Abstract
Background
The nature of the association between ghrelin, an orexigenic hormone produced mainly in the stomach, and Helicobacter pylori (H pylori), a bacterium that colonises the stomach, is still controversial. We examined available evidence to determine whether an association exists between the two; and if one exists, in what direction.
Methods
We reviewed original English language studies on humans reporting circulating ghrelin levels in H pylori infected and un-infected participants; and circulating ghrelin levels before and after H pylori eradication. Meta-analyses were conducted for eligible studies by combining study specific estimates using the inverse variance method with weighted average for continuous outcomes in a random effects model.
Results
Seventeen out of 27 papers that reported ghrelin levels in H pylori positive and negative subjects found lower circulating ghrelin levels in H pylori positive subjects; while 10 found no difference. A meta-analysis of 19 studies with a total of 1801 participants showed a significantly higher circulating ghrelin concentration in H pylori negative participants than in H pylori positive participants (Effect estimate (95%CI) = -0.48 (-0.60, -0.36)). However, eradicating H pylori did not have any significant effect on circulating ghrelin levels (Effect estimate (95% CI) = 0.08 (-0.33, 0.16); Test for overall effect: Z = 0.67 (P = 0.5)).
Conclusions
We conclude that circulating ghrelin levels are lower in H pylori infected people compared to those not infected; but the relationship between circulating ghrelin and eradication of H pylori is more complex.
Background
The relationship between ghrelin, a 28-amino acid peptide secreted primarily by the oxyntic cells of the stomach [1] and involved in body mass regulation, and Helicobacter pylori (H pylori), a bacterium that colonises the stomach, has remained controversial. The first report suggesting an association between the two was that by Nwokolo et al [2] who examined the effect of H pylori eradication on plasma ghrelin levels in 12 healthy adult male and female subjects. They reported that eradicating H pylori from the subjects was associated with an increase in plasma ghrelin levels. At about the same time, Gockel et al [3] reported that H pylori had no effect on plasma ghrelin levels in a study of 39 age- and BMI-matched H pylori positive and negative women. Subsequently a number of other papers, including animal studies, have explored this relationship [4-7]. A number of review articles have also appeared exploring this relationship [8,9]; but none of these has been conducted systematically.
Considering the putative role of ghrelin in body mass regulation, understanding this association could help in maximizing its benefits, and also provide further insight into the physiology of appetite and body mass regulation. The objective of this review is to examine available evidence to determine whether or not a relationship exists between ghrelin and H pylori infection; and where one exist, to investigate the direction of the association. Specifically, this review sets out to answer three questions: 1) Is H pylori infection associated with circulating ghrelin levels? 2) what is the effect of eradicating H pylori infection on circulating ghrelin levels?; and 3) what is the effect of H pylori infection on ghrelin producing cells in the stomach?
Methods
Literature search strategy and data extraction
A comprehensive search of the scientific literature (Medline (OVID), OvidMedline (R) 1950 - October Week 2 plus In-process & Non-indexed citations, Embase (1980 to 2010 week 41), and ISI Web of Knowledge) was conducted using the search terms "ghrelin AND helicobacter pylori". The search was repeated several times. The last search was conducted on October 29, 2010. Further searches were conducted using Google scholar; while the bibliography of original and review articles were searched for studies with ghrelin and helicobacter pylori in their titles. Duplicate searches were first removed; thereafter, the abstracts of retrieved articles were reviewed for relevance prior to accessing the full paper. Only English-language primary studies on humans were included provided that the authors assessed at least one of the following: 1) compared circulating ghrelin concentration in H pylori positive and negative subjects; 2) compared the effect of eradicating H pylori on circulating ghrelin levels; or 3) compared gastric ghrelin in H pylori positive and negative subjects or changes in gastric ghrelin after H pylori eradication. Letters in response to published articles, commentaries, and editorials were excluded. Conference abstracts that had not been published as full papers were included where the full abstracts could be retrieved, provided that such conference abstract contained enough information for either the qualitative or the quantitative synthesis. However, where a conference abstract has been published as a full paper, the full paper was retrieved and the conference proceeding excluded.
Efforts were made to contact authors of conference abstracts whose full paper publications could not be traced to inquire if the paper had been published as a full paper and if not, to get further details about the study. Efforts were also made to contact authors of papers where some relevant information was missing to request for the missing information or for further clarifications. We contacted 18 authors [2,6,10-25]; but only nine authors [2,14,18,21-26] responded and provided the needed information. We were unable to contact one author [27].
We also attempted to group the papers reviewed by study teams in other to assess the spread of the papers reviewed. In deciding whether different papers were published by the same research groups, similarity in authorship was examined. Where at least one author contributed to different publications, those publications were deemed to have emanated from the same research group.
Outcomes evaluated
Outcomes evaluated included: differences in circulating ghrelin levels between H pylori positive and negative subjects; changes in circulating ghrelin concentration after H pylori eradication; differences in ghrelin mRNA between H pylori positive and negative subjects; changes in ghrelin mRNA after H pylori eradication; differences in ghrelin immunoreactive cells between H pylori positive and negative subjects; changes in ghrelin immunoreactive cells after cure; correlation between ghrelin immunoreactive cells with severity of H pylori infection; correlation between gastric and plasma ghrelin; correlation between ghrelin mRNA and plasma ghrelin; and correlation between cells and plasma ghrelin.
Data synthesis
The data extracted were classified into three classes: 1) data comparing circulating ghrelin concentration in H pylori positive and negative subjects; 2) data comparing the circulating ghrelin concentration before and after H pylori eradication; and 3) data assessing any of the gastric ghrelin parameters. Each of these classes was supposed to answer a specific question (Table 1). The variables were re-coded in forms that would make analysis easier (Table 2). Table 3 lists the papers excluded from the review and the reasons for their exclusion.
Table 1.
Research questions explored by the review
| Research question | Explanatory data |
|---|---|
| Is H pylori infection associated with circulating ghrelin levels? | Data comparing circulating ghrelin concentration in H pylori positive and negative subjects |
| What is the effect of eradicating H pylori on circulating ghrelin levels? | Data comparing the circulating ghrelin concentration before and after H pylori eradication |
| What is the effect of H pylori infection on ghrelin expression in the stomach? | Data assessing any of the gastric ghrelin parameters |
Table 2.
Dictionary of variables used in the review
| Variable | Coding scheme |
|---|---|
| Study Team | A, B, C etc |
| Design | Cohort, Cross-sectional, Case control, Experimental |
| Healthy | Healthy only, Sick only, Both |
| Region | Asia, Africa, Europe, North America, South America |
| Gender | Male only, Female only, Both |
| Age | Children only, Adults only, Both |
| Number of methods used to assess H pylori | One method; two or more methods |
| Type of ghrelin assay used | Commercial RIA, in-house RIA, Commercial ELISA, Commercial EIA |
| Sample storage | -70°C and below; above -70°C |
| Sample type | Serum; Plasma |
| Weight | Normal, Low, Various, High |
| Difference in circulating ghrelin concentration between H pylori + & - subjects | Lower, no difference, higher |
| Changes in circulating ghrelin after cure | Increased, decreased, no change |
| Duration of follow-up | 4 weeks & below; Above 4 weeks |
| Sample size | Two categorizations were done: 1) 50 & below, 51-200, 201 and above; 2)Above 20, Below 20 |
Table 3.
Papers excluded from the review
| Reason for exclusion | |
|---|---|
| Suzuki et al, 2006 [54] | Did not report ghrelin levels in H pylori positive &H pylori negative patients |
| Nunes et al, 2006 [27] | Not sufficient information in abstract and authors could not be contacted for further clarifications |
| Campana et al, 2007 [56] | All subjects were H pylori negative |
| Isomoto et al, 2005 [52] | Compared only H pylori strains |
| Checchi et al, 2007 [10] | Did not compare serum ghrelin levels in H pylori positive &H pylori negative subjects |
| Wu et al, 2005[57] | Did not assess ghrelin |
| Shinomiya et al, 2005[58] | Did not compare the difference in ghrelin between H pylori positive &H pylori negative subjects |
| Suzuki et al, 2005[59] | Did not assess ghrelin |
| Sundbom et al, 2007[60] | Did not assess H pylori |
| Huang et al, 2007[61] | Did not assess H pylori |
| Nishizawa et al, 2006[62] | Did not assess H pylori |
| Ando et al, 2006[63] | Did not assess ghrelin |
| Kempa et al, 2007[64] | All subjects were H pylori negative |
| Ates et al, 2008[65] | Did not assess H pylori |
| Wang et al, 2006[66] | Did not assess ghrelin |
| Doki et al, 2006[67] | Did not assess H pylori |
| Gao et al, 2008[68] | Excluded people with H pylori |
| Cherian et al, 2009[69] | Did not assess ghrelin |
| Kebapcilar et al, 2009[70] | Did not assess ghrelin |
| Dutta et al, 2009[71] | Did not assess ghrelin |
| Gen et al, 2010[72] | Did not assess ghrelin |
| Taniaka-Shintani et al, 2005[1] | Examined only ghrelin immunoreactive cells |
Statistical analysis
Simple proportions were used to determine the frequency of occurrence of each categorical variable considered; and association between different variables assessed using Fisher's exact chi2 test. Continuous variables like sample size and duration of follow-up was initially summarized using medians and inter-quartile ranges and later categorized as shown in Table 2. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to assess confounding. The descriptive analysis was conducted using Stata version 8 (StataCorp LP, College Station, Texas, USA).
