Abstract
The Escherichia coli RNA binding protein Hfq is involved in many aspects of post-transcriptional gene expression. Tight binding of Hfq to polyadenylate sequences at the 3′ end of mRNAs influences exonucleolytic degradation, while Hfq binding to small noncoding RNAs (sRNA) and their targeted mRNAs facilitate their hybridization which in turn effects translation. Hfq binding to an A-rich tract in the 5′ leader region of the rpoS mRNA and to the sRNA DsrA have been shown to be important for DsrA enhanced translation initiation of this mRNA. The complexes of Hfq-A18 and Hfq-DsrA provide models for understanding how Hfq interacts with these two RNA sequence/structure motifs. Different methods have reported different values for the stoichiometry of Hfq-A18 and Hfq-DsrA. In this work, mass spectrometry and analytical ultracentrifugation provide direct evidence that the strong binding mode of the Hfq hexamer (Hfq6) for A18 and domain II of DsrA (DsrADII) involve 1:1 complexes. This stoichiometry was also supported by fluorescence anisotropy and a competition gel mobility shift experiment using wild-type and truncated Hfq. More limited studies of Hfq binding to DsrA as well as to the sRNAs RprA, OxyS, and an 18-nt segment of OxyS were also consistent with 1:1 stoichiometry. Mass spectrometry of cross-linked samples of Hfq6, A18, and DsrADII exhibit intensity corresponding to a ternary 1:1:1 complex; however, the small intensity of this peak and fluorescence anisotropy experiments did not provide evidence that this ternary complex is stable in solution.
Keywords: Hfq, DsrA, RprA, OxyS, MALDI-TOF
INTRODUCTION
The Hfq protein of Escherichia coli is a RNA binding protein and a key factor in post-transcriptional gene regulation (Valentin-Hansen et al. 2004; Majdalani et al. 2005; Brennan and Link 2007; Waters and Storz 2009). E. coli Hfq and its bacterial homologs have been implicated in various facets of bacterial metabolism, including stress-induced sRNA regulation of mRNA translation as well as mRNA stability. In addition to its well-documented interaction with RNA, Hfq has been found associated with DNA (Takada et al. 1997; Azam et al. 2000; Updegrove et al. 2010) as well as a number of proteins (Butland et al. 2005). The nature of Hfq's interactions with DNA and many of the proteins are not well understood; however, there is increasing recognition that they may reflect additional functions of Hfq (Le Derout et al. 2010).
Considerable attention has been focused on the role of Hfq in gene regulation by noncoding small RNAs (sRNAs). A number of sRNAs, such as OxyS, SgrS, DsrA, RprA, Spot42, and Qrr1-4, require Hfq to facilitate their regulation of mRNA translation (Sledjeski et al. 2001; Majdalani et al. 2002; Moller et al. 2002a,b; Zhang et al. 2002; Lenz et al. 2004; Kawamoto et al. 2006). In vitro studies suggest that Hfq's role is to enhance the association rate and/or stability of a sRNA to its mRNA target site near the start codon (Geissmann and Touati 2004; Kawamoto et al. 2006; Soper and Woodson 2008; Updegrove et al. 2008). The formation of a sRNA–mRNA hybrid can inhibit or enhance ribosome accessibility to mRNA, thus providing either negative or positive regulation of translation (Majdalani et al. 2005; Waters and Storz 2009). Hfq's presence in the cell enhances sRNA stability and its capacity for functional interaction with mRNA targets. Hfq has also been shown to influence mRNA stability in vivo by enhancing sRNA–mRNA interaction or by binding mRNA directly (Tsui et al. 1997; Vytvytska et al. 1998; Masse et al. 2003; Morita et al. 2005).
In addition to its interactions with the translational initiation regions of mRNAs, Hfq also influences the stability of some mRNAs through its interaction with their 3′ ends. It has been estimated that >90% of the E. coli transcriptome possess post-transcriptionally added poly(A) tails (Mohanty and Kushner 2006). Studies show that Hfq stimulates the addition of poly(A) tails to the 3′ end of some mRNAs by poly(A) polymerase I (PAP) (Le Derout et al. 2003; Mohanty et al. 2004; Folichon et al. 2005). In vivo, inactivation of the hfq gene reduces the length of poly(A) tails synthesized at the 3′ end of the rpsO mRNA by PAP, and in vitro, the addition of Hfq increases the processivity of PAP on rpsO mRNA. The addition of poly(A) tails has been shown to enhance mRNA decay in eubacteria (Steege 2000). Studies also indicate that Hfq binding to poly(A) tails can prevent mRNAs from binding to enzymes involved in RNA degradation (Folichon et al. 2003, 2005; Mohanty et al. 2004). Understanding the role of Hfq in the degradation of mRNAs requires understanding how Hfq binds to the 3′ ends of mRNAs with poly(A) tails, as well as with PAP and possibly other RNA processing enzymes.
Initial studies on Hfq binding to RNA homopolymers and oligomers demonstrated that Hfq has a strong affinity for poly(A) and An oligomers with n > 15 (Carmichael et al. 1975; de Haseth and Uhlenbeck 1980b). Studies on the binding of mutant Hfq to An oligomers indicated that the distal surface of the Hfq hexamer (Hfq6) interacts with poly(A) sequences (Mikulecky et al. 2004; Sun and Wartell 2006). A binding model proposed to accommodate information on the complex (Brennan and Link 2007), and a recent crystal structure of E. coli Hfq and A15 imply that the Hfq6 forms a 1:1 complex with An oligomers. However, experimental studies employing several methodologies suggested different stoichiometries for Hfq and oligoriboadenylates. Isothermal titration calorimetry suggested one Hfq6 bound to two A18 (Mikulecky et al. 2004), while fluorescence anisotropy, fluorescence quenching and a gel shift assay supported a model in which two Hfq6 was bound to one A18 (Sun and Wartell 2006).
DsrA is an 87-nucleotide (nt) sRNA that acts as a positive regulator for the translation of the stationary phase sigma factor RpoS. Hfq facilitates DsrA binding to the leader region of the rpoS mRNA and releases an inhibitory stem–loop that sequesters the Shine-Delgarno (SD) sequence (Cunning et al. 1998). Hfq binds both DsrA and rpoS mRNA with similar affinities (Soper and Woodson 2008; Updegrove et al. 2008). Studies have explored the number of Hfq molecules binding to each RNA participant. Gel shift measurements yielded data supporting a 2:1 (Hfq6:RNA) binding model for a 138-nt segment of rpoS mRNA, DsrA (Lease and Woodson 2004), and DsrADII (Sun and Wartell 2006), while isothermal titration calorimetry indicated a 1:1 complex for Hfq6 binding to DsrA and a segment of rpoS mRNA (Mikulecky et al. 2004).
The ability of Hfq to stimulate sRNA–mRNA duplex formation has been observed under both in vitro and in vivo conditions. How Hfq recognizes and binds each of the RNAs and facilitates their pairing remains obscure. Evidence that Hfq can alter secondary and/or tertiary structure of some sRNAs and mRNAs lends support to the notion that Hfq acts as a chaperone and modulates the sRNA and/or mRNA structure, making one or the other RNA more amendable for heteroduplex formation. Another role ascribed to Hfq is an ability to bind and hold two pairing RNA molecules simultaneously, thus bringing them in close proximity and driving the reaction to favor sRNA–mRNA duplex formation. However, we note that the ability of Hfq to separately bind two complementary RNAs is not always sufficient to promote RNA pairing (Arluison et al. 2007). Exactly how Hfq brings together two independent RNA molecules depends on the number of Hfq hexamers required to bind each RNA molecule and the number and type of RNAs that can simultaneously bind each Hfq hexamer. The stoichiometry of Hfq6 binding to RNA is clearly pertinent to understanding the mechanism of how Hfq promotes ribo-regulation.
