Abstract
Larvae of an anhydrobiotic insect, Polypedilum vanderplanki, accumulate very large amounts of trehalose as a compatible solute on desiccation, but the molecular mechanisms underlying this accumulation are unclear. We therefore isolated the genes coding for trehalose metabolism enzymes, i.e. trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase (TPP) for the synthesis step, and trehalase (TREH) for the degradation step. Although computational prediction indicated that the alternative splicing variants (PvTpsα/β) obtained encoded probable functional motifs consisting of a typical consensus domain of TPS and a conserved sequence of TPP, PvTpsα did not exert activity as TPP, but only as TPS. Instead, a distinct gene (PvTpp) obtained expressed TPP activity. Previous reports have suggested that insect TPS is, exceptionally, a bifunctional enzyme governing both TPS and TPP. In this article, we propose that TPS and TPP activities in insects can be attributed to discrete genes. The translated product of the TREH ortholog (PvTreh) certainly degraded trehalose to glucose. Trehalose was synthesized abundantly, consistent with increased activities of TPS and TPP and suppressed TREH activity. These results show that trehalose accumulation observed during anhydrobiosis induction in desiccating larvae can be attributed to the activation of the trehalose synthetic pathway and to the depression of trehalose hydrolysis.
Keywords: anhydrobiosis, trehalase, trehalose, trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase
Introduction
The sleeping chironomid, Polypedilum vanderplanki, can withstand drought stress by the induction of an ametabolic state termed ‘cryptobiosis’ or ‘anhydrobiosis’ [1,2]. Many anhydrobiotic organisms, including bacteria, fungi, plants and invertebrates, are known to accumulate a nonreducing sugar, such as trehalose or sucrose, at high concentrations prior to or on desiccation [3,4], although several tardigrades, including Milnesium tardigradum, and bdelloid rotifers, including Philodina roseola and Adineta vaga, can enter anhydrobiosis without trehalose or trehalose accumulation [5,6]. Trehalose, the focus of this paper, is thought to effectively protect organisms from severe desiccation stress owing to its ability for water replacement and vitrification [3,4,7]. In P. vanderplanki, as larvae are undergoing desiccation, a large amount of trehalose is produced in the fat body cells [8] and redistributed to other cells and tissues through a facilitated trehalose transporter, TRET1 [9]. The transported trehalose has been shown to vitrify in the completely desiccated insects [7]. Thus, the mechanisms underlying the diffusion of accumulated trehalose over the entire insect body, and the protective effect of trehalose on cell components, have been established. Nevertheless, the molecular mechanisms involved in trehalose accumulation in P. vanderplanki remain obscure.
In addition to its role as an anhydroprotectant, trehalose is generally known as a carbon and energy source for bacteria and yeast [10]. In bacteria and yeast, trehalose is synthesized from glucose-6-phosphate and UDP-glucose, catalyzed by trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS; EC 2.4.1.15) and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase (TPP; EC 3.1.3.12), and the relevant genes have been cloned and well characterized (Fig. 1A). This synthetic pathway is considered to be conserved in a wide range of taxa, including unicellular and multicellular organisms, because these genes have been found in algae, fungi, plants and invertebrates [11].
Fig. 1.
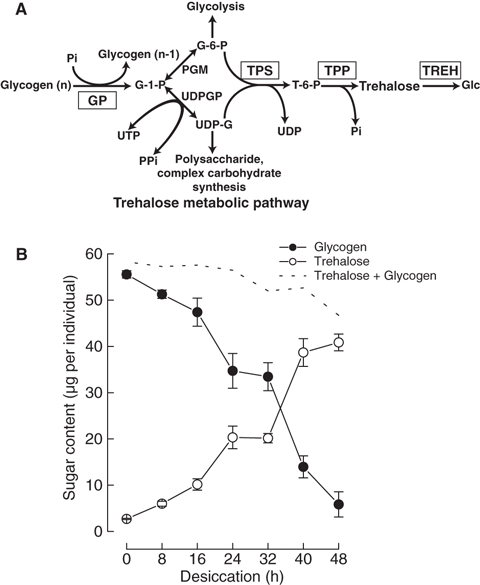
Schematic representation of the trehalose metabolic pathway (A) and changes in glycogen and trehalose content in P. vanderplanki larvae during desiccation treatment (B). Filled circles and open circles represent glycogen and trehalose content, respectively; the broken line represents the amount of total carbohydrate. G-1-P, glucose-1-phosphate; G-6-P, glucose-6-phosphate; Glc, glucose; PGM, phosphoglucomutase; UDPGP, UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase; Pi, inorganic phosphate; PPi, pyrophosphate; T-6-P, trehalose-6-phosphate.
In numerous insect species, trehalose is the main hemolymph sugar, although many exceptions, including dipteran, hymenopteran and lepidopteran species, have been reported to contain both trehalose and glucose and even to completely lack trehalose, depending on the physiological conditions [12,13]. Trehalose is synthesized predominantly in the fat body, and then released into the hemolymph. After uptake by trehalose-utilizing cells and tissues, trehalose is hydrolyzed to glucose by trehalase (TREH; EC 3.2.1.28). To date, TREH has been studied extensively in many insect species because of its role as the enzyme responsible for the rate-limiting step in trehalose catabolism in eukaryotes [12]. In Bombyx mori, Tenebrio molitor, Pimpla hypochondriaca, Apis mellifera, Spodoptera exsigua and Omphisa fuscidentalis, TREH genes have been cloned and demonstrated to be implicated in certain physiological events [12,14–18]. Several biochemical studies on insect TPS and TPP have been reported [12], but these are markedly less complete relative to those on TREH. Tps genes have been reported in many invertebrate species, including a model nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans, an anhydrobiotic nematode, Aphelenchus avenae, a crustacean, Callinectes sapidus, and insects, Drosophila melanogaster, Helicoverpa armigera and Spodoptera exigua [19–23]. Furthermore, insect genome projects have shown that Tps gene sequences are found in Apis mellifera, Triboliumcastaneum, Locusta migratoria, Anopheles gambiae and Culex pipiens. Among the insect genes, Drosophila tps1 (dtps1) and Helicoverpa Tps (Har-Tps) are expressed heterologously, and TPS activity has been confirmed in the resultant proteins [21,22]. Furthermore, the effects of overexpression of dtps1 on trehalose levels in relation to anoxia tolerance [21], and the involvement of Har-Tps in diapause induction [22], have been reported. No information on the insect Tpp gene has been obtained, but, instead, it has been suggested that DTPS1 and Har-TPS may act not only as TPS, but also as TPP [21–23]. The basis for this suggestion is that TPSs comprise both the Glyco_transf_20 (GT-20) motif responsible for trehalose-6-phosphate synthesis, and the trehalose_PPase (TrePP) motif, according to motif analysis on the Pfam (protein family) database (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/). However, on balance, the regulation of trehalose metabolism in insects has not been studied comprehensively.
Thus, the elucidation of how enzymes control the rapid accumulation of trehalose in response to desiccation stress should provide important information for understanding the molecular mechanism of anhydrobiosis induction in P. vanderplanki as well as fundamental insect physiology. In this study, we identified the genes involved in trehalose metabolism and analyzed their expression and the functions of the gene products.
Results
Changes in trehalose and glycogen contents in P. vanderplanki during desiccation
In insects, glycogen is the major substrate for trehalose synthesis [12,13,24]. During desiccation in P. vanderplanki, changes in trehalose and glycogen contents were correlated, i.e. the conversion of glycogen into trehalose (Fig. 1B). As the sum of trehalose and glycogen was fairly constant, the fluctuations in trehalose and glycogen contents during desiccation indicate that trehalose is likely to be synthesized from glucose-6-phosphate and UDP-glucose originating from the glycogen stored in fat body cells.
