Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) administration produces an increase in plasma triglycerides that may be due to inhibition of adipose lipoprotein lipase activity and/or a stimulation of hepatic lipogenesis. We now report that TNF administration to insulinopenic diabetic rats increases serum triglycerides (2 h, 2.4-fold; 17 h, 4.3-fold). Adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase activity was markedly decreased in diabetic animals compared with controls and was not further inhibited by TNF. Incorporation of tritiated water into fatty acids in the liver was increased 45% 1-2 h after TNF and 87% at 16-17 h. These results indicate that the TNF-induced increase in circulating lipid levels can occur in the absence of a TNF-induced inhibition of adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase activity. Moreover, the clearance from the circulation of triglycerides in chylomicrons was similar in control and TNF-treated animals; these results provide further evidence that the removal of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins is not altered in the TNF-treated animals. Our data suggest that the TNF-induced stimulation of hepatic lipid synthesis may play an important role in the increase in serum triglycerides. In addition, TNF administration to diabetic animals leads to an elevation in serum glucose levels (73% at 17 h) without a change in serum insulin levels. Thus, TNF stimulation of hepatic lipogenesis is independent of changes in insulin.
Full text
PDF

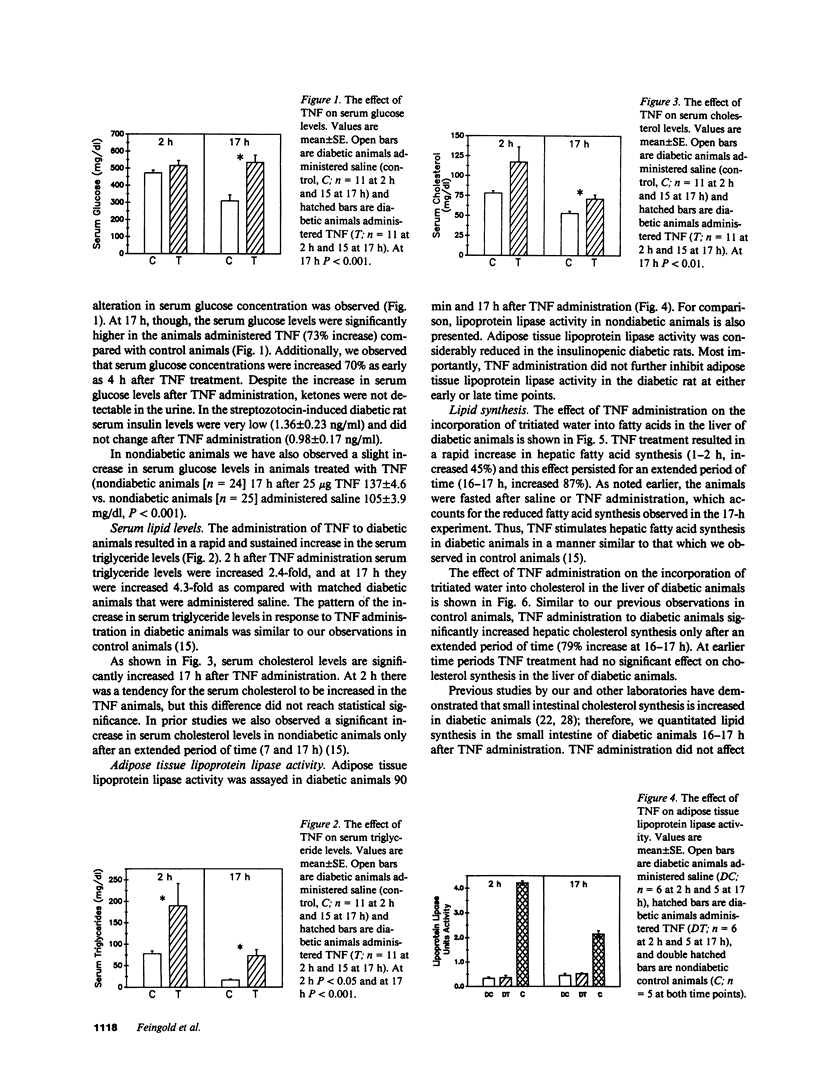
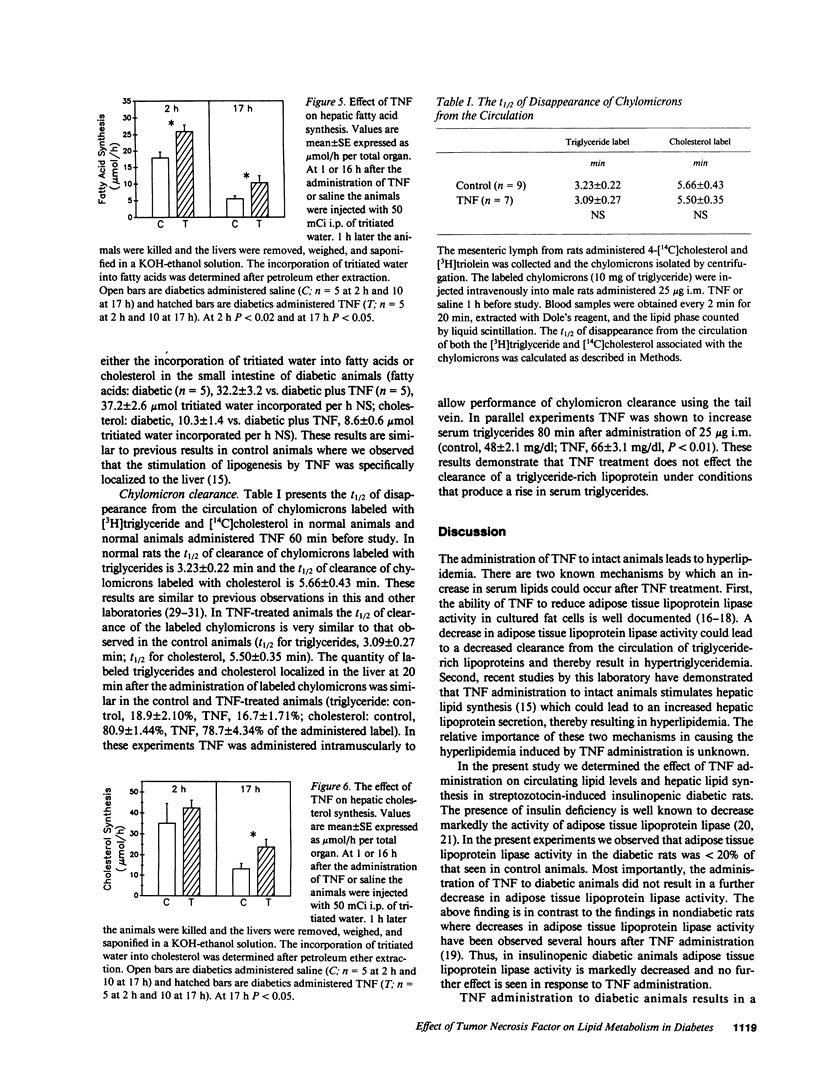


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagby G. J., Spitzer J. A. Lipoprotein lipase activity in rat heart and adipose tissue during endotoxic shock. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):H325–H330. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.238.3.H325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel W. R. Metabolic response to infection. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:9–20. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.000301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Mier J. W. Interleukins. Annu Rev Med. 1986;37:173–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.37.020186.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Grunfeld C. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates hepatic lipogenesis in the rat in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):184–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI113046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Lear S. R., Felts J. M. The disappearance from the circulation of chylomicrons obtained from control and diabetic rats. Endocrinology. 1987 Aug;121(2):475–480. