Abstract
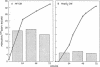
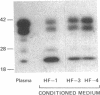
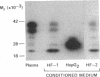
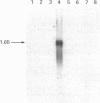
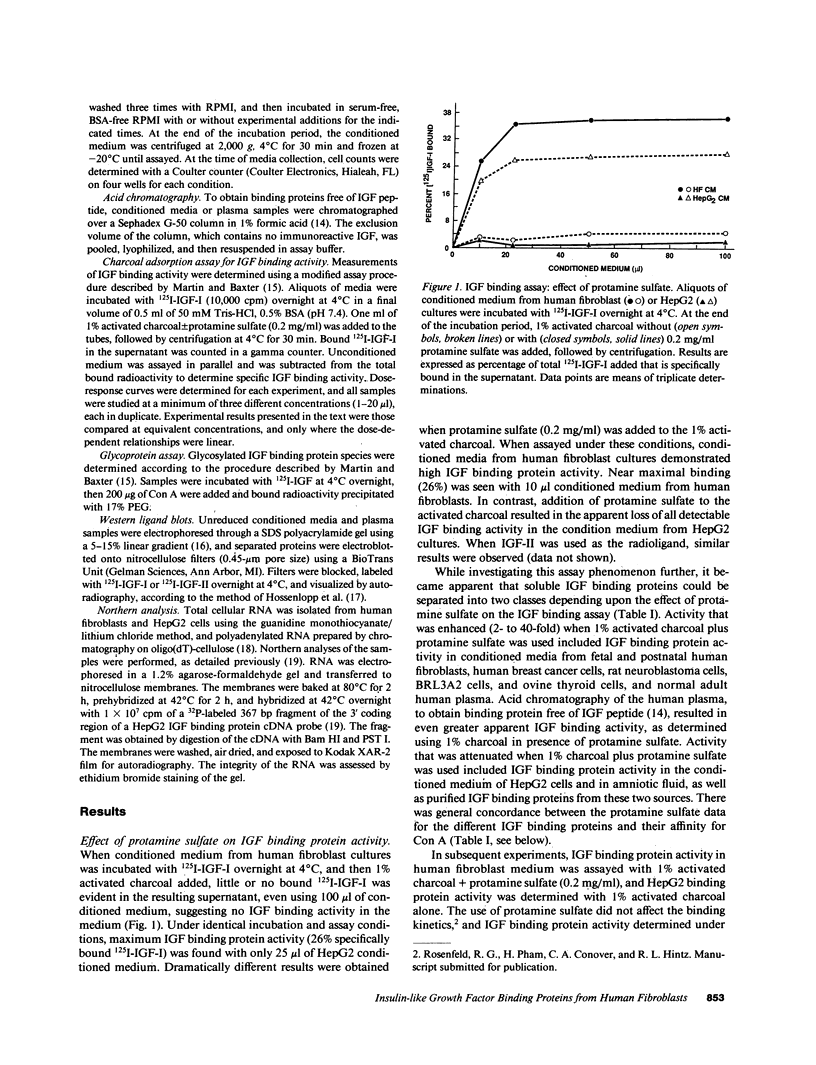
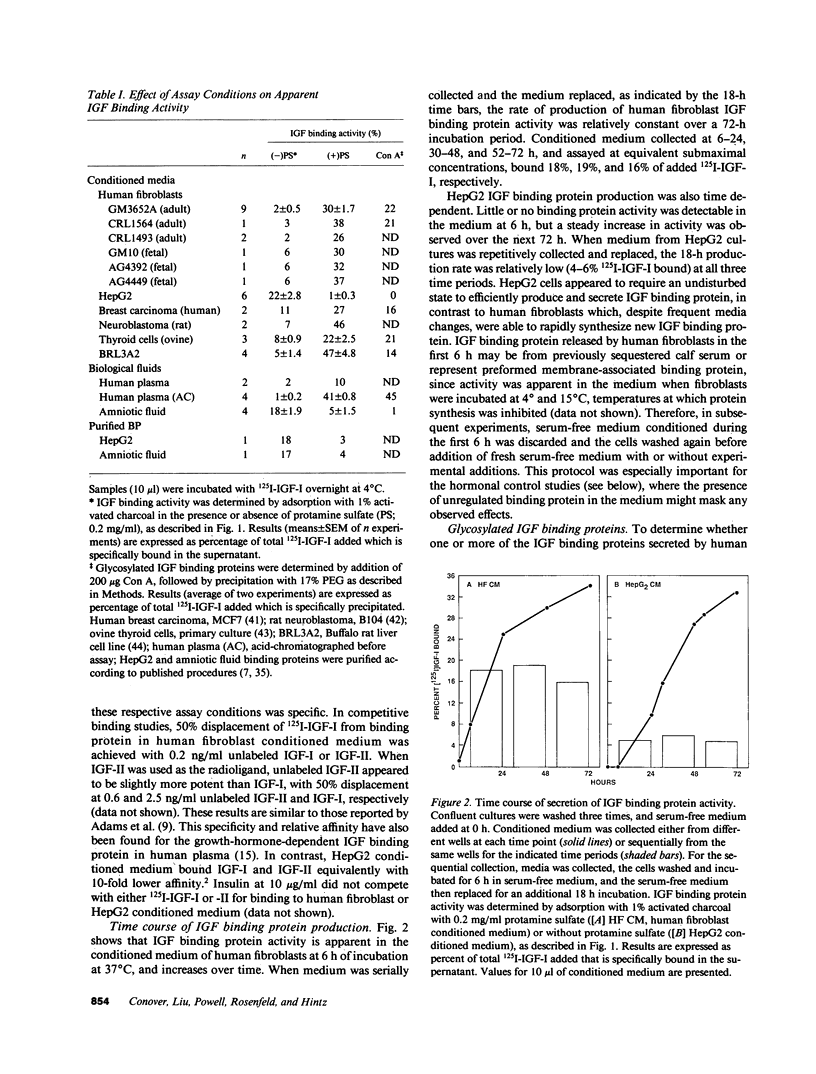
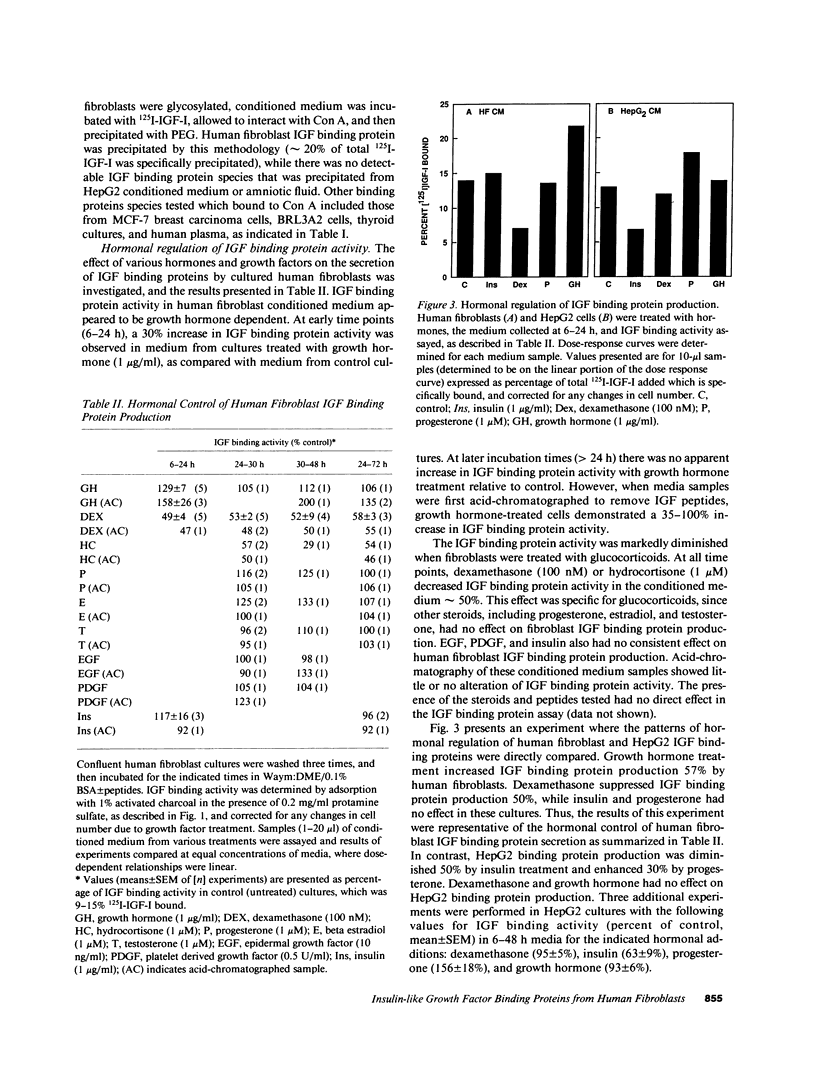
Specific, high affinity insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins are secreted by human fibroblasts in culture. By multiple criteria, the species of IGF binding proteins produced by human fibroblasts are distinct from the HepG2/amniotic fluid IGF binding protein, but share many characteristics with the growth hormone-dependent IGF binding protein forms predominant in normal adult human plasma. Treatment of cultured human fibroblasts with growth hormone produced an increase in IGF binding protein activity in the medium, while addition of glucocorticoids markedly diminished IGF binding activity. Insulin, epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and progesterone had no effect on IGF binding activity in fibroblast media. In comparison, HepG2 IGF binding activity was enhanced by progesterone, decreased by insulin, and unaffected by growth hormone or glucocorticoid treatment. Five molecular forms of IGF binding proteins were identified by Western ligand blots in human fibroblast conditioned medium, with Mr = 41,500, 37,000, 32,000, 28,000, and 23,000. In human fibroblast conditioned medium, the Mr = 41,500 and 37,000 IGF binding protein species were abundant, as in normal human plasma, with a major Mr = 23,000 form which was a minor component in plasma.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. O., Kapadia M., Mills B., Daughaday W. H. Release of insulin-like growth factors and binding protein activity into serum-free medium of cultured human fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1984 Aug;115(2):520–526. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-2-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach L. K., Eggo M. C., Hintz R. L., Burrow G. N. Insulin-like growth factors in sheep thyroid cells: action, receptors and production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):861–867. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Francis G. L., Ross M., Bagley C. J., May B., Wallace J. C. Natural and synthetic forms of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and the potent derivative, destripeptide IGF-1: biological activities and receptor binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Radioimmunoassay of growth hormone-dependent insulinlike growth factor binding protein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1504–1512. doi: 10.1172/JCI112742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Tyler M. I., Howden M. E. Growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human plasma differs from other human IGF binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1256–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Wood M. H. Two immunoreactive binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors in human amniotic fluid: relationship to fetal maturity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Sep;65(3):423–431. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Elgin R. G., Han V. K., Casella S. J., D'Ercole A. J., Van Wyk J. J. Cultured fibroblast monolayers secrete a protein that alters the cellular binding of somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1548–1556. doi: 10.1172/JCI112470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R. Multiple hormones stimulate the production of somatomedin by cultured human fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 May;58(5):850–856. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-5-850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Hormonal control of immunoreactive somatomedin production by cultured human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):10–19. doi: 10.1172/JCI110001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Dollar L. A., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Insulin-like growth factor I/somatomedin-C (IGF-I/SM-C) and glucocorticoids synergistically regulate mitosis in competent human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Aug;116(2):191–197. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041160210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Leon D. D., Bakker B., Wilson D. M., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Demonstration of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I and -II) receptors and binding protein in human breast cancer cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):398–405. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80727-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drop S. L., Valiquette G., Guyda H. J., Corvol M. T., Posner B. I. Partial purification and characterization of a binding protein for insulin-like activity (ILAs) in human amniotic fluid: a possible inhibitor of insulin-like activity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1979 Mar;90(3):505–518. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0900505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin R. G., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R. An insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein enhances the biologic response to IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W. The somatomedin C binding protein: evidence for a heterologous subunit structure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jul;51(1):12–19. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Jen P., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in human circulating cells and fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):747–751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourmelen M., Girard F., Binoux M. Serum somatomedin/insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and IGF carrier levels in patients with Cushing's syndrome or receiving glucocorticoid therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 May;54(5):885–892. