Abstract
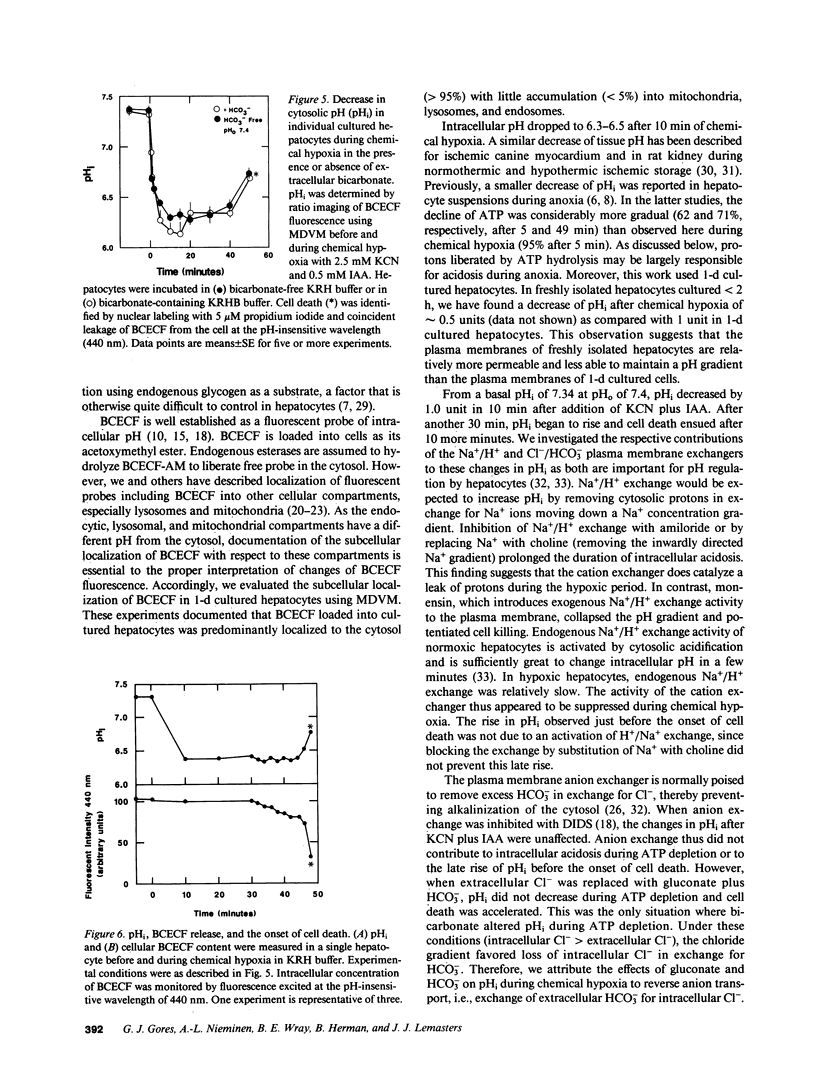
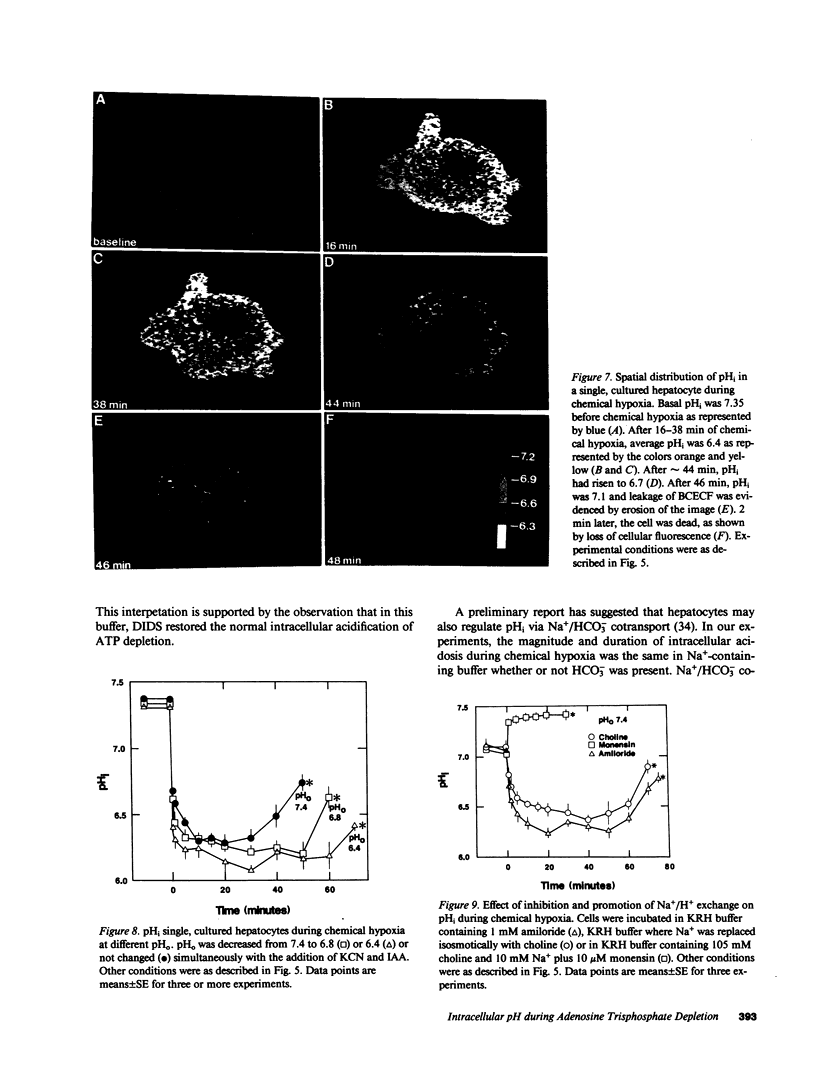
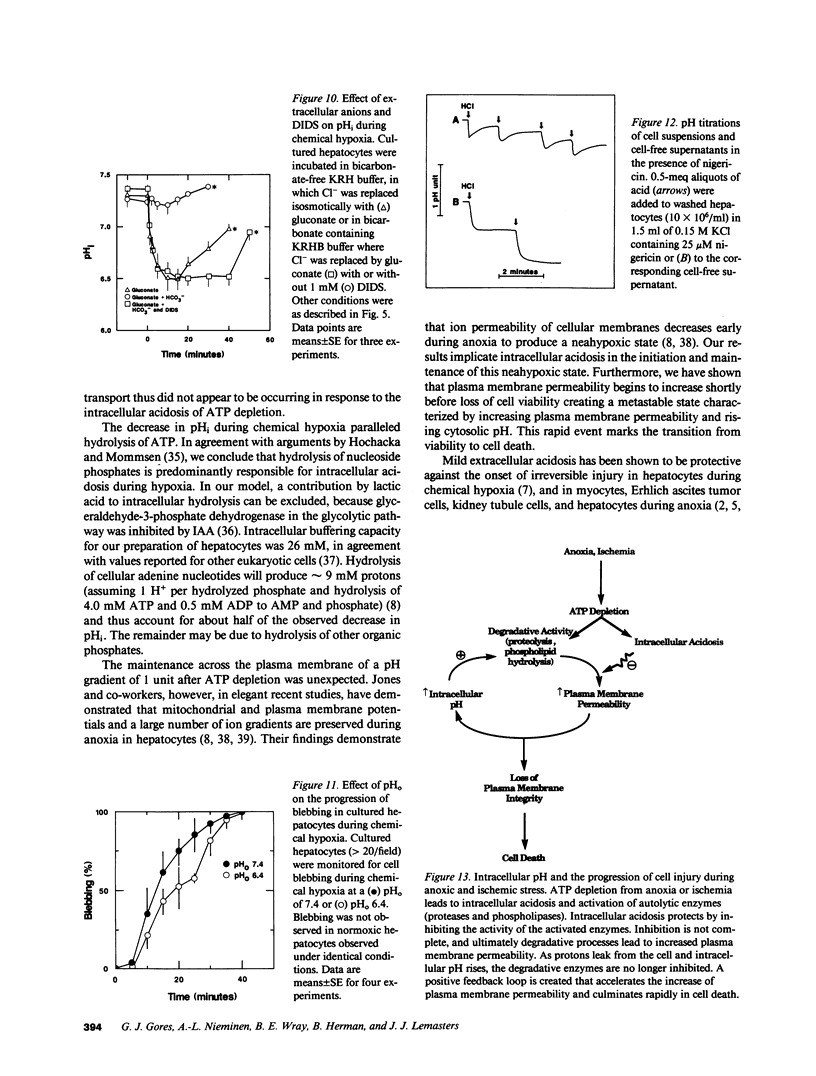
The relationships between extracellular pH (pHo), intracellular pH (pHi), and loss of cell viability were evaluated in cultured rat hepatocytes after ATP depletion by metabolic inhibition with KCN and iodoacetate (chemical hypoxia). pHi was measured in single cells by ratio imaging of 2',7'-biscarboxy-ethyl-5,6-carboxyfluorescein (BCECF) fluorescence using multiparameter digitized video microscopy. During chemical hypoxia at pHo of 7.4, pHi decreased from 7.36 to 6.33 within 10 min. pHi remained at 6.1-6.5 for 30-40 min (plateau phase). Thereafter, pHi began to rise and cell death ensued within minutes, as evidenced by nuclear staining with propidium iodide and coincident leakage of BCECF from the cytoplasm. An acidic pHo produced a slightly greater drop in pHi, prolonged the plateau phase of intracellular acidosis, and delayed the onset of cell death. Inhibition of Na+/H+ exchange also prolonged the plateau phase and delayed cell death. In contrast, monensin or substitution of gluconate for Cl- in buffer containing HCO3- abolished the pH gradient across the plasma membrane and shortened cell survival. The results indicate that intracellular acidosis after ATP depletion delays the onset of cell death, whereas reduction of the degree of acidosis accelerates cell killing. We conclude that intracellular acidosis protects against hepatocellular death from ATP depletion, a phenomenon that may represent a protective adaptation against hypoxic and ischemic stress.
Full text
PDF


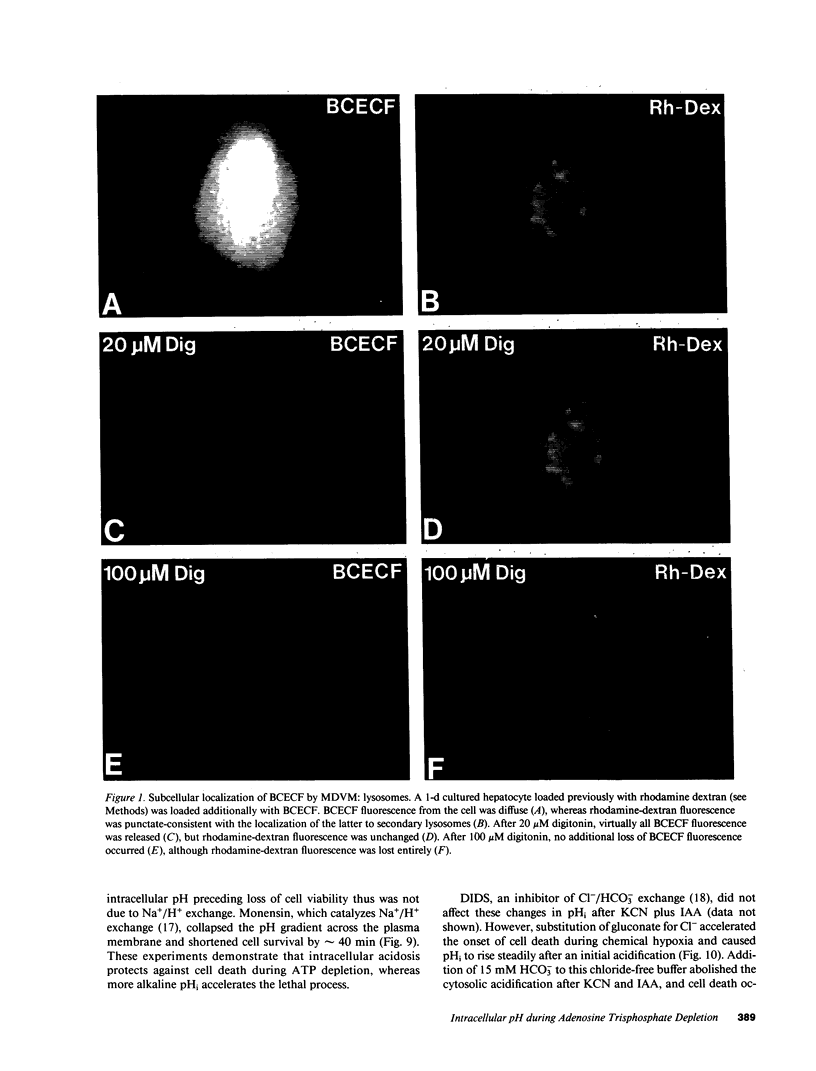
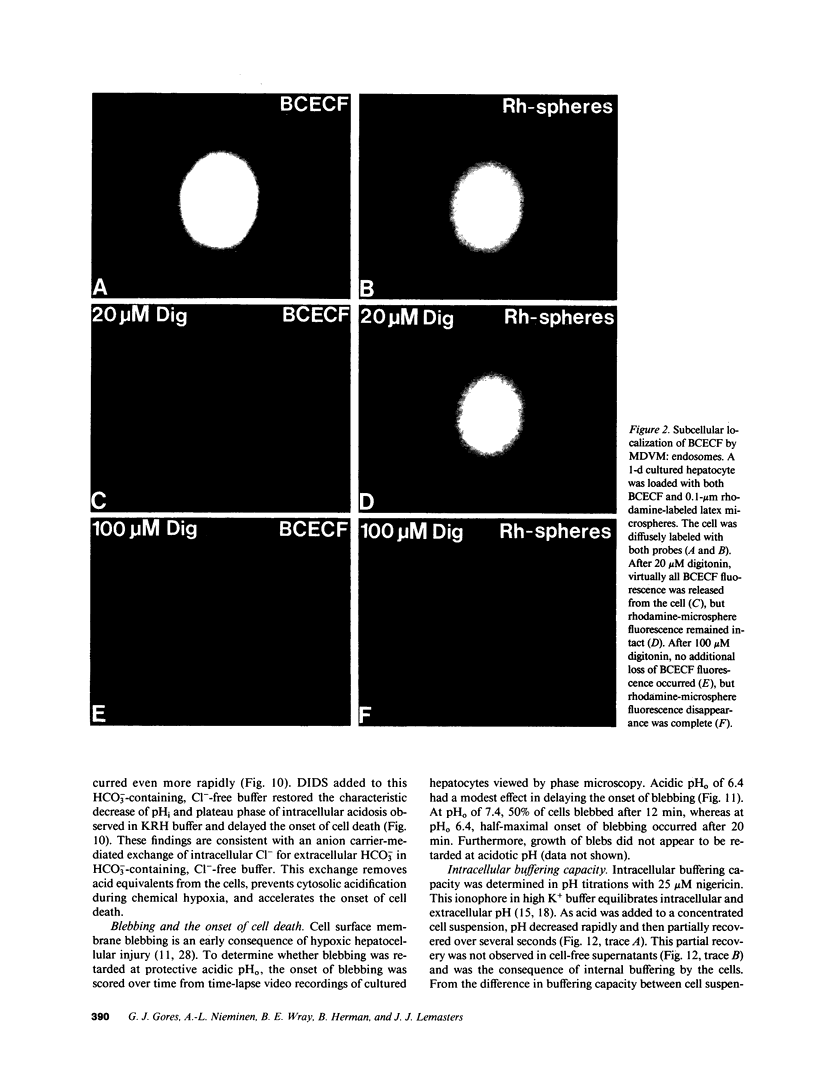
