Abstract
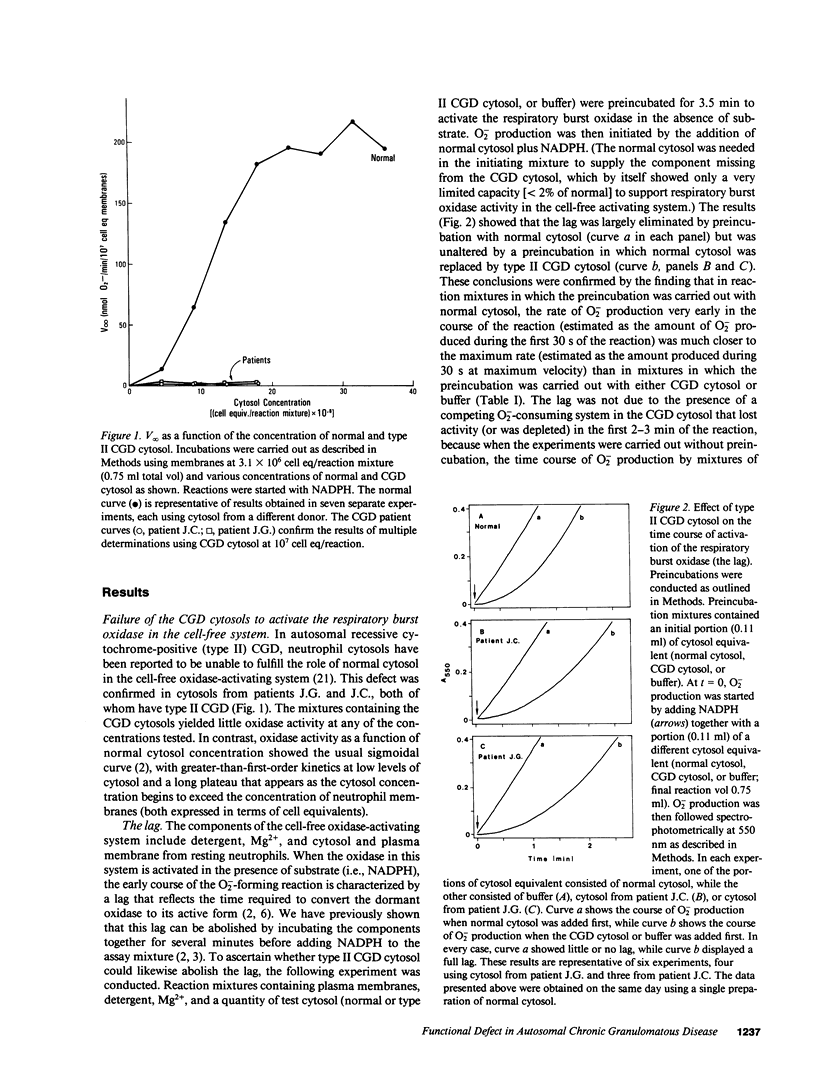
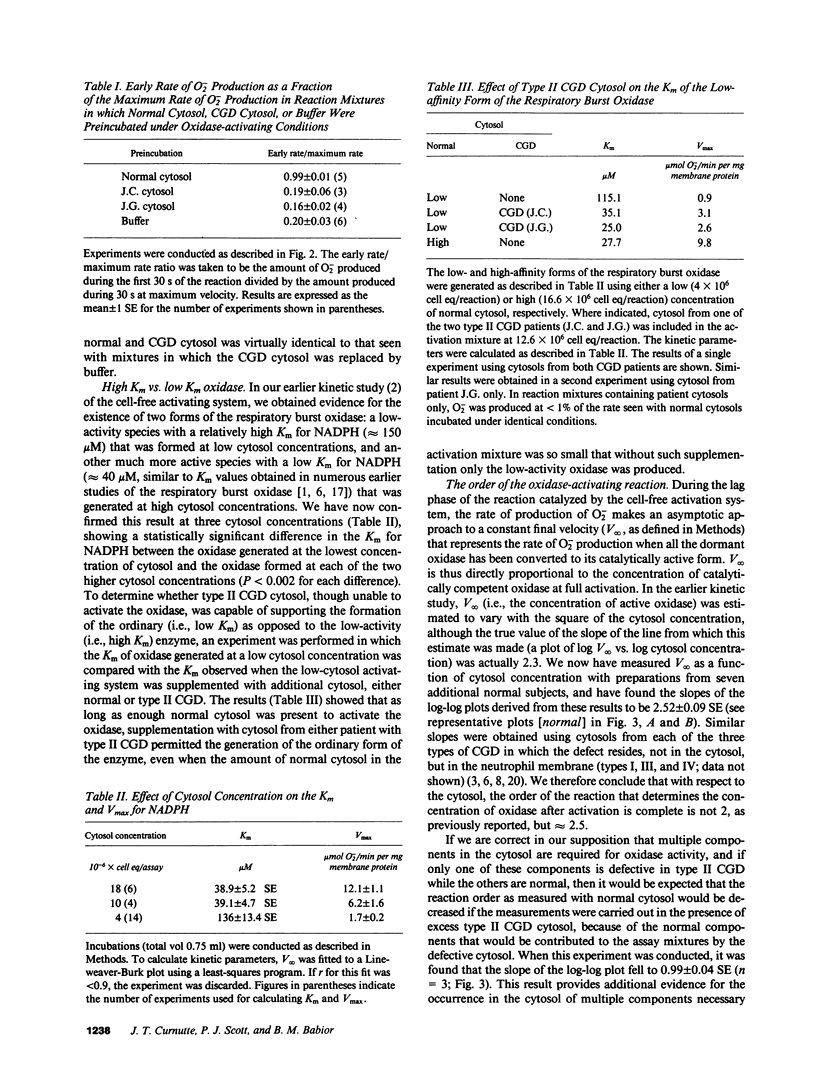
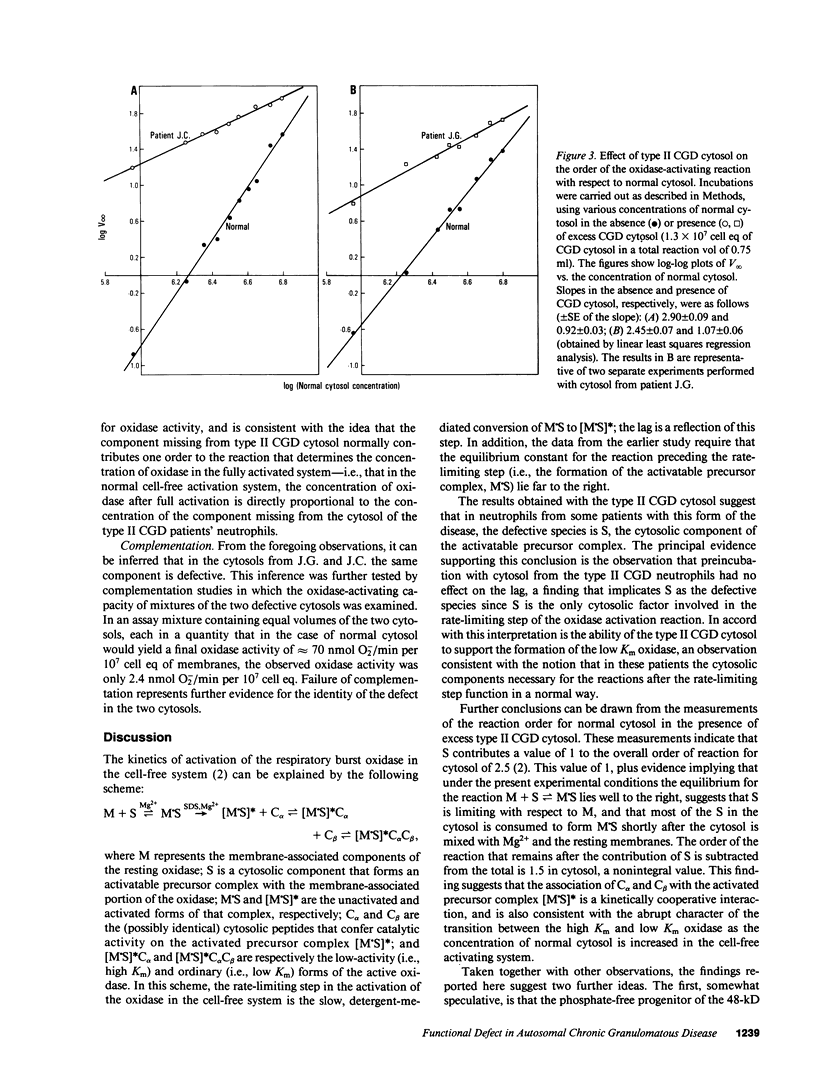
The kinetics of activation of the respiratory burst oxidase in the cell-free oxidase-activating system have been explained by a three-stage mechanism in which the membrane-associated oxidase components M: (a) take up a cytosolic factor S to form a complex M.S that is (b) slowly converted in the second stage to a precatalytic species [M.S]*, which finally (c) takes up two more (possibly identical) cytosolic components, C alpha and C beta, to successively generate [M.S]*C alpha, a low-activity (i.e., high Km) oxidase, and finally [M.S]*C alpha C beta, the ordinary (i.e., low Km) oxidase (Babior, B.M., R. Kuver, and J.T. Curnutte. 1988. J. Biol. Chem. 263:1713-1718). Studies with the cell-free oxidase-activating system from normal neutrophils and from neutrophils obtained from two patients with type II (autosomal recessive cytochrome-positive) chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) have suggested that (a) the defective element in the cytosol from patient neutrophils is S; (b) in normal neutrophil cytosol, S is limiting with respect to M; and (c) C alpha and C beta interact cooperatively with the activated precursor complex [M.S]*. It was further speculated that S might be identical to the nonphosphorylated progenitor of the phosphorylated 48-kD proteins that are missing in certain forms of CGD, and that other forms of type II CGD besides the one described in this report remain to be discovered.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M., Kuver R., Curnutte J. T. Kinetics of activation of the respiratory burst oxidase in a fully soluble system from human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1713–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. The respiratory burst oxidase. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):201–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badwey J. A., Curnutte J. T., Berde C. B., Karnovsky M. L. Cytochalasin E diminishes the lag phase in the release of superoxide by human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 14;106(1):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellavite P., Corso F., Dusi S., Grzeskowiak M., Della-Bianca V., Rossi F. Activation of NADPH-dependent superoxide production in plasma membrane extracts of pig neutrophils by phosphatidic acid. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8210–8214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg Y., Pick E. Activation of NADPH-dependent superoxide production in a cell-free system by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13539–13545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg Y., Pick E. Unsaturated fatty acids stimulate NADPH-dependent superoxide production by cell-free system derived from macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 1;88(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Leidal K. G., Pearson D. W., Nauseef W. M. NADPH oxidase of human neutrophils. Subcellular localization and characterization of an arachidonate-activatable superoxide-generating system. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4065–4074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T. Activation of human neutrophil nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, reduced (triphosphopyridine nucleotide, reduced) oxidase by arachidonic acid in a cell-free system. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1740–1743. doi: 10.1172/JCI111885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Babior B. M. Chronic granulomatous disease. Adv Hum Genet. 1987;16:229–297. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0620-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Berkow R. L., Roberts R. L., Shurin S. B., Scott P. J. Chronic granulomatous disease due to a defect in the cytosolic factor required for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):606–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI113360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T. Classification of chronic granulomatous disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):241–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Kuver R., Babior B. M. Activation of the respiratory burst oxidase in a fully soluble system from human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6450–6452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Kuver R., Scott P. J. Activation of neutrophil NADPH oxidase in a cell-free system. Partial purification of components and characterization of the activation process. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5563–5569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Scott P. J., Mayo L. A. Cytosolic components of the respiratory burst oxidase: resolution of four components, two of which are missing in complementing types of chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Orkin S. H., Brown R., Jesaitis A. J., Parkos C. A. The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus is a component of the neutrophil cytochrome b complex. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):717–720. doi: 10.1038/327717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita I., Takeshige K., Minakami S. Characterization of the NADPH-dependent superoxide production activated by sodium dodecyl sulfate in a cell-free system of pig neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 22;931(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabig T. G., English D., Akard L. P., Schell M. J. Regulation of neutrophil NADPH oxidase activation in a cell-free system by guanine nucleotides and fluoride. Evidence for participation of a pertussis and cholera toxin-insensitive G protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1685–1690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyneman R. A., Vercauteren R. E. Activation of a NADPH oxidase from horse polymorphonuclear leukocytes in a cell-free system. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Dec;36(6):751–759. doi: 10.1002/jlb.36.6.