Meta-analysis
We conducted meta-analyses of summary statistics from individual studies that compared circulating ghrelin levels between H pylori positive and H pylori negative subjects; and for studies that compared circulating ghrelin levels before and after eradication of H pylori. For each study, the mean circulating ghrelin concentrations and standard deviations (sd) for the different comparison groups were used to generate standardized mean differences (SMDs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) since different studies used different units to measure ghrelin concentration, and some studies measured plasma ghrelin while others measured serum ghrelin. For studies that reported standard errors of mean, standard deviation was derived using the formula provided in the Cochrane Handbook of clinical reviews: SD = SEM × √N (http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/homepages/106568753/handbook.pdf). Studies that reported only medians and 95% CI or interquartile ranges (IQR) [2,6] were not included in the meta-analysis. Table 4 lists studies excluded from the meta-analysis and the reasons for their exclusion.
Table 4.
Papers excluded from the meta-analysis
| Nwokolo et al, 2003[2] | Reported median values & 95% CI; also measured integrated ghrelin levels rather than the discrete measurement that other authors used. The authors stated that the median values were used because the sample size was small and the data were skewed |
| Mendez-Sanchez et al, 2007 [49] | Studied ghrelin immuno-reactive cells, did not provide data on plasma ghrelin levels |
| Salles et al, 2006[19] | Ghrelin values not provided. Only P-values |
| Gao et al, 2009[15] | Ghrelin values not provided |
| Choe et al, 2007[6] | Median & IQR provided. Further clarifications not provided by the authors |
| Czesnikiewicz-Guzik et al, 2005[12] | Insufficient information for meta-analysis |
| Czesnikiewicz-Guzik et al, 2007 [13] | Insufficient information for meta-analysis |
| Masaoka et al [51] | This was a case study with only one subject |
| Stec-Michalska et al, 2009[24] | Measured only gastric ghrelin |
| Liew et al, 2006[47] | Assessed only gastric ghrelin |
| Konturek et al, 2006[17] | The numbers of H pylori positive and negative participants were not provided and the authors did not respond to requests for further information. |
Study specific estimates were combined using the inverse variance method with weighted average for continuous outcomes in a random effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using the chi-squared method and the I2 method described by Higgins et al [28,29]. For studies that reported different sub-groups separately [30-32] those sub-groups were included as separate papers in the meta-analysis. Chuang et al, [30] reported ghrelin levels for males and females separately. While the data for males did not increase the heterogeneity of the studies, inclusion of the data for females introduced significant heterogeneity to the analysis. All the papers that resulted in significant heterogeneity of the studies in the meta-analysis were removed from the meta-analysis. A separate meta-analysis conducted for this sub-group of excluded studies revealed a significant heterogeneity (P=0.0001; I2 = 86%) and the effect size was very small and not significant (SMD -0.13 [-0.33, 0.06], Test for overall effect: Z = 1.36 (P = 0.17)). These papers were therefore completely excluded from the meta-analysis and described in a narrative. Sensitivity analysis was conducted to assess the contribution of each study to the pooled estimate by excluding individual studies one at a time and recalculating the pooled SMD estimates for the remaining studies. Funnel plots were used initially to assess publication bias and later confirmed using Begg's and Egger's tests. The meta-analyses were conducted using Review Manager Version 5 (RevMan 5; http://www.cc-ims.net/revman/download), while the Begg's and Egger's tests were conducted using Stata version 8 after downloading the installation files for the tests from the internet.
Results
Search results
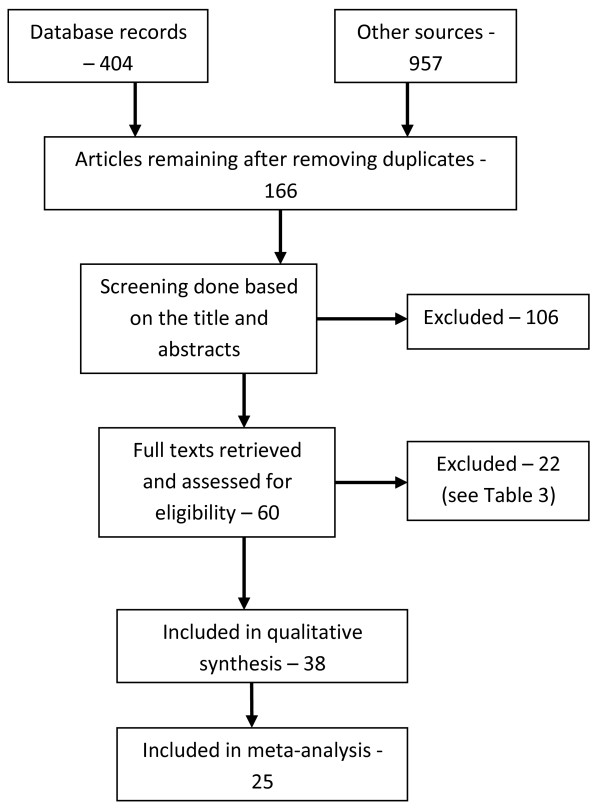
The literature search yielded 1361 papers (404 from databases and 957 from Google Scholar) plus one unpublished paper. After removing duplicate articles, reviews, commentaries and letters (written in response to published articles), 166 papers (including one conference abstract and one unpublished paper) were left. These were further screened using titles and abstract to assess for eligibility, resulting in the exclusion of 106 articles (Figure 1). The full texts of the remaining 60 articles (excluding the conference abstract) were retrieved. Twenty-two papers were subsequently dropped from the review (Table 3), and another 11 from the meta-analysis (Table 4).
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow chart showing information flow in the selection of papers for the review
Is H pylori infection associated with circulating ghrelin levels?
Table 5 is an evidence table of studies that compared circulating ghrelin levels in H pylori positive and H pylori negative individuals. Twenty-six studies compared circulating ghrelin levels between H pylori positive and negative subjects. The analysis of one of the studies [30] was stratified by gender, yielding different results; this study was therefore entered into the evidence table as two separate papers with each gender representing one paper, bringing the total number of papers reviewed to 27. One paper [22] was not included in the evidence table because the grouping of the subjects studied did not permit a straight forward comparison of the H pylori positive and H pylori negative subjects. The paper was therefore reviewed in a separate narrative. Table 6 summarises the characteristics of the studies included in the evidence table. Most of the studies (77%) investigated both males and females, 85% studied only adults and 52% studied sick subjects mainly subjects with gastrointestinal symptoms (64.7%) and Cancer (17.65%). Thirteen (48.2%) of the studies [15,21,30,33-41] were conducted in Asia; 11 (40.7%) [3,11,12,17,19,26,31,32,42-44] in Europe and three (11.1%) [14,18,45] in North America. Twenty-two percent of the studies reviewed were contributed by one research group alone, while Japan contributed 30% of the papers. More than two-thirds of the studies used radioimmunoassay to measure serum or plasma ghrelin, 55.6% assessed H pylori using two or more methods, and in all the studies except one, samples were collected after overnight fast. All comparisons were based on the pre-meal ghrelin levels. In most of the studies (70.4%), the samples were stored at a temperature of -70°C or below until analysed; ghrelin was measure in plasma samples in 63% of the studies, while the participants were of normal weight in 58% of the studies. The sample sizes for the different studies ranged from 13 to 538 (median: 89; IQR: 62, 180).
Table 5.
