Abstract
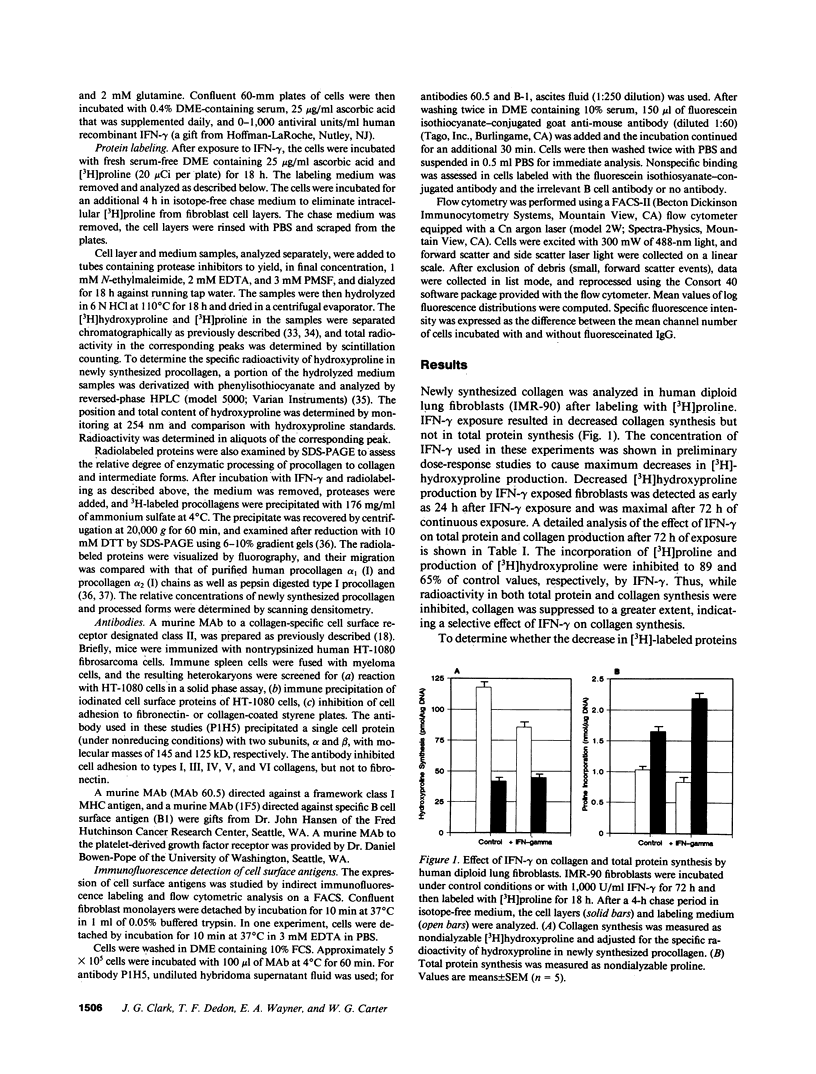
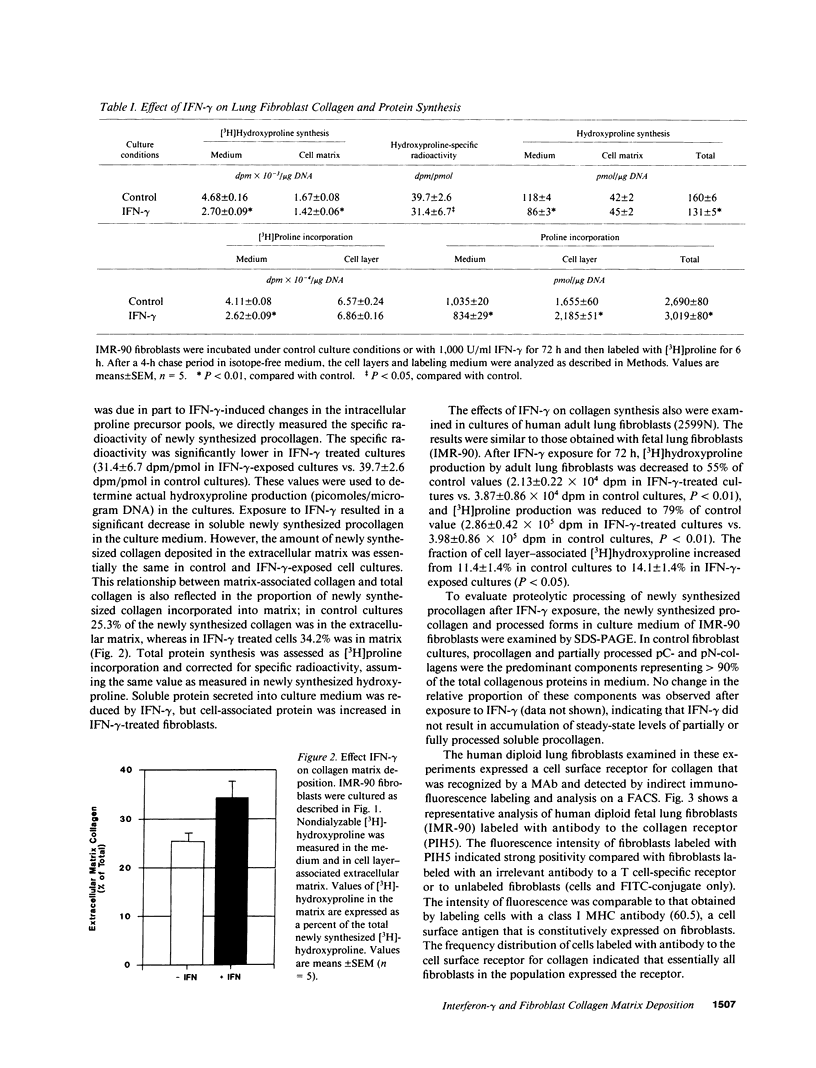
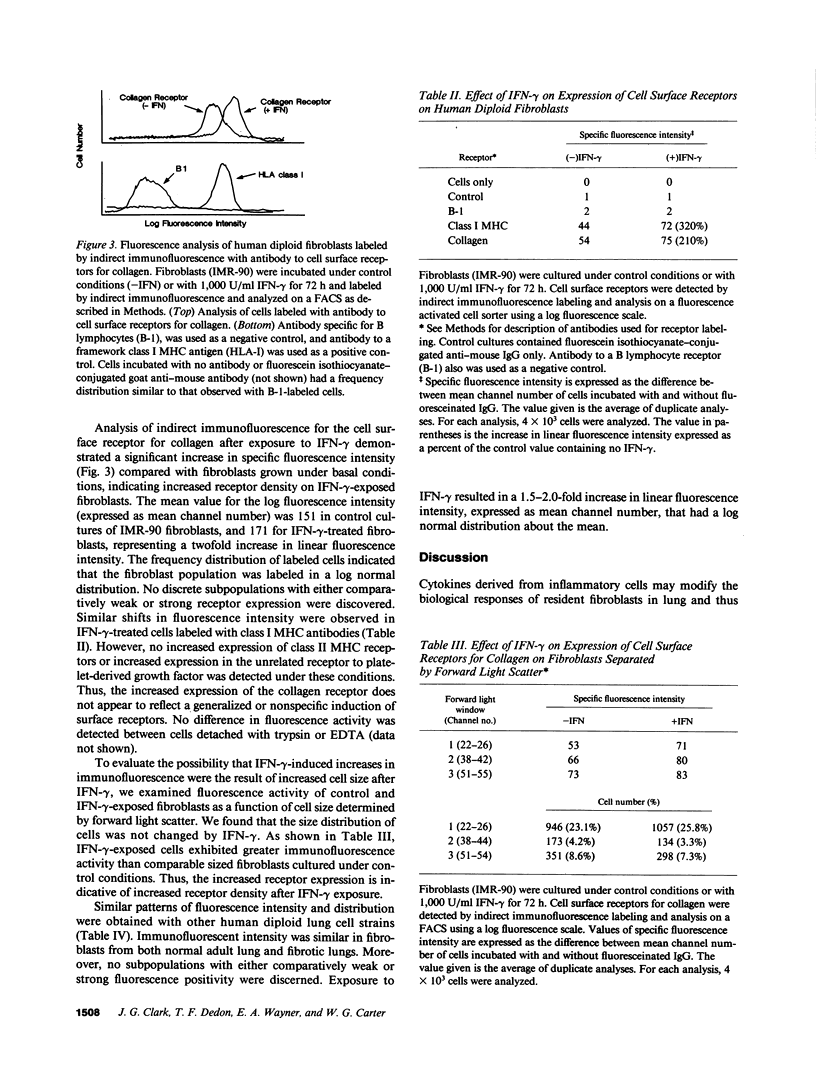
We used cultured human diploid lung fibroblasts as a model system to examine the effects of recombinant IFN-gamma on synthesis of collagen, matrix deposition of newly synthesized collagen, and the expression of cell surface receptors for collagen. Using [3H]proline-labeled cells we found that IFN-gamma resulted in dose-dependent inhibition of fibroblast collagen synthesis. Pulse-chase experiments to analyze compartmentalization of newly synthesized collagen showed that the decrease in collagen synthesis was confined to the soluble pool of procollagen in the medium, while extracellular matrix associated collagen was not changed, indicating that a larger proportion of newly synthesized collagen was deposited into the matrix in IFN-gamma exposed fibroblasts (34.2 vs. 25.3%). This increase in the efficiency of collagen matrix deposition was associated with enhanced expression of a cell surface receptor for collagen as detected by indirect immunofluorescence labeling and analysis by flow cytometry. Fibroblasts (IMR-90) cultured in the presence of IFN-gamma (1,000 U/ml) exhibited a twofold increase in mean linear fluorescence intensity compared with cells cultured under control conditions. The distribution of log fluorescence intensity in both control and IFN-gamma exposed cells was normally distributed about the mean, indicating that discrete subpopulations with respect to receptor expression were not present. Increased fluorescence intensity and log normal distribution of fluorescence intensity also were identified in IFN-gamma-treated lung fibroblasts from a normal adult individual and two strains obtained from patients with pulmonary fibrosis. These results indicate that IFN-gamma modulates fibroblast collagen matrix deposition as well as collagen synthesis. The associated increase in collagen receptors suggests that cytokine-mediated modulation of the cell surface maybe a contributing factor in regulation of fibroblast collagen accumulation in the extracellular matrix or in cellular interaction with collagen-containing matrix. Such an effect could modulate the interaction of fibroblasts with extracellular matrix at sites of inflammation and play an important role in the remodeling of matrix during repair from tissue injury.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen-Hoffmann B. L., Mosher D. F. Matrix assembly sites for exogenous fibronectin are decreased on human fibroblasts after treatment with agents which increase intracellular cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14361–14365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amento E. P., Bhan A. K., McCullagh K. G., Krane S. M. Influences of gamma interferon on synovial fibroblast-like cells. Ia induction and inhibition of collagen synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI112041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman J. F., Cole W. G., Pillow J. J., Ramshaw J. A. Induction of procollagen processing in fibroblast cultures by neutral polymers. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4198–4203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beresini M. H., Lempert M. J., Epstein L. B. Overlapping polypeptide induction in human fibroblasts in response to treatment with interferon-alpha, interferon-gamma, interleukin 1 alpha, interleukin 1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):485–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birk D. E., Trelstad R. L. Extracellular compartments in matrix morphogenesis: collagen fibril, bundle, and lamellar formation by corneal fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2024–2033. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birk D. E., Trelstad R. L. Extracellular compartments in tendon morphogenesis: collagen fibril, bundle, and macroaggregate formation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):231–240. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breul S. D., Bradley K. H., Hance A. J., Schafer M. P., Berg R. A., Crystal R. G. Control of collagen production by human diploid lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5250–5260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G. The role of intermolecular disulfide bonding in deposition of GP140 in the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):105–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Hilderbran J. N. Fibroblast procollagen production rates in vitro based on [3H]hydroxyproline production and procollagen hydroxyproline specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):478–485. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Kostal K. M., Marino B. A. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. An alveolar macrophage product increases fibroblast prostaglandin E2 and cyclic adenosine monophosphate and suppresses fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):2082–2091. doi: 10.1172/JCI111173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Kostal K. M., Marino B. A. Modulation of collagen production following bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. Presence of a factor in lung that increases fibroblast prostaglandin E2 and cAMP and suppresses fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8098–8105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Kuhn C., 3rd, McDonald J. A., Mecham R. P. Lung connective tissue. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1983;10:249–331. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363710-9.50011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Starcher B. C., Uitto J. Bleomycin-induced synthesis of type I procollagen by human lung and skin fibroblasts in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 13;631(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaja M. J., Weiner F. R., Eghbali M., Giambrone M. A., Eghbali M., Zern M. A. Differential effects of gamma-interferon on collagen and fibronectin gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13348–13351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedhar S., Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. A cell surface receptor complex for collagen type I recognizes the Arg-Gly-Asp sequence. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):585–593. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M. R., Berman B. Gamma interferon is the lymphokine and beta interferon the monokine responsible for inhibition of fibroblast collagen production and late but not early fibroblast proliferation. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):516–527. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert R. F. Amino acid analysis by HPLC: optimized conditions for chromatography of phenylthiocarbamyl derivatives. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 1;154(2):431–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and collagen and their incorporation into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4337–4345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., Freundlich B., Rosenbloom J. Selective inhibition of human diploid fibroblast collagen synthesis by interferons. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):1112–1116. doi: 10.1172/JCI111480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Nugent D. J., Staats S. J., Orchekowski R. P., Wayner E. A., Carter W. G. The human fibroblast class II extracellular matrix receptor mediates platelet adhesion to collagen and is identical to the platelet glycoprotein Ia-IIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4516–4519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. A., Kelley D. G., Broekelmann T. J. Role of fibronectin in collagen deposition: Fab' to the gelatin-binding domain of fibronectin inhibits both fibronectin and collagen organization in fibroblast extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):485–492. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. A., Quade B. J., Broekelmann T. J., LaChance R., Forsman K., Hasegawa E., Akiyama S. Fibronectin's cell-adhesive domain and an amino-terminal matrix assembly domain participate in its assembly into fibroblast pericellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):2957–2967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Collins T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Gitlin J. D., Fiers W., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Burakoff S. J., Reiss C. S. Lymphocytes recognize human vascular endothelial and dermal fibroblast Ia antigens induced by recombinant immune interferon. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):726–729. doi: 10.1038/305726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghu G., Striker L. J., Hudson L. D., Striker G. E. Extracellular matrix in normal and fibrotic human lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Feb;131(2):281–289. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. J., Birkenmeier T. M., McQuillan J. J., Akiyama S. K., Yamada S. S., Chen W. T., Yamada K. M., McDonald J. A. Transforming growth factor beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and of both subunits of the human fibronectin receptor by cultured human lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4586–4592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbloom J., Feldman G., Freundlich B., Jimenez S. A. Transcriptional control of human diploid fibroblast collagen synthesis by gamma-interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90422-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E. Complexing of fibronectin glycosaminoglycans and collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 13;631(2):350–358. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E., Hayman E. G. Fibronectin: current concepts of its structure and functions. Coll Relat Res. 1981;1(1):95–128. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(80)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolstoshev P., Berg R. A., Rennard S. I., Bradley K. H., Trapnell B. C., Crystal R. G. Procollagen production and procollagen messenger RNA levels and activity in human lung fibroblasts during periods of rapid and stationary growth. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3135–3140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss T., Bornstein P. Regulation of type I collagen mRNA levels in fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jun 2;157(2):433–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Fellous M., Revel M. Preferential effect of gamma interferon on the synthesis of HLA antigens and their mRNAs in human cells. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):833–836. doi: 10.1038/299833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Carter W. G. Identification of multiple cell adhesion receptors for collagen and fibronectin in human fibrosarcoma cells possessing unique alpha and common beta subunits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1873–1884. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