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-2-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Wiley M. H., MacRae G., Lear S., Moser A. H., Zsigmond G., Siperstein M. D. De novo sterologenesis in the intact rat. Metabolism. 1983 Jan;32(1):75–81. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Wiley M. H., MacRae G., Moser A. H., Lear S. R., Siperstein M. D. The effect of diabetes mellitus on sterol synthesis in the intact rat. Diabetes. 1982 May;31(5 Pt 1):388–395. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.5.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiser R. H., Denniston J. C., Beisel W. R. Infection with Diplococcus pneumoniae and Salmonella typhimurium in monkeys: changes in plasma lipids and lipoproteins. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jan;125(1):54–60. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. The metabolism of chylomicron cholesterol ester in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1886–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI104645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Kaye D., O'Leary W. M. Serum lipids in infection. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 13;281(20):1081–1086. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911132812001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin L. A., McMahon F., Moeller M. Modulation of adipose lipoprotein lipase by thyroid hormone and diabetes. The significance of the low T3 state. Diabetes. 1985 Dec;34(12):1266–1271. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.12.1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths J., Groves A. C., Leung F. Y. The relationship of plasma catecholamines to serum triglycerides in canine gram-negative bacteremia. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1972 May;134(5):795–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guckian J. C. Role of metabolism in pathogenesis of bacteremia due to Diplococcus pneumoniae in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jan;127(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH R. L., MCKAY D. G., TRAVERS R. I., SKRALY R. K. HYPERLIPIDEMIA, FATTY LIVER, AND BROMSULFOPHTHALEIN RETENTION IN RABBITS INJECTED INTRAVENOUSLY WITH BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:563–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSLER J. I. Effect of diabetes and insulin on the activity of myocardial and adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase of rats. J Clin Invest. 1963 Mar;42:362–367. doi: 10.1172/JCI104722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann R. L., Matson C. F., Beisel W. R. Hypertriglyceridemia produced by endotoxin: role of impaired triglyceride disposal mechanisms. J Infect Dis. 1976 May;133(5):548–555. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.5.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann R. L., Matson C. F., Rowberg A. H., Beisel W. R. Defective lipid disposal mechanisms during bacterial infection in rhesus monkeys. Metabolism. 