Abstract
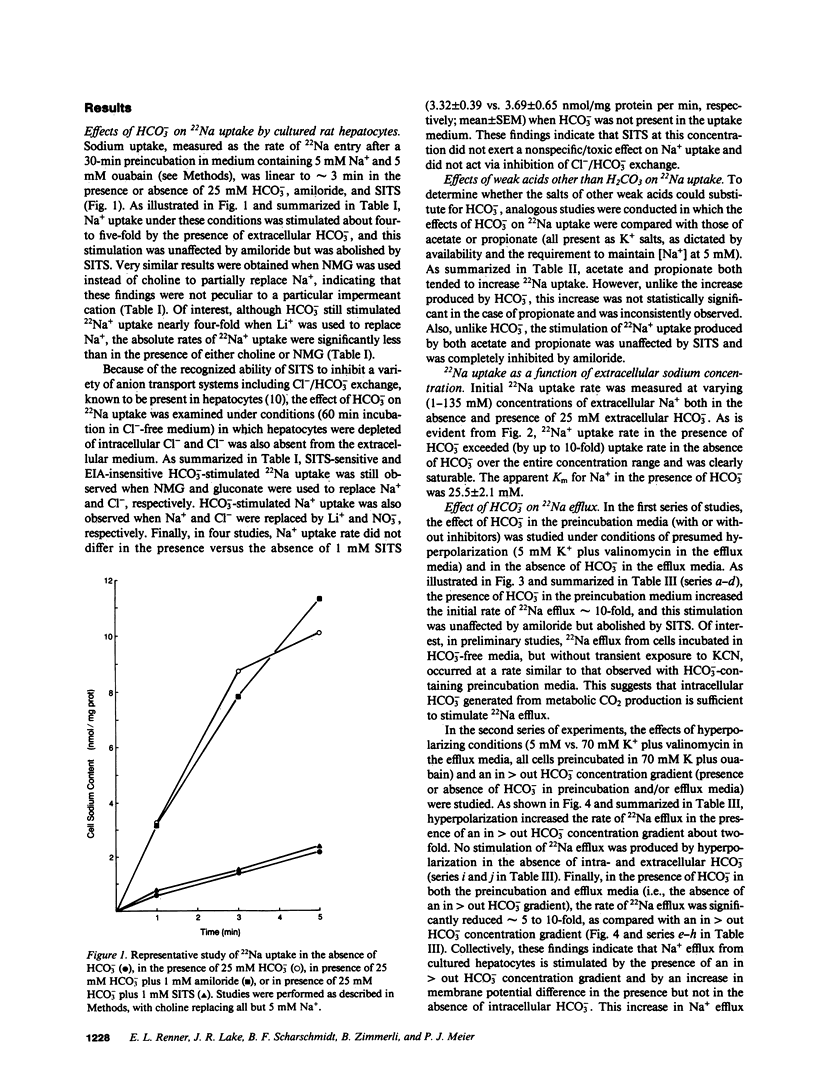
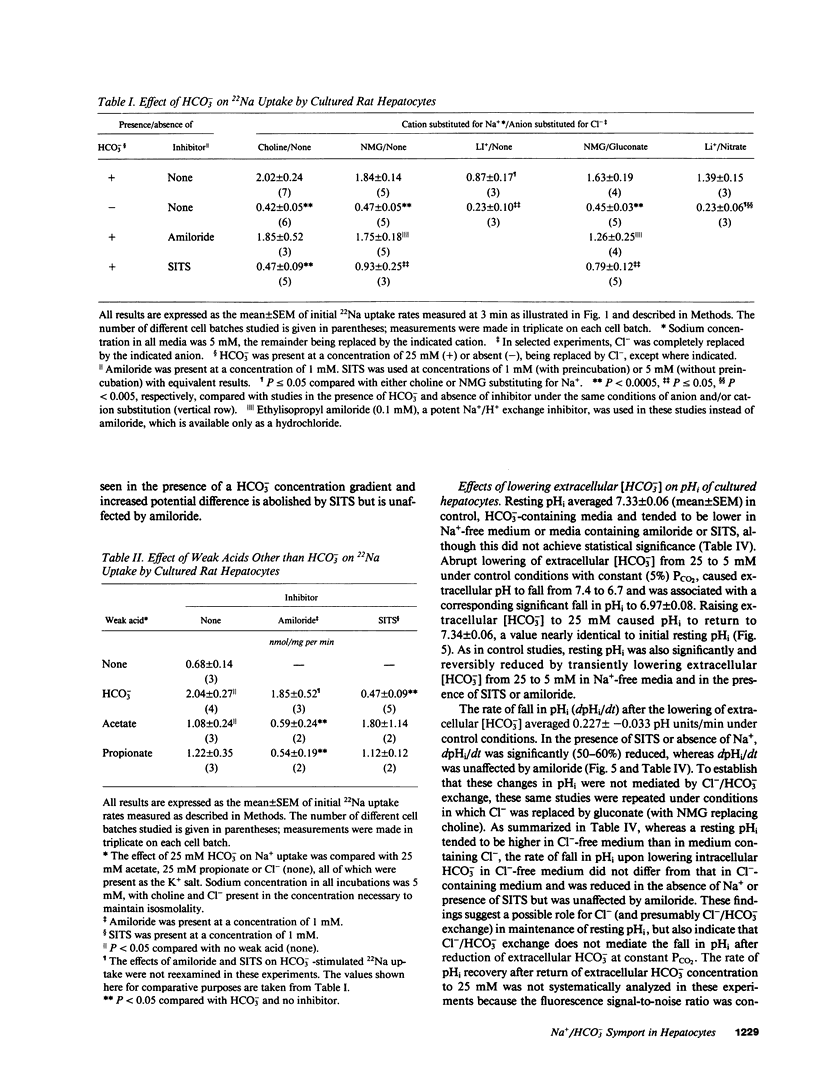
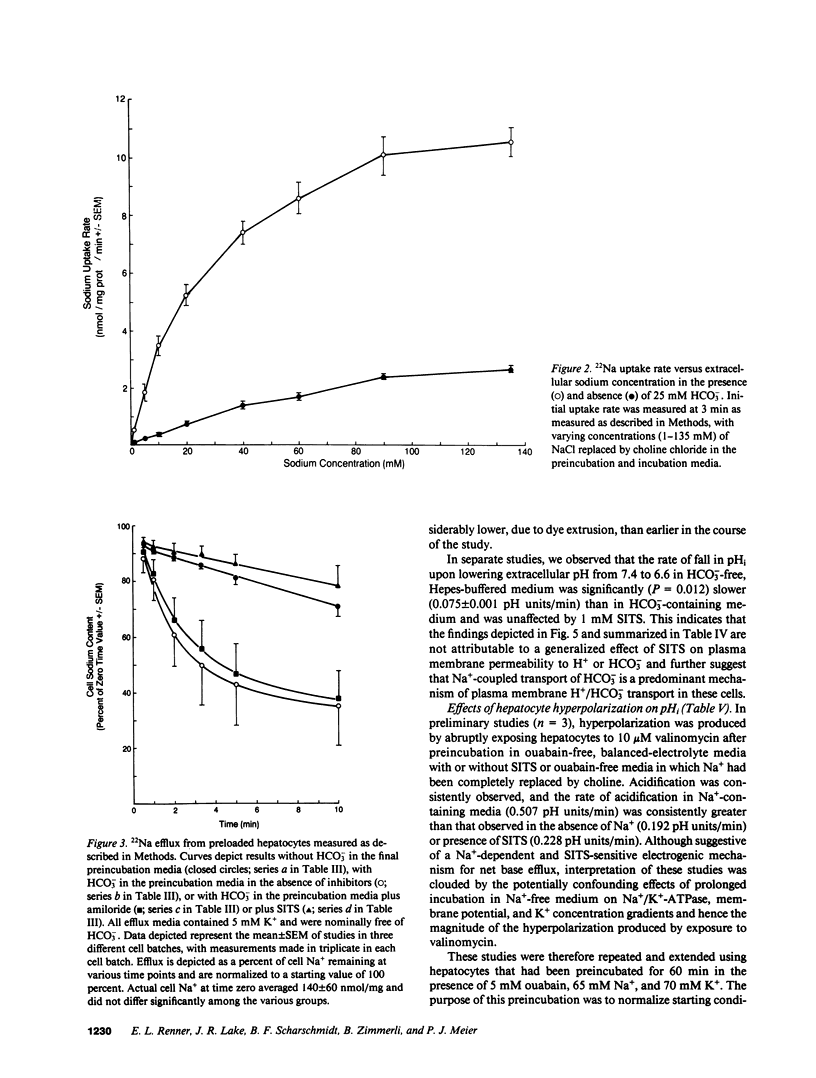
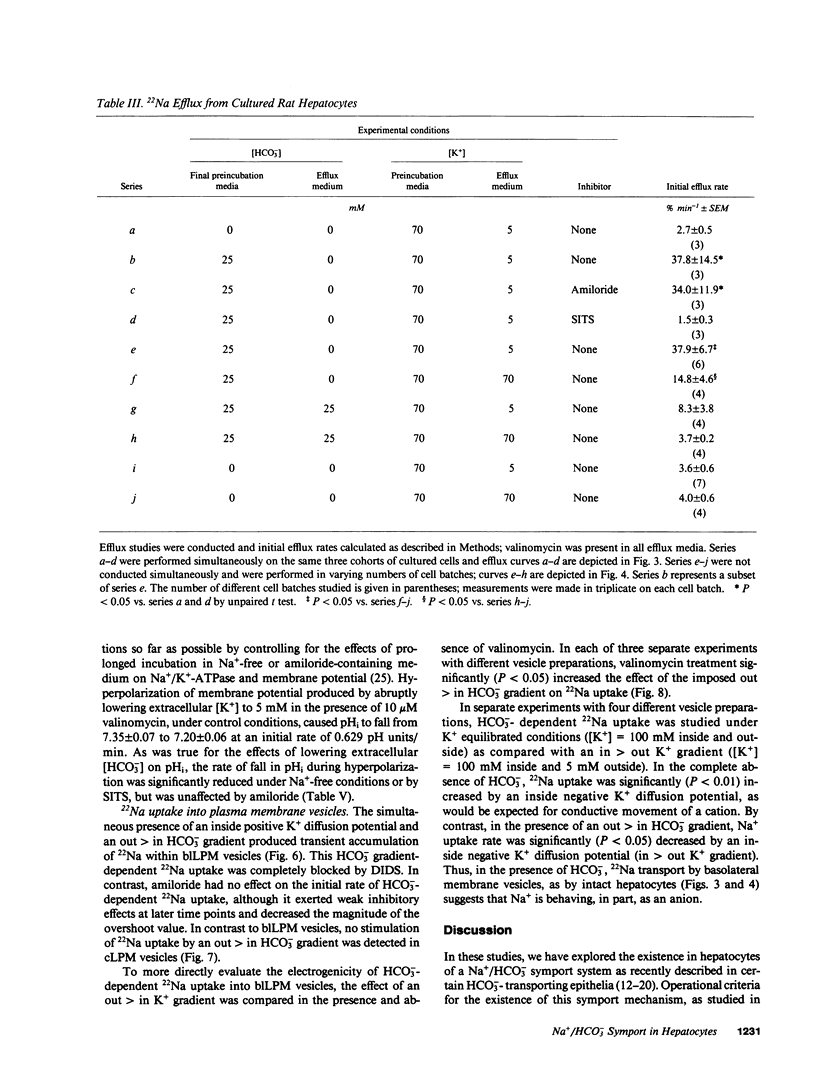
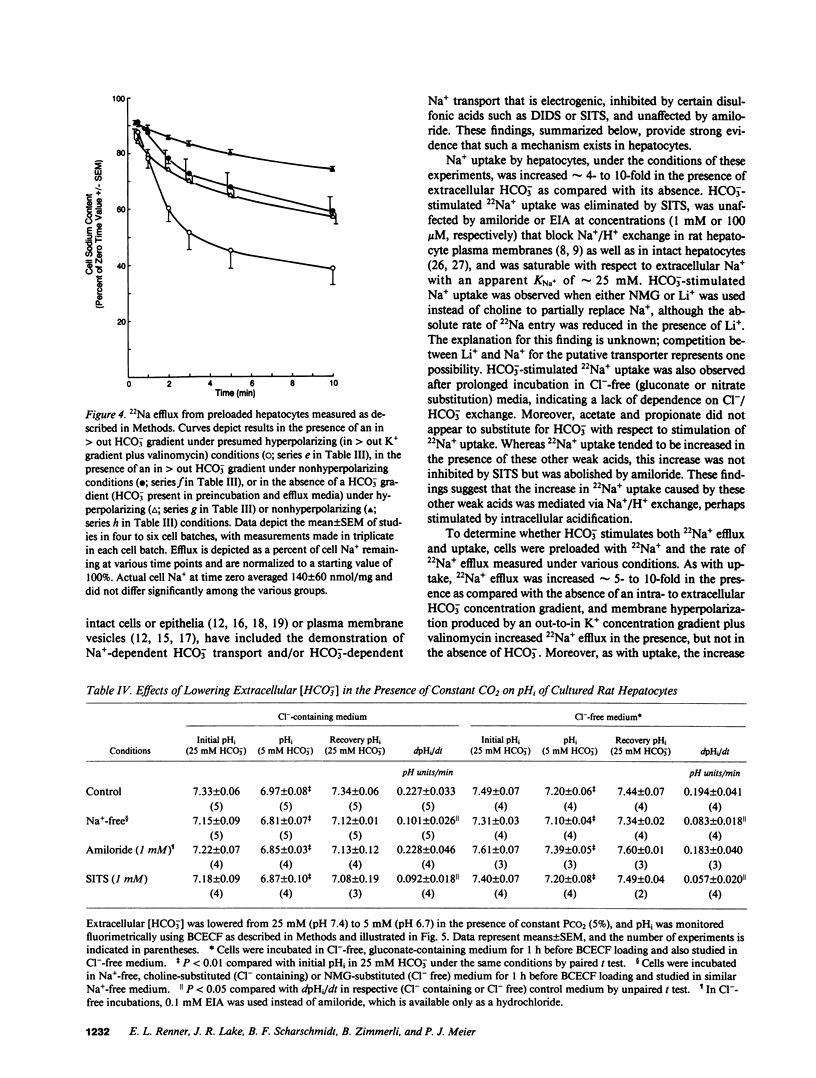
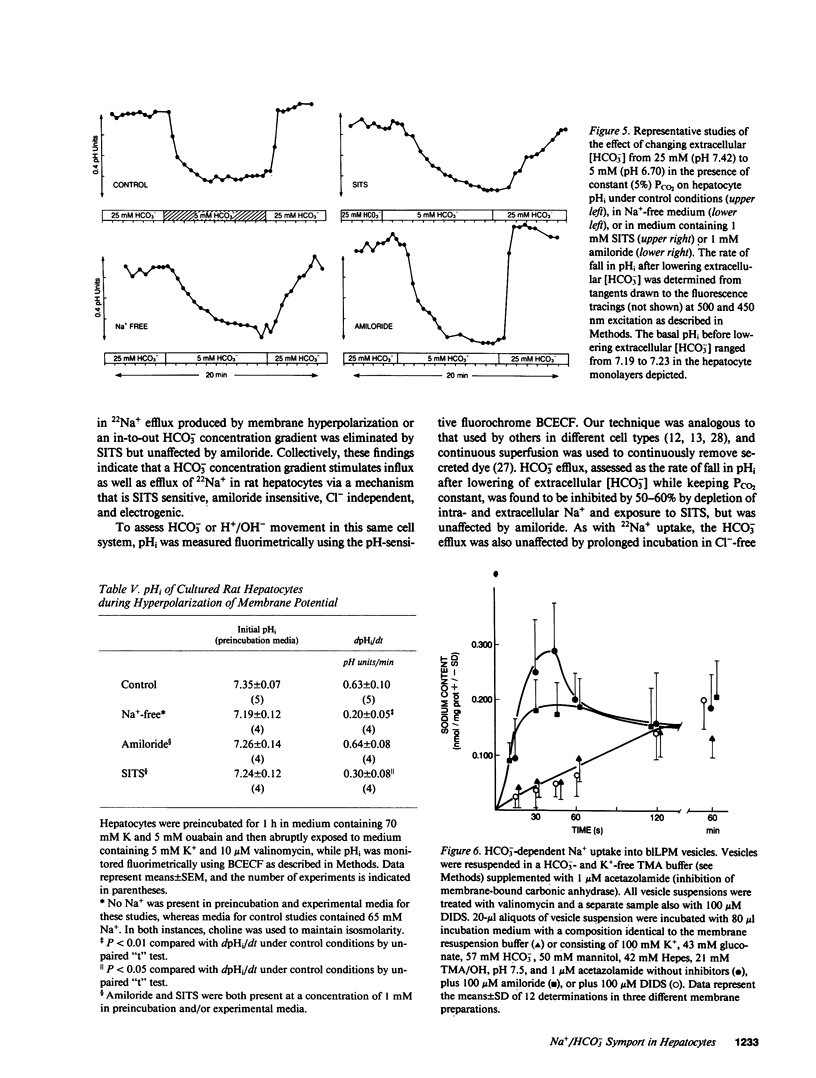
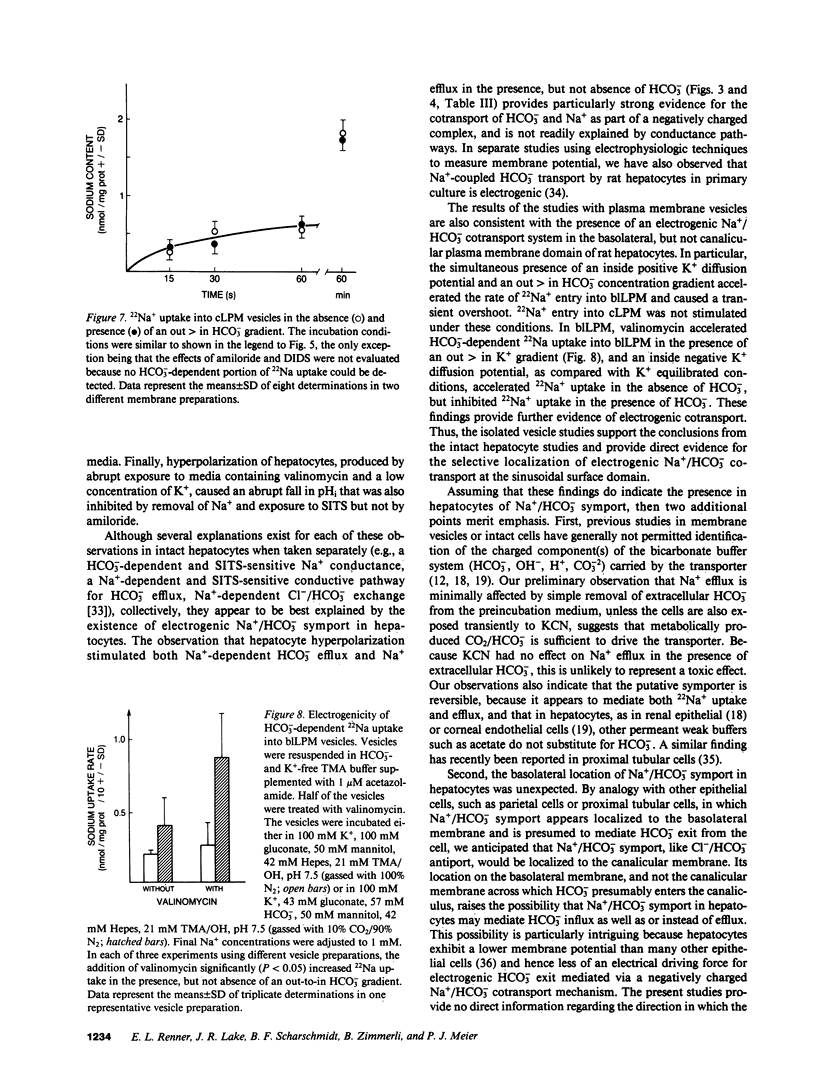
Primary cultures and plasma membrane vesicles were used to characterize Na+ and HCO3- transport by rat hepatocytes. Na+ uptake into hepatocytes was stimulated approximately 10-fold by 25 mM extracellular HCO3-.HCO3--stimulated Na+ uptake was saturable, abolished by 4-acetamido-4'-isothiocyano-2,2'-disulfonic acid stilbene (SITS), and unaffected by amiloride or Cl- removal. Neither propionate nor acetate reproduced this effect of HCO3-. 22Na efflux from preloaded hepatocytes was similarly increased approximately 10-fold by an in greater than out HCO3- concentration gradient. 22Na efflux was also increased by valinomycin and an in greater than out K+ concentration gradient in the presence but not absence of HCO3-. Intracellular pH (pHi) measured with the pH-sensitive fluorochrome 2',7'-bis-(2-carboxyethyl)-5-(and 6-)carboxyfluorescein (BCECF) decreased at a rate of 0.227 (+/- 0.074 SEM) pH units/min when extracellular HCO3- concentration was lowered from 25 to 5 mM at constant PCO2. This intracellular acidification rate was decreased 50-60% in the absence of Na+ or presence of SITS, and was unaffected by amiloride or Cl- removal. Membrane hyperpolarization produced