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligeti E., Doussiere J., Vignais P. V. Activation of the O2(.-)-generating oxidase in plasma membrane from bovine polymorphonuclear neutrophils by arachidonic acid, a cytosolic factor of protein nature, and nonhydrolyzable analogues of GTP. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):193–200. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., Shirley P. S., Clayton C. C., Snyderman R. Activation of the respiratory burst enzyme from human neutrophils in a cell-free system. Evidence for a soluble cofactor. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1735–1739. doi: 10.1172/JCI111884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Curnutte J. T., Roberts R. L., Babior B. M. Relationship of protein phosphorylation to the activation of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Defects in the phosphorylation of a group of closely related 48-kDa proteins in two forms of chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6777–6782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Dinauer M. C., Walker L. E., Allen R. A., Jesaitis A. J., Orkin S. H. Primary structure and unique expression of the 22-kilodalton light chain of human neutrophil cytochrome b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Bromberg Y., Shpungin S., Gadba R. Activation of the superoxide forming NADPH oxidase in a cell-free system by sodium dodecyl sulfate. Characterization of the membrane-associated component. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16476–16483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Cross A. R., Garcia R. C., Borregaard N., Valerius N. H., Soothill J. F., Jones O. T. Absence of cytochrome b-245 in chronic granulomatous disease. A multicenter European evaluation of its incidence and relevance. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 3;308(5):245–251. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302033080503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Heyworth P. G., Cockcroft S., Barrowman M. M. Stimulated neutrophils from patients with autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease fail to phosphorylate a Mr-44,000 protein. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):547–549. doi: 10.1038/316547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Schultz G. Fatty-acid-induced activation of NADPH oxidase in plasma membranes of human neutrophils depends on neutrophil cytosol and is potentiated by stable guanine nucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 2;162(3):563–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Corbeel L., de Boer M., Lutter R., van Zwieten R., Hamers M. N., Roos D. Cytochrome b deficiency in an autosomal form of chronic granulomatous disease. A third form of chronic granulomatous disease recognized by monocyte hybridization. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):915–920. doi: 10.1172/JCI111792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