The focus of the current work was to determine the stoichiometry of the strong binding complexes of Hfq with A18 and DsrADII. The oligoriboadenylate A18 mimics the size and sequence of poly(A) tails at the 3′ end of mRNAs, and results on how this oligonucleotide interacts with Hfq may be of functional significance in terms of Hfq's role and mechanism in facilitating polyadenylation by poly(A) polymerase. DsrADII, a 38-nt portion of DsrA (nucleotides 23–60), competes with DsrA for binding to Hfq (Brescia et al. 2003). It contains a stem–loop and U-rich segment of DsrA that binds Hfq. Mass spectrometry, fluorescence anisotropy, and analytical ultracentrifugation provide evidence supporting a 1:1 stoichiometry for Hfq6 and oligo A18 as well as for Hfq6 and DsrADII. A competition electrophoretic gel mobility shift assay also supports 1:1 complexes for Hfq6 binding to A18 as well as to full-length DsrA, RprA, and OxyS.
RESULTS
MALDI-TOF mass spectroscopy indicates Hfq6 forms a 1:1 complex with DsrADII, A18, and OxyS-18
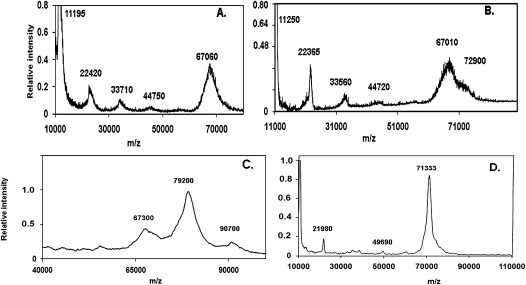
MALDI-TOF (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight) mass spectrometry was first used to examine the molecular mass of E. coli Hfq alone and then as a complex with A18. These experiments were done in the absence of cross-linking as well as after EDC cross-linking of the Hfq-A18 complex prior to mass spectrometric analysis. The MALDI-TOF spectrum of Hfq shown in Figure 1a was carried out with EDC cross-linking and reveals discrete ions with m/z ratios corresponding to the Hfq monomer and multimers up to the hexamer (67,060 Da; theoretical mass, 66,998 Da). This observation is in agreement with a previous study (Moller et al. 2002a) and illustrates that Hfq can stably exist as multimers up to the hexamer in the laser desorption ionization process. We note that macromolecules are generally expected to be singly charged ions in MALDI-TOF experiments (Karas et al. 2000).
FIGURE 1.
MALDI-TOF m/z spectra of 2 μM Hfq6 (A), 2 μM Hfq6 and 0.7 μM A18 (B), 8 μM Hfq6 and 4 μM DsrA domain II (C), and 4 μM Hfq6 and 2 μM OxyS-18 (D). All samples were prepared in the 0.2 M Na+ solvent and matrix solution as described in Materials and Methods.
The addition of 0.7 μM A18 to 2 μM Hfq6 resulted in the formation of an additional peak corresponding to a molecular mass of 72,900 Da (Fig. 1b). Since the theoretical mass of A18 is 5,840 Da, this new peak is very close to an expected complex with a 1:1 ratio of Hfq6 to A18 (theoretical mass, 72,839 Da). No peaks were observed at the molecular mass corresponding to 2:1 or 1:2 ratios of Hfq6 to A18. Similar results were also obtained when 0.07 μM A18 and 0.2 μM Hfq6 were employed with and without EDC cross-linking (data not shown). The addition of EDC increased the relative signal intensities of the Hfq6 and Hfq6•A18 complex over the Hfq subunit multimers, consistent with suppression of hexamer dissociation.
The Hfq6–DsrADII complex required a more robust cross-linking agent to withstand the conditions imposed by the MALDI-TOF experiment. Formaldehyde proved to be an efficient cross-linker and allowed detection of the Hfq6–DsrADII complex. Figure 1c shows a spectrum resulting from a mixture of 8 μM Hfq6 with 4 μM DsrADII. A pronounced peak occurs at a m/z ratio of 79,200 flanked by less pronounced peaks of 67,300 and 90,700. Since the theoretical molecular weight of DsrADII is 12,031 Da, the large middle peak is consistent with one Hfq6 bound to one DsrADII. The smaller and larger molecular weight peaks are consistent with Hfq6 and one Hfq6 bound to two DsrADII molecules, respectively. DsrADII has been shown to form two bands at low μM concentrations in a polyacrylamide gel environment (Sun and Wartell 2006). When 2 μM Hfq6 was added to 1 μM DsrADII, only the 79,000 and 67,000 m/z peaks were observed (data not shown). Unfortunately a MALDI-TOF experiment with full-length DsrA and Hfq gave weak or negligible signals barely above background at the m/z ratio expected for Hfq6•DsrA or higher masses. The larger negative charge intrinsic to the full-length DsrA molecule appears to compromise a study of this complex by this method.
OxyS is a 109-nt sRNA that was shown to bind Hfq in vitro and in vivo and acts as a negative regulator for the translation of the rpoS mRNA. A 18-nt portion of OxyS sRNA that spans nucleotides 64–81 is thought to be critical for Hfq binding based on the observation that an oligonucleotide complementary to this region strongly inhibits Hfq from binding to the full-length OxyS molecule (Zhang et al. 2002). MALDI-TOF was used to assess the stoichiometry of Hfq binding to this segment of OxyS. When 4 μM of Hfq6 was added to 2 μM OxyS-18 and formaldehyde is used as the cross-linking agent, only one extremely large peak was observed at an m/z ratio of 71333 (Fig. 1d). With the theoretical molecular weight of OxyS-18 being 5769.6 Da, the large peak in Figure 1d is in good agreement with one Hfq hexamer bound to one OxyS-18. No peak was detected at an m/z ratio corresponding to either 1:2 or 2:1 Hfq6 to OxyS-18 stoichiometry.
Analytical ultracentrifugation analysis of Hfq•A18 complex in solution
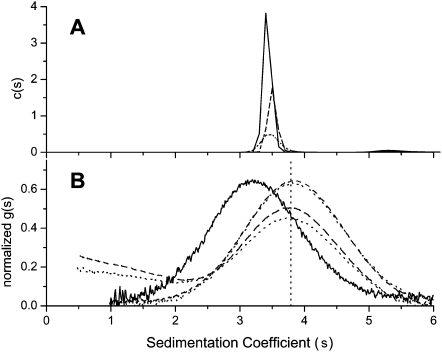
Analytical ultracentrifugation analysis was employed to determine the stoichiometry of the Hfq-A18 complex in aqueous solution. Sedimentation velocity of Hfq alone in 0.5 M NaCl and 20 mM Tris (8.2) indicated a single major species with a sedimentation coefficient (s) of s = 3.42 sec <3.41, 3.44> and no more than 2% of a higher molecular weight aggregate with s = 5.56 S. Figure 2a shows the results of a sedimentation velocity experiment of Hfq analyzed using the c(s) method (Schuck et al. 2002). The sedimentation coefficient distribution was independent of loading concentrations from 3.2–12.1 μM Hfq in moles hexamer. Direct boundary fitting of the sedimentation velocity data using SedAnal (Stafford and Sherwood 2004) indicated a molecular weight for the 3.42 S species of 64,815 Da <59,733, 70,301>. This value is slightly lower than the expected value of 66,998 Da and is consistent with the hexamer being the dominant Hfq species at these concentrations. The slightly lower than expected value can be explained by uncertainty in the partial specific volume employed or the influence of the minor aggregate on the fit. (Traces of sediment velocity run and model fitting using SedAnal are given in Supplemental Fig. S1.)
FIGURE 2.
(A) Sedimentation coefficient distribution c(s) determined by program Sedfit for three different Hfq6 concentrations, 3.2, 5.7, and 12 μM shown as dotted, dashed, and solid lines, respectively. The average integrated value for these data is 3.51 ± 0.03 S. (B) Sedimentation coefficient distribution displayed as normalized g(s) for Hfq6 at 6.9 μM alone as solid line (average integrated value for Hfq data is 3.42 ± 0.04 S), and with 4.4 μM and 8.3 μM FAM-A18 added. Upper pair of overlapping dashed and dotted lines show the 6.9:4.4 mixture evaluated by absorbance at 274 nm and 495 nm, respectively. Lower pair of dashed and dotted lines display the 6.9:8.3 mixture evaluated at the same two wavelengths. Lack of alignment of c(s) and g(s) peaks for Hfq6 alone (3.51 S vs. 3.42 S) is attributed to minor components affecting the main c(s) peak.