Changes in the activities of trehalose metabolism enzymes in P. vanderplanki during desiccation
The activities of the enzymes involved in trehalose metabolism were investigated during the desiccation of P. vanderplanki. As desiccation progressed, the activities of TPS and TPP were enhanced prior to and parallel with trehalose accumulation, respectively, whereas TREH activity decreased (Fig. 2B–D). Glycogen phosphorylase (GP) activity is generally controlled not only by gene expression, but also by reversible phosphorylation. Thus, GPb (inactive form) is reversibly converted into GPa (active form) by phosphorylation. In the results of GP assays, the GPa activity and total activity originating from both forms of GP protein were constant throughout the desiccation process (Fig. 2A). These results indicate that changes in the activity of TPS, TPP and TREH, rather than GP, are responsible for the accumulation of trehalose originating from glycogen.
Fig. 2.
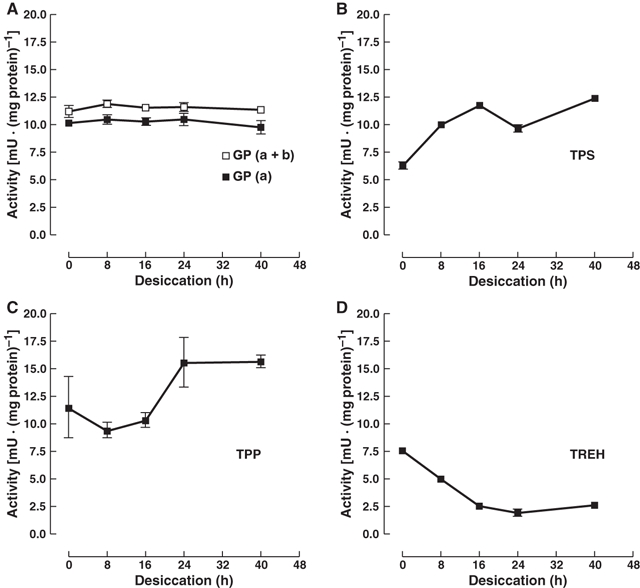
Changes in the activities of the enzymes involved in trehalose metabolism during desiccation. Using total protein extracted from the larvae sampled at various times of desiccation treatment, enzyme activities of GP (A), TPS (B), TPP (C) and TREH (D) were determined. In the GP assay, filled symbols represent the activity of the active form a, and open symbols represent the total activity including the inactive form b.
Cloning of PvTpsα/β, PvTpp and PvTreh cDNA
To elucidate the molecular mechanisms of the enhancement of the trehalose biosynthetic activity during desiccation in P. vanderplanki, we cloned the genes for TPS, TPP and TREH.
Full-length cDNAs of PvTps and PvTreh were isolated by RT-PCR and/or 5′- and 3′-RACE. For the isolation of cDNAs, degenerated primer sets were designed on the basis of the nucleotide sequences of Tps and Treh cDNAs that have been reported previously in many organisms [12,25–32]. After cDNA fragments corresponding to each gene had been obtained, 5′- and 3′-RACE were performed. Information on the nucleotide sequence of PvTpp was obtained by screening in an expressed sequence tag (EST) database constructed with sequences of cDNAs prepared from desiccating larvae [33], and the full-length cDNA was determined by 5′-RACE.
As a result of 3′-RACE on PvTps, we isolated two distinct mRNAs, named PvTpsα and PvTpsβ, that were different at each 3′-end of the nucleotide sequence. PvTpsα cDNA consisted of 3026 bp (Fig. 3A). Because nucleotides (nt) 69–71 represent a stop codon (TAA), the downstream nt 90–92 were regarded as the initiation codon (ATG). nt 2628–2630 also represented a stop codon (TGA), thus suggesting a 2538-bp ORF (846 amino acids with a molecular mass of 95 300). PvTpsβ cDNA consisted of 3094 bp; 68 nucleotides were inserted between nt 2291 and 2292 of PvTpsα. Because a frame shift occurred by insertion, the ORF in PvTpsβ was shortened to 2373 bp, encoding 791 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 89 500 (Fig. 3A). The genomic DNA sequence of the PvTps gene confirmed that PvTpsα and PvTpsβ were generated by alternative splicing (Fig. 3A). In the same manner, cDNAs of PvTpp and PvTreh were defined to consist of 1044 bp, including an 882-bp ORF (294 amino acids with a molecular mass of 33 400), and 2177 bp, including a 1734-bp ORF (578 amino acids with a molecular mass of 66 400), respectively (Fig. 3B, C).
Fig. 3.
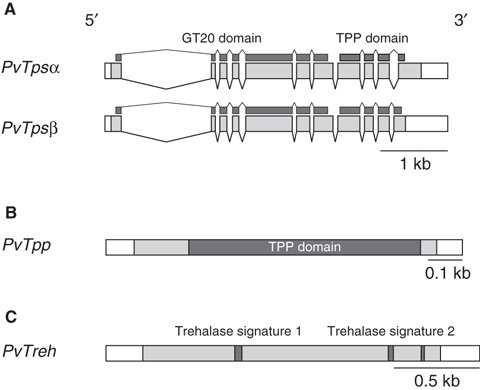
Schematic representation of desiccation-inducible genes isolated from P. vanderplanki. (A) Genomic structures of PvTpsα and PvTpsβ. Exons are indicated by boxes (shaded boxes corresponding to ORF) and introns by straight lines. Filled bars indicate representative motifs encoded in the genes. (B, C) Diagrams of cDNAs of PvTpp and PvTreh, respectively. Shaded regions indicate ORF. Filled boxes represent consensus motifs encoded in the nucleotide sequence. Scale bars are displayed at the bottom right of each diagram.
The deduced amino acid sequences of PvTPSα/β, PvTPP and PvTREH were subjected to Pfam search. PvTPSα and PvTPSβ have both the GT-20 and TrePP motifs, whereas PvTPP has the TrePP motif only (Fig. 3A, B). The GT-20 motif, belonging to the glycosyl transferase family 20, is found in every TPS and several TPP proteins, and the TrePP motif is found in several TPSs and every TPP protein [32]. In PvTREH, we found TREH signature 1, TREH signature 2 and a glycine-rich region, which are the consensus sequences of the TREH protein (Fig. 3C). Thus, PvTpsα/β, PvTpp and PvTreh seemed to encode TPS, TPP and TREH, respectively, of P. vanderplanki.
Functional analysis of PvTpsα/β, PvTpp and PvTreh
To corroborate whether these genes encode functional proteins, recombinant proteins were prepared using an in vitro transcription and translation system (TnT, Promega, Madison, WI). First, we checked that protein synthesis was successful via SDS/PAGE and western blot analysis (Fig. 4A). The expression of PvTPP protein was very faint. The coexistence of both PvTpsα and PvTpsβ cDNAs with PvTpp cDNA in the TnT reaction mixture was successful for the expression of these proteins, although the expression levels were slightly lower. In the TPS assay, PvTPSα and PvTPSβ showed no activity; trehalose-6-phosphate was not produced from glucose-6-phosphate and UDP-glucose (data not shown). TPS activity was also not detected when PvTPSβ and PvTPP were present with PvTPSα. In the TPP assay with PvTPP only, or mixed with PvTPSα and PvTPSβ, catalyzed dephosphorylation of trehalose-6-phosphate into trehalose occurred (Fig. 4B). As neither PvTPSα nor PvTPSβ (or both) was able to dephosphorylate trehalose-6-phosphate, we conclude that PvTPP is responsible for dephosphorylation. The incubation of PvTREH with trehalose resulted in the production of glucose, indicating that PvTREH functions as TREH by hydrolysis of the α-1,1-glycosidic bond in trehalose (Fig. 4C, D).
