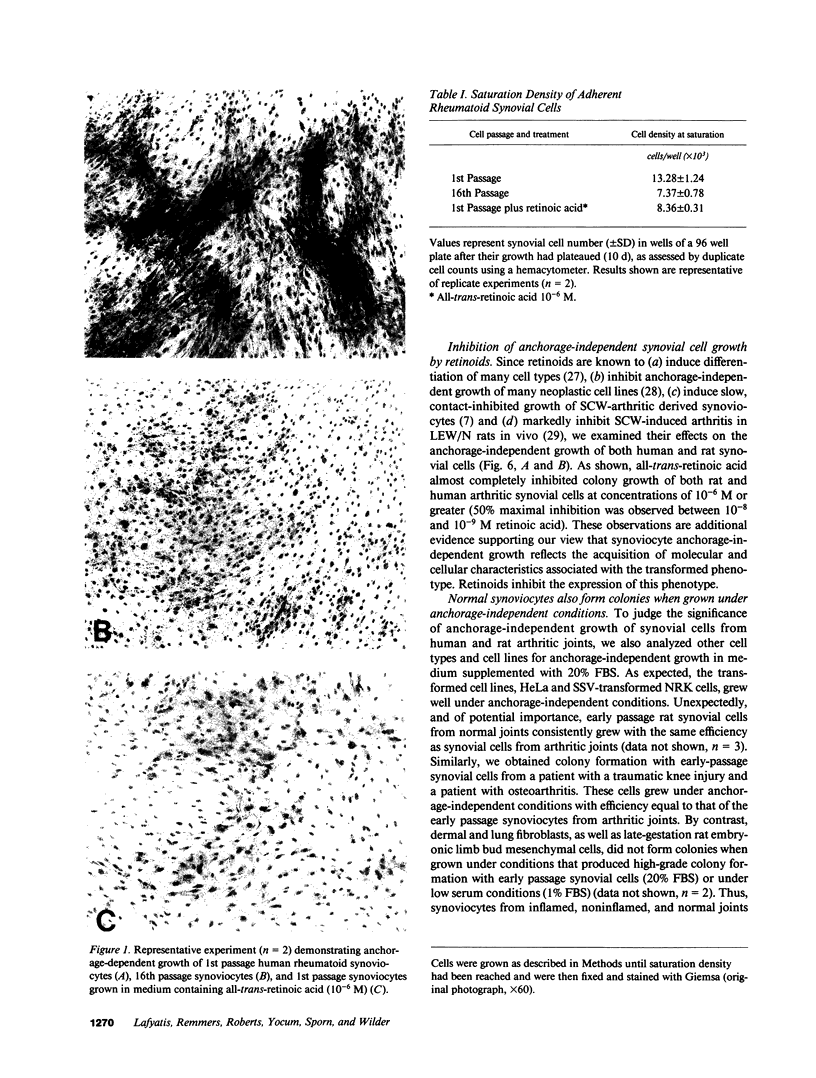
Abstract
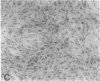
Exuberant tumor-like synovial cell proliferation with invasion of periarticular bone is a feature of rheumatoid arthritis in humans and of streptococcal cell wall (SCW)-induced arthritis in rats. These histologic observations prompted us to examine synoviocytes from arthritic joints for phenotypic characteristics of transformed cells. The capacity to grow in vitro under anchorage-independent conditions is a characteristic that correlates closely with potential in vivo tumorigenicity. In medium supplemented with 20% serum or in basal media supplemented with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), early passage synoviocytes from both SCW-induced and rheumatoid arthritic joints formed colonies in soft agarose. Epidermal growth factor (EGF), interleukin 1 (IL-1), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) did not support growth, although EGF enhanced PDGF-dependent growth. On the other hand, TGF-beta, as well as all-trans-retinoic acid, inhibited colony growth. Early passage normal rat and human synoviocytes also grew under the same conditions, but lung, skin, and late-gestation embryonic fibroblast-like cells did not. Considered in the context of other published data our findings provide cogent evidence that synoviocytes, but not other types of fibroblast-like cells, readily acquire phenotypic characteristics commonly associated with transformed cells. Expression of the transformed phenotype in the inflammatory site is likely regulated by paracrine growth factors, such as PDGF and TGF-beta.