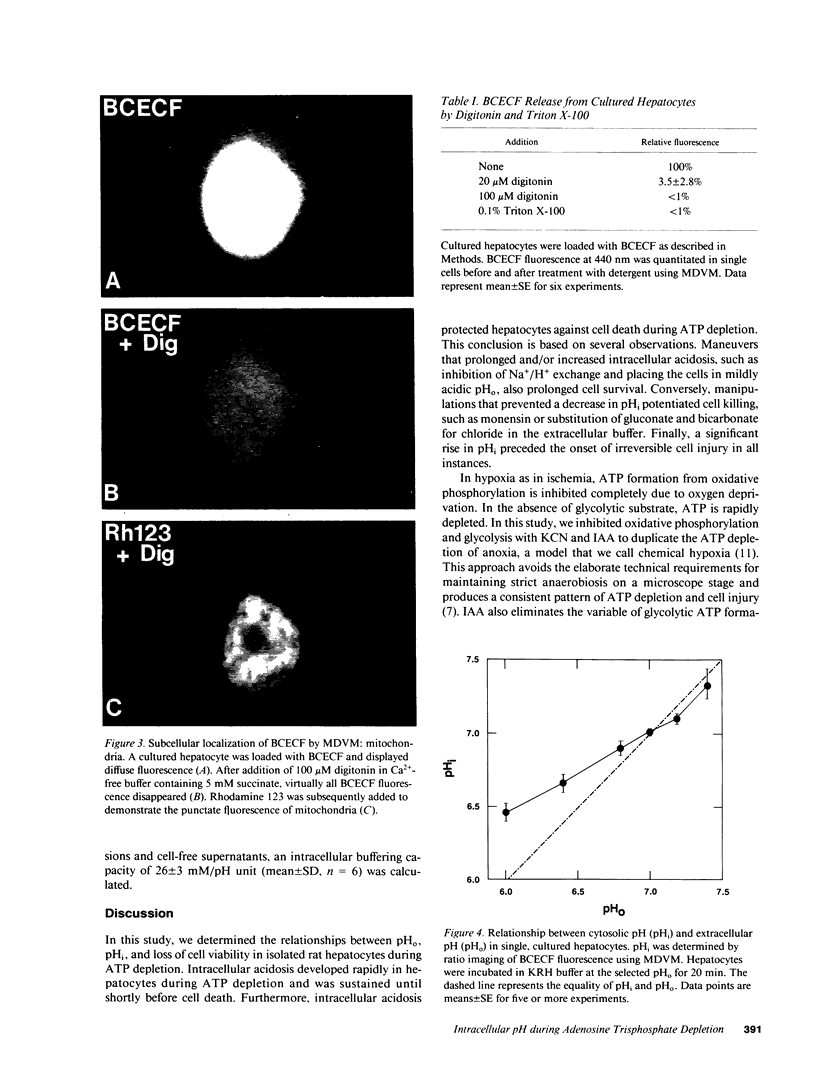


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschuld R. A., Hostetler J. R., Brierley G. P. Response of isolated rat heart cells to hypoxia, re-oxygenation, and acidosis. Circ Res. 1981 Aug;49(2):307–316. doi: 10.1161/01.res.49.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson B. S., Aw T. Y., Jones D. P. Mitochondrial transmembrane potential and pH gradient during anoxia. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):C349–C355. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.4.C349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson B. S., Jones D. P. Use of digitonin fractionation to determine mitochondrial transmembrane ion distribution in cells during anoxia. Anal Biochem. 1985 Apr;146(1):164–172. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anundi I., King J., Owen D. A., Schneider H., Lemasters J. J., Thurman R. G. Fructose prevents hypoxic cell death in liver. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):G390–G396. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.3.G390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aw T. Y., Andersson B. S., Jones D. P. Mitochondrial transmembrane ion distribution during anoxia. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):C356–C361. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.4.C356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Aronow M. S., Brock T. A., Cragoe E., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Angiotensin II-stimulated Na+/H+ exchange in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5057–5064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing O. H., Brooks W. W., Messer J. V. Heart muscle viability following hypoxia: protective effect of acidosis. Science. 