Fig. 4.
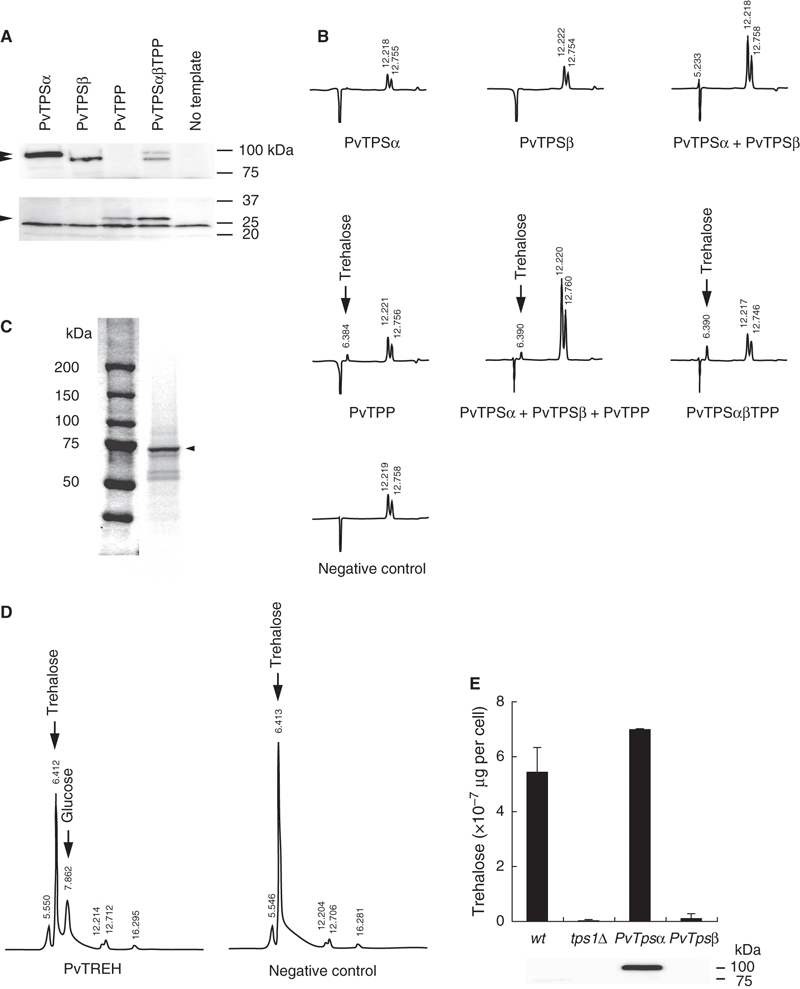
Functional analyses of PvTPSα, PvTPSβ, PvTPP and PvTREH proteins. (A, C) Confirmation of protein production by in vitro transcription and translation (A: PvTPSα, PvTPSβ and PvTPP; C: PvTREH). Aliquots of non-labeled or [35S]-labeled proteins were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and western blotting (A) or autoradiography (C). (B, D) HPLC analyses of the resultant products from enzymatic assays for TPP (B) and TREH (D). Arrowhead indicates the position of the target protein. Arrows represent the elution positions of trehalose and glucose. (E) Trehalose estimation in yeast transformants. Top: the ability to produce trehalose was evaluated in each yeast strain transformed with PvTpsα/β-containing vector. Bottom: western blot analysis of PvTPSα/β expression. Total protein was extracted from the aliquot of the culture used for trehalose measurement and subjected to SDS/PAGE and western blotting with anti-PvTPS IgG.
TPS activity was not detected in the recombinant PvTPSα or PvTPSβin vitro. Genetic techniques using yeast deletion mutants are also a powerful tool for the functional analysis of TPS [34–36]. In order to confirm the function of PvTPSα and PvTPSβ, we employed yeast tps1 deletion mutants. The yeast deletion mutant of TPS1 (tps1Δ), lacking the TPS1 gene corresponding to TPS, was transformed with the PvTpsα or PvTpsβ expression vector. These transformants were examined for their ability to synthesize trehalose. The tps1Δ+ PvTpsα strain, but not the tps1Δ+ PvTpsβ strain, accumulated trehalose comparably to the wild-type (Fig. 4E). We checked the expression of the PvTPSα and PvTPSβ proteins in each transformant, and found that PvTPSα was successfully expressed, but that PvTPSβ was not (Fig. 4E). From these results, the catalytic activity of the PvTPSα protein was demonstrated, although the function of PvTPSβ as an enzyme was not shown.
Complementation of the yeast tps1 or tps2 deletion mutant phenotype by the corresponding PvTpsα or PvTpp gene
The yeast deletion mutant tps1Δ has been reported to be osmosensitive [34–36]. In the tps2Δ strain, the yeast deletion mutant lacking the TPS2 gene corresponding to TPP, thermosensitivity to high temperature was reported [37,38]. Thus, we examined whether PvTpsα/β in tps1Δ and PvTpp in tps2Δ rescued the deletion mutants from osmosensitivity and thermosensitivity, respectively (Fig. 5). The tps1Δ+ PvTpsα strain grew at the same level as the wild-type on hypertonic medium containing 1 m NaCl, 50% sucrose or 1.5 m sorbitol (Fig. 5A). However, the tps1Δ+ PvTpsβ strain showed little improvement in growth rate compared with the tps1Δ strain on 1 m NaCl and 50% sucrose plates (Fig. 5A); these results are consistent with the absence of PvTPSβ expression (Fig. 4E). Nevertheless, tps1Δ+ PvTpsβ on 1.5 m sorbitol plates showed slightly lower growth than the tps1Δ+ PvTpsα strain (Fig. 5A). At present, we have no adequate explanation for this modest rescue; it may be caused by a kind of side-effect of transformation or the presence of trace amounts of the PvTPSβ protein.
Fig. 5.
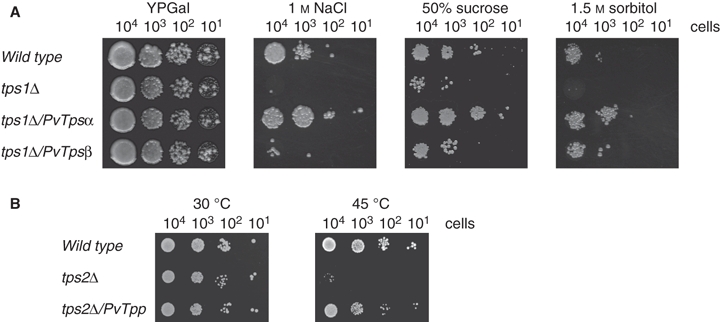
Complementation assay using yeast deletion mutants. (A) Complementation of S. cerevisiae tps1 deletion mutant by PvTpsα/β. Yeast cells were grown on a plate containing YP medium with galactose (YPGal) under hyperosmotic conditions (1 m NaCl, 50% sucrose and 1.5 m sorbitol). (B) Complementation of S. cerevisiae tps2 deletion by PvTpp. Yeast cells were plated on SD agar medium containing galactose and lacking uracil and methionine. To confirm whether the transformants rescued thermosensitivity, yeasts were incubated at 45 °C for 5 h and then grown at 30 °C. Representative results of three independent experiments are shown.