by valinomycin and an in greater than out K+ concentration gradient caused pHi to fall; the rate of fall was decreased 50-70% by Na+ removal or SITS, but not amiloride. An inside positive K+ diffusion potential and a simultaneous out greater than in HCO3- gradient produced a transient 4,4'-diisothiocyano-2,2' disulfonic acid stilbene (DIDS) sensitive, amiloride-insensitive 22Na accumulation in basolateral but not canalicular membrane vesicles. Rat hepatocytes thus exhibit electrogenic basolateral Na+/HCO3- cotransport.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiba T., Alpern R. J., Eveloff J., Calamina J., Warnock D. G. Electrogenic sodium/bicarbonate cotransport in rabbit renal cortical basolateral membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1472–1478. doi: 10.1172/JCI112738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J. Mechanism of basolateral membrane H+/OH-/HCO-3 transport in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. A sodium-coupled electrogenic process. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Nov;86(5):613–636. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.5.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwer M. S., Hegner D. Role of inorganic electrolytes in bile acid-independent canalicular bile formation. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):G116–G124. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.2.G116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias I. M., Forgac M. The sinusoidal domain of the plasma membrane of rat hepatocytes contains an amiloride-sensitive Na+/H+ antiport. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5406–5408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell D. M., Guzelian P. S. Phenotypic stability of adult rat hepatocytes in primary monolayer culture. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;349:85–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb29518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Basolateral HCO3- transport. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):53–94. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curci S., Debellis L., Frömter E. Evidence for rheogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransport in the basolateral membrane of oxyntic cells of frog gastric fundus. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(5):497–504. doi: 10.1007/BF00585075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont M., Erlinger S., Uchman S. Hypercholeresis induced by ursodeoxycholic acid and 7-ketolithocholic acid in the rat: possible role of bicarbonate transport. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):82–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitz J. G., Scharschmidt B. F. Regulation of transmembrane electrical potential gradient in rat hepatocytes in situ. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 1):G56–G64. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.1.G56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassl S. M., Aronson P. S. Na+/HCO3-co-transport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8778–8783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Wood C. A. Importance of bicarbonate in bile salt independent fraction of bile flow. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E158–E164. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. M., Graf J., Boyer J. L. Na-H exchange regulates intracellular pH in isolated rat hepatocyte couplets. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 1):G109–G113. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.1.G109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Schwartz P., Schill B. S., Langner B., Lepple A. P., Keller S. K., Wiederholt M. Kinetic properties of the sodium bicarbonate (carbonate) symport in monkey kidney epithelial cells (BSC-1). Interactions between Na+, HCO-3, and pH. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10673–10679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Stahlknecht T. R., Hollwede H., Fischer D. G., Keller S. K., Wiederholt M. A bicarbonate-dependent process inhibitable by disulfonic stilbenes and a Na+/H+ exchange mediate 22Na+ uptake into cultured bovine corneal endothelium. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):795–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitani K., Kanai S. Effect of ursodeoxycholate on the bile flow in the rat. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 1;31(18):1973–1985. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Berry C. A., Alpern R. J., Rector F. C., Jr Regulation of cell pH by ambient bicarbonate, carbon dioxide tension, and pH in the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):381–389. doi: 10.1172/JCI113330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Allemain G., Paris S., Pouysségur J. Role of a Na+-dependent Cl-/HCO3- exchange in regulation of intracellular pH in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4877–4883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., Knickelbein R., Moseley R. H., Dobbins J. W., Boyer J. L. Evidence for carrier-mediated chloride/bicarbonate exchange in canalicular rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1256–1263. doi: 10.1172/JCI111824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., St Meier-Abt A., Barrett C., Boyer J. L. Mechanisms of taurocholate transport in canalicular and basolateral rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. Evidence for an electrogenic canalicular organic anion carrier. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10614–10622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., Sztul E. S., Reuben A., Boyer J. L. Structural and functional polarity of canalicular and basolateral plasma membrane vesicles isolated in high yield from rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):991–1000. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley R. H., Meier P. J., Aronson P. S., Boyer J. L. Na-H exchange in rat liver basolateral but not canalicular plasma membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 1):G35–G43. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.1.G35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner E. L., Lake J. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Scharschmidt B. F. Amiloride and amiloride analogs inhibit Na+/K+-transporting ATPase and Na+-coupled alanine transport in rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 3;938(3):386–394. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner E. L., Lake J. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Van Dyke R. W., Scharschmidt B. F. Ursodeoxycholic acid choleresis: relationship to biliary HCO-3 and effects of Na+-H+ exchange inhibitors. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):G232–G241. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.2.G232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Lake J. R., Renner E. L., Licko V., Van Dyke R. W. Fluid phase endocytosis by cultured rat hepatocytes and perfused rat liver: implications for plasma membrane turnover and vesicular trafficking of fluid phase markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9488–9492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Stephens J. E. Transport of sodium, chloride, and taurocholate by cultured rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):986–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Van Dyke R. W., Stephens J. E. Chloride transport by intact rat liver and cultured rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jun;242(6):G628–G633. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.242.6.G628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani M., Grassi S. M., Aronson P. S. Stoichiometry of Na+-HCO-3 cotransport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1172/JCI112948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke R. W., Scharschmidt B. F. (Na,K)-ATPase-mediated cation pumping in cultured rat hepatocytes. Rapid modulation by alanine and taurocholate transport and characterization of its relationship to intracellular sodium concentration. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12912–12919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke R. W., Stephens J. E., Scharschmidt B. F. Effects of ion substitution on bile acid-dependent and -independent bile formation by rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):505–517. doi: 10.1172/JCI110642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitomi K., Burckhardt B. C., Frömter E. Rheogenic sodium-bicarbonate cotransport in the peritubular cell membrane of rat renal proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):360–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00595689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