Evidence table of studies that compared circulating ghrelin levels in Hp+ and Hp- individuals
| Reference & Country | Study Team | Design | Healthy | Gender | Age | Method of H pylori assessment | Ghrelin assay kit | Overnight fast | Sample storage | Sample type | Weight | Sample size | Ghrelin levels in Hp+ vs Hp- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kawashima et al, 2009; Japan [38] | A | Cohort | Both | Both | Adults | Serology | Commercial EIA | Yes | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 220 | Lower |
| Plonka et al, 2006; Poland [32] | B | Cohort | Healthy | Both | Both | Modified UBT plus ELISA | Commercial RIA | Yes | -80 | Serum | 538 | Lower | |
| Isomoto et al, 2005; Japan[36] | C | Cohort | Sick | Both | Adults | RUT, histology (Giemsa stain) | In-house RIA | Yes | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 81 | Lower |
| Roper et al, 2008; USA [18] | D | Cross-sectional | Healthy | Men | Adults | serology, histology & RUT or positive culture | Commercial EIA | Yes | -20 | Serum | Normal | 256 | No Difference |
| Pacifico et al, 2008; Italy [26] | E | Cohort | Both | Both | Children | Culture of gastric specimen or histology + RUT | Commercial RIA | Yes | -70 | Serum | Normal | 85 | No Difference |
| Gokcel, 2003; Turkey [3] | F | Case control | Sick | Women | Adults | Not stated | Commercial EIA | Yes | Not stated | Plasma | Normal | 39 | No Difference |
| Plonka et al, 2006; Poland [43] | B | Case control | Healthy | Both | Children | Serology and UBT | Commercial RIA | Yes | -80 | Serum | Various | 287 | Lower |
| Shiotani et al, 2005; Japan [21] | G | Case control | Healthy | Both | Adults | Detection of HP IgG ab in the urine | Commercial ELISA | Yes | Not stated | Serum | Various | 132 | Lower |
| Osawa et al, 2005; Japan [40] | C | Case control | Sick | Men | Adults | Culture & histology | In-house RIA | Yes | -30 | Plasma | Normal | 160 | Lower |
| Chuang et al*, 2009; Taiwan [30] | H | Cross-sectional | Sick | Men | Adults | Not described | Commercial RIA | Yes | -72 | Plasma | low to normal | 145 | Lower |
| Chuang et al*, 2009; Taiwan [30] | H | Cross-sectional | Sick | Women | Adults | Not described | Commercial RIA | Yes | -72 | Plasma | low to normal | 196 | No Difference |
| Alonso et al, 2007; Spain[42] | P | Cross-sectional | Sick | Both | Adults | UBT, histology (Giemsa stain) | Commercial RIA | Yes | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 15 | Lower |
| Salles et al, 2006; France[19] | I | Cross-sectional | Sick | Both | Adults | UBT, serology, culture, histology & PCR | Commercial RIA | Yes | -80 | Plasma | low to normal | 62 | Lower |
| Jun et al, 2007; Korea [37] | J | Cross-sectional | Sick | Both | Adults | RUT, histology (Giemsa stain) | Commercial RIA | Yes | -70 | Plasma | Normal | 63 | No Difference |
| D'Onghia et al, 2007; Italy [31] | K | Case control | Both | Both | Adults | ELISA | RIA | Yes | -20 | Serum | Various | 79 | Lower |
| Gao et al, 2009; China [15] | L | Case control | Healthy | Both | Adults | Serology & UBT. | Commercial RIA | Yes | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 100 | Lower |
| Isomoto et al, 2005; Japan[35] | C | Cross-sectional | Sick | Both | Adults | Anti-IgG antibody, 13C-UBT, or RUT | In-house RIA | Yes | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 89 | Lower |
| Isomoto et al, 2005; Japan[41] | C | Cross- sectional | Sick | Both | Adults | Serology, UBT or RUT | In-house RIA | Yes | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 249 | Lower |
| An et al, 2007; Korea[33] | Q | Cohort | Sick | Both | Adults | Not stated | Commercial ELISA | Yes | -70 | Plasma | Normal | 41 | No difference |
| Nishi et al, 2005; Japan [39] | C | Cross-sectional | Both | Both | Adults | Serology & UBT | In-house RIA | Yes | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 74 | Lower |
| Czesnikiewicz-Guzik et al, 2005; Poland [12] | B | Cross-sectional | Healthy | Women | Adults | UBT | Not stated | Not stated | Not stated | Serum | Not Stated | 100 | Lower |
| Konturek et al, 2006; Poland [17] | B | Cross-sectional | Healthy | Both | Both | UBT & serology | Human RIA | Yes | -80 | Serum | Not Stated | 180 | Lower |
| Cindoruk et al, 2007; Turkey [11] | M | Cohort | Sick | Both | Adults | Either histology or UBT | RIA | Yes | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 50 | No Difference |
| Isomoto et al, 2004; Japan [34] | C | Cohort | Sick | Both | Adults | Serology | Commercial RIA | Yes | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 68 | Lower |
| de Martel, 2007; USA [14] | N | Case control | Sick | Both | Adults | In-house ELISA | Commercial ELISA | Yes | -80 | Serum | Various | 110 | No Difference |
| Shak et al, 2008, USA[45] | R | Cohort | Healthy | Both | Adults | Serology | Commercial EIA | Yes | -20 | Plasma | Obese | 24 | No difference |
| Uzzan et al, 2007[44] | S | Cohort | Healthy | Both | Adults | Histology | Commercial RIA | Yes | Not stated | Serum | Obese | 13 | No difference |
* These are from the same paper reporting the same study but were separated because the analysis was stratified by gender and the results for males and females were completely different; hence the decision to separate them.
Table 6.
Summary of the characteristics of the studies reviewed in Table 5
| Characteristic | n | n % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study Design | Case control | 7 | 25.93 |
| Cohort | 9 | 33.33 | |
| Cross-sectional | 11 | 40.74 | |
| Gender studied | Both | 21 | 77.78 |
| Men | 3 | 11.11 | |
| Women | 3 | 11.11 | |
| Region | Asia | 13 | 48.15 |
| Europe | 11 | 40.74 | |
| North America | 3 | 11.11 | |
| Health status | Both | 4 | 14.81 |
| Healthy | 9 | 33.33 | |
| Sick | 14 | 51.85 | |
| Age Group | Adults | 23 | 85.19 |
| Both | 2 | 7.41 | |
| Children | 2 | 7.41 | |
| Type of Sickness | Cancer | 3 | 17.65 |
| GI symptoms | 11 | 64.71 | |
| Others† | 3 | 17.64 | |
| HP assessment methods used | Not Described | 5 | 18.52 |
| One | 7 | 25.93 | |
| Two or more | 15 | 55.56 | |
| Assay Type | Commercial EIA | 4 | 14.81 |
| Commercial ELISA | 3 | 11.11 | |
| Commercial RIA | 14 | 51.85 | |
| In-house RIA | 5 | 18.52 | |
| Not stated | 1 | 3.7 | |
| Sample Size | 50 and below | 6 | 22.22 |
| 51-200 | 16 | 59.26 | |
| 201 and above | 5 | 18.52 | |
| Sample Storage | -70C and above | 19 | 70.37 |
| Below -70C | 4 | 14.81 | |
| Not Described | 4 | 14.81 | |
| Sample type | Plasma | 17 | 62.96 |
| Serum | 10 | 37.04 | |
| BMI of participants | Normal | 15 | 57.69 |
| Not Stated | 2 | 7.69 | |
| Obese | 2 | 7.69 | |
| Various | 4 | 15.38 | |
| low to normal | 3 | 11.54 |
†Others include Crohn's disease (1), diabetes mellitus (1) and multiple conditions (1)
Overall, 17 studies (63%) reported that circulating ghrelin concentrations were lower in H pylori positive subjects. Ten studies from Asia (76.9%) and seven from Europe (63.6%) found that circulating ghrelin levels in H pylori positive subjects were lower compared to H pylori negative subjects. The rest of the studies, including the three from the USA did not find any difference between H pylori positive and negative subjects. There was a weak association between the region of the world where the study was conducted and the finding of a lower circulating ghrelin level in H pylori positive subjects compared to H pylori negative subjects (Fisher's exact test = 0.07). This completely disappeared after controlling for gender, age, health status, type of sample used, storage conditions, BMI, and the sample size.
Zub-Pokrowiecka et al [22] investigated ghrelin changes in the plasma and gastric mucosa among participants with various gastric diseases. Their subjects were divided into four groups - Group 1 had gastric cancer and concomitant H pylori infection; group 2 had antral gastritis, duodenal ulcer and H pylori infection; group 3 had atrophic gastritis of the fundus and corpus of the stomach but no H pylori infection; while group 4 had no gastric lesions and no H pylori infection. These researchers reported that the fasting plasma ghrelin concentrations varied among the different groups as follows (in descending order): group 2, group 4, group 1 and group 3.