Thermosensitivity in the tps2Δ+ PvTpp strain was rescued to almost the same level as the wild-type (Fig. 5B). These results clearly demonstrate that PvTpsα and PvTpp function genetically as Tps and Tpp, respectively.
Expression profiles of PvTpsα/β, PvTpp and PvTreh mRNAs and proteins
As shown in Fig. 1B, in P. vanderplanki, trehalose is likely to be synthesized from glycogen en route to anhydrobiosis. In eukaryotes, the metabolic pathway from glycogen to trehalose is highly conserved (Fig. 1A). Hence, in order to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the regulation of the enzymes involved in trehalose metabolism on desiccation, we first investigated the expression profiles of PvTpsα/β, PvTpp and PvTreh mRNAs (Fig. 6A). The accumulation of PvTpsα/β and PvTpp mRNAs was induced within 1 h and 3 h, respectively, during desiccation treatment. For PvTreh, the induction of mRNA accumulation was delayed by 48 h after the beginning of desiccation treatment compared with the other two genes. Real-time PCR analyses of these mRNAs confirmed the results (data not shown). However, the amount of PvGp mRNAs remained constant during treatment, which is consistent with the constancy of GP activity on desiccation (Fig. 2A). Western blot analyses revealed that the proteins of PvTPSα/β, PvTPP and PvTREH were also accumulated, as were the corresponding mRNAs (Fig. 6B).
Fig. 6.
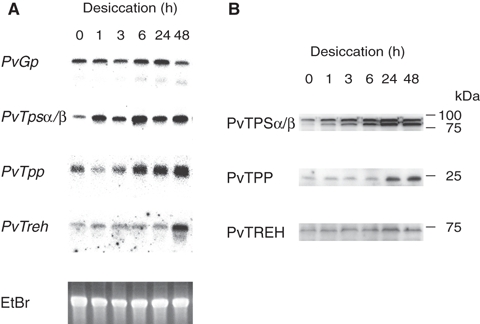
Expression profiles of mRNAs and proteins of the genes involved in trehalose metabolism during desiccation. Total RNA and protein were prepared from larvae treated under desiccation conditions, and analyzed by northern blotting (A) and western blotting (B).
Discussion
In this study, we have isolated and characterized three desiccation-inducible genes, PvTpsα/β, PvTpp and PvTreh, encoding the enzymes involved in trehalose metabolism in P. vanderplanki (Fig. 3). In addition to P. vanderplanki, many anhydrobiotes, such as A. avenae, and Artemia cysts accumulate trehalose as they undergo desiccation. In these organisms, trehalose accumulation correlates significantly with anhydrobiosis induction [3,4,39]. In contrast, several rotifers and tardigrades enter anhydrobiosis without trehalose accumulation, but possess other anhydroprotectants, such as late embryogenesis abundant proteins [4,6]. The induction of trehalose synthesis is necessary for P. vanderplanki to achieve anhydrobiosis. The larvae, if rapidly dehydrated, cannot enter anhydrobiosis because of an insufficient amount of trehalose [40,41]. Furthermore, it has been hypothesized that trehalose is replaced with water or can vitrify to exert its protective function against dehydration [3,4,7]. Indeed, trehalose is produced in fat body cells in desiccating P. vanderplanki larvae [8], redistributed to other cells and tissues through a facilitated trehalose transporter, TRET1 [9], and vitrified in completely desiccated insects [7]. Thus, the successful induction of anhydrobiosis in P. vanderplanki must occur via a sequence of events: expression of trehalose metabolism-related genes, de novo synthesis and accumulation of trehalose, redistribution and vitrification.
PvTpsα rescued the growth of the yeast tps1Δ mutant, and PvTpp rescued the growth of the tps2Δ mutant, providing evidence that PvTpsα and PvTpp encode genetically functional trehalose synthases (Fig. 5). Furthermore, we confirmed the enzymatic activities for PvTPSαin vivo (Fig. 4E) and PvTPP in vitro (Fig. 4B), but not for PvTPSβ. Thus far, all cloned insect Tps genes encode both GT-20 and TrePP motifs, and insect TPP has been proposed to be identical to TPS [21–23]. Although PvTpsα/β also has both of these motifs, we cloned a PvTpp gene distinguishable from PvTpsα/β and demonstrated the TPP activity of PvTPP. This is the first report of an insect Tpp gene. BlastP and Pfam searches have shown that TPP orthologs possessing only the TrePP motif are likely to occur in several insects, including four dipteran species, such as Culex quinquefasciatus, Anopheles gambiae, Aedes aegypti, Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila pseudoobscura, and a hemipteran species, Maconellicoccus hirsutus (CPIJ009402 in C. quinquefasciatus; AGAP008225 in Anopheles gambiae; AAEL010684 in Aedes aegypti; CG5171 and CG5177 in D. melanogaster; GA18712 and GA18709 in D. pseudoobscura; and ABN12077 in M. hirsutus). We therefore propose that insect Tps and Tpp genes exist independently, as reported in other organisms, e.g. bacteria, yeast and plants [32].
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, trehalose synthase forms a heterotetramer with TPS1, TPS2, TPS3 and TSL1 subunits [42,43]. In the complex, the TPS3 and TSL1 subunits, both of which possess GT-20 and TrePP motifs without TPS or TPP activity, act as regulators [27,28,42–44]. In addition, the activity of TPS is enhanced by its aggregation, indicating that heteromeric and/or homomeric multimerization of the TPS–TPP complex should be important for the production of TPS activity [45]. Similar to S. cerevisiae, other regulatory subunits might constitute the trehalose synthase complex in P. vanderplanki. No cDNAs homologous to TPS3 and TSL1 have been found thus far in the EST database of P. vanderplanki. Although we could not detect TPS activity in PvTPSβ (Fig. 5A), acceleration of its expression by desiccation (Fig. 7) suggests that the protein also plays a role in anhydrobiosis induction. PvTPSβ might act as a regulatory subunit, in a similar manner to TPS3 and TSL1, interacting with PvTPSα and PvTPP. The absence of enzymatic activity in PvTPSα/β proteins prepared by an in vitro transcription and translation system might be caused by the inappropriate interaction of components. If PvTPSα also possesses the same property as TPS in yeast, aggregation of PvTPSα caused by dehydration could lead to an enhancement of its activity en route to anhydrobiosis. Further investigation is required to answer these questions.
Fig. 7.
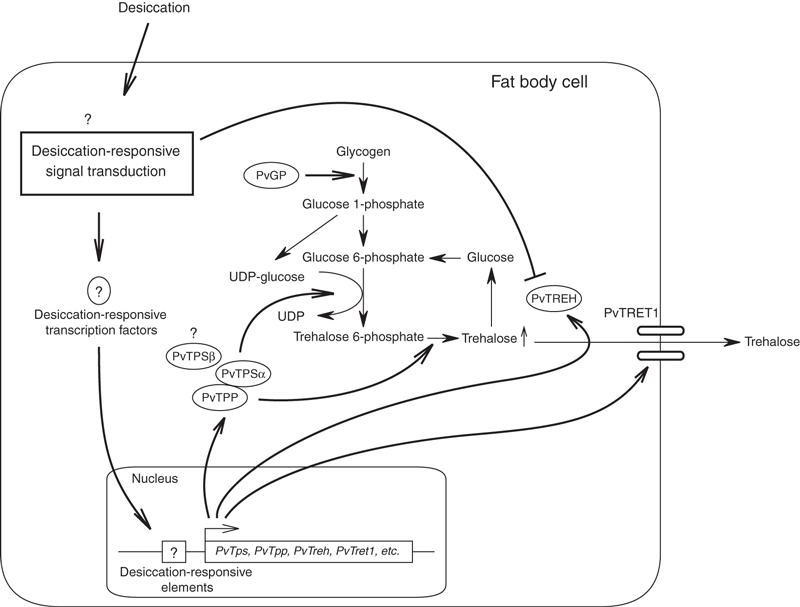
Proposed molecular mechanism of desiccation-inducible trehalose accumulation in P. vanderplanki.
