):467–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa T., Huang I. Y., Ikuta T., Yoshida A. Human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: primary structure and cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4157–4161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa T., Yoneyama Y., Miwa S., Yoshida A. A single nucleotide base transition is the basis of the common human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variant A (+). Genomics. 1987 Nov;1(3):228–231. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toncheva D., Evrev T., Tzoneva M. G6PD in immature and mature human brain. Electrophoretic and enzyme kinetic studies. Hum Hered. 1982;32(3):193–196. doi: 10.1159/000153290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliamy T. J., D'Urso M., Battistuzzi G., Estrada M., Foulkes N. S., Martini G., Calabro V., Poggi V., Giordano R., Town M. Diverse point mutations in the human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene cause enzyme deficiency and mild or severe hemolytic anemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5171–5175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]