1976 Jun;25(6):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Pekala P. H., Lane M. D., Cerami A. Lipoprotein lipase suppression in 3T3-L1 cells by an endotoxin-induced mediator from exudate cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):912–916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees R. S., Fiser R. H., Jr, Beisel W. R., Bartelloni P. J. Effects of an experimental viral infection on plasma lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Metabolism. 1972 Sep;21(9):825–833. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTEL P. J., HAVEL R. J., BEZMAN A. METABOLISM OF CONSTITUENT LIPIDS OF DOG CHYLOMICRONS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Aug;42:1313–1321. doi: 10.1172/JCI104815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. S., Peters P. M., McCabe J., Crase D., Hansen S., Chen A. B., Liggitt D. Development of partial tolerance to the gastrointestinal effects of high doses of recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rodents. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1587–1596. doi: 10.1172/JCI113245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. S., Shepard H. M., Wilking H., Lewis G., Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Gavin L. A., Grunfeld C. Interferons and tumor necrosis factors have similar catabolic effects on 3T3 L1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8313–8317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekala P. H., Kawakami M., Angus C. W., Lane M. D., Cerami A. Selective inhibition of synthesis of enzymes for de novo fatty acid biosynthesis by an endotoxin-induced mediator from exudate cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2743–2747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pykälistö O. J., Vogel W. C., Bierman E. L. The tissue distribution of triacylglycerol lipase, monoacylglycerol lipase and phospholipase A in fed and fasted rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 18;369(2):254–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNATZ J. D., WILLIAMS R. H. The effect of acute insulin deficiency in the rat on adipose tissue lipolytic activity and plasma lipids. Diabetes. 1963 Mar-Apr;12:174–178. doi: 10.2337/diab.12.2.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semb H., Peterson J., Tavernier J., Olivecrona T. Multiple effects of tumor necrosis factor on lipoprotein lipase in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8390–8394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. L., Saudek C. D., Crawford S. A. Total hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA reductase activity in the small intestine and liver of insulin-deficient rats. J Lipid Res. 1982 Feb;23(2):266–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


