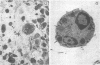
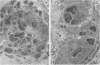
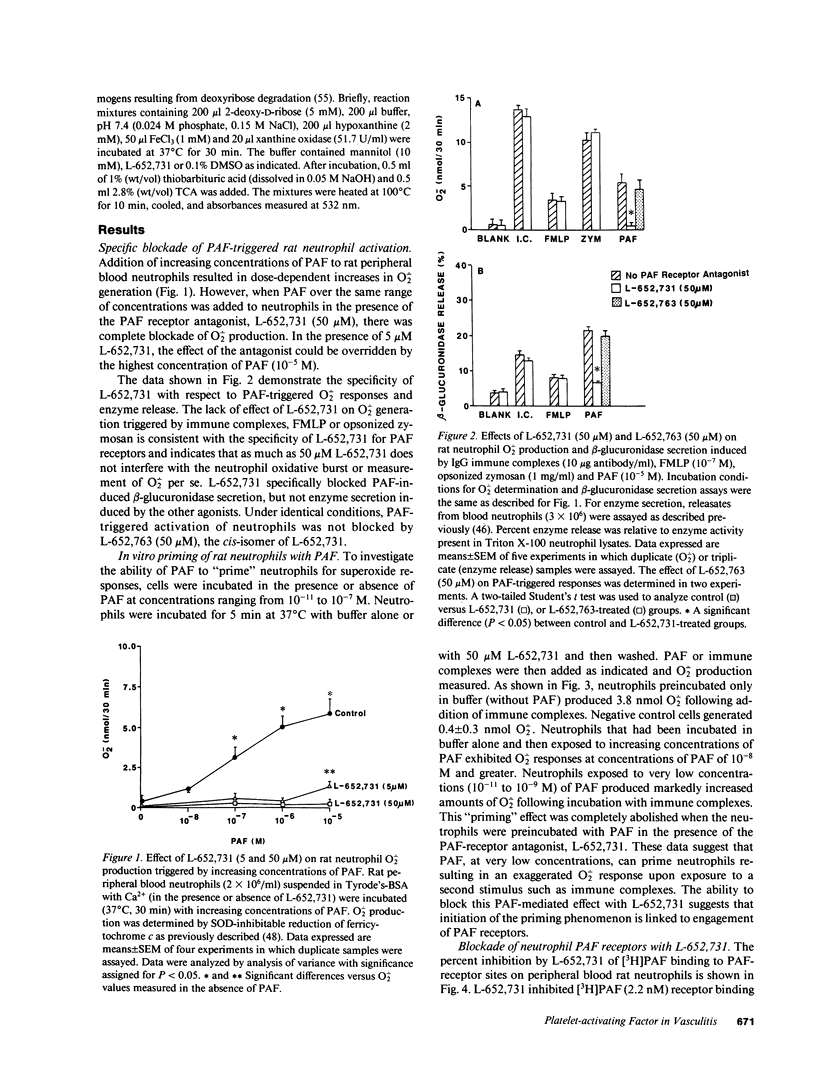
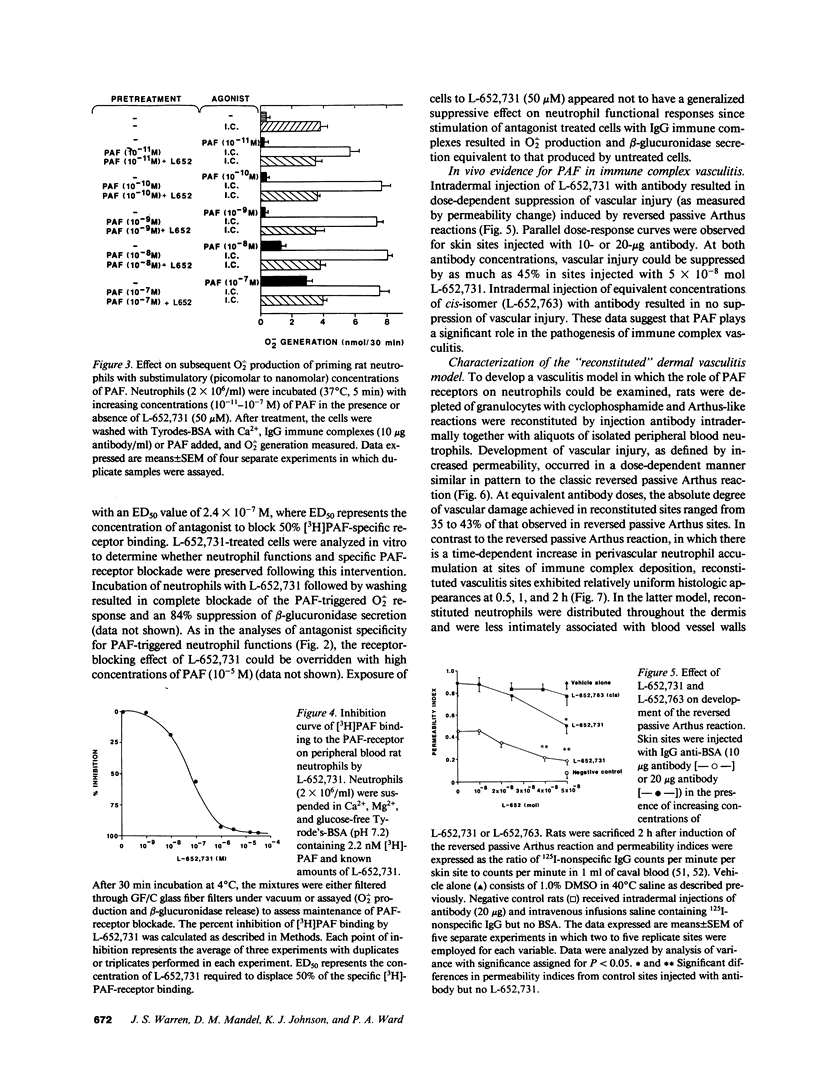
Abstract
These studies were designed to determine the role of platelet-activating factor (PAF) in the pathogenesis of immune complex (IgG) induced dermal vasculitis in the rat. In vitro, very low (pM and nM) concentrations of PAF "primed" rat neutrophils for enhanced O2-. responses to IgG immune complexes while higher concentrations were directly stimulatory. The PAF receptor antagonist, L-652,731, blocked responses (O2-. production and enzyme release) of rat neutrophils stimulated with PAF but did not block responses triggered by immune complexes, formyl chemotactic peptide or opsonized zymosan particles. When L-652,731 was added to the antibody employed in the reversed passive Arthus reaction, the injury resulting from immune complex-induced vasculitis was significantly attenuated. In order to determine if in vivo protection provided by L-652,731 was related to neutrophils, we developed a new model in which rats are systemically depleted of neutrophils by cyclophosphamide and then locally reconstituted with intact neutrophils in a manner that allows restoration of immune complex-induced vascular injury. With this model, we demonstrated that the effects of neutrophil reconstitution are substantially diminished if the cells are pretreated with L-652,731 and then washed. By priming neutrophils with substimulatory concentrations of PAF, we have also provided in vivo evidence that neutrophil priming can increase the magnitude of vascular injury. These data provide evidence that vascular injury associated with immune complex dermal vasculitis is related to availability of PAF receptors on neutrophils, suggesting a mechanism through which PAF may function as a mediator in the pathogenesis of immune complex vasculitis.
Full text
PDF


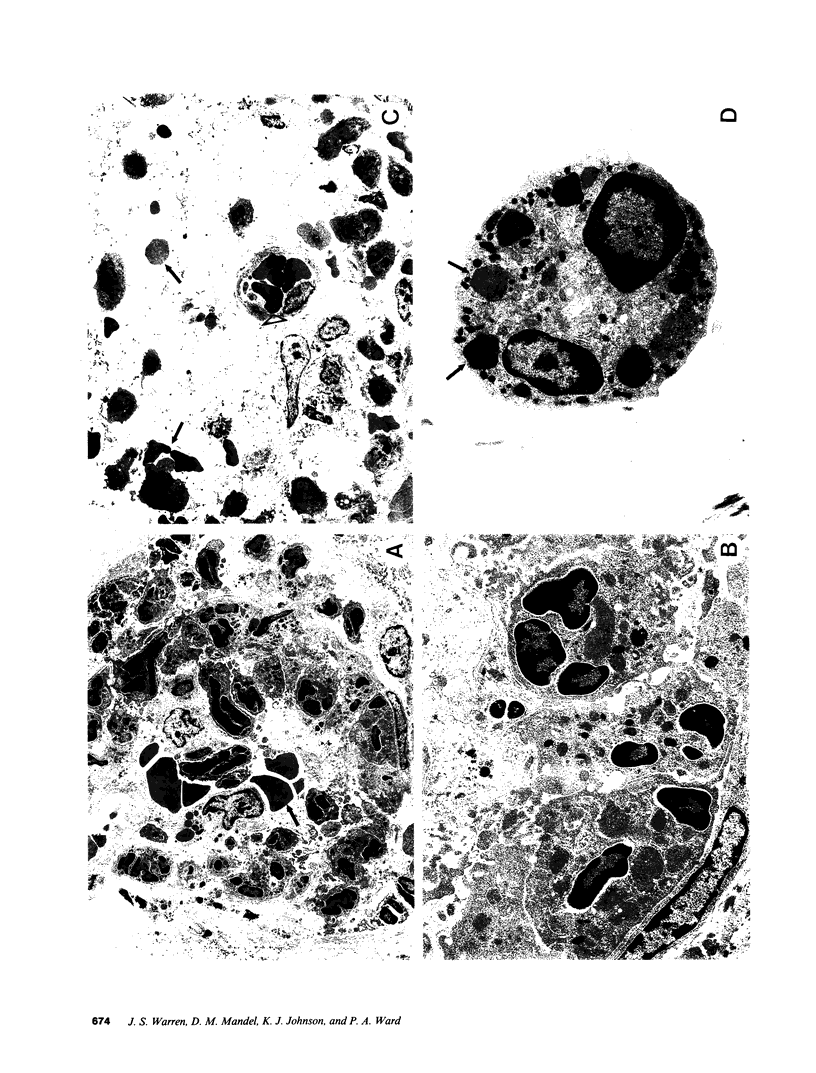
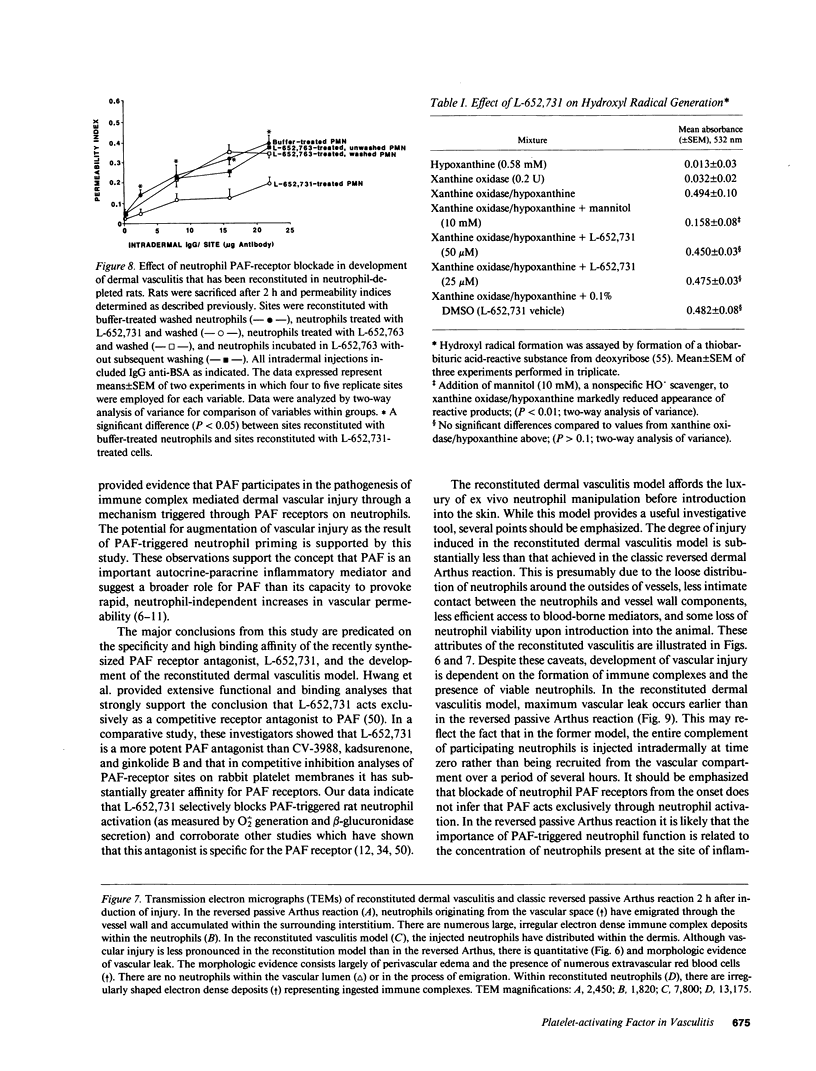



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M. L., Snyder F., Byers L. W., Brooks B., Muirhead E. E. Antihypertensive activity of an alkyl ether analog of phosphatidylcholine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 29;90(4):1194–1200. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Platelet activating factors alters calcium homeostasis in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 2):H1086–H1092. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.250.6.H1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Aglietta M., Sanavio F., Stacchini A., Lauri D., Camussi G. Alkyl-ether phosphoglycerides influence calcium fluxes into human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2748–2753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Camussi G., Aglietta M., Braquet P., Bosia A., Pescarmona G., Sanavio F., D'Urso N., Marchisio P. C. Human endothelial cells are target for platelet-activating factor. I. Platelet-activating factor induces changes in cytoskeleton structures. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2439–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and platelet-activating factor production by heat-aggregated immunoglobulin G in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13758–13761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Bussolino F., Tetta C., Caligaris Cappio F., Coda R., Macchiorlatti E., Alberton M., Roffinello C., Segoloni G. Effect of prostacyclin (PGI2) on immune-complex-induced neutropenia. Immunology. 1983 Apr;48(4):625–633. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Pawlowski I., Bussolino F., Caldwell P. R., Brentjens J., Andres G. Release of platelet activating factor in rabbits with antibody-mediated injury of the lung: the role of leukocytes and of pulmonary endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1802–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Tetta C., Coda R., Benveniste J. Release of platelet-activating factor in human pathology. I. Evidence for the occurrence of basophil degranulation and release of platelet-activating factor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lab Invest. 1981 Mar;44(3):241–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Tetta C., Deregibus M. C., Bussolino F., Segoloni G., Vercellone A. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) in experimentally-induced rabbit acute serum sickness: role of basophil-derived PAF in immune complex deposition. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):86–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Tetta C., Segoloni G., Chiara Deregibus M., Bussolino F. Neutropenia induced by platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) released from neutrophils: the inhibitory effect of prostacyclin (PGI2). Agents Actions. 1981 Dec;11(6-7):550–553. doi: 10.1007/BF01978735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. W., Feddersen C. O., Henson P. M., Voelkel N. F. Platelet-activating factor mediates hemodynamic changes and lung injury in endotoxin-treated rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1498–1509. doi: 10.1172/JCI112980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Aikin B. S. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes in immunologic reactions. The destruction of vascular basement membrane in vivo and in vitro. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):733–752. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doebber T. W., Wu M. S., Biftu T. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) mediation of rat anaphylactic responses to soluble immune complexes. Studies with PAF receptor antagonist L-652,731. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4659–4668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doebber T. W., Wu M. S., Shen T. Y. Platelet activating factor intravenous infusion in rats stimulates vascular lysosomal hydrolase secretion independent of blood neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):980–987. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englberger W., Bitter-Suermann D., Hadding U. Influence of lysophospholipids and PAF on the oxidative burst of PMNL. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1987;9(3):275–282. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(87)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantone J. C., Ward P. A. Role of oxygen-derived free radicals and metabolites in leukocyte-dependent inflammatory reactions. Am J Pathol. 