Meta-analysis
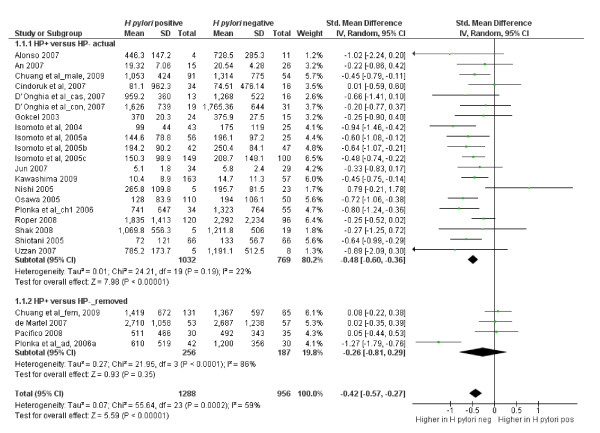
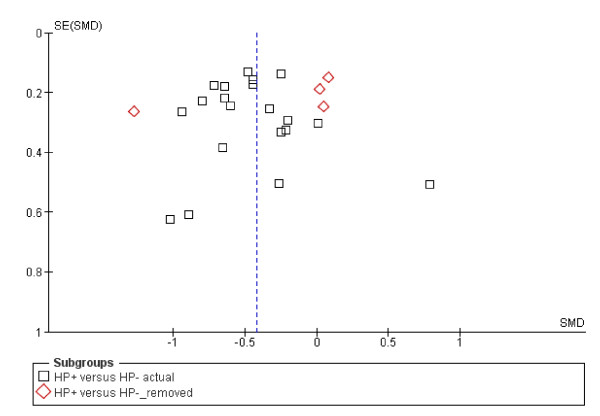
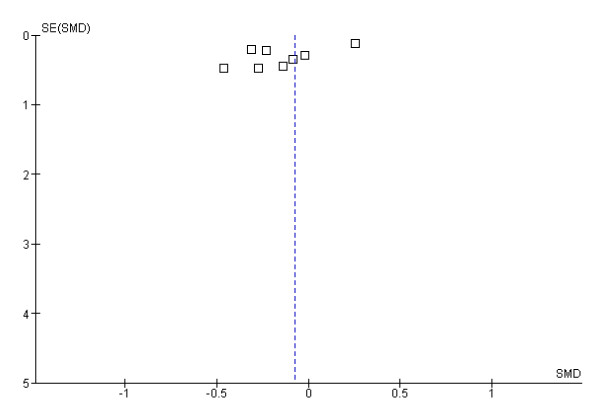
Twenty-one of the 26 studies reviewed in this section qualified for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Of these 21 studies, three studies provided ghrelin values for the different categories of subjects studied. Chuang et al [30] presented their results by gender; D'Onghia et al [31] presented their results according to whether the subjects were healthy controls or had colo-rectal cancer; and Plonka et al [32] presented their results for adults and children separately. Because each of these features could affect the circulating ghrelin concentration, the different categories were entered into the meta-analysis as separate papers bringing the total number of papers included to 24 with a total of 2244 participants. Table 4 lists studies excluded from the meta-analysis. Four papers were subsequently removed from the final analysis because they added significant heterogeneity to the analysis (Figure 2). The analysis showed that circulating ghrelin concentration was significantly lower in H pylori positive participants than in H pylori negative participants (Effect estimate (95%CI) = -0.48 [-0.60, -0.36]). Figure 2 is a forest plot of SMDs of circulating ghrelin concentration between H pylori positive and H pylori negative subjects. There was no significant heterogeneity among the studies (Heterogeneity: Chi² = 24.21, df = 19 (P = 0.19); I² = 22%). Examination of the funnel plot (Figure 3) suggests some publication bias but the Egger and Begg's tests indicated no publication bias (Begg's test: z = 1.20 (continuity corrected), P = 0.23 (continuity corrected); Egger's bias coefficient = -59.99, P = 0.116). A sensitivity analysis indicated that all the studies included in the meta-analysis contributed approximately equally to the pooled estimate (Table 7). Three of the studies dropped from the meta-analysis did not find any difference in the circulating ghrelin levels between H pylori positive and H pylori negative subjects [14,26,30]. However, Plonka et al [32] found a significantly lower circulating ghrelin levels among a group of H pylori positive Polish shepherds compared to their H pylori negative controls. Adding these four papers (excluded because of heterogeneity) only slightly increased the effect estimate (-0.42 [-0.57, -0.27]) but still showed that H pylori infection was associated with a lower circulating ghrelin concentration.
Figure 2.
Forest plot of SMDs of circulating ghrelin concentration between H pylori positive and H pylori negative subjects (the top forest plot labelled 'actual' represents the analysis on which the inference was made. The lower forest plot labelled 'removed' were studies excluded from the meta-analysis but displayed here to demonstrate their characteristics for readers that might be interested. The values at the bottom of the forest plot represents the overall effect size for both the 'actual' and the 'removed'
Figure 3.
Funnel plot of SMDs of circulating ghrelin concentration between H pylori positive and H pylori negative subjects
Table 7.
Sensitivity analysis of studies included in the meta-analysis
| Studies excluded | SMD (95%CI) | Test for overall effect |
|---|---|---|
| Alonso et al, 2007 | -0.47 [-0.59, -0.35] | Z = 7.80 (P < 0.00001) |
| An et al, 2007 | -0.49 [-0.61, -0.37] | Z = 7.88 (P < 0.00001) |
| Chuang et al_male, 2009 | -0.48 [-0.61, -0.35] | Z = 7.39 (P < 0.00001) |
| Cindoruk et al, 2007 | -0.49 [-0.61, -0.38] | Z = 8.48 (P < 0.00001) |
| D'Onghia et al_case, 2007 | -0.47 [-0.60, -0.35] | Z = 7.64 (P < 0.00001) |
| D'Onghia et al_control, 2007 | -0.49 [-0.61, -0.37] | Z = 7.95 (P < 0.00001) |
| Gokcel et al, 2003 | -0.49 [-0.61, -0.36] | Z = 7.84 (P < 0.00001) |
| Isomoto et al, 2004 | -0.46 [-0.57, -0.35] | Z = 7.96 (P < 0.00001) |
| Isomoto et al, 2005a | -0.47 [-0.60, -0.35] | Z = 7.47 (P < 0.00001) |
| Isomoto et al, 2005b | -0.47 [-0.59, -0.34] | Z = 7.43 (P < 0.00001) |
| Isomoto et al, 2005c | -0.48 [-0.61, -0.35] | Z = 7.14 (P < 0.00001) |
| Jun et al, 2007 | -0.49 [-0.61, -0.36] | Z = 7.72 (P < 0.00001) |
| Kawashima et al, 2009 | -0.48 [-0.61, -0.35] | Z = 7.32 (P < 0.00001) |
| Nishi et al, 2005 | -0.49 [-0.59, -0.39] | Z = 9.72 (P < 0.00001) |
| Osawa et al, 2005 | -0.46 [-0.58, -0.34] | Z = 7.45 (P < 0.00001) |
| Plonka et al_ch1 2006 | -0.46 [-0.58, -0.34] | Z = 7.65 (P < 0.00001) |
| Roper et al, 2008 | -0.51 [-0.63, -0.39] | Z = 8.37 (P < 0.00001) |
| Shak et al, 2008 | -0.48 [-0.60, -0.36] | Z = 7.79 (P < 0.00001) |
| Shiotani et al, 2005 | -0.46 [-0.59, -0.34] | Z = 7.33 (P < 0.00001) |
| Uzzan et al, 2007 | -0.47 [-0.59, -0.35] | Z = 7.76 (P < 0.00001) |
What is the effect of eradicating H pylori on circulating ghrelin levels?
Table 8 presents an evidence table of the studies that reported the effect of eradicating H pylori on circulating ghrelin levels. Thirteen papers were reviewed 12 of which were cohort studies and one RCT. Five of the 13 studies were conducted in Japan; 3 in Korea (both in Asia) and four in Europe. The only study from Africa was an unpublished paper by our team. Table 9 is a summary of the characteristics of the studies in Table 8.
Table 8.
Evidence table of studies that examined changes in circulating ghrelin levels following H pylori eradication
| Reference & Country | Study Team | Design | Healthy | Gender | Age category | HP assess | Ghrelin assay Kit | Sample storage | Sample type | Weight | Sample size | Circulating Ghrelin levels after cure | Follow-up (wks) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nwokolo et al, 2003; UK [2] | A | Cohort | Healthy | Both | Adults | Serology and UBT | Commercial RIA | -20 | Plasma | Various | 10 | Increased | 6 |
| Jang et al, 2008; Korea [16] | B | Cohort | Sick | Both | Adults | RUT plus histology & confirmed by UBT | Commercial RIA | -70 | Plasma | Normal | 16 | Increased | Not stated |
| Osawa et al, 2006; Japan [46] | C | Cohort | Healthy | Men | Adults | Bacterial culture & histology | In-house RIA | Not stated | Plasma | Normal | 134 | Decreased | 12 |
| Czesnikiewicz-Guzik et al, 2007; Poland [13] | D | Cohort | Sick | Women | Adults | UBT; culture of saliva & supragingival dental plaques + serology | Commercial RIA | -80 | Plasma | Not stated | 49 | Increased | 4 |
| Lee et al, 2010; Korea [23] | B | RCT | Healthy | Both | Adults | RUT, histology (Giemsa stain) | ELISA | -70 | Plasma | Normal | 9 | No difference | 5 |
| Choe et al, 2007, Korea [6] | E | Cohort | Sick | Both | Adults | histology & PCR | Commercial ELISA | -70 | Plasma | Normal | 8 | No difference | 4 |
| Pacifico et al, 2008; Italy [26] | F | Cohort | Both | Both | Children | Culture of gastric specimen or histology + RUT | RIA | -70 | Serum | Normal | 22 | Decreased | 52 |
| Nweneka, et al, unpublished; Gambia | G | Cohort | Sick | Both | Children | UBT | Commercial RIA | -70 | Serum | Low | 3 | Decreased | 4 |
| Isomoto et al, 2005; Japan [36] | C | Cohort | Sick | Both | Adults | RUT, histology (Giemsa stain) | In-house RIA | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 43 | No difference | 4 |
| Isomoto et al, 2005; Japan[35] | C | Cohort | Sick | Both | Adults | RUT, histology (Giemsa stain) | In-house RIA | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 10 | No difference | 4 |
| Kawashima et al, 2009; Japan [38] | H | Cohort | Both | Both | Adults | Serology | Commercial EIA | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 49 | Increased | 23 |
| Cindoruk et al, 2007; Turkey [11] | I | Cohort | Sick | Both | Adults | Either histology or UBT | RIA | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 23 | No difference | 12 |
| Isomoto et al, 2004; Japan [34] | C | Cohort | Sick | Both | Adults | Serology | Commercial RIA | -80 | Plasma | Normal | 9 | No difference | 4 |
Table 9.