Figure 2b shows the normalized g(s) distribution of concurrently run sedimentation velocity experiments which examined 6.9 μM Hfq6 alone, 6.9 μM Hfq6 with 4.4 μM FAM-A18, and 6.9 μM Hfq6 with 8.3 μM FAM-A18. FAM-A18 binding increased the sedimentation coefficient of Hfq6 from 3.3S to 3.9S. At the concentration ratio of [FAM-A18]/[Hfq6] of 1.2, a trailing boundary of excess FAM-A18 is observed. Free FAM-A18 has a sedimentation coefficient of 1.355 S <1.345, 1.364> with no evidence of concentration dependence or additional species (data not shown). Using the SedAnal software, a good fit to the Hfq-A18 data was obtained with a model that assumed Hfq hexamer binds A18 with a 1:1 stoichiometry. The best Sedanal fit (constraining S for Hfq and FAM-A18) returned a K of 1.71 × 107 M−1 <0.85, UB>. The unbounded upper limit means all larger values of K are indistinguishable in the least-squares sense. A subsequent run with a new protein sample returned a larger K ∼1010 M−1 with 95% confidence limits of <7.5 × 107, UB>. Thus the data is consistent with a tight 1:1 Hfq-A18 complex with an affinity in excess of 107M−1.
Sedimentation equilibrium runs of 2, 4, and 8 μM Hfq6 alone and mixed with 1:1 molar ratios of FAM-A18 confirmed that the stoichiometry of the Hfq6•FAM-A18 complex in solution is not 2:1, but 1:1. The evaluated molecular weight of Hfq alone was 61.475 kDa <58.8, 64.2> (rms = 0.00596) (Supplemental Fig. S2), similar to the value obtained from sedimentation velocity analysis. Analysis of the sedimentation equilibrium data of the Hfq•FAM-A18 mixtures, monitored at the FAM-A18 absorbance peak of 495 nm, yielded a molecular weight of 68.93 kDa <67.4, 70.4> (rms = 0.00724) (Supplemental Fig. S2). This clearly does not correspond to a complex consisting of 2 Hfq6 molecules and one A18 molecule but is consistent with a 1:1 complex.
Gel mobility shift study of wild-type Hfq and Hfq-65 binding to A18 and other RNAs
Previous gel mobility experiments in which A18 or other RNAs were titrated with Hfq at concentrations above apparent Kd values indicated 2:1 Hfq6 to RNA stoichiometry (Lease and Woodson 2004; Sun and Wartell 2006; Updegrove et al. 2008) . Since these previous results conflict with the above findings, we examined the stoichiometry of Hfq•A18 complexes in the gel environment using a different approach that relies on a qualitative comparison rather than quantative analysis of band intensities. The Hfq•A18 complexes that formed in the presence of wild-type (wt) Hfq and Hfq-65 were determined. Hfq-65 is a truncated variant of wt Hfq consisting of 65 residues from the N-terminal end. This truncated Hfq was previously shown to bind DsrA two- to threefold less well than wt Hfq, and to A27 with an affinity similar to wt Hfq (Vecerek et al. 2008). Lane 3 of Figure 3a shows the gel-shift of the Hfq-65•A18 complex in a 6% PAG. The Hfq-65•A18 complex migrates with a slower mobility than the wt Hfq•A18 complex (lane 2) in spite of its reduced size. A plausible explanation of this phenomenon is the increased positive charge of Hfq-65 compared to wt Hfq. Hfq-65 has four less negatively charged residues (Asp 97, Glu 99, Glu 100, and Glu 102) and one less positively charged residue (Arg 66) than each wt Hfq subunit. When equimolar amounts of wt Hfq and Hfq-65 were mixed with A18 for 5 min and run into the gel, two bands were observed corresponding to wt Hfq•A18 and Hfq-65•A18 (Fig. 3a, lane 4). This result is consistent with a 1:1 stoichiometry for complexes of Hfq6 and A18. If the stoichiometry of the Hfq•A18 complexes were two Hfq6 and one A18, a band of intermediate mobility would be expected in lane 4. Changing the ratio of wt Hfq and Hfq-65 concentrations altered the intensity of the two bands in direct proportion, but no additional band is observed (Fig. 3a, lanes 5,6).
FIGURE 3.
DsrA and A18 bind both wt Hfq and Hfq-65 in a 1:1 stoichiometry. Varying concentrations in moles hexamer/L of wt Hfq and Hfq-65 were added to 1 μM FAM-A18 (A), 4 nM 32P-DsrA (B), and 1 μM 32P-DsrA (C). Similar results were obtained when 32P end-labeled RprA and OxyS sRNAs were added to both wt Hfq and Hfq-65.
When 4 nM 32P-labeled DsrA was added to 50 nM of either wt Hfq or Hfq-65 (moles hexamer), most of the RNA was shifted to a slower moving complex. Under these conditions, the DsrA•Hfq-65 complex migrates faster than the DsrA•wt Hfq complex (Fig. 3b, lanes 2,3). Since DsrA has considerably more negative charge than A18, it will likely dominate the charge differences between wt Hfq and Hfq-65. The size difference between wt Hfq and Hfq-65, rather than their intrinsic charge difference, appears to be the governing factor in the migration of these Hfq•DsrA complexes. When 25 nM wt Hfq and 25 nM Hfq-65 (moles hexamer) were added to 4 nM DsrA, only two apparent slow migrating bands were evident; one corresponding to the DsrA•wt Hfq complex and the other corresponding to the DsrA•Hfq-65 complex (Fig. 3b, lane 4). Similarly, when 1 μM each of wt Hfq and Hfq-65 was added to 1 μM DsrA, only two slow migrating bands were observed (Fig. 3c, lane 4). The outcome was the same when 25 nM wt Hfq and 25 nM Hfq-65 was added to 4 nM 32P-labeled OxyS or RprA (data not shown). The results are consistent with a 1:1 stoichiometry for Hfq6 binding to these RNAs.
Hfq binding to A18 or DsrADII monitored by fluorescence anisotropy.
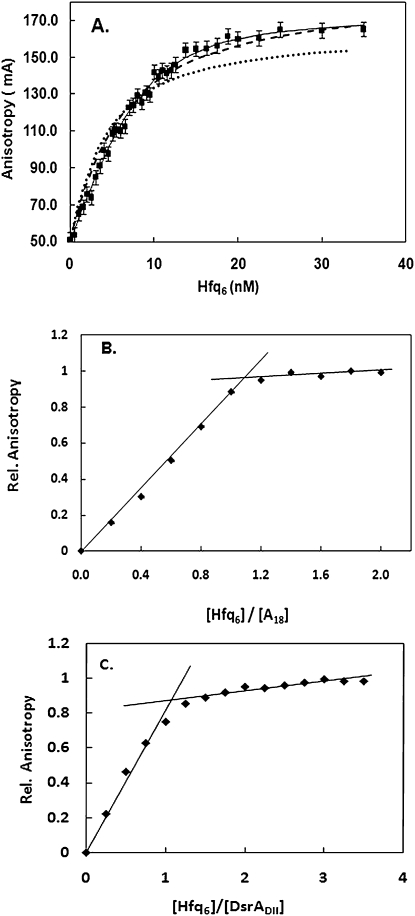
Another experimental approach that suggested two Hfq6 bound A18 was fluorescence anisotropy (Sun and Wartell 2006). A model in which two Hfq6 sequentially bound A18 gave a better fit to fluorescence anisotropy data than a model that assumed a 1:1 complex. We have re-examined and extended these measurements and the analyses in light of the above results. Figure 4a shows that the 2:1 binding model (solid line) does give the best fit to the titration of Hfq to 2 nM of FAM-labeled A18. The dotted line is the nonlinear least-squares fit of the 1:1 model (Equation 1 in the Materials and Methods), with Kd a variable parameter and the other parameters (Af, Ab, [R]T, [P]T) determined from the experimental data. The Ab value of 0.166 was determined from the horizontal asymptote to the anisotropy values of the four highest Hfq6 concentrations used in the experiment. If, however, one allows Ab to be somewhat flexible and assume a value of 0.185, the fit of the 1:1 model approaches that of the 2:1 model (dashed line). Considering that the 2:1 model has more variable parameters with which to fit the data, the difference between the two models no longer persuasively favors the 2:1 model. Both models indicate Kd values in the range of 5–10 nM.
