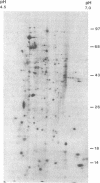
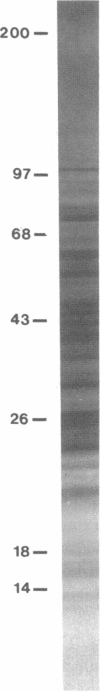
Abstract
Control and resolution of leishmanial infection depends primarily on T cell-mediated immune mechanisms. The nature of the leishmanial antigens involved in eliciting T cell immunity is unknown. We have examined the pattern of peripheral blood lymphocyte responses in patients with active, healed, or subclinical leishmanial infection to fractionated leishmanial antigens using a T cell immunoblotting method in which nitrocellulose-bound leishmanial antigen, resolved by one or two dimensional electrophoresis, are incorporated into lymphocyte cultures. The proliferative and IFN-gamma responses of cells from patients with healed mucosal or cutaneous leishmaniasis were remarkably heterogeneous and occurred to as many as 50-70 distinct antigens. In contrast, responses from subjects with active, nonhealing, diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis were either absent or present to only a small number of antigens. Control and resolution of leishmaniasis, and resistance to reinfection, is therefore associated with a T cell response to a large and diverse pool of parasite antigens. The method of T cell immunoblotting appears to offer a powerful, rapid, and relatively simple approach to the identification of antigens involved in eliciting a T cell response in human leishmaniasis.
Full text
PDF


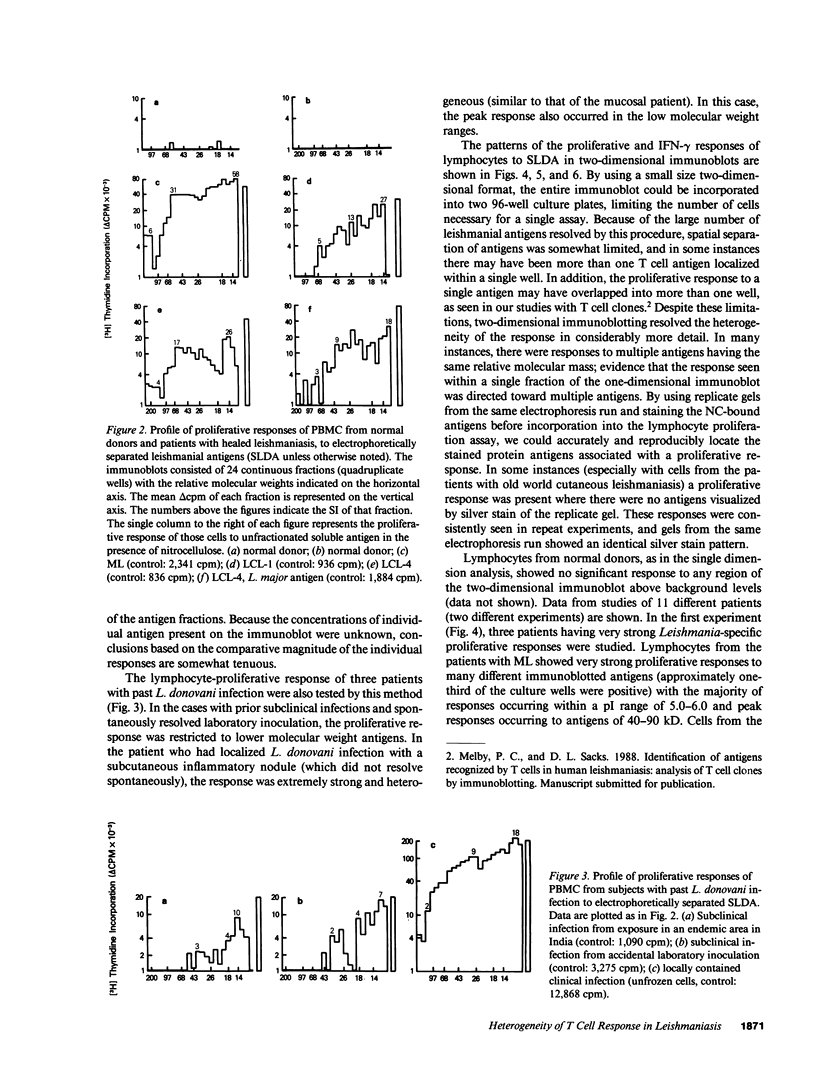

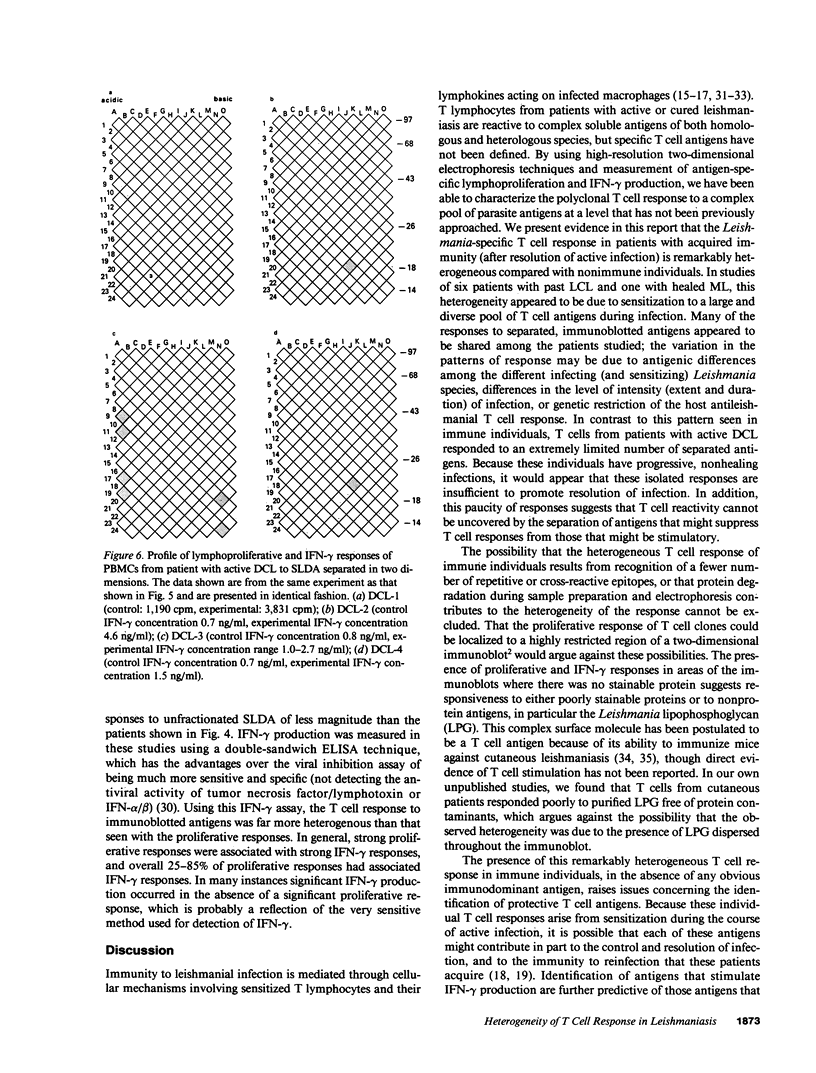


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badaró R., Jones T. C., Lorenço R., Cerf B. J., Sampaio D., Carvalho E. M., Rocha H., Teixeira R., Johnson W. D., Jr A prospective study of visceral leishmaniasis in an endemic area of Brazil. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):639–649. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzofsky J. A., Richman L. K., Killion D. J. Distinct H-2-linked Ir genes control both antibody and T cell responses to different determinants on the same antigen, myoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4046–4050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson A. D. Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis in Ethiopia. 3. Immunological studies. IV. Pathogenesis of diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1970;64(3):380–393. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(70)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson A. D. Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis in Ethiopia. I. The clinical and histological features of the disease. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1969;63(6):708–737. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(69)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho E. M., Badaró R., Reed S. G., Jones T. C., Johnson W. D., Jr Absence of gamma interferon and interleukin 2 production during active visceral leishmaniasis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2066–2069. doi: 10.1172/JCI112209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho E. M., Johnson W. D., Barreto E., Marsden P. D., Costa J. L., Reed S., Rocha H. Cell mediated immunity in American cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4144–4148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho E. M., Teixeira R. S., Johnson W. D., Jr Cell-mediated immunity in American visceral leishmaniasis: reversible immunosuppression during acute infection. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):498–500. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.498-500.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castés M., Agnelli A., Rondón A. J. Mechanisms associated with immunoregulation in human American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):279–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P., Chiao J. W. Cellular immunity of mice to Leishmania donovani in vitro: lymphokine-mediated killing of intracellular parasites in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7083–7087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convit J., Pinardi M. E., Rondón A. J. Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis: a disease due to an immunological defect of the host. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1972;66(4):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(72)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry R. C., Kiener P. A., Spitalny G. L. A sensitive immunochemical assay for biologically active MuIFN-gamma. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Nov 23;104(1-2):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90497-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirges S. Y. Natural and experimental re-infection of man with Oriental sore. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1971 Jun;65(2):197–205. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1971.11686746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar J. P., Ghose S., Saha K. C., Ghose A. C. Cell-mediated immune response in Indian kala-azar and post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):702–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.702-707.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Mitchell G. F. Immunization with Leishmania receptor for macrophages protects mice against cutaneous leishmaniasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5910–5914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Koech D. K., Iha D. W., Bryceson A. D. Immunosuppression in Kenyan visceral leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Feb;51(2):207–214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Siongok T. K., Lyerly W. H., Smith D. H. Prevalence and disease spectrum in a new focus of visceral leishmaniasis in Kenya. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(6):741–746. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser D. F., Harrington M. G., Hochstrasser A. C., Miller M. J., Merril C. R. Methods for increasing the resolution of two-dimensional protein electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1988 Sep;173(2):424–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G. Immunological regulation and control of experimental leishmaniasis. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1986;28:79–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Green N. Analysis of the antigen specificity of influenza haemagglutinin-immune human T lymphocyte clones: identification of an immunodominant region for T cells. Immunology. 1983 Dec;50(4):659–666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Young D. B. A novel approach to the identification of T-cell epitopes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis using human T-lymphocyte clones. Immunology. 1987 Jan;60(1):1–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANSON-BAHR P. E. Immunity in kala-azar. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1961 Nov;55:550–555. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(61)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. D. Mucosal leishmaniasis ("espundia" Escomel, 1911). Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(6):859–876. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Masur H., Keithly J. S. Cell-mediated immune response in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. I. Correlation between resistance to Leishmania donovani and lymphokine-generating capacity. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S., Leonard E. J., Wyler D. J. Intracellular replication and lymphokine-induced destruction of Leishmania tropica in C3H/HeN mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2381–2386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Wheeler D. A., Harrison L. H., Kay H. D. The immunobiology of leishmaniasis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):907–927. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.5.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rezai H. R., Ardehali S. M., Amirhakimi G., Kharazmi A. Immunological features of kala-azar. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Nov;27(6):1079–1083. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Lal S. L., Shrivastava S. N., Blackwell J., Neva F. A. An analysis of T cell responsiveness in Indian kala-azar. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):908–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr E., Kidane K., Yemaneberhan T., Wunderlich F. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in Ethiopia: I. Lymphocyte transformation and antibody titre. Trop Med Parasitol. 1986 Dec;37(4):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Pearce E., Natovitz P., Sher A. Vaccination against cutaneous leishmaniasis in a murine model. I. Induction of protective immunity with a soluble extract of promastigotes. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):221–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Pearce E., Natovitz P., Sher A. Vaccination against cutaneous leishmaniasis in a murine model. II. Immunologic properties of protective and nonprotective subfractions of soluble promastigote extract. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3118–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Lamb J. R. T lymphocytes respond to solid-phase antigen: a novel approach to the molecular analysis of cellular immunity. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):167–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]