Summary of the characteristics of the studies reviewed in Table 8
| Characteristic | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study Design | Cohort | 12 | 92.31 |
| RCT | 1 | 7.69 | |
| Gender studied | Both | 11 | 84.62 |
| Men | 1 | 7.69 | |
| Women | 1 | 7.69 | |
| Region | Africa | 1 | 7.69 |
| Asia | 8 | 61.54 | |
| Europe | 4 | 30.77 | |
| Health status | Both | 2 | 15.38 |
| Healthy | 3 | 23.08 | |
| Sick | 8 | 61.54 | |
| Age Group | Adults | 11 | 84.62 |
| Children | 2 | 15.38 | |
| Type of Sickness | GI Symptoms | 9 | 90 |
| PEM | 1 | 10 | |
| HP assessment methods used | One | 3 | 23.08 |
| Two or more | 10 | 76.92 | |
| Assay Type | ELISA | 2 | 15.38 |
| Commercial RIA | 8 | 61.54 | |
| In-house RIA | 3 | 23.08 | |
| Sample Size | Above 20 | 6 | 46.15 |
| Below 20 | 7 | 53.85 | |
| Sample Storage | -70°C and below | 11 | 84.62 |
| Above -70°C | 1 | 7.69 | |
| Not described | 1 | 7.69 | |
| Sample type | Plasma | 11 | 84.62 |
| Serum | 2 | 15.38 | |
| BMI of participants | Normal | 10 | 76.92 |
| Others | 3 | 23.07 | |
| Duration of follow-up | 4 weeks & below | 6 | 46.15 |
| Above 4 weeks | 6 | 46.15 | |
| Not recorded | 1 | 7.69 | |
| Change in ghrelin after cure | Decreased | 3 | 23.08 |
| Increased | 3 | 23.08 | |
| No difference | 7 | 53.85 | |
In 11 studies, the subjects fasted overnight, and for 3 hours (between 6am and 9am) in one study, before being bled. Osawa et al [46] did not indicate whether their subjects were fasted or not. The sample sizes varied from 3 to 134; median value was 16 (IQR: 9, 43). The duration of follow-up varied from 4 weeks to 52 weeks (median follow-up time: 4.5 weeks; IQR: 4 weeks, 12 weeks). Jang et al [16] were not clear on the duration of follow-up of their subjects.
In seven studies (53.9%) there was no significant difference in circulating ghrelin levels pre- and post H pylori eradication. Three studies (23.1%) reported an increase above the pre-eradication level while 3 (23.1%) reported a decrease below the pre-eradication levels. Cross tabulation of the following variables with change in circulating ghrelin levels following cure of H pylori infection did not show any association: the age of the participants, the type of sample used, duration of follow-up, sample size, weight of participants, temperature at which the blood samples were stored, the assay kit used to measure circulating ghrelin, the number of methods used to assess H pylori, gender, country and the region where the study was conducted. Although not statistically significant, the circulating ghrelin concentration decreased following H pylori eradication in the two studies that measured ghrelin using serum samples (Fisher's exact test 0.08). Similarly, the two studies conducted on children found a decrease in circulating ghrelin levels after H pylori cure. However, these two studies on children also utilised serum samples; while all the 11 studies conducted in adults used plasma samples. From this descriptive analysis, there is not sufficient data to make a conclusive statement on the effect of H pylori eradication on circulating ghrelin levels.
Meta-analysis
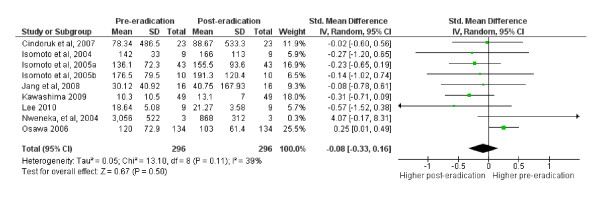
Nine (out of the 13 studies reviewed in this section) were included in a meta-analysis with a total population of 592. The excluded studies are listed in Table 4. The analysis showed that eradicating H pylori does not have any significant effect on circulating ghrelin levels (Effect estimate (95% CI) = -0.08 [-0.33, 0.16]; Test for overall effect: Z = 0.67 (P = 0.5)). Figure 4 is a forest plot of SMDs of circulating ghrelin concentration pre- and post-eradication of H pylori. The funnel plot indicated publication bias (Figure 5).
Figure 4.
Forest plot of SMDs of circulating ghrelin concentration pre- and post- eradication of h pylori
Figure 5.
Funnel plot of SMDs of circulating ghrelin concentration pre- and post- eradication of H pylori
What is the effect of H pylori infection on ghrelin expression in the stomach?
Thirteen studies examined the effects of H pylori infection on gastric ghrelin. This includes six cohort studies [6,36,44,46-48], 2 case-control studies [40,49], four cross-sectional studies [18,19,24,37] and one randomised controlled trial [23]. The participants included sick subjects (7), well subjects (3) and both well and sick subjects (2). Eight studies were conducted in Asia, two in France, one each in Poland, Brazil and USA. Ten studies recruited both males and females, and three recruited males only. All the sick participants had gastrointestinal symptoms. Different methods were used to assess H pylori infection either alone or in combination: histology (11 studies), culture (3), rapid urease assay (5), serology (3), urea breath test (2) and PCR (4). Ten of the 13 studies were conducted on normal weight subjects, two on obese subjects and one on subjects of different body weights. Due to the different gastric ghrelin parameters assessed, a meta-analysis was not possible.
Five studies assessed gastric ghrelin contents: one found it to be lower in H pylori positive subjects [36], three [6,18,44] found no significant difference between H pylori positive and negative participants, and one [24] found increased levels in H pylori positive participants. Isomoto et al [36] compared gastric ghrelin peptide contents in the endoscopic biopsies from the corpus of 56 H pylori positive and 25 H pylori negative subjects using radio-immunoassay. They reported significantly lower gastric ghrelin content in the H pylori positive subjects than the H pylori negative subjects. Roper et al [18] studied 216 adult males of normal BMI presenting for routine endoscopy consisting of 120 H pylori positive and 96 H pylori negative subjects. Although they did not find any significant difference in the gastric ghrelin levels between H pylori positive and H pylori negative subjects, they reported a very wide variation in the concentration of ghrelin in the gastric juice (from <80 to 776,000 pg/ml) with the H pylori positive subjects having higher gastric juice ghrelin levels than the H pylori negative subjects. Choe et al [6] did not find any significant difference in the gastric ghrelin levels between H pylori positive and H pylori negative subjects using biopsied tissues.
Four studies examined the expression of ghrelin mRNA in gastric mucosa [19,36,37,40]. Three studies found ghrelin mRNA expression to be lower in H pylori positive subjects than in H pylori negative subjects, while Jun et al [37] found no difference. Five studies assessed the quantity of ghrelin immunoreactive cells in the gastric mucosa [36,40,47-49]; all of which found that H pylori positive subjects had fewer ghrelin-producing cells than in uninfected subjects. However, in the study by Isomoto et al [36], this difference did not achieve statistical significance.
Five studies compared the various gastric ghrelin parameters before and after H pylori eradication [6,23,36,46,48]. Choe et al [6] did not find any significant difference in the ghrelin concentration in the antrum, corpus and fundus pre- and post- H pylori eradication. Lee et al [23] reported a randomized controlled trial on H pylori positive volunteers without peptic ulcer or any other gastrointestinal symptoms in which the treatment group received triple H pylori eradication regimen while the control group did not receive any treatment. These authors reported a significant increase in gastric ghrelin mRNA expression following eradication compared to the control group. Osawa et al [46] also reported an increase in ghrelin mRNA expression following H pylori cure. Although Isomoto et al [36] found a tendency towards increase in ghrelin mRNA expression following cure of H pylori, this increase was not significant. Tatsuguchi et al [48], on the other hand, found an increase in ghrelin immunoreactive cells following H pylori eradication in 50 patients with either peptic ulcer disease or gastritis, while in 11 patients who did not respond to eradication therapy, there was no difference in the number of ghrelin immunoreactive cells pre-and post-eradication therapy.
Three studies [36,47,49] found a negative correlation between ghrelin producing cells in the gastrum and the severity of H pylori infection. Gastric ghrelin content and gastric ghrelin mRNA expression were both positively correlated with plasma ghrelin concentration [36,46].