1982 Jun;107(3):395–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay J. C., Beckman J. K., Zaboy K. A., Lukens J. N. Modulation of neutrophil oxidative responses to soluble stimuli by platelet-activating factor. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):931–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRY R. J., CHIAMORI N., GOLUB O. J., BERKMAN S. Revised spectrophotometric methods for the determination of glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase, glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, and lactic acid dehydrogenase. Am J Clin Pathol. 1960 Oct;34:381–398. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/34.4_ts.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. Formation of thiobarbituric-acid-reactive substance from deoxyribose in the presence of iron salts: the role of superoxide and hydroxyl radicals. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley D. A., Arbeeny C. M., Lee M. L., Van Valen R. G., Saunders R. N. Effect of platelet activating factor on endothelial permeability to plasma macromolecules. Immunopharmacology. 1984 Dec;8(3-4):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(84)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellewell P. G., Williams T. J. A specific antagonist of platelet-activating factor suppresses oedema formation in an Arthus reaction but not oedema induced by leukocyte chemoattractants in rabbit skin. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):302–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Activation and desensitization of platelets by platelet-activating factor (PAF) derived from IgE-sensitized basophils. I. Characteristics of the secretory response. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):937–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Johnston R. B., Jr Tissue injury in inflammation. Oxidants, proteinases, and cationic proteins. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):669–674. doi: 10.1172/JCI112869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. M., McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Morphologic basis of increased vascular permeability induced by acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. Lab Invest. 1984 Jan;50(1):16–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. M., McManus L. M., Satouchi K., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Vasoactive properties of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine and analogues. Lab Invest. 1982 Apr;46(4):422–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Lam M. H., Biftu T., Beattie T. R., Shen T. Y. trans-2,5-Bis-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)tetrahydrofuran. An orally active specific and competitive receptor antagonist of platelet activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15639–15645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham L. M., Coates T. D., Allen J. M., Higgins C. P., Baehner R. L., Boxer L. A. Metabolic, membrane, and functional responses of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes to platelet-activating factor. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1259–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham L. M., Lafuze J. E., Boxer L. A., Baehner R. L. In vitro and in vivo effects of treatment by platelet-activating factor on N-formyl-met-leu-phe-mediated responses of polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Br J Haematol. 1987 Jun;66(2):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb01302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iñarrea P., Alonso F., Sanchez-Crespo M. Platelet-activating factor: an effector substance of the vasopermeability changes induced by the infusion of immune aggregates in the mouse. Immunopharmacology. 1983 Jun;6(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(83)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Acute immunologic pulmonary alveolitis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):349–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI107770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Lehmeyer J. E. Elaboration of toxic oxygen by-products by neutrophils in a model of immune complex disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):836–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI108359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kravis T. C., Henson P. M. Accumulation of platelets at sites of antigen-antibody-mediated injury: a possible role for IgE antibody and mast cells. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1569–1573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. M., Lotner G. Z., Betz S. J., Henson P. M. The release of a platelet-activating factor by stimulated rabbit neutrophils. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1219–1226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Day E. D., Jr Superoxide-dependent production of hydroxyl radical catalyzed by iron-EDTA complex. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. R., Harkin M. M., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Suppression by superoxide dismutase of immune-complex--induced pulmonary alveolitis and dermal inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jan;102(1):55–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mencia-Huerta J. M., Benveniste J. Platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) and macrophages. II. Phagocytosis-associated release of PAF-acether from rat peritoneal macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jan 15;57(2):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mencia-Huerta J. M., Lewis R. A., Razin E., Austen K. F. Antigen-initiated release of platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) from mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells sensitized with monoclonal IgE. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2958–2964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merican Z., Nott M. W., Sunbhanich M. Effects of increasing the frequency of twitches and of isoprenaline on maximal twitches and cyclic AMP levels in slow- and fast-contracting cat skeletal muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct;80(2):303–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Wykle R. L., Lees C. J., Shewmake T., McCall C. E., Thomas M. J. Neutrophil-degranulating action of 5,12-dihydroxy-6,8,10,14-eicosatetraenoic acid and 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. Comparison with other degranulating agents. Am J Pathol. 