Abstract
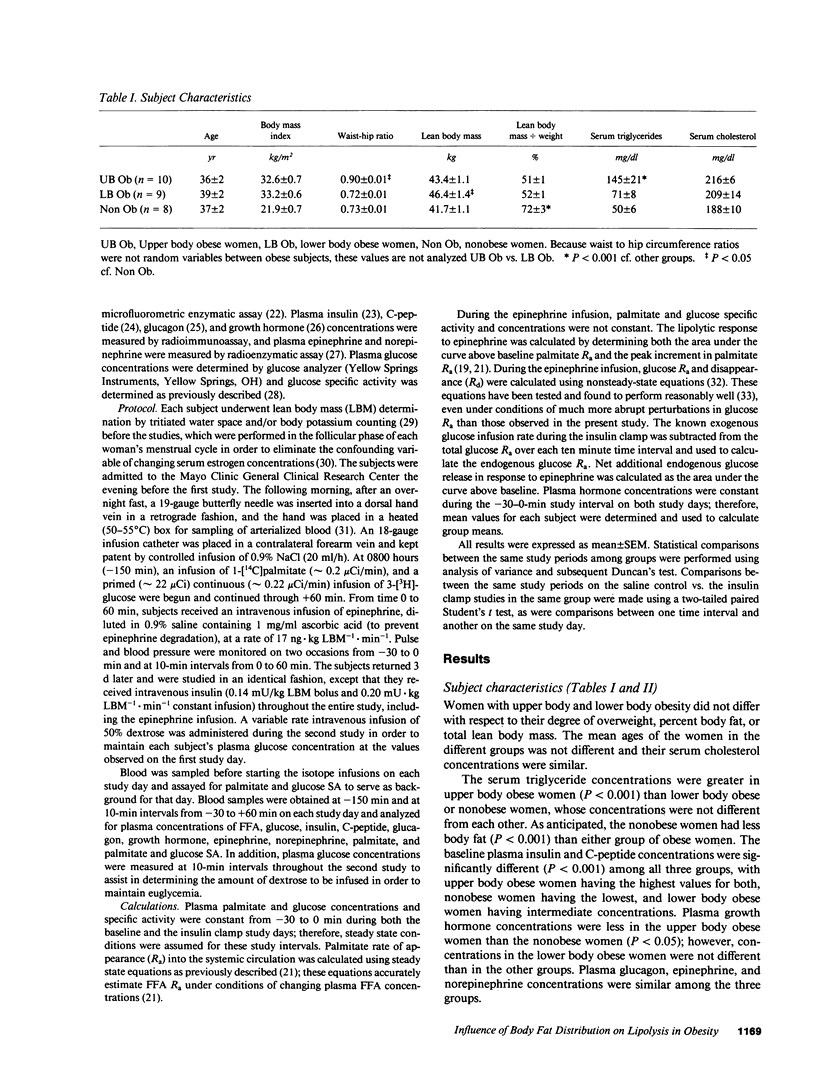
In order to determine whether differences in body fat distribution result in specific abnormalities of free fatty acid (FFA) metabolism, palmitate turnover, a measure of systemic adipose tissue lipolysis, was measured in 10 women with upper body obesity, 9 women with lower body obesity, and 8 nonobese women under overnight postabsorptive (basal), epinephrine stimulated and insulin suppressed conditions. Results: Upper body obese women had greater (P less than 0.005) basal palmitate turnover than lower body obese or nonobese women (2.8 +/- 0.2 vs. 2.1 +/- 0.2 vs. 1.8 +/- 0.2 mumol.kg lean body mass (LBM)-1.min-1, respectively), but a reduced (P less than 0.05) net lipolytic response to epinephrine (59 +/- 7 vs. 79 +/- 5 vs. 81 +/- 7 mumol palmitate/kg LBM, respectively). Both types of obesity were associated with impaired suppression of FFA turnover in response to euglycemic hyperinsulinemia compared to nonobese women (P less than 0.005). These specific differences in FFA metabolism may reflect adipocyte heterogeneity, which may in turn affect the metabolic aberrations associated with different types of obesity. These findings emphasize the need to characterize obese subjects before studies.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abumrad N. N., Rabin D., Diamond M. P., Lacy W. W. Use of a heated superficial hand vein as an alternative site for the measurement of amino acid concentrations and for the study of glucose and alanine kinetics in man. Metabolism. 1981 Sep;30(9):936–940. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasse E. Influence of norepinephrine, growth hormone and fasting on FFA mobilization and glucose metabolism in lean and obese subjects. Diabetologia. 1968 Jan;4(1):20–25. doi: 10.1007/BF01241029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P., Bergman H., Varnauskas E., Lindholm B. Lipid mobilization in relation to body composition in man. Metabolism. 1969 Oct;18(10):840–851. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P., Bergman H., Varnauskas E. Plasma free fatty acid turnover rate in obesity. Acta Med Scand. 1969 Apr;185(4):351–356. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1969.tb07347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolinder J., Kager L., Ostman J., Arner P. Differences at the receptor and postreceptor levels between human omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue in the action of insulin on lipolysis. Diabetes. 1983 Feb;32(2):117–123. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr Starvation in man. N Engl J Med. 1970 Mar 19;282(12):668–675. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197003192821209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Hoffmann R. G., Kalkhoff R. K., Kissebah A. H. Relationship of body fat topography to insulin sensitivity and metabolic profiles in premenopausal women. Metabolism. 1984 Jan;33(1):68–75. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Murray R., Kissebah A. H. Relationship between skeletal muscle insulin resistance, insulin-mediated glucose disposal, and insulin binding. Effects of obesity and body fat topography. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1515–1525. doi: 10.1172/JCI111565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Binder C., Markussen J., Heding L. G., Naithani V. K., Kuzuya H., Blix P., Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H. Characterization of seven C-peptide antisera. Diabetes. 1978;27 (Suppl 1):170–177. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.s170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Barrett E. J., Bevilacqua S., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of fatty acids on glucose production and utilization in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1737–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golay A., Swislocki A. L., Chen Y. D., Jaspan J. B., Reaven G. M. Effect of obesity on ambient plasma glucose, free fatty acid, insulin, growth hormone, and glucagon concentrations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Aug;63(2):481–484. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-2-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldrick R. B., McLoughlin G. M. Lipolysis and lipogenesis from glucose in human fat cells of different sizes. Effects of insulin, epinephrine, and theophylline. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1213–1223. doi: 10.1172/JCI106335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., NAIMARK A., BORCHGREVINK C. F. Turnover rate and oxidation of free fatty acids of blood plasma in man during exercise: studies during continuous infusion of palmitate-1-C14. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42:1054–1063. doi: 10.1172/JCI104791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. V., Klimes I., Vasquez B., Brady D., Nagulesparan M., Unger R. H. The antilipolytic action of insulin in obese subjects with resistance to its glucoregulatory action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;58(3):544–548. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-3-544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. D., Braun J. S., Vetter R. J., Marsh H. M. Measurement of body potassium with a whole-body counter: relationship between lean body mass and resting energy expenditure. Mayo Clin Proc. 1988 Sep;63(9):864–868. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62688-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. D., Haymond M. W., Gerich J. E., Cryer P. E., Miles J. M. Lipolysis during fasting. Decreased suppression by insulin and increased stimulation by epinephrine. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):207–213. doi: 10.1172/JCI112785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. D., Rogers P. J., Ellman M. G., Miles J. M. Choice of infusion-sampling mode for tracer studies of free fatty acid metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):E562–E565. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.5.E562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissebah A. H., Alfarsi S., Adams P. W., Wynn V. Role of insulin resistance in adipose tissue and liver in the pathogenesis of endogenous hypertriglyceridaemia in man. Diabetologia. 1976 Dec;12(6):563–571. doi: 10.1007/BF01220632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissebah A. H., Vydelingum N., Murray R., Evans D. J., Hartz A. J., Kalkhoff R. K., Adams P. W. Relation of body fat distribution to metabolic complications of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):254–260. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krotkiewski M., Björntorp P., Sjöström L., Smith U. Impact of obesity on metabolism in men and women. Importance of regional adipose tissue distribution. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):1150–1162. doi: 10.1172/JCI111040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillioja S., Bogardus C., Mott D. M., Kennedy A. L., Knowler W. C., Howard B. V. Relationship between insulin-mediated glucose disposal and lipid metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1106–1115. doi: 10.1172/JCI111804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUTALEN C., SMITH R. W., Jr EFFECTS OF TRIIODOTHYRONINE AND THYROXIN ON THE LIPOLYTIC ACTION OF EPINEPHRINE IN MARKEDLY OBESE SUBJECTS. Am J Clin Nutr. 1965 Apr;16:363–369. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/16.4.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. M., Ellman M. G., McClean K. L., Jensen M. D. Validation of a new method for determination of free fatty acid turnover. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 1):E431–E438. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.3.E431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J., Glasscock R., Aikens J., Gerich J., Haymond M. A microfluorometric method for the determination of free fatty acids in plasma. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow P. G., Marshall W. P., Kim H. J., Kalkhoff R. K. Metabolic response to starvation. II. Effects of sex steroid administration to pre- and postmenopausal women. Metabolism. 1981 Mar;30(3):274–278. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P. J., Ishikawa T., Goldrick R. B. Diminished plasma free fatty acid clearance in obese subjects. Metabolism. 1978 May;27(5):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORTH R. D., WILLIAMS R. H. Response of plasma NEFA levels to epinephrine infusions in normal and obese women. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 May;104:119–120. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Hjøllund E., Sørensen N. S. Insulin receptor binding and insulin action in human fat cells: effects of obesity and fasting. Metabolism. 1982 Sep;31(9):884–895. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDLE P. J., GARLAND P. B., HALES C. N., NEWSHOLME E. A. The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1963 Apr 13;1(7285):785–789. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Experimental validation of measurements of glucose turnover in nonsteady state. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):E84–E93. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.1.E84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravussin E., Lillioja S., Anderson T. E., Christin L., Bogardus C. Determinants of 24-hour energy expenditure in man. Methods and results using a respiratory chamber. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1568–1578. doi: 10.1172/JCI112749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R., Verdonk C., Miles J., Service F. J., Gerich J. Effect of intermittent endogenous hyperglucagonemia on glucose homeostasis in normal and diabetic man. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1119–1123. doi: 10.1172/JCI109404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. D., Clutter W. E., Cryer P. E. External and internal standards in the single-isotope derivative (radioenzymatic) measurement of plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Dec;106(6):624–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith U., Hammersten J., Björntorp P., Kral J. G. Regional differences and effect of weight reduction on human fat cell metabolism. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;9(5):327–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb00892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. R., Peters E. J., Klein S., Holland O. B., Rosenblatt J., Gary H., Jr Effect of short-term fasting on lipolytic responsiveness in normal and obese human subjects. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 1):E189–E196. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.2.E189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