FIGURE 4.
Fluorescence anisotropy titration of FAM-A18 with Hfq. (A) Comparison of experimental data with 2 nM FAM-A18 (squares) to best fit of 2:1 model (solid line), 1:1 model with Kd variable (circles), and 1:1 model with variable Kd and Ab (dotted line). Parameters for: 2:1 model; K1 = 10.1 nM, K2 = 5 nM, Ab1 = 0.148, Ab2 = 0.172. For 1:1 models; K1 = 4.4 nM, Ab = 0.166 for dotted line, K1 = 5 nM, Ab = 0.185 for dashed line. (B) Experimental anisotropy measurements of 5 μM FAM-A18 titrated with Hfq6. (C) Experimental anisotropy measurements of 2 μM DsrADII titrated with Hfq6.
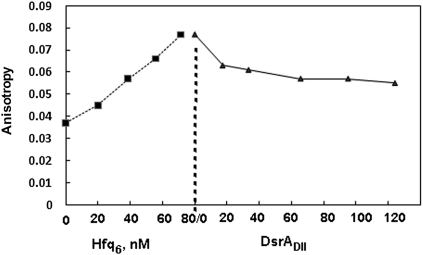
To further examine the stoichiometry of Hfq6 binding to A18 using this experimental approach, the titration of A18 with Hfq was carried out at concentrations well above the Kd (5 μM A18) where stoichiometric binding is expected. Figure 4b shows that the anisotropy change of A18 saturates at a ratio of Hfq6 and A18 consistent with a 1:1 stoichiometry. A similar experiment conducted with 2 μM DsrADII also showed a break in the plot at a 1:1 molar ratio of Hfq6 and DsrADII (Fig. 4c). The Kd of Hfq6 binding to DsrADII under the conditions of the experiment (0.1 M NaCl + 20 mM Tris) was ∼4 nM (Supplemental Fig. S3).
Hfq interaction with both A18 and DsrADII
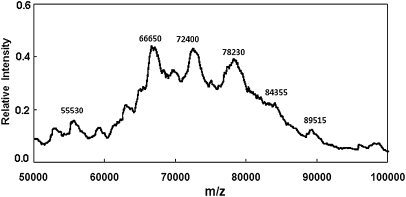
Polyacrylamide gel mobility shift experiments have previously demonstrated that Hfq can form a complex with a poly(A) sequence and DsrA (Brescia et al. 2003). The observation of a “super shifted” gel band consisting of the above three components indicates a ternary complex but does not exclude the possibility that more than one Hfq hexamer is needed to form this complex. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry was employed to examine if a mass could be detected consistent with a complex formed by Hfq6, DsrADII, and A18. We mixed 10 μM Hfq6 with 5 μM DsrADII and 5 μM A18 for 15 min, which was treated with formaldehyde as described in Materials and Methods. Figure 5 shows the MALDI-TOF spectrum of this sample. Peaks were observed corresponding to molecular masses very similar to Hfq6 (66,650 Da; theoretical mass, 66,998 Da), Hfq6•A18 (72,400 Da; theoretical mass, 72,839 Da), and Hfq6•DsrADII (78,230 Da; theoretical mass, 79,029 Da). A small but reproducible peak was observed in the region corresponding to a mass of 84,355 Da, consistent with the combined mass of one Hfq6, one A18, and one DsrADII (theoretical mass, 84,869 Da). We note that the lower observed masses compared to theoretical masses (by 350–700 Da) appears to be due to external calibration error.
FIGURE 5.
MALDI-TOF m/z spectrum of 10 μM Hfq6 plus 5 μM DsrADII and 5 μM A18 prepared in the 0.2 M Na+ solvent, cross-linked with formaldehyde, and mixed with matrix solution as described in Material and Methods.
The small peak corresponding to a mass of 55,530 Da is consistent with five subunits of Hfq (theoretical mass, 55,832 Da). Small nearby peaks were reproducibly observed and may be related to four or five subunits of Hfq with A18, DsrADII, or both. The intensities of peaks corresponding to the unbound forms of four and five Hfq subunits were slightly higher (relative to the Hfq monomer peak) in the presence of both DsrADII and A18 (∼3%) compared to when only one RNA was present (∼2%). Not surprisingly, the Hfq•A18 and Hfq•DsrADII peaks were smaller by about 2.5-fold when both DsrADII and A18 were present compared with spectra of Hfq and only one RNA. The small peak at 89,515 is consistent with one Hfq6 and a dimer of DsrADII and is similar to the small peak observed with Hfq and DsrADII (Fig. 1c).
The intensity in the region of the 84,355 Da mass in Figure 5 is consistent with a 1:1:1 Hfq6•A18•DsrADII ternary complex; however, this peak was considerably smaller than the peaks corresponding to Hfq6•A18 or Hfq6•DsrADII. This may reflect an intrinsic instability of this ternary complex or a limitation of the method in reporting complexes of Hfq6 with two RNAs.
To explore this question in solution, we examined the effect of adding DsrADII on the fluorescence anisotropy of a preformed complex of Hfq6•FAM-A18. Hfq6 was added to 100 nM FAM-A18 in a solvent of 0.1 M NaCl+ 20 mM Tris (8.3), increasing the anisotropy from 0.037 to 0.080, about 45% of the maximum anisotropy change induced by saturating Hfq6. Adding aliquots of DsrADII to produce a final solution with 75 nM FAM-A18, 65 nM DsrADII, and 63 nM Hfq6 reduced the anisotropy by about 30% (Fig. 6). If a ternary Hfq6•A18•DsrADII complex is stable relative to the 1:1 Hfq6•RNA complexes, an increase rather than decrease in anisotropy is expected. This experiment was repeated using the complete DsrA, surmising its higher molecular weight and strong binding to Hfq6 may be required to observe the expected anisotropy increase resulting from formation of a ternary complex. However the outcome was similar (data not shown). When Hfq and FAM-DsrADII were preformed and A18 or polyA added to the solution, a similar decrease in anisotropy was observed (data not shown). The above results were surprising given the outcome of gel shift experiments (Brescia et al. 2003; Mikulecky et al. 2004; Updegrove et al. 2008) that clearly show complexes can form involving Hfq6, DsrA, and a poly A sequence. The apparently disparate implications of the two types of experiments may, however, be reconcilable as discussed below.
FIGURE 6.
Fluorescence anisotropy experiment of FAM-A18 with Hfq and DsrADII. Hfq was titrated to 100 nM FAM-A18 to give 0.080, ∼45% of the maximum anisotropy. Then aliquots of unlabeled DsrADII were added to give the concentrations shown.
DISCUSSION
The results from mass spectrometry, analytical ultracentrifugation, fluorescence anisotropy, and competition gel mobility shift assay all point to a 1:1 stoichiometry for the Hfq6•A18 and Hfq6•DsrADII complexes. The more limited studies on Hfq binding to the RNAs DsrA, RprA, OxyS and OxyS-18 support a similar conclusion. These experiments were carried out with RNA concentrations from 4 nM to 5 μM in solvents with 0.1–0.5 M Na+. The 1:1 stoichiometry is the same value determined by isothermal titration calorimetry measurements of Hfq6 binding DsrA or a 140-nt rpoS mRNA segment (Mikulecky et al. 2004), but differs from the 2:1 (Hfq6:RNA) stoichiometry inferred from gel shift assays of Hfq6 binding to DsrA, a 138-nt rpoS RNA (Lease and Woodson 2004), DsrADII (Sun and Wartell 2006), and RprA (Updegrove et al. 2008), as well as the fluorescence anisotropy and fluorescence quenching study of Hfq6 binding to A18 (Sun and Wartell 2006). Since two methods used in the current work, mass spectrometry and sedimentation equilibrium, are robust model-independent approaches, our results raise the question why a 2:1 stoichiometry was inferred from previous investigations.
