Abstract
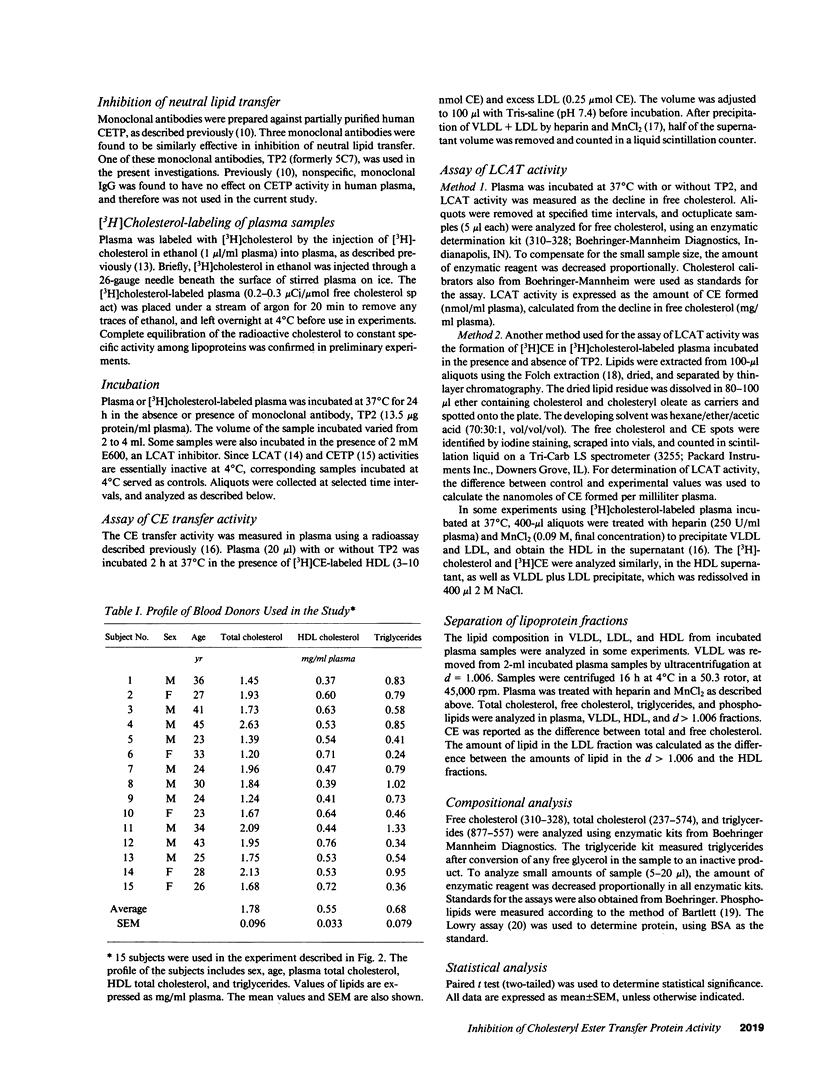
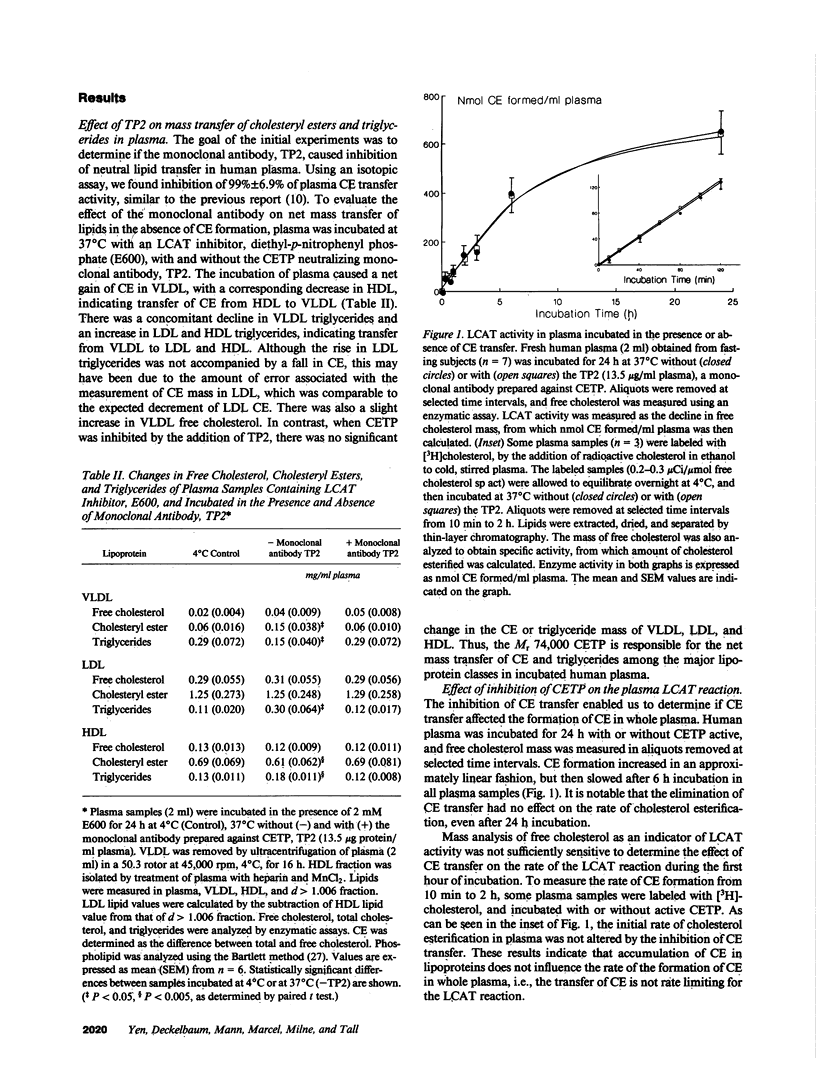
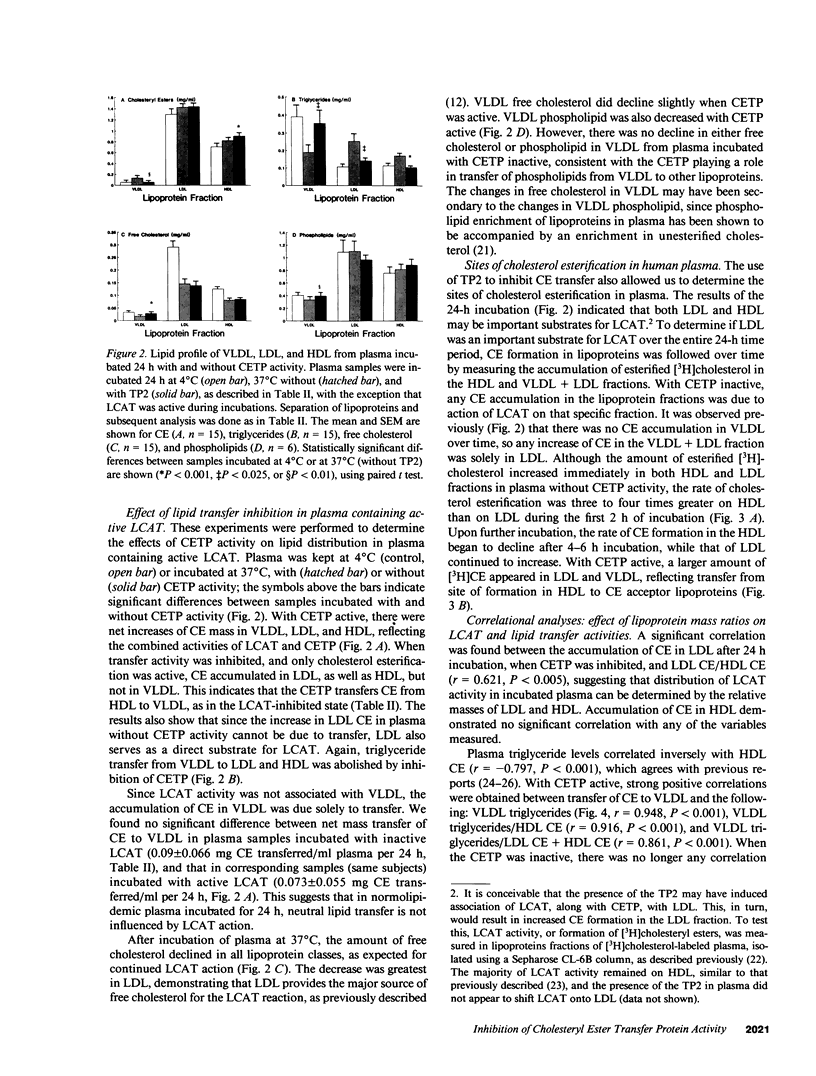
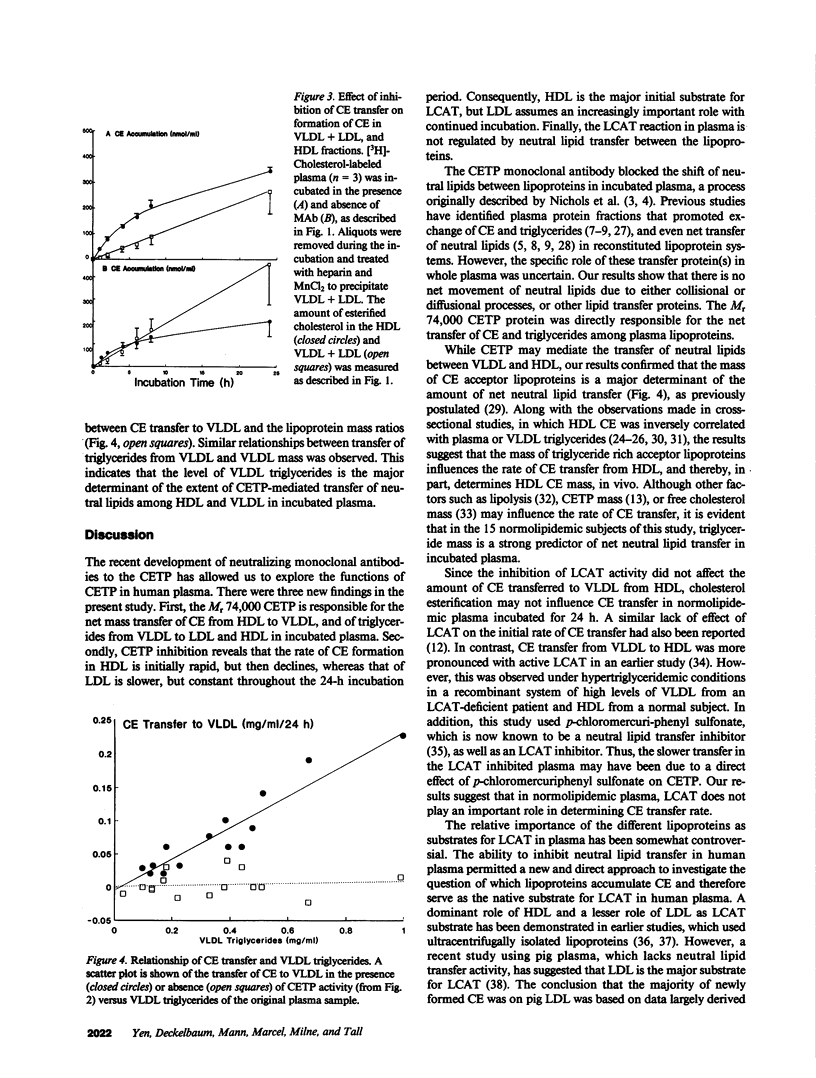
We have employed a neutralizing monoclonal antibody, prepared against the Mr 74,000 cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), to investigate the regulation of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) activity by cholesteryl ester (CE) transfer, and also to determine which lipoproteins are substrates for LCAT in human plasma. The incubation of normolipidemic plasma led to transfer of CE from HDL to VLDL, and of triglycerides from VLDL to LDL and HDL. This net mass transfer of neutral lipids between the lipoproteins was eliminated by the monoclonal antibody. However, CE transfer inhibition had no effect on the rate of plasma cholesterol esterification in plasma incubated from 10 min to 24 h at 37 degrees C. In the absence of CE transfer, HDL and LDL exhibited cholesterol esterification activity, whereas VLDL did not. The rate of CE formation in HDL was three to four times greater than in LDL during the first hour of incubation, but CE formation in HDL decreased after 6-8 h, while that in LDL continued. Thus, (a) the Mr 74,000 CETP is responsible for all neutral lipid mass transfer in incubated human plasma, (b) the rate of CE formation in plasma is not regulated by CE transfer from HDL to other lipoproteins, and (c) HDL is the major initial substrate for LCAT; LDL assumes a more significant role only after prolonged incubation of plasma.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barter P. J., Hopkins G. J., Gorjatschko L. Comparison of human plasma low- and high-density lipoproteins as substrates for lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 17;792(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barter P. J., Hopkins G. J. Relative rates of incorporation of esterified cholesterol into human very low density lipoproteins and low density lipoproteins. In vitro studies of two separate pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 22;751(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaier C. L., Sachdev O. P., Lee E. S., Williams K. J., Blum C. B., Glickman R. M. Effect of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase on distribution of apolipoprotein A-IV among lipoproteins of human plasma. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jun;28(6):693–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Aron L., Fielding C. J. Interaction of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and cholesteryl ester transfer protein in the transport of cholesteryl ester into sphingomyelin liposomes. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 5;19(16):3673–3677. doi: 10.1021/bi00557a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Fielding C. J. Isolation and characterization of a human serum cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3445–3449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. B., Hopkins G. J., Barter P. J. Particle size distribution of high density lipoproteins as a function of plasma triglyceride concentration in human subjects. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Jul;56(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Abano D., Byrne R., Scanu A. M. In vitro mass: activity distribution of lecithin--cholesterol acyltransferase among human plasma lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. 1982 Oct;45(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(82)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckelbaum R. J., Eisenberg S., Oschry Y., Butbul E., Sharon I., Olivecrona T. Reversible modification of human plasma low density lipoproteins toward triglyceride-rich precursors. A mechanism for losing excess cholesterol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6509–6517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckelbaum R. J., Eisenberg S., Oschry Y., Granot E., Sharon I., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Conversion of human plasma high density lipoprotein-2 to high density lipoprotein-3. Roles of neutral lipid exchange and triglyceride lipases. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5201–5208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckelbaum R. J., Granot E., Oschry Y., Rose L., Eisenberg S. Plasma triglyceride determines structure-composition in low and high density lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):225–231. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Gavish D., Oschry Y., Fainaru M., Deckelbaum R. J. Abnormalities in very low, low and high density lipoproteins in hypertriglyceridemia. Reversal toward normal with bezafibrate treatment. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):470–482. doi: 10.1172/JCI111444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Cholesterol transport between cells and body fluids. Role of plasma lipoproteins and the plasma cholesterol esterification system. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Mar;66(2):363–373. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Evidence for a lipoprotein carrier in human plasma catalyzing sterol efflux from cultured fibroblasts and its relationship to lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3911–3914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Regulation of human plasma lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase activity by lipoprotein acceptor cholesteryl ester content. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2102–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOMSET J. A. The mechanism of the plasma cholesterol esterification reaction: plasma fatty acid transferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Nov 19;65:128–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Norum K. R., King W. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: lipid composition and reactivity in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1827–1837. doi: 10.1172/JCI106400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesler C. B., Swenson T. L., Tall A. R. Purification and characterization of a human plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2275–2282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesler C. B., Tall A. R., Swenson T. L., Weech P. K., Marcel Y. L., Milne R. W. Monoclonal antibodies to the Mr 74,000 cholesteryl ester transfer protein neutralize all of the cholesteryl ester and triglyceride transfer activities in human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5020–5023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihm J., Quinn D. M., Busch S. J., Chataing B., Harmony J. A. Kinetics of plasma protein-catalyzed exchange of phosphatidylcholine and cholesteryl ester between plasma lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1982 Dec;23(9):1328–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipping G., Birchbauer A., Steyrer E., Kostner G. M. Action of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase on low-density lipoproteins in native pig plasma. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7945–7953. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcel Y. L., Vezina C., Teng B., Sniderman A. Transfer of cholesterol esters between human high density lipoproteins and triglyceride-rich lipoproteins controlled by a plasma protein factor. Atherosclerosis. 1980 Feb;35(2):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(80)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton R. E. Free cholesterol is a potent regulator of lipid transfer protein function. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12235–12241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton R. E., Zilversmit D. B. Inter-relationship of lipids transferred by the lipid-transfer protein isolated from human lipoprotein-deficient plasma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11751–11757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLS A. V., SMITH L. EFFECT OF VERY LOW-DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS ON LIPID TRANSFER IN INCUBATED SERUM. J Lipid Res. 1965 Apr;6:206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols A. V. Human serum lipoproteins and their interrelationships. Adv Biol Med Phys. 1967;11:109–158. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4832-3107-5.50008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips N. R., Havel R. J., Kane J. P. Serum apolipoprotein A-I levels: relationship to lipoprotein lipid levels and selected demographic variables. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Aug;116(2):302–313. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REHNBORG C. S., NICHOLS A. V. THE FATE OF CHOLESTERYL ESTERS IN HUMAN SERUM INCUBATED IN VITRO AT 38 DEGREES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 2;84:596–603. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajaram O. V., Barter P. J. Reactivity of human lipoproteins with purified lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase during incubations in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 14;835(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson T. L., Brocia R. W., Tall A. R. Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein has binding sites for neutral lipids and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5150–5157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Green P. H. Incorporation of phosphatidylcholine into spherical and discoidal lipoproteins during incubation of egg phosphatidylcholine vesicles with isolated high density lipoproteins or with plasma. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):2035–2044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Sammett D., Vita G. M., Deckelbaum R., Olivecrona T. Lipoprotein lipase enhances the cholesteryl ester transfer protein-mediated transfer of cholesteryl esters from high density lipoproteins to very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9587–9594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A., Granot E., Brocia R., Tabas I., Hesler C., Williams K., Denke M. Accelerated transfer of cholesteryl esters in dyslipidemic plasma. Role of cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1217–1225. doi: 10.1172/JCI112940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A., Sammett D., Granot E. Mechanisms of enhanced cholesteryl ester transfer from high density lipoproteins to apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1163–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI112417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnick G. R., Albers J. J. A comprehensive evaluation of the heparin-manganese precipitation procedure for estimating high density lipoprotein cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jan;19(1):65–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