Discussion
The potential role of ghrelin in body mass regulation makes understanding its interactions with Helicobacter pylori, a highly prevalent gastrointestinal infection, important. To address this issue, we asked three questions: how does H pylori infection affect circulating ghrelin levels; how does eradicating H pylori affect circulating ghrelin; and how does H pylori infection affect gastric ghrelin and ghrelin producing cells.
The results of our analysis has conclusively shown that circulating ghrelin levels are significantly higher in H pylori negative people than in those infected with H pylori (P = 0.00001). Our results also suggest that eradicating H pylori does not have any significant effect on circulating ghrelin. Although there was no significant heterogeneity between the group of studies that compared circulating ghrelin concentrations before and after H pylori eradication, this result should be interpreted with the following caveats in mind: 1) three of the studies [34-36] included in the meta-analysis came from the same research group; and together accounted for 29% of the effect size; 2) the paper by Osawa et al [46] which reported higher ghrelin levels before H pylori eradication compared to the levels after eradication on its own contributed 26.2% of the effect; and 3) the sample sizes of most of the other studies were relatively small. Interestingly, all the smaller studies, except one, found higher circulating ghrelin levels post-eradication. Even among the subjects studied by Osawa et al [46], plasma ghrelin increased in 50 patients and decreased in 84 patients, although the overall effect was a decrease post-eradication. They were however, able to show that pre-eradication elevation of ghrelin was associated with a fall in ghrelin post-eradication. In our unpublished data, we also found that elevated ghrelin concentration pre-eradication was associated with a fall post-eradication. These two observations suggest that in addition to other factors, the pre-eradication ghrelin level determines the direction of response of ghrelin post-eradication.
The heterogeneity of the studies examining the effect of H pylori on gastric ghrelin expression as well as the small number of studies that examined different aspects of this relationship did not allow a meta-analysis to be performed. However, the descriptive data suggests that available evidence is still discrepant; although the weight of evidence seems to favour lower ghrelin mRNA and ghrelin immunoreactive cells in association with H pylori infection [19,36,40,47-49]. The ultimate effect of H pylori on gastric ghrelin appears to be dependent on the duration of infection and the extent of H pylori-induced damage to the gastric mucosa. At least three studies found a negative correlation between number of ghrelin producing cells and the severity of H pylori infection [36,47,49].
The close anatomical proximity between the site of H pylori infection and the site of ghrelin production might result in the loss of ghrelin producing cells as part of the H pylori associated gastritis, causing reduced ghrelin production. However, such effect will not be restricted to H pylori infection and could occur in any other condition associated with gastritis. For example, Checchi et al [10] studied 233 patients with autoimmune gastritis (indicated by elevated parietal cell antibody (PCA)) and 211 control subjects, and found that mean serum ghrelin levels in PCA positive patients were significantly lower than in PCA negative patients, similar to the results found in H pylori infection by some studies. This decrease remained significant even after excluding patients with H pylori infection, suggesting that the H pylori infection was not necessarily responsible for the reduction in serum ghrelin. Again, the region of the stomach biopsied could also affect the results. Jang et al [16] reported that after ulcer healing and H pylori eradication, there was a significant increase in the levels of ghrelin mRNA. But while corpus ghrelin mRNA increased after cure and H pylori eradication, anthral ghrelin mRNA decreased, suggesting a differential response by the ghrelin producing cells in the different regions of the stomach. In healthy H pylori infected subjects however, Lee et al [23] found a significant increase in fundic ghrelin mRNA after eradication of H pylori (P = 0.0002) but no change in the anthral ghrelin mRNA (P = 0.5), suggesting a more complex relationship between gastric ghrelin production and H pylori infection. Teasing out this relationship will require more rigorous investigation.
If H pylori infection is associated with a lower circulating ghrelin, it is biologically plausible that its eradication will be associated with an increase in circulating ghrelin. But if H pylori reduces circulating ghrelin by destroying ghrelin producing cells, then the effect of eradicating it on circulating ghrelin would depend on the duration of infection, the amount of damage to ghrelin-producing cells, and the time it takes for these cells to regenerate. Indeed several studies have found a negative correlation between the number of ghrelin producing cells and the severity of gastritis [36,47,49]. And in one study, there was no change in ghrelin levels post-eradication after 4 weeks of follow-up, but the level progressively increased with follow-up, achieving, in some subjects, significant increase after 6 months of follow-up [36]. In contrast, mice infected with H pylori for 6-8 months had higher ghrelin levels compared to time-matched controls, which normalised two months post-eradication [50]. However, Masaoka et al [51] did not find any change in circulating ghrelin levels 2 years after successful eradication of H pylori in an adult man.
The discrepancy in the response to H pylori eradication could also be related to the strain of H pylori. Isomoto et al [52] found that strain diversity in H pylori was associated with plasma and gastric ghrelin levels in humans. Patients with type I strain (which express the virulence factors cytotoxin-associated gene product (CagA) and Vacuolating cytotoxin A (VacA)) have lower circulating ghrelin levels than those with the less virulent type II strain which does not express the virulence factors. This finding also argues for a possible racial difference in the association between circulating ghrelin levels and H pylori infection: in regions where type I strain is dominant, one would expect to see reduced circulating ghrelin levels. While such speculation is attractive, it might not be entirely correct [53]. In this review, the effect of region and country of study on the relationship between H pylori and ghrelin was very weak, and appears to be confounded by several other factors.
The underlying clinical condition of the subject might also be affecting the results. Suzuki et al [54] studied plasma ghrelin in patients with peptic ulcer disease. They found that plasma ghrelin levels were significantly higher in patients with duodenal ulcer as well as those with gastric ulcer compared to those with chronic gastritis. Among the subjects that were H pylori positive, plasma ghrelin was significantly higher in patients with duodenal or gastric ulcer than in those with non-ulcer chronic gastritis. After treatment for the ulcer (with healing), no significant change was found in the plasma ghrelin levels (i.e. pre-and post eradication levels were similar). Most of the studies reviewed here recruited subjects with varying degrees and types of gastrointestinal pathology. If each of these gastrointestinal diseases affects ghrelin production differently as suggested by Suzuki et al [54], then the discrepancies noted in this review are to be expected. Compensation from other sources of ghrelin production might also explain the various inconsistencies highlighted in this review. For example, Suzuki et al [55] infected Mongolian gerbils with H pylori and assessed the plasma and gastric ghrelin levels at 17 and 23 weeks after the infection. They found a significant decrease in gastric ghrelin in the H pylori positive gerbils compared to the controls, but also found a significant increase in plasma ghrelin levels in the H pylori positive group. This same group also found increased plasma ghrelin and decreased gastric ghrelin levels in IL-1R1 knockout mice [4] suggesting that other sources of ghrelin might have contributed to the increased plasma ghrelin.
Limitations and implications for research and practice
The major limitation of this review is the use of only English language papers, which raises the possibility of some publication bias. Another limitation in conducting this review is that all except one of the papers were observational studies, most of which did not primarily set out to assess the relationship between ghrelin and H pylori; but assessed both parameters in relation to other objectives. Well designed randomised clinical trials are needed to verify the conclusions made by this review. Also, many of the studies included participants with diverse disease conditions whose impacts on ghrelin secretion have not been investigated before. The best approach to solve the riddle of the relationship between ghrelin and helicobacter pylori might be to study otherwise healthy participants with asymptomatic H pylori infection.
Conclusions
From available evidence, circulating ghrelin concentration is lower in people infected with H pylori compared to those not infected with the bacterium. However, a more complex relationship exists between circulating ghrelin levels and eradication of H pylori. This relationship may be modulated by the strain of infecting H pylori, the duration of follow-up, the extent of H pylori-induced gastritis and other underlying pathology. More studies are needed to further elucidate the impact of H pylori eradication on circulating ghrelin concentration.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Funding for this study was provided by the UK Medical Research Council.
Authors' contributions
CVN conceived the paper, conducted the literature search, initial analysis and took lead in the writing. AMP critically reviewed the analysis, and the initial drafts, and participated in writing subsequent drafts. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:
Contributor Information
Chidi V Nweneka, Email: cnweneka@mrc.gm.
Andrew M Prentice, Email: Andrew.Prentice@lshtm.ac.uk.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge all the authors that responded to our inquiries particularly those that provided us with their raw data sets.