The results described by Figure 4a provide an explanation why a 2:1 stoichiometry was previously misinterpreted from the fluorescence anisotropy measurements of Hfq binding to FAM-A18 at low nanomolar concentrations. The anisotropy of the fully bound FAM-A18, Ab, appears to have been previously underestimated. Increasing the experimentally derived value of Ab by ∼11% produced a much better fit to the data using the 1:1 model. Assuming some flexibility in the Ab value can be justified since there is uncertainty in the Hfq6 concentration required to saturate binding of FAM-A18. With this adjustment to Ab, the difference between the predictions of the 2:1 model versus the 1:1 model no longer persuasively favors the 2:1 model.
The 2:1 stoichiometry inferred from the gel shift assay was suggested by equilibrium binding analyses of gel shift data obtained using 2–4 nM RNA that indicated a Hill coefficient above 2, as well as from data obtained with 400 nM to 1.0 μM of RNA, concentrations above the Kd (Lease and Woodson 2004; Sun and Wartell 2006). Since similar outcomes came from different laboratories, it seems unlikely that differences in binding activity of Hfq preparations influenced this outcome. Also, the Hfq used in the current experiments, which yield a 1:1 stoichiometry, reproduced the outcome of the gel shift assay (data not shown). While a definitive argument cannot yet be made why the gel shift assay yielded a 2:1 stoichiometry, several factors that might complicate interpretation of gel shift data may provide an explanation.
The equilibrium established in the sample solution may be altered as the low ionic strength buffer (0.5× TBE) exchanges with the loading buffer as the macromolecules enter the gel or during electrophoresis (Bloomfield et al. 2000). Although a low ionic strength solution may stabilize Hfq•RNA complexes, it has also been shown to produce well-ordered fibers of Hfq6 (Arluison et al. 2006). If Hfq6 aggregates in the gel environment it could alter the nature or amount of the Hfq•RNA complexes.
Factors governing the mass transport of Hfq•RNA complexes in a gel may also contribute to misleading interpretation of gel shift data, independent of the potential for Hfq6 aggregation. Using a phenomenological theory of gel electrophoresis, Cann (1989) simulated the gel patterns produced by several protein–DNA interactions employing association and dissociation rate constants representative of the interactions and experimentally derived transport parameters. The simulations validated the application of the gel shift method for determining binding constants and stoichiometry for strong interactions with association (ka) and dissociation (kd) rate constants of ka = 3 × 109 M−1sec−1, kd = 1.3 × 10−4 sec−1. However the simulation also showed that a significant amount of the initial protein–nucleic acid complex entering the gel can irreversibly dissociate during electrophoresis. When parameters mimicking an intermediate strength complex were used (ka = 1.3 × 106 M−1sec−1, kd = 1.3 × 10−4 sec−1) with 10 nM each of protein and nucleic acid, 49% of the initial protein–nucleic acid complex irreversibly dissociated from this band during electrophoresis. The extent of irreversible dissociation of the initial protein–nucleic acid complexes clearly depends on the concentrations used and the parameters of the system. The importance of these considerations has been demonstrated for properly interpreting gel shift data on a repressor-DNA operator system (Kleinschmidt et al. 1991).
It is worth noting that in the above example although electrophoresis depleted the amount of material in the nucleic acid–protein band, the unbound nucleic acid band could still be used to calculate the equilibrium dissociation constant to good accuracy (Cann 1989). Thus gel shift data can be used to evaluate binding constants, even when the nucleic acid–protein bands do not accurately reflect the initial amount of these complexes. We note that interpretation of the competition gel shift experiment described in Figure 3 does not depend on a quantitative evaluation of band intensities. The absence of a band intermediate between the shifted bands corresponding to RNA bound to wt-Hfq or Hfq-65 is consistent with 1:1 complexes.
The third method that suggested a 2:1 stoichiometry for Hfq6•A18 was fluorescence quenching of Hfq's tyrosines by A18. Quenching of Hfq fluorescence saturated when the amount of added A18 reached a molar ratio of 0.5:1 (A18: Hfq6) (Sun and Wartell 2006). Controls indicated that the inner filter effect (Lakowicz 2006) due to the absorbance of A18 at the excitation wavelength was negligible. We are currently unable to reconcile the apparent 2:1 stoichiometry implied from this experiment with the 1:1 stoichiometry determined in the current work. It is possible that A18 binding has a complex effect on the fluorescence of Hfq's three tyrosines such that a straightforward interpretation of the data is quantitatively flawed.
Several lines of evidence have shown that Hfq6 possesses two distinct RNA binding surfaces (Mikulecky et al. 2004). The proximal surface appears to be involved in Hfq binding to a single-stranded sequence with several uracils and/or adenines adjacent to one or more hairpins (Schumacher et al. 2002; Zhang et al. 2002; Geissmann and Touati 2004). The distal surface of Hfq6 binds to a repeated motif (ARN)n, n ≥ 4 (with R a purine, N any nucleoside) (Link et al. 2009). The latter motif includes the poly(A) sequence at the 3′ ends of mRNAs, and segments found in the 5′ leader region of at least two mRNAs (Soper and Woodson 2008; Salim and Feig 2010). With two distinct binding surfaces, a single Hfq hexamer has the potential to bind a mRNA and sRNA simultaneously.
The MALDI-TOF results suggest the existence of a Hfq6•A18•DsrADII complex; however, the small size of the peak does not support the notion that a 1:1:1 complex is very stable. The fluorescence anisotropy experiment in Figure 6 also does not provide evidence for a stable ternary complex in solution. DsrA and A18 do not appear to bind Hfq independently under the conditions of the experiment. This appears to contradict the observation that polyA sequences can form a ternary complex with Hfq6 and DsrA in polyacrylamide gels. A possible explanation of these observations may be related to the low ionic strength solvent and cage effect of the gel environment. Studies by de Haseth and Uhlenbeck (1980a) as well as the more recent demonstration of Hfq fibers (Arluison et al. 2006) indicate that low ionic strength solutions promote Hfq aggregation. The gel environment may promote Hfq6 aggregation and enable ternary complexes that involve more than one Hfq6. These complexes may not form in the 0.1 M Na+ solution employed in the anisotropy experiment.
A counter hypothesis that can explain why putative ternary complexes are not reported by fluorescence anisotropy is more difficult. If the dissociation lifetime of a ternary complex is shorter than its rotational correlation time (τc) it could go undetected. For a 1:1:1 complex of DsrA, FAM-A18, and Hfq6, τc can be estimated to be ∼60 nsec (Serdyuk et al. 2007). A dissociation lifetime this short is inconsistent with a stable ternary complex. The total anisotropy reflects the sum of each anisotropic species. Binding of DsrADII or DsrA to FAM-A18•Hfq6 is expected to slow the rotational correlation time and increase anisotropy. If binding also induces a conformational change that partially releases the FAM –A18, it may cancel the effect of the increased size on the rotational correlation time and in principle could reduce the anisotropy. In order to explain all of the results, this would also have to be true for A18 binding to DsrADII•Hfq6. This seems a less likely explanation of the data than displacement of the bound RNA from Hfq6 by the other RNA.