During the induction of dehydration in an anhydrobiotic nematode, A. avenae, lipid is used as the most likely carbon source to synthesize trehalose via the glyoxylate cycle, and glycogen degradation also contributes to trehalose synthesis [39,46]. In addition, in the trehalose synthesis mechanism of A. avenae during anhydrobiosis induction, it has been reported that the excess substrate influx into TPS is caused by the saturation of glycogen synthase as a result of the increase in UDP-glucose and glucose-6-phosphate as dehydration progresses [47]. However, as shown in Fig. 1B, glycogen degradation and trehalose accumulation during the induction of anhydrobiosis in P. vanderplanki occur as a mirror image. This result indicates that, in drying P. vanderplanki larvae, glycogen is the largest source of trehalose synthesis and is gradually converted into trehalose to act as an anhydroprotectant, although we have not yet verified the involvement of the glyoxylate cycle. Neither the expression of PvGp mRNA nor the activity of GP was elevated on desiccation (Figs 2A and 6A), indicating that PvGP is not involved in the degradation of glycogen. However, TPS and TPP activities increased prior to and parallel with trehalose accumulation, respectively, as a result of the upregulation of the expression of the corresponding mRNAs and proteins (Figs 2B, C and 6A, B). In contrast with the case of TPS and TPP, TREH activity was depressed during desiccation treatment, even though the mRNA and protein of PvTreh increased (Figs 2D and 6). These interesting results indicate that trehalose accumulation can be attributed to the enhancement of PvTps and PvTpp gene expression and the repression of enzymatic activity for PvTREH.
In vitro recombinant PvTREH without modification, such as phosphorylation, showed hydrolytic activity (Fig. 4C, D), implying that PvTREH activity in desiccating larvae might be negatively modified post-translationally. In insects, TREH activity is thought to depend on transcriptional regulation, as reported in the ovary and midgut of B. mori [48,49], or on the coexistence of a TREH inhibitor, as in the hemolymph of Periplaneta americana [50]. In S. cerevisiae, TREH is activated through phosphorylation by cdc28 and inactivated by an inhibitor of TREH (DCS1/YLR270W) [51–53]. Post-translational modification of PvTREH activity could be occurring in a similar manner, such as by phosphorylation or the coexistence of an inhibitor for rapid accumulation and breakdown (see [54]) of trehalose, in dehydrated and rehydrated larvae, respectively.
In P. vanderplanki, the expression and activity of the enzymes of trehalose metabolism are regulated by desiccation stress (Figs 2 and 6). This is the first report concerning the comprehensive analyses of trehalose metabolism enzymes and the corresponding genes in a single insect species, and provides evidence that multiple pathways control trehalose concentration appropriately according to its physiological role. In insects, including P. vanderplanki, trehalose production and utilization as a hemolymph sugar are under hormonal control via the central nervous system under normal conditions [12]. However, in dehydrating P. vanderplanki larvae, trehalose accumulation as an anhydroprotectant is independent of the control of the central nervous system [40], and is instead triggered by an increase in internal ion concentration [41]. A requirement for rapid adaptation to a desiccating environment could have led to the evolution of the cell autonomous responsive systems in P. vanderplanki larvae.
Here, we summarize a probable molecular mechanism underlying trehalose metabolism that is involved in anhydrobiosis induction in P. vanderplanki (Fig. 7). Once larvae are exposed to drying conditions, fat body cells receive the desiccation signal through the elevation of internal ion concentration and rapidly activate certain desiccation-responsive transcription factors to enhance the transcription of PvTpsα/β and PvTpp genes participating in trehalose synthesis. Indeed, mRNAs of PvGp, PvTpsα/β and PvTpp are abundantly expressed in fat body tissue, but the PvTreh mRNA level is less than that in other tissues (Fig. S1, Table S2 and Doc. S1). Furthermore, the PvTPSα/β protein localizes only to fat body tissue (Fig. S2 and Doc. S1). Concomitant with the accumulation of PvTPSα/β and PvTPP proteins, the aggregation of PvTPSα/β–TPP complexes, facilitated by dehydration of the cells, might potentiate the activity of the complex, resulting in the very rapid production of trehalose. Synthesized trehalose then diffuses via the hemolymph through TRET1 to protect all cells and tissues from irreversible desiccation damage (see [7–9]). Just before the completion of anhydrobiosis, the expression of PvTreh is accelerated, and the activity of PvTREH is depressed, for subsequent activation during rehydration. Consequently, strict temporal regulation of the pathway of trehalose metabolism, in response to desiccation stress, seems to be the key for the completion of anhydrobiosis in P. vanderplanki. Interestingly, P. nubifer, a desiccation-sensitive and congeneric chironomid to P. vanderplanki, contains trehalose at a comparable level to that in P. vanderplanki under normal conditions, but it does not accumulate trehalose during desiccation (data not shown). Therefore, among the chironomid species, P. vanderplanki seems to be specifically adapted to dehydration by controlling the expression of trehalose metabolism-related genes and the activities of the proteins. In future studies, the determination of the cis-elements and trans-factors of PvTps and other desiccation-inducible genes will be essential in order to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the regulatory mechanisms underlying the induction of anhydrobiosis. Such an understanding could also lead to the exploitation of desiccation-responsive heterologous gene expression systems that are crucial for the reconstitution of the anhydrobiotic state.
Experimental procedures
Insects
Polypedilum vanderplanki larvae were reared on a milk agar diet under a controlled photoperiod (13 h light : 11 h dark) at 27 °C [40,55]. Procedures for the desiccation treatment for the induction of anhydrobiosis-related genes have been described previously [41].
Determination of glycogen and trehalose content in P. vanderplanki
Larvae of P. vanderplanki desiccated for various periods were homogenized in 80% ethanol to obtain soluble and insoluble fractions. The soluble fractions were prepared for the determination of trehalose as described previously [40]. The insoluble fractions were boiled for 30 min in the presence of 30% KOH; glycogen was then precipitated in 80% ethanol and collected by centrifugation at 20 000 g for 15 min at room temperature. The resulting glycogen precipitates were dissolved in distilled water. The glycogen content was determined by the phenol–sulfuric acid method [56].