References
- Taniaka-Shintani M, Watanabe M. Distribution of ghrelin-immunoreactive cells in human gastric mucosa: comparison with that of parietal cells. Journal of gastroenterology. 2005;40(4):345–349. doi: 10.1007/s00535-004-1550-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwokolo CU, Freshwater DA, O'Hare P, Randeva HS. Plasma ghrelin following cure of Helicobacter pylori. Gut. 2003;52(5):637–640. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.5.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gokcel A, Gumurdulu Y, Kayaselcuk F, Serin E, Ozer B, Ozsahin AK, Guvener N. Helicobacter pylori has no effect on plasma ghrelin levels. European Journal of Endocrinology. 2003;148(4):423–426. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1480423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abiko Y, Suzuki H, Masaoka T, Nomura S, Kurabayashi K, Hosoda H, Kangawa K, Hibi T. Enhanced plasma ghrelin levels in Helicobacter pylori-colonized, interleukin-1-receptor type 1-homozygous knockout (IL-1R1-/-) mice. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11(27):4148–4153. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i27.4148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anania C, Pacifico L, Castronovo A, Neaga M, Ferrara E, Schiavo E, Bonamico M, Chiesa C. Long-term effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the levels of circulating ghrelin and leptin concentrations and on body composition in prepubertal children. Helicobacter. 2007;12(4):393–393. doi: 10.1530/EJE-07-0438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe YH, Lee JH, Lee HJ, Paik KH, Jin DK, Song SY, Lee JH. Ghrelin Levels in Gastric Mucosa before and after Eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Gut Liver. 2007;1(2):132–137. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2007.1.2.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi JY, Hahm KB. [Ghrelin; influences on Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric diseases] Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006;48(2):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa H. Ghrelin and Helicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(41):6327–6333. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigt J, Malfertheiner P. Influence of Helicobacter pylori on gastric regulation of food intake. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2009;12(5):522–525. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32832eb56e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checchi S, Montanaro A, Pasqui L, Ciuoli C, Cevenini G, Sestini F, Fioravanti C, Pacini F. Serum ghrelin as a marker of atrophic body gastritis in patients with parietal cell antibodies. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2007;92(11):4346–4351. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-0988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cindoruk M, Yetkin I, Deger SM, Karakan T, Kan E, Unal S. Influence of H pylori on plasma ghrelin in patients without atrophic gastritis. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2007;13(10):1595–1598. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i10.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czesnikiewicz-Guzik M, Bielanski W, Guzik TJ, Loster B, Konturek SJ. Helicobacter pylori in the oral cavity and its implications for gastric infection, periodontal health, immunology and dyspepsia. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2005;56(Suppl 6):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czesnikiewicz-Guzik M, Loster B, Bielanski W, Guzik TJ, Konturek PC, Zapala J, Konturek SJ. Implications of oral Helicobacter pylori for the outcome of its gastric eradication therapy. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. 2007;41(2):145–151. doi: 10.1097/01.mcg.0000225654.85060.3d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martel C, Haggerty TD, Corley DA, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N, Parsonnet J. Serum ghrelin levels and risk of subsequent adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2007;102(6):1166–1172. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X, Kuang H, Liu X, Duan P, Yang Y, Ma Z. Circulating ghrelin/obestatin ratio in subjects with Helicobacter pylori infection. Nutrition. 2009;25(5):506–511. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2008.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang EJ, Park SW, Park JS, Park SJ, Hahm KB, Paik SY, Sin MK, Lee ES, Oh SW, Park CY. et al. The influence of the eradication of Helicobacter pylori on gastric ghrelin, appetite, and body mass index in patients with peptic ulcer disease. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology. 2008;23(Suppl 2):S278–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek PC, Czesnikiewicz-Guzik M, Bielanski W, Konturek SJ. Involvement of Helicobacter pylori infection in neuro-hormonal control of food intake. Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology. 2006;57(Suppl 5):67–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roper J, Francois F, Shue PL, Mourad MS, Pei Z, Olivares de Perez AZ, Perez-Perez GI, Tseng CH, Blaser MJ. Leptin and ghrelin in relation to Helicobacter pylori status in adult males. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2008;93(6):2350–2357. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salles N, Menard A, Georges A, Salzmann M, de Ledinghen V, de Mascarel A, Emeriau JP, Lamouliatte H, Megraud F. Effects of Helicobacter pylori infection on gut appetite peptide (leptin, ghrelin) expression in elderly inpatients. Journals of Gerontology Series A-Biological Sciences & Medical Sciences. 2006;61(11):1144–1150. doi: 10.1093/gerona/61.11.1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo T, Futagami S, Hiratsuka T, Horie A, Hamamoto T, Ueki N, Kusunoki M, Miyake K, Gudis K, Tsukui T. et al. Comparison of Gastric Emptying and Plasma Ghrelin Levels in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia and Non-Erosive Reflux Disease. Digestion. 2009;79(2):65–72. doi: 10.1159/000205740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiotani A, Miyanishi T, Uedo N, Iishi H. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with reduced circulating ghrelin levels independent of body mass index. Helicobacter. 2005;10(5):373–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2005.00343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zub-Pokrowiecka A, Rembiasz K, Konturek SJ, Budzynski A, Konturek PC, Budzynski P. Ghrelin in diseases of the gastric mucosa associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Med Sci Monit. 2010;16(10):CR493–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee ES, Yoon YS, Park CY, Kim HS, Um TH, Baik HW, Jang EJ, Lee S, Park HS, Oh SW. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori increases ghrelin mRNA expression in the gastric mucosa. Journal of Korean Medical Science. 2010;25(2):265–271. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stec-Michalska K, Malicki S, Michalski B, Peczek L, Wisniewska-Jarosinska M, Nawrot B. Gastric ghrelin in relation to gender, stomach topography and Helicobacter pylori in dyspeptic patients. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2009;15(43):5409–5417. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H, Masaoka T, Hosoda H, Nomura S, Ohara T, Kangawa K, Ishii H, Hibi T. Plasma ghrelin concentration correlates with the levels of serum pepsinogen I and pepsinogen I/II ratio - A possible novel and non-invasive marker for gastric atrophy. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2004;51(59):1249–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacifico L, Anania C, Osborn JF, Ferrara E, Schiavo E, Bonamico M, Chiesa C. Long-term effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication on circulating ghrelin and leptin concentrations and body composition in prepubertal children. European Journal of Endocrinology. 2008;158(3):323–332. doi: 10.1530/EJE-07-0438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes FA, Alves JS, Diniz MTC, Barbosa AJA. Helicobacter pylori infection and density of gastric ghrelin-producing cells in obese and Nonobese patients. Helicobacter. 2006;11(4):368–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2006.00419_10.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–1558. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang CH, Sheu BS, Yang HB, Lee SC, Kao AW, Cheng HC, Chang WL, Yao WJ. Gender difference of circulating ghrelin and leptin concentrations in chronic Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 2009;14(1):54–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2009.00653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Onghia V, Leoncini R, Carli R, Santoro A, Giglioni S, Sorbellini F, Marzocca G, Bernini A, Campagna S, Marinello E. et al. Circulating gastrin and ghrelin levels in patients with colorectal cancer: correlation with tumour stage, Helicobacter pylori infection and BMI. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2007;61(2-3):137–141. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2006.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plonka M, Konturek PC, Bielanski W, Pawlik T, Brzozowski T, Konturek SJ. Relationship between ghrelin and Helicobacter pylori infection in Polish adult shepherds and their children. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2006;24:160–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.00040.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cindoruk M, Yetkin I, Deger SM, Karakan T, Kan E, Unal S. Influence of H pylori on plasma ghrelin in patients without atrophic gastritis. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(10):1595–1598. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i10.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomoto H, Nakazato M, Ueno H, Date Y, Nishi Y, Mukae H, Mizuta Y, Ohtsuru A, Yamashita S, Kohno S. Low plasma ghrelin levels in patients with Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis. American Journal of Medicine. 2004;117(6):429–432. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2004.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomoto H, Ueno H, Nishi Y, Wen CY, Nakazato M, Kohno S. Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection on ghrelin and various neuroendocrine hormones in plasma. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2005;11(11):1644–1648. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i11.1644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomoto H, Ueno H, Saenko VA, Mondal MS, Nishi Y, Kawano N, Ohnita K, Mizuta Y, Ohtsuru A, Yamashita S. et al. Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection on gastric and plasma ghrelin dynamics in humans. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2005;100(8):1711–1720. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jun DW, Lee OY, Lee YY, Choi HS, Kim TH, Yoon BC. Correlation between gastrointestinal symptoms and gastric leptin and ghrelin expression in patients with gastritis. Digestive Diseases & Sciences. 2007;52(10):2866–2872. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-9651-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima J, Ohno S, Sakurada T, Takabayashi H, Kudo M, Ro S, Kato S, Yakabi K. Circulating acylated ghrelin level decreases in accordance with the extent of atrophic gastritis. Journal of Gastroenterology. 