Regardless of the uncertainty and a definitive explanation for the stoichiometry reported by the previous gel results and the nature of the polyA-Hfq-DsrA complex observed in gels, the major conclusion from this work, that Hfq6 has a 1:1 binding stoichiometry with RNA at concentration and ionic strength conditions mimicking a cell environment, addresses a question important to understanding how Hfq facilitates interactions between RNAs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Purification and characterization of wt and mutant Hfq
The Impact-CN intein system (New England Biolabs) was used to purify Hfq proteins as previously described (Sun and Wartell 2006). The plasmids used to overexpress the Hfq proteins contained the E. coli hfq gene inserted into SapI-SmaI–digested pTYB11 plasmid (pEcHfq) or mutant derivatives (see below). Protein purification was carried out according to the recommendation of the manufacturer using strain ER2566. Cell lysis was carried out using a French press. The cell lysate was centrifuged and the supernatant loaded onto a chitin column. The column was extensively washed with the lysis/wash buffer of 20 mM Tris (pH 8.3) and 1 M NaCl prior to incubation of the column with this buffer plus 40 mM dithiothreitol. The eluted protein was concentrated and buffer-exchanged to 0.5 M NaCl and 20 mM Tris (pH 8.3) using centrifugation filtration units.
To remove contaminating nucleic acids, Hfq preparations were subjected to a micrococcal nuclease treatment. Twenty-five microliters of 300 U/mL micrococal nuclease (Worthington Biochemical) was added to 1 mL of 0.3–0.4 OD274nm Hfq in 0.2 M NaCl, 20 mM Tris (pH 8.5), and 5 mM CaCl2 and incubated for 45 min at 37°C. This nuclease has a strict dependence on Ca2+. Ten microliters of 0.5 M Na2EDTA was added, and sample was washed and concentrated in 15 mL of 0.5 M NaCl and 20 mM Tris (pH 8.3) using 30 kDa MWCO Amicon Utrafiltration cell.
The mutant Hfq protein, Hfq-65, was produced for this study from the plasmid pHfq-65, which was generated from pEcHfq using the QuikChange Mutagenesis Kit from Stratagene (Sun and Wartell 2006). Oligonucleotides employed placed a stop codon at position 66 of the hfq gene: 5′- GCGATTTCTACTGTTGTC CCGTCTTAGCCGGTTTCTCATCACAG-3′ and 5′-CTGTGATGAGAA ACCGGCTAAGACGGGAC AACAGTAGAAATCGC-3′. The plasmid construct was verified by DNA sequencing. The purification procedure for the mutant protein was similar to that used for wt Hfq. All proteins displayed expected molecular weights on a denaturing sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Concentrations were determined using an extinction coefficient of ε = 2900 M−1 cm−1 at 274 nm for the truncated protein and 4250 M−1 cm−1 for wt Hfq (Gill and von Hippel 1989). Ultraviolet spectra showed absorbance ratios of A275nm/A255nm (peak to valley) of ≥1.8. Analysis of the spectra indicated <5% contaminating nucleic acids (Sun and Wartell 2006).
RNA synthesis and purification
The following RNAs were purchased commercially (Integrated DNA Technologies) and purified by HPLC: DsrADII (AACGAAUUUUUUAAGUGCUUCUUGCUUAAGCAAGUUUC), OxyS-18 (GAAUAACUAAAGCCAACG), and A18. DsrADII and A18 were also purchased with 6-carboxyfluorescein (FAM) linked to their 5′ end. The full-length DsrA, OxyS, and RprA RNAs were cloned as described previously and transcribed using a T7 MEGAscript High Yield RNA transcription kit (Ambion) (Updegrove et al. 2008). They were 32P-labeled at their 5′ end using standard phosphatase and kinase reactions and purified by gel extraction (Sambrook and Russell 2001).
Mass spectrometry and cross-linking of Hfq to RNA
Twenty microliter samples were prepared by adding Hfq to fixed amounts of A18, DsrADII, or OxyS-18 in phosphate binding buffer (0.2 M NaCl, 20 mM Na2HPO4 at pH 7.8). Concentrations are described in Results. For the Hfq-A18 mixture, 10 μL of 0.2 M EDC (1-ethyl-3-3-dimethylaminopropyl carbodiimide hydrochloride; Pierce) was added and allowed to react for 4 h at room temperature. For the other Hfq-RNA mixtures, 2 μL of a 3% formaldehyde solution was added and allowed to react for 15 min at room temperature. One microliter of 3 M glycine (in water) was then added to quench the reaction (Niranjanakumari et al. 2002). Twenty microliters of the Hfq-RNA solutions described above was then concentrated to 3 μL with a C4 ZipTip (Millipore) and then mixed with 3 μL of matrix solution. The matrix solution was prepared by adding 20 mg of sinapinic acid and 50 mg ammonium citrate in 500 μL of 18 MΩ deionized water. One microliter of analyte-matrix mixture was then deposited onto a 100-well stainless steel MALDI plate. The MALDI-MS experiments were performed using a Voyager DE STR MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer (Applied Biosystems) equipped with a 337-nm N2 laser (3 Hz). The accelerating voltage, grid voltage, and delay time were typically 25 kV, 91%, and 1500 nsec, respectively. The laser intensity was checked daily to obtain the best signal-to-noise ratio. Mass spectra were obtained by averaging 10–50 laser shots.
Analytical ultracentrifugation
Sedimentation velocity
Sedimentation studies were performed in a Beckman Optima XLA analytical ultracentrifuge equipped with absorbance optics and an An60 Ti rotor at 19.7°C. Temperature was calibrated as described previously (Liu and Stafford 1995). Velocity data were typically collected at the appropriate speeds using 274 nm for Hfq and 495 nm for FAM-A18 at a spacing of 0.01 cm with one flash at each point in a continuous-scan mode. When collecting data at multiple wavelengths, care must be taken to collect data at peaks to avoid dramatic signal variations due to wavelength uncertainty (±4 nm) with the XLA. All experiments were initially analyzed with Sedfit to produce c(s) distributions (Schuck et al. 2002) and with DCDT+2 to produce g(s) distributions and weight average S value (Philo 2006). Direct boundary fitting of velocity data to discrete models can also be performed with the program Sedanal (Stafford and Sherwood 2004). Analysis with Sedanal requires input of molecular weight, extinction coefficients, and density increments (typically estimated from 1-vbar*rho values). The buffer solution density was estimated in Sednterp to be 1.01920 gm/mL at 19.7°C. The vbar of Hfq was estimated with Sednterp (Laue et al. 1992) to be 0.7248. The vbar of FAM-A18 is assumed to be 0.55. The extinction coefficient of FAM-A18 at 495 nm is 75,000 M−1cm−1 or, using a molecular weight of 6113 Da, 12.269 mL/mg/cm. The extinction coefficient of Hfq at 274 nm is 0.400 mL/mg/cm (Stafford and Sherwood 2004). Parameter uncertainty is calculated with an Fstat routine within Sedanal at the 95% confidence interval and reported in a <, > format.
Sedimentation equilibrium
Hfq alone (at 2, 4, and 8 μM) or mixed at a 1:1 ratio with FAM-A18 was spun at 19.7°C and at 12K, 16K, and 20K in six-channel double sector cells. Data on Hfq alone were collected at 274 nm. Data with mixtures of Hfq and FAM-A18 were collected at 495 nm. Equilibrium at each speed was judged with the software utility WinMATCH (http://www.biotech.uconn.edu/auf/?i=aufftp). This program makes a least-square comparison of successive scans to establish that equilibrium has been achieved. Values for density, vbar, and extinction coefficients were as described under Sedimentation Velocity. Nine data sets from three concentrations and three speeds were best fit to a single species model using Sedanal. Molecular weight uncertainty is calculated with Fstat as described above.
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
Gel mobility shift assay
Binding reactions of Hfq and FAM-A18 were carried out in the phosphate binding buffer (0.2 M NaCl, 20 mM Na2HPO4 at pH 7.8). wt Hfq, Hfq-65, or both were added to FAM-A18 and the reactions allowed to equilibrate at 25°C for 10 min prior to the addition of 3.2 μL of gel loading buffer (100 mM Tris-Cl at pH 6.8, 4% [w/v] SDS, 0.2% [w/v] bromophenol blue, 20% [v/v] glycerol). Final reaction volumes were 20 μL and contained 0.6% SDS. The SDS was added in order to enhance the negative charge of the Hfq•A18 complexes and enable them to migrate into the gel prior to the free A18 running out the bottom. The concentration of Hfq (moles hexamer) in each reaction varied between 2 and 3 μM, and the concentration of FAM-A18 was 1 μM. The total reaction volumes were electrophoresed into a 6% polyacrylamide (29:1) gel with 4% glycerol that was layered onto a 2.5-cm bottom plug consisting of 15% polyacrylamide (29:1). The latter was employed to slow and retain the free A18. The gel was 20 cm × 20 cm × 1.5 mm. Electrophoresis was conducted at 120 V at 4°C using 1× TBE buffer for ∼8 h. Analysis of the gels used excitation and emission wavelengths of 473 and 520 nm, respectively, of the Fujifilm Image Reader FLA-3000.
