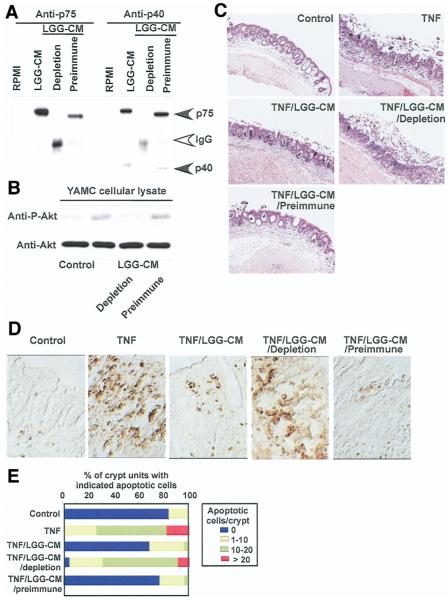
Figure 7.
Immunodepletion of p75 and p40 blocks LGG-CM’s antiapoptotic effects on colon epithelial cells. Immunodepletion of p75 and p40 was performed by sequential immunoprecipitation of LGG-CM with anti-p75 and p40 antibodies, characterized in Figure 1, to remove both p75 and p40 from LGG-CM. Preimmune sera were used as a control. Proteins present in LGG-CM, LGG-CM immunodepleted with antibodies (LGG-CM depletion), or preimmune sera (LGG-CM preimmune) were separated by SDS-PAGE for Western blot analysis with anti-p75 and p40 antibodies (A). LGG-CM, LGG-CM depletion, and LGG-CM preimmune were used to treat YAMC cells to detect Akt activation as shown in Figure 2 (B) or C57BL/6 mouse colon explants described as in Figure 5 in the presence or absence of TNF (100 ng/mL) for 24 hours. Paraffin-embedded tissue sections were stained with H&E for light microscopic assessment of epithelial damage (C; original magnification, ×10) and ISOL staining to detect epithelial cell apoptosis using DIC microscopy (D; original magnification, ×40). The percentage of crypts with indicated apoptotic cells is shown (E). Data represent mean scores from at least 3 experiments.