2009;44(10):1046–1054. doi: 10.1007/s00535-009-0120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H, Nishizawa T, Tsuchimoto K, Hibi T. [Helicobacter pylori infected gastric mucosa--inflammation, atrophy and carcinogenesis] Nippon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2005;60(3):453–457. doi: 10.3412/jsb.60.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa H, Nakazato M, Date Y, Kita H, Ohnishi H, Ueno H, Shiiya T, Satoh K, Ishino Y, Sugano K. Impaired production of gastric ghrelin in chronic gastritis associated with Helicobacter pylori. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2005;90(1):10–16. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomoto H, Nishi Y, Ohnita K, Mizuta Y, Kohno S, Ueno H, Nakazato M. The Relationship between Plasma and Gastric Ghrelin Levels and Strain Diversity in Helicobacter pylori Virulence. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100(6):1425–1427. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41929_7.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso N, Granada ML, Salinas I, Reverter JL, Flores L, Ojanguren I, Martinez-Caceres EM, Sanmarti A. Plasma ghrelin concentrations in type 1 diabetic patients with autoimmune atrophic gastritis. European Journal of Endocrinology. 2007;157(6):763–769. doi: 10.1530/EJE-07-0300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plonka M, Bielanski W, Konturek SJ, Targosz A, Sliwowski Z, Dobrzanska M, Kaminska A, Sito E, Konturek PC, Brzozowski T. Helicobacter pylori infection and serum gastrin, ghrelin and leptin in children of Polish shepherds. Digestive & Liver Disease. 2006;38(2):91–97. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2005.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzzan B, Catheline JM, Lagorce C, Bon C, Cohen R, Perret GY, Benamouzig R. Expression of ghrelin in fundus is increased after gastric banding in morbidly obese patients. Obesity Surgery. 2007;17(9):1159–1164. doi: 10.1007/s11695-007-9197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shak JR, Roper J, Perez-Perez GI, Tseng CH, Francois F, Gamagaris Z, Patterson C, Weinshel E, Fielding GA, Ren C. et al. The effect of laparoscopic gastric banding surgery on plasma levels of appetite-control, insulinotropic, and digestive hormones. Obesity Surgery. 2008;18(9):1089–1096. doi: 10.1007/s11695-008-9454-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa H, Kita H, Ohnishi H, Nakazato M, Date Y, Bowlus CL, Ishino Y, Watanabe E, Shiiya T, Ueno H. et al. Changes in plasma ghrelin levels, gastric ghrelin production, and body weight after Helicobacter pylori cure. Journal of Gastroenterology. 2006;41(10):954–961. doi: 10.1007/s00535-006-1880-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew PL, Lee WJ, Lee YC, Chen WY. Gastric ghrelin expression associated with Helicobacter pylori infection and chronic gastritis in obese patients. Obes Surg. 2006;16(5):612–619. doi: 10.1381/096089206776945002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsuguchi A, Miyake K, Gudis K, Futagami S, Tsukui T, Wada K, Kishida T, Fukuda Y, Sugisaki Y, Sakamoto C. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on ghrelin expression in human gastric mucosa. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99(11):2121–2127. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.30291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez-Sanchez N, Pichardo-Bahena R, Vasquez-Fernandez F, Lezama-Mora JI, Leon-Canales AL, Barredo-Prieto B, Gonzalez-Avila D, Ponciano-Rodriguez G, Uribe M. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on gastric ghrelin expression and body weight. Revista de Gastroenterologia de Mexico. 2007;72(4):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bercik P, Verdu EF, Foster JA, Lu J, Scharringa A, Kean I, Wang L, Blennerhassett P, Collins SM. Role of gut-brain axis in persistent abnormal feeding behavior in mice following eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. American Journal of Physiology - Regulatory Integrative & Comparative Physiology. 2009;296(3):R587–594. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.90752.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaoka T, Suzuki H, Imaeda H, Hosoda H, Ohara T, Morishita T, Ishii H, Kangawa K, Hibi T. Long-term strict monitoring of plasma ghrelin and other serological markers of gastric diseases after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2005;52(61):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomoto H, Nishi Y, Ohnita K, Mizuta Y, Kohno S, Ueno H, Nakazato M. The Relationship between Plasma and Gastric Ghrelin Levels and Strain Diversity in Helicobacter pylori Virulence. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2005;100(6):1425–1427. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41929_7.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussein NR, Mohammadi M, Talebkhan Y, Doraghi M, Letley DP, Muhammad MK, Argent RH, Atherton JC. Differences in virulence markers between Helicobacter pylori strains from Iraq and those from Iran: potential importance of regional differences in H. pylori-associated disease. Journal of clinical microbiology. 2008;46(5):1774–1779. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01737-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H, Masaoka T, Nomoto Y, Hosoda H, Mori M, Nishizawa T, Minegishi Y, Kangawa K, Hibi T. Increased levels of plasma ghrelin in peptic ulcer disease. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics. 2006;24:120–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.00034.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H, Masaoka T, Hosoda H, Ota T, Minegishi Y, Nomura S, Kangawa K, Ishii H. Helicobacter pylori infection modifies gastric and plasma ghrelin dynamics in Mongolian gerbils. Gut. 2004;53(2):187–194. doi: 10.1136/gut.2003.021568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campana D, Nori F, Pagotto U, De Iasio R, Morselli-Labate AM, Pasquali R, Corinaldesi R, Tomassetti P. Plasma acylated ghrelin levels are higher in patients with chronic atrophic gastritis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2007;67(5):761–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu MS, Lee WJ, Wang HH, Huang SP, Lin JT. A case-control study of association of Helicobacter pylori infection with morbid obesity in Taiwan. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2005;165(13):1552–1555. doi: 10.1001/archinte.165.13.1552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T, Fukunaga M, Akamizu T, Irako T, Yokode M, Kangawa K, Nakai Y, Nakai Y. Plasma acylated ghrelin levels correlate with subjective symptoms of functional dyspepsia in female patients. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology. 2005;40(6):648–653. doi: 10.1080/00365520510015403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H, Masaoka T, Sakai G, Ishii H, Hibi T. Improvement of gastrointestinal quality of life scores in cases of Helicobacter pylori-positive functional dyspepsia after successful eradication therapy. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology. 2005;20(11):1652–1660. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.04039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundbom M, Holdstock C, Engstrom E, Karlsson FA. Early changes in ghrelin following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: Influence of vagal nerve functionality? Obesity Surgery. 2007;17(3):304–310. doi: 10.1007/s11695-007-9056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Q, Fan YZ, Ge BJ, Zhu Q, Tu ZY. Circulating ghrelin in patients with gastric or colorectal cancer. Digestive diseases and sciences. 2007;52(3):803–809. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-9508-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa T, Suzuki H, Nomoto Y, Masaoka T, Hosoda H, Mori M, Ohara T, Morishita T, Kangawa K, Hibi T. Enhanced plasma ghrelin levels in patients with functional dyspepsia. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2006;24:104–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.00032.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ando T, Minami M, Ishiguro K, Maeda O, Watanabe O, Mizuno T, Fujita T, Takahashi H, Noshiro M, Goto H. Changes in biochemical parameters related to atherosclerosis after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2006;24:58–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.00026.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kempa A, Krzyzanowska-Swiniarska B, Miazgowski T, Pilarska K. Not insulin but insulin sensivity, leptin, and cortisol are major factors regulating serum acylated ghrelin level in healthy women. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation. 2007;30:659–665. doi: 10.1007/BF03347446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ates Y, Degertekin B, Erdil A, Yaman H, Dagalp K. Serum ghrelin levels in inflammatory bowel disease with relation to disease activity and nutritional status. Digestive diseases and sciences. 2008;53(8):2215–2221. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-0113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang HH, Lee WJ, Liew PL, Yang CS, Liang RJ, Wang W, Lin JT, Wu MS. The influence of Helicobacter pylori infection and corpus gastritis on the postoperative outcomes of laparoscopic vertical banded gastroplasty. Obesity Surgery. 2006;16(3):297–307. doi: 10.1381/096089206776116417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doki Y, Takachi K, Ishikawa O, Miyashiro I, Sasaki Y, Ohigashi H, Nakajima H, Hosoda H, Kangawa K, Sasakuma F. et al. Ghrelin reduction after esophageal substitution and its correlation to postoperative body weight loss in esophageal cancer patients. Surgery. 2006;139(6):797–805. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2005.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao XY, Kuang HY, Liu XM, Ma ZB, Nie HJ, Guo H. Plasma obestatin levels in men with chronic atrophic gastritis. Peptides. 2008;29(10):1749–1754. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2008.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherian S, Forbes D, Sanfilippo F, Cook A, Burgner D. Helicobacter pylori, helminth infections and growth: a cross-sectional study in a high prevalence population. Acta Paediatrica. 2009;98(5):860–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2009.01221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebapcilar L, Sari I, Renkal AH, Alacacioglu A, Yuksel A, Ilhan E, Alkan B, Yuksel D, Kozaci DL, Gunay N. The Influence of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Leptin, Soluble CD40 Ligand, Oxidative Stress and Body Composition in Patients with Peptic Ulcer Disease. Internal Medicine. 2009;48(24):2055–2059. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.48.2562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta SK, Arora M, Kireet A, Bashandy H, Gandsas A. Upper Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Associated Disorders in Morbidly Obese Patients: A Prospective Study. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2009;54(6):1243–1246. doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0485-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gen R, Demir M, Ataseven H. Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Insulin Resistance, Serum Lipids and Low-Grade Inflammation. Southern Medical Journal. 2010;103(3):190–196. doi: 10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3181cf373f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]