Similar competition gel assays were carried out in which wt Hfq, Hfq-65, or both were bound with 32P-labeled DsrA, RprA, or OxyS in 15 μL binding solution (50 mM NaCl, 50 mM KCl, 100 mM NH4Cl, 20 mM Tris-HCl at pH 8.0, 4% glycerol). The indicated amounts of Hfq were added to the indicated amount of sRNA and the reaction allowed to equilibrate for 10 min at 25°C prior to running on a 8% polyacrylamide (29:1) gel with 3% glycerol. Electrophoresis was conducted at 120 V at 4°C using 1× TBE buffer for ∼2 h. Imaging and analysis of the gels were made using the Fujifilm Image Reader FLA-3000.
Fluorescence anisotropy measurements
Fluorescence anisotropy measurements of Hfq binding to FAM-A18 were carried out at room temperature in the 0.5 M NaCl and 20 mM Tris (pH 8.3) solvent as previously described (Sun and Wartell 2006). The L-format was employed with the excitation monochromator at 490 nm and emission monochromator at 522 nm. Anisotropy values were obtained from the average of 10 iterations using an integration time of 4–8 sec for each measurement depending on FAM-A18 concentration. The slits employed were set at 1 or 2 mm. wt Hfq was serially titrated into fluorescence cells with a working volume of 1 mL or 0.5 mL for FAM-A18 at 2 nM. When 5 μM of FAM-A18 was employed, a 50 μL micro-cell was employed. The fluorescence intensity of FAM-A18 showed a small decrease with Hfq binding after accounting for dilution (∼2%). Similar anisotropy experiments were carried using DsrADII with FAM attached to its 5′ end. The solvent employed for the FAM-DsrADII experiments was 0.1 M NaCl and 20 mM Tris (8.3) since Hfq affinity for DsrADII increased with decreasing salt concentration and conditions favoring strong binding were sought (data not shown). Unlike FAM-A18, Hfq binding decreased the fluorescence intensity of FAM-DsrADII, indicating that the quantum yield of the bound fluorophore was less than the free molecule. The ratio of quantum yield for bound versus free FAM-DsrADII, Qb/Qf, was determined to be 0.70 by saturating FAM-DsrADII. The change in anisotropy was corrected for this factor (Lundblad et al. 1996).
Analysis of fluorescence anisotropy data
The two models employed in the analysis of Hfq binding to FAM-A18 at low concentration (nM) were described by Sun and Wartell (2006). Both assume that Hfq exists only as hexamers. The first model assumes a one-to-one complex forms between the Hfq hexamer and FAM-A18. An equation describing the fluorescence anisotropy in terms of the dissociation constant Kd and other parameters of the experiment can be derived (Lundblad et al. 1996) and is given by Equation 1.
where β = Rt + Pt + Kd. A is the measured anisotropy of FAM-A18 during the titration; Af and Ab are the anisotropy of the free and bound FAM-A18 respectively; and Rt and Pt are the total concentrations of FAM-A18 and Hfq hexamer respectively. Nonlinear least-squares fit of the equation to data was made. For a situation where binding quenches the fluorescence of the RNA (i.e., DsrADII), Equation 1 has to be corrected for the difference in quantum yields for free and bound RNA (Qf, Qb). Defining α = [β − [β2 − 4 Rt Pt]½]/2Rt one obtains
The second model assumed that Hfq hexamers bind FAM-A18 in a two-step reaction. The binding reaction is described by a dissociation constant K1 for binding the first Hfq hexamer, and a dissociation constant K2 for binding a subsequent Hfq hexamer:
P corresponds to Hfq hexamer and R is FAM-A18. Data were fit to the second model using the BIOEQS program (Royer and Beechem 1992; Royer 1993). This algorithm performs a nonlinear least-squares fit of Equation 3 to the anisotropy data using parameters corresponding to the standard state free energies related to K1 and K2, anisotropies of free RNA, RNA in the RP complex, and RNA in the RP2 complex. The anisotropy of the free FAM-A18 was fixed to the experimental value, and the remaining four parameters fit to the data. Supplementary information for Figures S1 to S3 is available upon request.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Supplemental material is available for this article.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We were supported by a Georgia Tech/CDC seed grant and funding from the NASA Astrobiology Institute as well as a URS award to C.T. by the Institute of Bioengineering and Biosciences.
Footnotes
Article published online ahead of print. Article and publication date are at http://www.rnajournal.org/cgi/doi/10.1261/rna.2452111.
REFERENCES
- Arluison V, Mura C, Guzman MR, Liquier J, Pellegrini O, Gingery M, Regnier P, Marco S 2006. Three-dimensional structures of fibrillar Sm proteins: Hfq and other Sm-like proteins. J Mol Biol 356: 86–96 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arluison V, Hohng S, Roy R, Pellegrini O, Regnier P, Ha T 2007. Spectroscopic observation of RNA chaperone activities of Hfq in post-transcriptional regulation by a small non-coding RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 35: 999–1006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azam TA, Hiraga S, Ishihama A 2000. Two types of localization of the DNA-binding proteins within the Escherichia coli nucleoid. Genes Cells 5: 613–626 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield VA, Crothers DM, Tinoco I 2000. Nucleic acids: Structures, properties, and functions. University Science Books, Sausalito, CA [Google Scholar]
- Brennan RG, Link TM 2007. Hfq structure, function and ligand binding. Curr Opin Microbiol 10: 125–133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brescia CC, Mikulecky PJ, Feig AL, Sledjeski DD 2003. Identification of the Hfq-binding site on DsrA RNA: Hfq binds without altering DsrA secondary structure. RNA 9: 33–43 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butland G, Peregrin-Alvarez JM, Li J, Yang W, Yang X, Canadien V, Starostine A, Richards D, Beattie B, Krogan N, et al. 2005. Interaction network containing conserved and essential protein complexes in Escherichia coli. Nature 433: 531–537 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann JR 1989. Phenomenological theory of gel electrophoresis of protein-nucleic acid complexes. J Biol Chem 264: 17032–17040 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael GG, Weber K, Niveleau A, Wahba AJ 1975. The host factor required for RNA phage Qbeta RNA replication in vitro. Intracellular location, quantitation, and purification by polyadenylate-cellulose chromatography. J Biol Chem 250: 3607–3612 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunning C, Brown L, Elliott T 1998. Promoter substitution and deletion analysis of upstream region required for rpoS translational regulation. J Bacteriol 180: 4564–4570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haseth PL, Uhlenbeck OC 1980a. Interaction of Escherichia coli host factor protein with oligoriboadenylates. Biochemistry 19: 6138–6146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haseth PL, Uhlenbeck OC 1980b. Interaction of Escherichia coli host factor protein with Q beta ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry 19: 6146–6151 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folichon M, Arluison V, Pellegrini O, Huntzinger E, Regnier P, Hajnsdorf E 2003. The poly(A) binding protein Hfq protects RNA from RNase E and exoribonucleolytic degradation. Nucleic Acids Res 31: 7302–7310 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folichon M, Allemand F, Regnier P, Hajnsdorf E 2005. Stimulation of poly(A) synthesis by Escherichia coli poly(A)polymerase I is correlated with Hfq binding to poly(A) tails. FEBS J 272: 454–463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissmann TA, Touati D 2004. Hfq, a new chaperoning role: Binding to messenger RNA determines access for small RNA regulator. EMBO J 23: 396–405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill SC, von Hippel PH 1989. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal Biochem 182: 319–326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karas M, Gluckmann M, Schafer J 2000. Ionization in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization: Singly charged molecular ions are the lucky survivors. J Mass Spectrom 35: 1–12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto H, Koide Y, Morita T, Aiba H 2006. Base-pairing requirement for RNA silencing by a bacterial small RNA and acceleration of duplex formation by Hfq. Mol Microbiol 61: 1013–1022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt C, Tovar K, Hillen W 1991. Computer simulations and experimental studies of gel mobility patterns for weak and strong non-cooperative protein binding to two targets on the same DNA: Application to binding of tet repressor variants to multiple and single tet operator sites. Nucleic Acids Res 19: 1021–1028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz JR 2006. Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Springer, New York [Google Scholar]
