Abstract
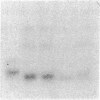
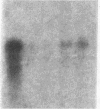
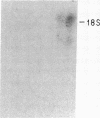
Expression of transforming growth factor alpha (TGF alpha), and transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) was assessed in isolated primary rat intestinal epithelial cells as well as a rat intestinal crypt cell-derived cell line (IEC-6). A gradient in TGF beta was present, with high concentrations of a 2.5-kb transcript found in undifferentiated crypt cells and progressively lower amounts of the TGF beta transcript in increasingly differentiated villus cell populations. In contrast, the concentration of 4.5-kb TGF alpha transcript was higher in differentiated villus cells than in mitotically active, undifferentiated populations of crypt epithelial cells. The concentrations of transforming growth factors alpha and beta as determined by radioreceptor binding inhibition assay and direct assessment of transforming growth factor biological activity correlated with Northern blot analysis. Although gradients in the expression of the TGFs were present, equivalent binding was observed in the different intestinal cell populations when assessed with 125I-TGF beta and 125I-EGF (TGF alpha). No EGF transcripts were detected in any intestinal cell population, suggesting that the true ligand of the EGF receptor was TGF alpha. IEC-6 cells expressed both TGF alpha and TGF beta transcripts. In addition to the transcripts identified in the primary intestinal cells, this cell line contained an additional larger TGF alpha transcript (4.8 kb) and smaller TGF beta transcripts (2.2 and 1.8 kb). TGF alpha and TGF beta may play a significant role in the regulation of the balance between proliferative and differentiated cell compartments in the intestinal epithelium through both autocrine and paracrine mechanisms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carroll K. M., Wong T. T., Drabik D. L., Chang E. B. Differentiation of rat small intestinal epithelial cells by extracellular matrix. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 1):G355–G360. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.3.G355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Derynck R., Wilcox J. N., Bringman T. S., Goustin A. S., Moses H. L., Pittelkow M. R. Production and auto-induction of transforming growth factor-alpha in human keratinocytes. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):817–820. doi: 10.1038/328817a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Goustin A. S., Soderquist A. M., Shipley G. D., Wolfshohl J., Carpenter G., Moses H. L. Transforming growth factor alpha and beta expression in human colon cancer lines: implications for an autocrine model. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 1;47(17):4590–4594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Shipley G. D., Moses H. L. Production of transforming growth factors by human colon cancer lines. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1164–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Sipes N. J., Bascom C. C., Graves-Deal R., Pennington C. Y., Weissman B. E., Moses H. L. Growth modulation of mouse keratinocytes by transforming growth factors. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 15;48(6):1596–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Roberts A. B., Winkler M. E., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-alpha: precursor structure and expression in E. coli. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90550-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: structure and biological activities. J Cell Biochem. 1986;32(4):293–304. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240320406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobner P. R., Kawasaki E. S., Yu L. Y., Bancroft F. C. Thyroid or glucocorticoid hormone induces pre-growth-hormone mRNA and its probable nuclear precursor in rat pituitary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2230–2234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolik C. A., Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Sporn M. B. Characterization of a membrane receptor for transforming growth factor-beta in normal rat kidney fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10995–11000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonnella P. A., Siminoski K., Murphy R. A., Neutra M. R. Transepithelial transport of epidermal growth factor by absorptive cells of suckling rat ileum. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):22–32. doi: 10.1172/JCI113051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoosein N. M., Brattain D. E., McKnight M. K., Levine A. E., Brattain M. G. Characterization of the inhibitory effects of transforming growth factor-beta on a human colon carcinoma cell line. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 1;47(11):2950–2954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokowa M., Lynch K., Podolsky D. K. Effects of growth factors on an intestinal epithelial cell line: transforming growth factor beta inhibits proliferation and stimulates differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):775–782. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91481-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Endo T., Nadal-Ginard B. Type beta transforming growth factor is an inhibitor of myogenic differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8206–8210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Ignotz R. A., Boyd F. T. Multiple type-beta transforming growth factors and their receptors. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1987;Suppl 5:43–47. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messer M., Dahlqvist A. A one-step ultramicro method for the assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):376–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. Gene expression in rat brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5497–5520. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Coffey R. J., Jr, Leof E. B., Lyons R. M., Keski-Oja J. Transforming growth factor beta regulation of cell proliferation. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1987;Suppl 5:1–7. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménard D., Arsenault P., Pothier P. Biologic effects of epidermal growth factor in human fetal jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1988 Mar;94(3):656–663. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A., Wands J., Trelstad R. L., Isselbacher K. J. Epithelioid cell cultures from rat small intestine. Characterization by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):248–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff E., Rizzino A. Preparation and binding of radioactively labeled porcine transforming growth factor type beta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):714–719. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80555-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Fong N., Selby M., Rutter W. J., Bell G. I. Structure of a mouse submaxillary messenger RNA encoding epidermal growth factor and seven related proteins. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):236–240. doi: 10.1126/science.6602382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo M. K., Lynch K. E., Podolsky D. K. Multiplicity of transforming growth factors in human malignant effusions. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1792–1797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., de Crombrugghe B. Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F. Specific receptors for epidermal growth factor in rat intestinal microvillus membranes. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 1):G429–G435. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.3.G429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Intestinal epithelial cell surface membrane glycoprotein synthesis. I. An indicator of cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]