1973 Jun 22;180(4092):1297–1298. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4092.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell D. M., Arenson D. M., Maher J. J., Roll F. J. Support of cultured hepatocytes by a laminin-rich gel. Evidence for a functionally significant subendothelial matrix in normal rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):801–812. doi: 10.1172/JCI112887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V., Cheung J. Y. Effects of metabolic acidosis on viability of cells exposed to anoxia. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 1):C149–C159. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.1.C149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bright G. R., Fisher G. W., Rogowska J., Taylor D. L. Fluorescence ratio imaging microscopy: temporal and spatial measurements of cytoplasmic pH. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1019–1033. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. H., Altschuld R. A., Jung D. W., Brierley G. P. Estimation of intramitochondrial pCa and pH by fura-2 and 2,7 biscarboxyethyl-5(6)-carboxyfluorescein (BCECF) fluorescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 30;149(1):40–45. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91602-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. B., Radda G. K., Seeley P. J. Studies of acidosis in the ischaemic heart by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 15;184(3):547–554. doi: 10.1042/bj1840547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good N. E., Winget G. D., Winter W., Connolly T. N., Izawa S., Singh R. M. Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):467–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gores G. J., Nieminen A. L., Fleishman K. E., Dawson T. L., Herman B., Lemasters J. J. Extracellular acidosis delays onset of cell death in ATP-depleted hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 1):C315–C322. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.3.C315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman B., Nieminen A. L., Gores G. J., Lemasters J. J. Irreversible injury in anoxic hepatocytes precipitated by an abrupt increase in plasma membrane permeability. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):146–151. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.2.3342967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochachka P. W., Mommsen T. P. Protons and anaerobiosis. Science. 1983 Mar 25;219(4591):1391–1397. doi: 10.1126/science.6298937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwagura T., Deutsch C. J., Taylor J., Erecińska M., Wilson D. F. Dependence of gluconeogenesis, urea synthesis, and energy metabolism of hepatocytes on intracellular pH. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. R., Van Dyke R. W., Scharschmidt B. F. Acidic vesicles in cultured rat hepatocytes. Identification and characterization of their relationship to lysosomes and other storage vesicles. Gastroenterology. 1987 May;92(5 Pt 1):1251–1261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemasters J. J., DiGuiseppi J., Nieminen A. L., Herman B. Blebbing, free Ca2+ and mitochondrial membrane potential preceding cell death in hepatocytes. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):78–81. doi: 10.1038/325078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemasters J. J., Stemkowski C. J., Ji S., Thurman R. G. Cell surface changes and enzyme release during hypoxia and reoxygenation in the isolated, perfused rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):778–786. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Milani D., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Fura-2 measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in monolayers and suspensions of various types of animal cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicotera P., Hartzell P., Baldi C., Svensson S. A., Bellomo G., Orrenius S. Cystamine induces toxicity in hepatocytes through the elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ and the stimulation of a nonlysosomal proteolytic system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14628–14635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso A. M., Negulescu P. A., Machen T. E. Na+-H+ and Cl(-)-OH-(HCO3-) exchange in gastric glands. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 1):G524–G534. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.4.G524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttila A., Trump B. F. Extracellular acidosis protects Ehrlich ascites tumor cells and rat renal cortex against anoxic injury. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):277–278. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Cytoplasmic pH and free Mg2+ in lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):189–196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouslin W., Erickson J. L. Factors affecting the loss of mitochondrial function in autolyzing cardiac muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1986 Nov;18(11):1187–1195. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(86)80044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouslin W. Protonic inhibition of the mitochondrial oligomycin-sensitive adenosine 5'-triphosphatase in ischemic and autolyzing cardiac muscle. Possible mechanism for the mitigation of ATP hydrolysis under nonenergizing conditions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9657–9661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehr P. A., Bore P. J., Papatheofanis J., Radda G. K. Non-destructive measurement of metabolites and tissue pH in the kidney by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Br J Exp Pathol. 1979 Dec;60(6):632–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger M., Paradiso A. M., Machen T. E. Steady state regulation of intracellular pH in isolated rabbit gastric glands. Roles for Na/H and Cl/OH (HCO3) exchange. Gastroenterology. 1987 Apr;92(4):957–965. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90970-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S. F., Bilezikian J. P., Al-Awqati Q. Fura-2 fluorescence is localized to mitochondria in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 1):C744–C747. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.5.C744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. J. Ionic requirements for intracellular pH regulation in rainbow trout hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 2):R24–R29. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.1.R24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]