- Laue TM, Shah BD, Ridgeway TM and Pelletier SL 1992. Analytical ultracentrifugation in biochemistry and polymer sciences. (ed. Harding SE, et al. ) Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, UK [Google Scholar]
- Le Derout J, Folichon M, Briani F, Deho G, Regnier P, Hajnsdorf E 2003. Hfq affects the length and the frequency of short oligo(A) tails at the 3′ end of Escherichia coli rpsO mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 31: 4017–4023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Derout J, Boni IV, Regnier P, Hajnsdorf E 2010. Hfq affects mRNA levels independently of degradation. BMC Mol Biol 11: 17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lease RA, Woodson SA 2004. Cycling of the Sm-like protein Hfq on the DsrA small regulatory RNA. J Mol Biol 344: 1211–1223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz DH, Mok KC, Lilley BN, Kulkarni RV, Wingreen NS, Bassler BL 2004. The small RNA chaperone Hfq and multiple small RNAs control quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio cholerae. Cell 118: 69–82 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link TM, Valentin-Hansen P, Brennan RG 2009. Structure of Escherichia coli Hfq bound to polyriboadenylate RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106: 19292–19297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S, Stafford WF III 1995. An optical thermometer for direct measurement of cell temperature in the Beckman instruments XL-A analytical ultracentrifuge. Anal Biochem 224: 199–202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad JR, Laurance M, Goodman RH 1996. Fluorescence polarization analysis of protein-DNA and protein-protein interactions. Mol Endocrinol 10: 607–612 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majdalani N, Hernandez D, Gottesman S 2002. Regulation and mode of action of the second small RNA activator of RpoS translation, RprA. Mol Microbiol 46: 813–826 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majdalani N, Vanderpool CK, Gottesman S 2005. Bacterial small RNA regulators. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 40: 93–113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masse E, Escorcia FE, Gottesman S 2003. Coupled degradation of a small regulatory RNA and its mRNA targets in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev 17: 2374–2383 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikulecky PJ, Kaw MK, Brescia CC, Takach JJ, Sledjeski D, Feig AL 2004. Escherichia coli Hfq has distinct interaction surfaces for DsrA, rpoS and poly(A) RNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 1206–1214 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty BK, Kushner SR 2006. The majority of Escherichia coli mRNAs undergo post-transcriptional modification in exponentially growing cells. Nucleic Acids Res 34: 5695–5704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty BK, Maples VF, Kushner SR 2004. The Sm-like protein Hfq regulates polyadenylation dependent mRNA decay in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 54: 905–920 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller T, Franch T, Hojrup P, Keene DR, Bachinger HP, Brennan RG, Valentin-Hansen P 2002a. Hfq: A bacterial Sm-like protein that mediates RNA-RNA interaction. Mol Cell 9: 23–30 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller T, Franch T, Udesen C, Gerdes K, Valentin-Hansen P 2002b. Spot 42 RNA mediates discoordinate expression of the E. coli galactose operon. Genes Dev 16: 1696–1706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T, Maki K, Aiba H 2005. RNase E-based ribonucleoprotein complexes: Mechanical basis of mRNA destabilization mediated by bacterial noncoding RNAs. Genes Dev 19: 2176–2186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niranjanakumari S, Lasda E, Brazas R, Garcia-Blanco MA 2002. Reversible cross-linking combined with immunoprecipitation to study RNA-protein interactions in vivo. Methods 26: 182–190 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philo JS 2006. Improved methods for fitting sedimentation coefficient distributions derived by time-derivative techniques. Anal Biochem 354: 238–246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer CA 1993. Improvements in the numerical analysis of thermodynamic data from biomolecular complexes. Anal Biochem 210: 91–97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer CA, Beechem JM 1992. Numerical analysis of binding data: Advantages, practical aspects, and implications. Methods Enzymol 210: 481–505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim NN, Feig AL 2010. An upstream Hfq binding site in the fhlA mRNA leader region facilitates the OxyS-fhlA interaction. PLoS ONE 5: e13029 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J, Russell DW 2001. Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY [Google Scholar]
- Schuck P, Perugini MA, Gonzales NR, Howlett GJ, Schubert D 2002. Size-distribution analysis of proteins by analytical ultracentrifugation: Strategies and application to model systems. Biophys J 82: 1096–1111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher MA, Pearson RF, Moller T, Valentin-Hansen P, Brennan RG 2002. Structures of the pleiotropic translational regulator Hfq and an Hfq-RNA complex: A bacterial Sm-like protein. EMBO J 21: 3546–3556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serdyuk IN, Zaccai NR, Zaccai G 2007. Methods in molecular biophysics: Structure, dynamics, function. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge [Google Scholar]
- Sledjeski DD, Whitman C, Zhang A 2001. Hfq is necessary for regulation by the untranslated RNA DsrA. J Bacteriol 183: 1997–2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soper TJ, Woodson SA 2008. The rpoS mRNA leader recruits Hfq to facilitate annealing with DsrA sRNA. RNA 14: 1907–1917 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford WF, Sherwood PJ 2004. Analysis of heterologous interacting systems by sedimentation velocity: Curve fitting algorithms for estimation of sedimentation coefficients, equilibrium and kinetic constants. Biophys Chem 108: 231–243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steege DA 2000. Emerging features of mRNA decay in bacteria. RNA 6: 1079–1090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X, Wartell RM 2006. Escherichia coli Hfq binds A18 and DsrA domain II with similar 2:1 Hfq6/RNA stoichiometry using different surface sites. Biochemistry 45: 4875–4887 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada A, Wachi M, Kaidow A, Takamura M, Nagai K 1997. DNA binding properties of the hfq gene product of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 236: 576–579 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui HC, Feng G, Winkler ME 1997. Negative regulation of mutS and mutH repair gene expression by the Hfq and RpoS global regulators of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 179: 7476–7487 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Updegrove T, Wilf N, Sun X, Wartell RM 2008. Effect of Hfq on RprA-rpoS mRNA pairing: Hfq-RNA binding and the influence of the 5′ rpoS mRNA leader region. Biochemistry 47: 11184–11195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Updegrove TB, Correia JJ, Galletto R, Bujalowski W, Wartell RM 2010. E. coli DNA associated with isolated Hfq interacts with Hfq's distal surface and C-terminal domain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1799: 588–596 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Hansen P, Eriksen M, Udesen C 2004. The bacterial Sm-like protein Hfq: a key player in RNA transactions. Mol Microbiol 51: 1525–1533 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecerek B, Rajkowitsch L, Sonnleitner E, Schroeder R, Blasi U 2008. The C-terminal domain of Escherichia coli Hfq is required for regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 36: 133–143 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vytvytska O, Jakobsen JS, Balcunaite G, Andersen JS, Baccarini M, von Gabain A 1998. Host factor I, Hfq, binds to Escherichia coli ompA mRNA in a growth rate-dependent fashion and regulates its stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95: 14118–14123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters LS, Storz G 2009. Regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Cell 136: 615–628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A, Wassarman KM, Ortega J, Steven AC, Storz G 2002. The Sm-like Hfq protein increases OxyS RNA interaction with target mRNAs. Mol Cell 9: 11–22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]