Cloning of PvTps, PvTpp, PvTreh and PvGp cDNAs
Full-length cDNAs of PvTps, PvTreh and PvGp were isolated by RT-PCR with degenerated primers and/or by 5′- and 3′-RACE with a SMART RACE cDNA amplification kit (Clontech, Mountain View, CA). The degenerated primers used for RT-PCR were as follows: PvTPS-F1, 5′-GACTCITAYTAYAAYGGITGYTGYAA-3′; PvTPS-F2, 5′-TGGCCIYTITTYCAWSIATGCC-3′; PvTPS-R1, 5′-GGRAAIGGIATWGGIARRAARAA-3′; PvTPS-R2, 5′-ARCATIARRTGIACRTCWGG-3′; PvTREH-F1, 5′-ATHRTICCIGGIGGIMGITT-3′; PvTREH-R1, 5′-TTIGGIDMRTCCCAYTGYTC-3′; PvGP-F1, 5′-AAYGGIGGIYTIGGIMGIYTIGCIGC-3′; PvGP-R1, 5′-TGYTTIARICKIARYTCYTTICC-3′. PvTpp cDNA was obtained from the Pv-EST database [33] and subsequent 5′-RACE. The primers for 5′- and 3′-RACE are shown in Table S1. The nucleotide sequences for the isolated cDNAs were analyzed by GENETYX-MAC (Genetyx, Tokyo, Japan) with the Pv-EST database and subcloned into the appropriate vectors for subsequent experiments. The deduced amino acid sequences of PvTPSα/β, PvTPP and PvTREH were subjected to Pfam search (pfam.sanger.ac.uk) for motif analysis.
Determination of the PvTps gene structure
Genomic DNA was extracted from the larvae of P. vanderplanki using a DNeasy Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The construction of the fosmid library and the screening of the clones containing the PvTps gene were entrusted to TaKaRa Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan. The positive clones were subjected to sequencing analysis, and the structure of the PvTps gene was determined. The primer sets used are shown in Table S1.
Northern blot analysis
Total RNA was isolated from dehydrating larvae using TRIzol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). Northern blot analysis was performed as described previously [9,33]. Briefly, 15 μg of RNA was electrophoresed on 1% agarose–20 mm guanidine isothiocyanate gels, blotted onto Hybond N-plus membrane (GE Healthcare Bioscience, Piscataway, NJ) and probed with the full length of the corresponding cDNA fragments labeled with [α-32P]dATP using a Strip-EZ labeling kit (Ambion, Austin, TX). The hybridized blot was analyzed by BAS 2500 (Fuji Film, Tokyo, Japan).
Protein extraction
For western blot analyses, the larvae were homogenized in a 10-fold volume of SDS/PAGE sample buffer without dye reagent, and boiled for 10 min. The homogenates were centrifuged at 20 000 g for 10 min at room temperature, and the supernatants were collected. The concentration of protein was determined as described previously [14]. The preparation of yeast protein extract was carried out according to Clontech’s Yeast Protocols Handbook (PT3024-1; http://www.clontech.com). For the determination of enzyme activities, the larvae were homogenized in a 20-fold volume of protein extraction buffer (T-PER; Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, IL) containing a protease inhibitor cocktail (Complete; Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland), and the supernatants containing the crude protein were obtained by centrifugation at 20 000 g for 5 min at 4 °C. The concentration of protein was determined with a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA).
Western blot analysis
Using the protein extracts described above, western blot analysis was performed as described previously [9,33]. The blots were treated with anti-PvTPS, TPP or TREH polyclonal IgGs as the primary antibodies to detect the corresponding proteins, and subsequently with goat anti-rabbit IgG (H + L) conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (American Qualex, La Mirada, CA) as the secondary antibody, and reacted with Immobilon Western Chemiluminescent HRP substrate (Millipore, Billerica, CA) to analyze the chemiluminescent signals by LAS-3000 (Fuji Film). The recognition sites of antibodies for PvTPS, TPP and TREH are the following amino acid sequences: (592)GIEGITYAGNHGLE(605) of PvTPSα/β, (108)GIDGIVYAGNHGLE(121) of PvTPP and (109)LDKISDKNFRD(119) of PvTREH.
In vitro transcription and translation
In vitro transcription and translation of PvTPSα/β, PvTPP and PvTREH were performed using a TnT® T7 Quick for PCR DNA kit (Promega). Briefly, approximately 200 ng of each PCR product, flanked by a T7 promoter at the 5′-end and a poly(A) at the 3′-end of the ORF, were incubated for 90 min at 30 °C in a 50-μL reaction mixture containing 1 μL of 1 mm methionine or [35S]methionine (> 37 TBq·mmol−1, 400 MBq·mL−1; Muromachi Chemical, Tokyo, Japan). The reaction products were separated by 15% SDS/PAGE, and the gel was applied to western blot analyses as described above, or for autoradiography to confirm protein synthesis.
Determination of enzyme activity
GP (EC 2.4.1.1) assays were performed as follows: 100 μL of 45 mm potassium-phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), containing 0.1 mm EDTA, 15 mm MgCl2, 4 μm glucose-1,6-bisphosphate, 0.1 U phosphoglucomutase, 0.6 U glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, 2 mg·mL−1 glycogen, 0.4 mm NADP and 10 μL of protein extract, were incubated at 30 °C for 30 min, monitoring the change in the absorbance at 340 nm (A340). Because the inactive form of GP is activated by an allosteric effector, such as AMP, to determine total GP (active ‘a’ form and inactive ‘b’ form) activity, the reactions were performed in the presence of an additional 1 mm 5′-AMP.
For TPS assays, 200 μL of reaction mixture, containing 2.5 mm glucose-6-phosphate, 2.5 mm UDP-glucose, 2.5 mm MgCl2, 100 mm KCl, 1.25 mm phosphoenolpyruvate, 20 μL pyruvate kinase/lactate dehydrogenase (34 μL·mL−1), 0.3 mm NADH, 30 mm Tris/HCl (pH 7.4) and 5 μL of protein extract, were incubated at 30 °C for 30 min, monitoring the change in A340 that depends on NADH oxidation. In the case of samples from in vitro transcription and translation, 1.2 μL each of the products were incubated at 30 °C for 2 h, and then at 95 °C for 10 min to stop the reaction.
Assays for TPP activity were performed in 200 μL of reaction mixture containing 2.5 mm trehalose-6-phosphate, 2.5 mm MgCl2, 30 mm Tris/HCl (pH 7.4) and 20 μL of protein extract. In assays for the in vitro transcription and translation products, 1.2 μL of each of the preparations was used. The mixtures were incubated at 30 °C for 1 h, and then at 95 °C for 10 min to stop the reaction. The reaction product (trehalose) was measured by HPLC [40].
TREH activity was assayed in 250 μL of 15 mm phosphate buffer (pH 6.0) containing 20 mm trehalose and an appropriate amount of protein preparation. After incubation at 30 °C for 0.5–1 h, the reaction mixture was boiled for 5 min. As a control, another reaction mixture was immediately boiled without incubation. The reaction products (trehalose and glucose) were measured by HPLC [40].
A desiccation treatment of 48 h is required to completely desiccate larvae under laboratory conditions [40,41]. Enzyme activities in the larvae were measured from 0 to 40 h after the beginning of desiccation, as it seems likely that no metabolic activity would be detectable in vivo in completely desiccated larvae [2].