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-5-885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardouin S., Hossenlopp P., Segovia B., Seurin D., Portolan G., Lassarre C., Binoux M. Heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and relationships between structure and affinity. 1. Circulating forms in man. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):121–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L. Plasma forms of somatomedin and the binding protein phenomenon. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner J. M., Liu F., Hintz R. L. Comparison of [125I]somatomedin A and [125I]somatomedin C radioreceptor assays for somatomedin peptide content in whole and acid-chromatographed plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Dec;47(6):1287–1295. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-6-1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Binoux M. Identification of an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein in human cerebrospinal fluid with a selective affinity for IGF-II. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):439–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Hardouin S., Binoux M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factor binding proteins using western blotting: use of the method for titration of the binding proteins and competitive binding studies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia B., Portolan G., Binoux M. Heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins between structure and affinity. 2. Forms released by human and rat liver in culture. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):133–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. L., Hintz R. L., James P. M., Lee P. D., Shively J. E., Powell D. R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein complementary deoxyribonucleic acid from human HEP G2 hepatoma cells: predicted protein sequence suggests an IGF binding domain different from those of the IGF-I and IGF-II receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 May;2(5):404–411. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-5-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Wharton W., van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and somatomedin C regulate G1 progression in competent BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein from human plasma. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8754–8760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuli C., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. NSILA-carrier protein abolishes the action of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S) on perfused rat heart. Diabetologia. 1978 Apr;14(4):255–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01219425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Freinkel A. J., Knowles B. B., Aden D. P. Demonstration that a human hepatoma cell line produces a specific insulin-like growth factor carrier protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 May;56(5):1003–1008. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-5-1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley S. P., Short P. A., Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Coon H. G. Proliferation of Buffalo rat liver cells in serum-free medium does not depend upon multiplication-stimulating activity (MSA). Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):441–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. R., Lee P. D., Shively J. E., Eckenhausen M., Hintz R. L. Method for purification of an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein produced by human HEP G2 hepatoma cells. J Chromatogr. 1987 Sep 4;420(1):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Póvoa G., Enberg G., Jörnvall H., Hall K. Isolation and characterization of a somatomedin-binding protein from mid-term human amniotic fluid. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):199–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Póvoa G., Isaksson M., Jörnvall H., Hall K. The somatomedin-binding protein isolated from a human hepatoma cell line is identical to the human amniotic fluid somatomedin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutanen E. M., Kärkkäinen T., Lundqvist C., Pekonen F., Ritvos O., Tanner P., Welin M., Weber T. Monoclonal antibodies to the 27-34K insulin-like growth factor binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):208–215. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80701-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. D., Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Production of insulin-like growth factor I and its binding protein by adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Endocrinology. 1985 Mar;116(3):1094–1101. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-3-1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suikkari A. M., Koivisto V. A., Rutanen E. M., Yki-Järvinen H., Karonen S. L., Seppälä M. Insulin regulates the serum levels of low molecular weight insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Feb;66(2):266–272. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-2-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström T., Seppälä M. Placental protein 12 (PP12) is induced in the endometrium by progesterone. Fertil Steril. 1984 May;41(5):781–784. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)47851-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. R., D'Ercole A. J. Affinity-labeled plasma somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I binding proteins. Evidence of growth hormone dependence and subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1350–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI111836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Jagars G., Sand I., Grunwald J., Froesch E. R. Inhibition of the action of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity on isolated rat fat cells by binding to its carrier protein. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):1077–1084. doi: 10.1172/JCI109377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]