Full text
PDF



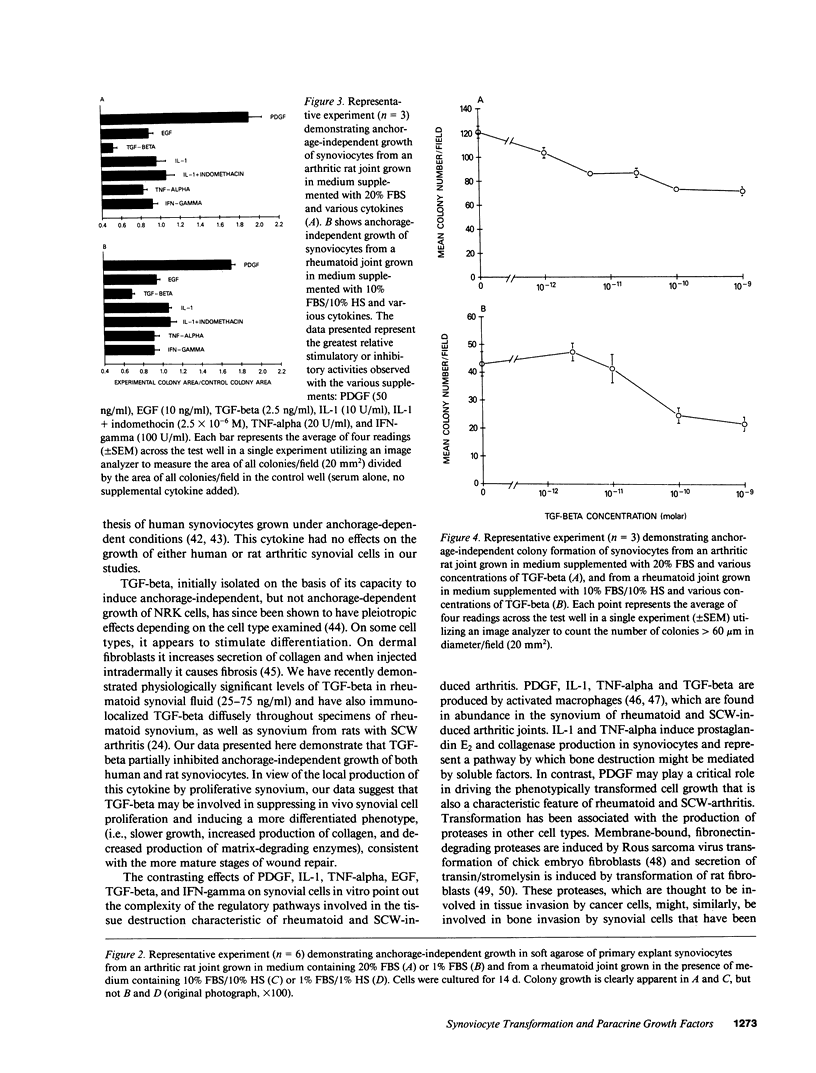


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. B., Malone D. G., Wahl S. M., Calandra G. B., Wilder R. L. Role of the thymus in streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis and hepatic granuloma formation. Comparative studies of pathology and cell wall distribution in athymic and euthymic rats. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1042–1056. doi: 10.1172/JCI112057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amento E. P., Bhan A. K., McCullagh K. G., Krane S. M. Influences of gamma interferon on synovial fibroblast-like cells. Ia induction and inhibition of collagen synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI112041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anzano M. A., Roberts A. B., Meyers C. A., Komoriya A., Lamb L. C., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B. Synergistic interaction of two classes of transforming growth factors from murine sarcoma cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Nov;42(11):4776–4778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K., Fleurdelys B. E., Stevenson H. C., Miller P. J., Madtes D. K., Raines E. W., Ross R., Sporn M. B. Expression and secretion of type beta transforming growth factor by activated human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6020–6024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K., Grotendorst G. R., Miller D. M., Sporn M. B. Cellular transformation by coordinated action of three peptide growth factors from human platelets. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):804–806. doi: 10.1038/309804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K., Komoriya A., Meyers C. A., Miller D. M., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor-beta in human platelets. Identification of a major storage site, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7155–7160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer E. A., Cooper T. W., Huang J. S., Altman J., Deuel T. F. Stimulation of in vitro human skin collagenase expression by platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4132–4136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsholtz C., Westermark B., Ek B., Heldin C. H. Coexpression of a PDGF-like growth factor and PDGF receptors in a human osteosarcoma cell line: implications for autocrine receptor activation. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinckerhoff C. E., Guyre P. M. Increased proliferation of human synovial fibroblasts treated with recombinant immune interferon. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3142–3146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinckerhoff C. E., Harris E. D., Jr Survival of rheumatoid synovium implanted into nude mice. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jun;103(3):411–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinckerhoff C. E., Sheldon L. A., Benoit M. C., Burgess D. R., Wilder R. L. Effect of retinoids on rheumatoid arthritis, a proliferative and invasive non-malignant disease. Ciba Found Symp. 1985;113:191–211. doi: 10.1002/9780470720943.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromley M., Woolley D. E. Histopathology of the rheumatoid lesion. Identification of cell types at sites of cartilage erosion. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):857–863. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. M., Chen W. T. Fibronectin-degrading proteases from the membranes of transformed cells. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cifone M. A., Fidler I. J. Correlation of patterns of anchorage-independent growth with in vivo behavior of cells from a murine fibrosarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1039–1043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colburn N. H., Bruegge W. F., Bates J. R., Gray R. H., Rossen J. D., Kelsey W. H., Shimada T. Correlation of anchorage-independent growth with tumorigenicity of chemically transformed mouse epidermal cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):624–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., de Rochemonteix B., Burrus B., Demczuk S., Dinarello C. A. Human recombinant interleukin 1 stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):645–648. doi: 10.1172/JCI112350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fassbender H. G., Simmling-Annefeld M., Stofft E. Transformation der Synovialzellen bei rheumatoider Arthritis. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1980;64:193–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Tsai V., Zvaifler N. J. Cellular immunity in the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of chronic synovitis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1987 Aug;13(2):191–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Zvaifler N. J. Peripheral blood and synovial fluid monocyte activation in inflammatory arthritis. II. Low levels of synovial fluid and synovial tissue interferon suggest that gamma-interferon is not the primary macrophage activating factor. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Aug;30(8):864–871. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman V. H., Shin S. I. Cellular tumorigenicity in nude mice: correlation with cell growth in semi-solid medium. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. A. Hypothesis: in vitro evidence for the invasive and tumor-like properties of the rheumatoid pannus. J Rheumatol. 1983 Dec;10(6):845–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haraoui B., Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Sporn M. B., Helfgott R. K., Brinckerhoff C. E. Dose-dependent suppression by the synthetic retinoid, 4-hydroxyphenyl retinamide, of streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis in rats. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(6):903–916. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(85)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr Recent insights into the pathogenesis of the proliferative lesion in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Jan-Feb;19(1):68–72. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Deuel T. F. Transforming protein of simian sarcoma virus stimulates autocrine growth of SSV-transformed cells through PDGF cell-surface receptors. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Glaichenhaus N., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor and oncogenes induce transcription of the same cellular mRNA in rat fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miossec P., Dinarello C. A., Ziff M. Interleukin-1 lymphocyte chemotactic activity in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Apr;29(4):461–470. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neugut A. I., Weinstein I. B. The use of agarose in the determination of anchorage-independent growth. In Vitro. 1979 May;15(5):351–355. doi: 10.1007/BF02616141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Orth D. N. Human plasma epidermal growth factor/beta-urogastrone is associated with blood platelets. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):249–259. doi: 10.1172/JCI110964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridge S. C., Zabriske J. B., Oronsky A. L., Kerwar S. S. Streptococcal cell wall arthritis: studies with nude (athymic) inbred Lewis rats. Cell Immunol. 1985 Nov;96(1):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzino A., Ruff E., Rizzino H. Induction and modulation of anchorage-independent growth by platelet-derived growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, and transforming growth factor-beta. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):2816–2820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Allen J. B., Anderle S. K., Dalldorf F., Eisenberg R., Cromartie W. J. Relationship of complement to experimental arthritis induced in rats with streptococcal cell walls. Immunology. 1982 May;46(1):83–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Peptide growth factors and inflammation, tissue repair, and cancer. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):329–332. doi: 10.1172/JCI112580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Roche N. S., Kagechika H., Shudo K. Mechanism of action of retinoids. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986 Oct;15(4 Pt 2):756–764. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70231-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Role of retinoids in differentiation and carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1983 Jul;43(7):3034–3040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., de Crombrugghe B. Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitham S. E., Murphy G., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Smith B. J., Lyons A., Harris T. J., Reynolds J. J., Herrlich P., Docherty A. J. Comparison of human stromelysin and collagenase by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):913–916. doi: 10.1042/bj2400913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Hansen C. Thymus-dependent and -independent regulation of Ia antigen expression in situ by cells in the synovium of rats with streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis. Differences in site and intensity of expression in euthymic, athymic, and cyclosporin A-treated LEW and F344 rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1160–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI112933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Calandra G. B., Garvin A. J., Wright K. D., Hansen C. T. Strain and sex variation in the susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1064–1072. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. D., Ihrie E. J., Dinarello C. A., Cohen P. L. Isolation of an interleukin-1-like factor from human joint effusions. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Aug;26(8):975–983. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum D. E., Allen J. B., Wahl S. M., Calandra G. B., Wilder R. L. Inhibition by cyclosporin A of streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis and hepatic granulomas in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Feb;29(2):262–273. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum D. E., Lafyatis R., Remmers E. F., Schumacher H. R., Wilder R. L. Hyperplastic synoviocytes from rats with streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis exhibit a transformed phenotype that is thymic-dependent and retinoid inhibitable. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jul;132(1):38–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]