Yeast complementation assay
The S. cerevisiae deletion mutants were purchased from Open Biosystems, Huntsville, AL. The deletion strains for TPS1 (MATα; his3Δ1; leu2Δ0; lys2Δ0; ura3Δ0; YBR126c::kanMX4) and TPS2 (MATα; his3Δ1; leu2Δ0; lys2Δ0; ura3Δ0; YDR074w::kanMX4) were transformed with pUG35 (http://mips.gsf.de/proj/yeast/info/tools/hegemann/gfp.html; U. Gueldener and J. H. Hegemann, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, unpublished results), which contains the ORF of PvTpsα, PvTpsβ and PvTpp under the MET25 promoter [57]. For the positive and negative controls, wild-type and deletion mutants were transformed with pUG35 containing the GFP ORF instead of the target genes. After selection on synthetic defined (SD) medium lacking uracil, transformants were confirmed by colony PCR. Three independent colonies were picked up for each strain. For the complementation test of the tps1 mutant, transformants of the tps1 deletion mutant with PvTpsα and PvTpsβ were grown in SD medium containing 2% galactose and lacking uracil and methionine at 30 °C to an exponential phase. After harvesting of the yeast cells, a dilution series of 104–101 cells was prepared, and each solution was spotted onto yeast extract and peptone (YP) medium containing galactose conditioned in hyperosmolarity with 1 m NaCl, 50% sucrose or 1.5 m sorbitol. For complementation tests of the tps2 mutant, diluted series of transformants of the tps2 deletion mutant with PvTpp were prepared as for tps1. Each cell suspension was spotted onto SD medium containing 2% galactose and lacking methionine and uracil. To confirm the rescue of the temperature sensitivity of the tps2Δ mutant, the plates were incubated at 45 °C for 5 h and then at 30 °C for 3–4 days.
Quantification of trehalose by HPLC
The amount of trehalose was determined by HPLC according to Watanabe et al. [40]. For the determination of intracellular trehalose content, PvTpsα- or PvTpsβ-introduced yeast strains were cultured in SD medium containing galactose and lacking uracil and methionine at 30 °C for 48 h until the growth curve entered the stationary phase. Yeast cells were harvested and homogenized with glass beads in 80% ethanol. After centrifugation at 20 000 g for 30 min, the supernatants were collected and subjected to sample preparation for HPLC analysis [40].
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor J. S. Clegg and Dr Peter Wilson for providing critical and helpful comments on the manuscript and for improving the English. We also thank A. Fujita, T. Shiratori and Y. Saito for their assistance in the laboratory. In addition, we are grateful to anonymous reviewers for improving the manuscript. This study was supported in part by the Promotion of Basic Research Activities for Innovative Bioscience (PROBRAIN), and by KAKENHI, a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (A).
Glossary
Abbreviations
- EST
expressed sequence tag
- GP
glycogen phosphorylase
- GT-20
glycosyl transferase family 20
- TPP
trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase
- TPS
trehalose-6-phosphate synthase
- TREH
trehalase
- TrePP
trehalose-phosphatase
Supporting information
The following supplementary material is available:
Fig. S1. Tissue specificity of expression of PvGp, PvTps α/β, PvTpp and PvTreh in P. vanderplanki larvae.
Fig. S2. Immunostaining of PvTPS protein in desiccating larvae.
Doc S1. Experimental procedures for supplementary data.
Table S1. Primers for 5′- and 3′-RACE, and for the determination of PvTps gene structure.
Table S2. Primers for real-time PCR.
This supplementary material can be found in the online version of this article.
Please note: As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer-reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
References
- 1.Hinton H. A new chironomid from Africa, the larva of which can be dehydrated without injury. Proc Zool Soc London. 1951;121:371–380. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hinton HE. Cryptobiosis in the larva of Polypedilum vanderplanki Hint. (Chironomidae) J Insect Physiol. 1960;5:286–300. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Clegg JS. Cryptobiosis – a peculiar state of biological organization. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2001;128:613–624. doi: 10.1016/s1096-4959(01)00300-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Crowe J, Carpenter J, Crowe L. The role of vitrification in anhydrobiosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1998;60:73–103. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.60.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hengherr S, Heyer AG, Köhler H-R, Schill RO. Trehalose and anhydrobiosis in tardigrades – evidence for divergence in responses to dehydration. FEBS J. 2008;275:281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lapinski J, Tunnacliffe A. Anhydrobiosis without trehalose in bdelloid rotifers. FEBS Lett. 2003;553:387–390. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)01062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sakurai M, Furuki T, Akao K-I, Tanaka D, Nakahara Y, Kikawada T, Watanabe M, Okuda T. Vitrification is essential for anhydrobiosis in an African chironomid, Polypedilum vanderplanki. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:5093–5098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706197105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Watanabe M, Kikawada T, Fujita A, Okuda T. Induction of anhydrobiosis in fat body tissue from an insect. J Insect Physiol. 2005;51:727–731. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2005.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kikawada T, Saito A, Kanamori Y, Nakahara Y, Iwata K-I, Tanaka D, Watanabe M, Okuda T. Trehalose transporter 1, a facilitated and high-capacity trehalose transporter, allows exogenous trehalose uptake into cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:11585–11590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702538104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Argüelles JC. Physiological roles of trehalose in bacteria and yeasts: a comparative analysis. Arch Microbiol. 2000;174:217–224. doi: 10.1007/s002030000192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Paul MJ, Primavesi LF, Jhurreea D, Zhang Y. Trehalose metabolism and signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2008;59:417–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Thompson SN. Trehalose – the insect ‘blood’ sugar. Adv Insect Physiol. 2003;31:205–283. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wyatt G. The biochemistry of sugars and polysaccharides in insects. Adv Insect Physiol. 1967;4:287–360. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mitsumasu K, Azuma M, Niimi T, Yamashita O, Yaginuma T. Membrane-penetrating trehalase from silkworm Bombyx mori. Molecular cloning and localization in larval midgut. Insect Mol Biol. 2005;14:501–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2005.00581.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Parkinson NM, Conyers CM, Keen JN, MacNicoll AD, Smith I, Weaver RJ. cDNAs encoding large venom proteins from the parasitoid wasp Pimpla hypochondriaca identified by random sequence analysis. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2003;134:513–520. doi: 10.1016/s1532-0456(03)00041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee J-H, Saito S, Mori H, Nishimoto M, Okuyama M, Kim D, Wongchawalit J, Kimura A, Chiba S. Molecular cloning of cDNA for trehalase from the European honeybee, Apis mellifera L., and its heterologous expression in Pichia pastoris. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2007;71:2256–2265. doi: 10.1271/bbb.70239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tang B, Chen X, Liu Y, Tian H, Liu J, Hu J, Xu W, Zhang W. Characterization and expression patterns of a membrane-bound trehalase from Spodoptera exigua. BMC Mol Biol. 2008;9:51. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-9-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tatun N, Singtripop T, Tungjitwitayakul J, Sakurai S. Regulation of soluble and membrane-bound trehalase activity and expression of the enzyme in the larval midgut of the bamboo borer Omphisa fuscidentalis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;38:788–795. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2008.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pellerone FI, Archer SK, Behm CA, Grant WN, Lacey MJ, Somerville AC. Trehalose metabolism genes in Caenorhabditis elegans and filarial nematodes. Int J Parasitol. 2003;33:1195–1206. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(03)00173-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Goyal K, Browne JA, Burnell AM, Tunnacliffe A. Dehydration-induced tps gene transcripts from an anhydrobiotic nematode contain novel spliced leaders and encode atypical GT-20 family proteins. Biochimie. 2005;87:565–574. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2005.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen Q, Haddad GG. Role of trehalose phosphate synthase and trehalose during hypoxia: from flies to mammals. J Exp Biol. 2004;207:3125–3129. doi: 10.1242/jeb.01133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xu J, Bao B, Zhang Z-F, Yi Y-Z, Xu W-H. Identification of a novel gene encoding the trehalose phosphate synthase in the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. Glycobiology. 2009;19:250–257. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwn127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chung JS. A trehalose 6-phosphate synthase gene of the hemocytes of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus: cloning, the expression, its enzyme activity and relationship to hemolymph trehalose levels. Saline Syst. 2008;4:18. doi: 10.1186/1746-1448-4-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Steele JE. The role of carbohydrate metabolism in physiological function. In: Downer RGH, editor. Energy in Metabolism in Insects. New York: Plenum Press; 1981. pp. 101–134. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Boos W, Ehmann U, Bremer E, Middendorf A, Postma P. Trehalase of Escherichia coli. Mapping and cloning of its structural gene and identification of the enzyme as a periplasmic protein induced under high osmolarity growth conditions. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:13212–13218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ruf J, Wacker H, James P, Maffia M, Seiler P, Galand G, von Kieckebusch A, Semenza G, Matei N. Rabbit small intestinal trehalase. Purification, cDNA cloning, expression, and verification of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchoring. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:15034–15039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bell W, Klaassen P, Ohnacker M, Boller T, Herweijer M, Schoppink P, Van der Zee P, Wiemken A. Characterization of the 56-kDa subunit of yeast trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and cloning of its gene reveal its identity with the product of CIF1, a regulator of carbon catabolite inactivation. Eur J Biochem. 1992;209:951–959. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vuorio OE, Kalkkinen N, Londesborough J. Cloning of two related genes encoding the 56-kDa and 123-kDa subunits of trehalose synthase from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1993;216:849–861. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kopp M, Müller H, Holzer H. Molecular analysis of the neutral trehalase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:4766–4774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Destruelle M, Holzer H, Klionsky DJ. Isolation and characterization of a novel yeast gene, ATH1, that is required for vacuolar acid trehalase activity. Yeast. 1995;11:1015–1025. doi: 10.1002/yea.320111103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Müller J, Aeschbacher RA, Wingler A, Boller T, Wiemken A. Trehalose and trehalase in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001;125:1086–1093. doi: 10.1104/pp.125.2.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Avonce N, Mendoza-Vargas A, Morett E, Iturriaga G. Insights on the evolution of trehalose biosynthesis. BMC Evol Biol. 2006;6:109. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-6-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kikawada T, Nakahara Y, Kanamori Y, Iwata K-I, Watanabe M, McGee B, Tunnacliffe A, Okuda T. Dehydration-induced expression of LEA proteins in an anhydrobiotic chironomid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;348:56–61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zentella R, Mascorro-Gallardo JO, Van Dijck P, Folch-Mallol J, Bonini B, Van Vaeck C, Gaxiola R, Covarrubias AA, Nieto-Sotelo J, Thevelein JM, et al. A Selaginella lepidophylla trehalose-6-phosphate synthase complements growth and stress-tolerance defects in a yeast tps1 mutant. Plant Physiol. 1999;119:1473–1482. doi: 10.1104/pp.119.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Soto T, Fernandez J, Vicente-Soler J, Cansado J, Gacto M. Accumulation of trehalose by overexpression of tps1, coding for trehalose-6-phosphate synthase, causes increased resistance to multiple stresses in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65:2020–2024. doi: 10.1128/aem.65.5.2020-2024.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vogel G, Fiehn O, Jean-Richard-dit-Bressel L, Boller T, Wiemken A, Aeschbacher RA, Wingler A. Trehalose metabolism in Arabidopsis: occurrence of trehalose and molecular cloning and characterization of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase homologues. J Exp Bot. 2001;52:1817–1826. doi: 10.1093/jexbot/52.362.1817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vogel G, Aeschbacher RA, Müller J, Boller T, Wiemken A. Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatases from Arabidopsis thaliana: identification by functional complementation of the yeast tps2 mutant. Plant J. 1998;13:673–683. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shima S, Matsui H, Tahara S, Imai R. Biochemical characterization of rice trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatases supports distinctive functions of these plant enzymes. FEBS J. 2007;274:1192–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Crowe J, Madin K, Loomis S. Anhydrobiosis in nematodes: metabolism during resumption of activity. J Exp Zool. 1977;201:57–64. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Watanabe M, Kikawada T, Minagawa N, Yukuhiro F, Okuda T. Mechanism allowing an insect to survive complete dehydration and extreme temperatures. J Exp Biol. 2002;205:2799–2802. doi: 10.1242/jeb.205.18.2799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Watanabe M, Kikawada T, Okuda T. Increase of internal ion concentration triggers trehalose synthesis associated with cryptobiosis in larvae of Polypedilum vanderplanki. J Exp Biol. 2003;206:2281–2286. doi: 10.1242/jeb.00418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Reinders A, Bürckert N, Hohmann S, Thevelein JM, Boller T, Wiemken A, De Virgilio C. Structural analysis of the subunits of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their function during heat shock. Mol Microbiol. 1997;24:687–695. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.3861749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bell W, Sun W, Hohmann S, Wera S, Reinders A, De Virgilio C, Wiemken A, Thevelein JM. Composition and functional analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae trehalose synthase complex. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:33311–33319. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.50.33311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.De Virgilio C, Bürckert N, Bell W, Jenö P, Boller T, Wiemken A. Disruption of TPS2, the gene encoding the 100-kDa subunit of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, causes accumulation of trehalose-6-phosphate and loss of trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase activity. Eur J Biochem. 1993;212:315–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chaudhuri P, Basu A, Ghosh AK. Aggregation dependent enhancement of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1780:289–297. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2007.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Madin K, Loomis S, Crowe J. Anhydrobiosis in nematodes: control of carbon flow through the glyoxylate cycle. J Exp Zool. 1985;234:341–350. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Loomis S, O’Dell S, Crowe J. Anhydrobiosis in nematodes: control of the synthesis of trehalose during induction. J Exp Zool. 1980;211:321–330. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Su ZH, Ikeda M, Sato Y, Saito H, Imai K, Isobe M, Yamashita O. Molecular characterization of ovary trehalase of the silkworm, Bombyx mori and its transcriptional activation by diapause hormone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1218:366–374. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mitsumasu K, Azuma M, Niimi T, Yamashita O, Yaginuma T. Changes in the expression of soluble and integral-membrane trehalases in the midgut during metamorphosis in Bombyx mori. Zool Sci. 2008;25:693–698. doi: 10.2108/zsj.25.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hayakawa Y, Jahagirdar AP, Yaguchi M, Downer RG. Purification and characterization of trehalase inhibitor from hemolymph of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:16165–16169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ubersax JA, Woodbury EL, Quang PN, Paraz M, Blethrow JD, Shah K, Shokat KM, Morgan DO. Targets of the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk1. Nature. 2003;425:859–864. doi: 10.1038/nature02062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Souza AC, De Mesquita JF, Panek AD, Silva JT, Paschoalin VMF. Evidence for a modulation of neutral trehalase activity by Ca2+ and cAMP signaling pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2002;35:11–16. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2002000100002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.De Mesquita JF, Panek AD, de Araujo PS. In silico and in vivo analysis reveal a novel gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae trehalose metabolism. BMC Genomics. 2003;4:45. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-4-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Watanabe M, Nakahara Y, Sakashita T, Kikawada T, Fujita A, Hamada N, Horikawa DD, Wada S, Kobayashi Y, Okuda T. Physiological changes leading to anhydrobiosis improve radiation tolerance in Polypedilum vanderplanki larvae. J Insect Physiol. 2007;53:573–579. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2007.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kikawada T, Minakawa N, Watanabe M, Okuda T. Factors incuding successful anhydrobiosis in the African chironomid Polypedilum vanderplanki: significance of the larval tubular nest. Integr Comp Biol. 2005;45:710–714. doi: 10.1093/icb/45.5.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.DuBois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem. 1956;28:350–356. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Solow S, Sengbusch J, Laird M. Heterologous protein production from the inducible MET25 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Prog. 2008;21:617–620. doi: 10.1021/bp049916q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