1981 Dec;105(3):264–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Farr R. S., Hanahan D. J. Physicochemical and functional identity of rabbit platelet-activating factor (PAF) released in vivo during IgE anaphylaxis with PAF released in vitro from IgE sensitized basophils. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1847–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirotzky E., Page C. P., Roubin R., Pfister A., Paul W., Bonnet J., Benveniste J. PAF-acether-induced plasma exudation in rat skin is independent of platelets and neutrophils. Microcirc Endothelium Lymphatics. 1984 Feb;1(1):107–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramesha C. S., Pickett W. C. Platelet-activating factor and leukotriene biosynthesis is inhibited in polymorphonuclear leukocytes depleted of arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7592–7595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O., Pinckard R. N., Ferrigni K. S., McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J. Activation of human neutrophils with 1-O-hexadecyl/octadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphorylcholine (platelet activating factor). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1250–1255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Crespo M., Alonso F., Egido J. Platelet-activating factor in anaphylaxis and phagocytosis. I. Release from human peripheral polymorphonuclears and monocytes during the stimulation by ionophore A23187 and phagocytosis but not from degranulating basophils. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):645–655. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Crespo M., Alonso F., Iñarrea P., Alvarez V., Egido J. Vascular actions of synthetic PAF-acether (a synthetic platelet-activating factor) in the rat: evidence for a platelet independent mechanism. Immunopharmacology. 1982 Apr;4(2):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(82)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., Yin H. Q., Gustafson K. S., Nelson R. D., Jacob H. S. Platelet-activating factor primes neutrophil responses to agonists: role in promoting neutrophil-mediated endothelial damage. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):1100–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virella G., Lopes-Virella M. F., Shuler C., Sherwood T., Espinoza G. A., Winocour P., Colwell J. A. Release of PAF by human polymorphonuclear leucocytes stimulated by immune complexes bound to Sepharose particles and human erythrocytes. Immunology. 1983 Sep;50(1):43–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G. BOUND COMPLEMENT AND IMMUNOLOGIC INJURY OF BLOOD VESSELS. J Exp Med. 1965 Feb 1;121:215–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Till G. O., Kunkel R., Beauchamp C. Evidence for role of hydroxyl radical in complement and neutrophil-dependent tissue injury. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):789–801. doi: 10.1172/JCI111050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedmore C. V., Williams T. J. Control of vascular permeability by polymorphonuclear leukocytes in inflammation. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):646–650. doi: 10.1038/289646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]