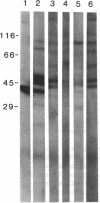
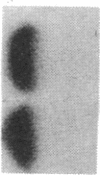
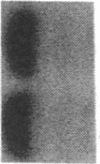
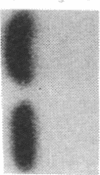
Abstract
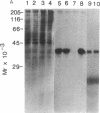
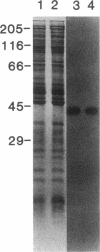
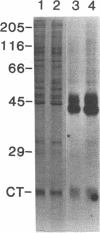
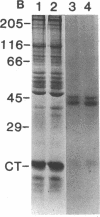
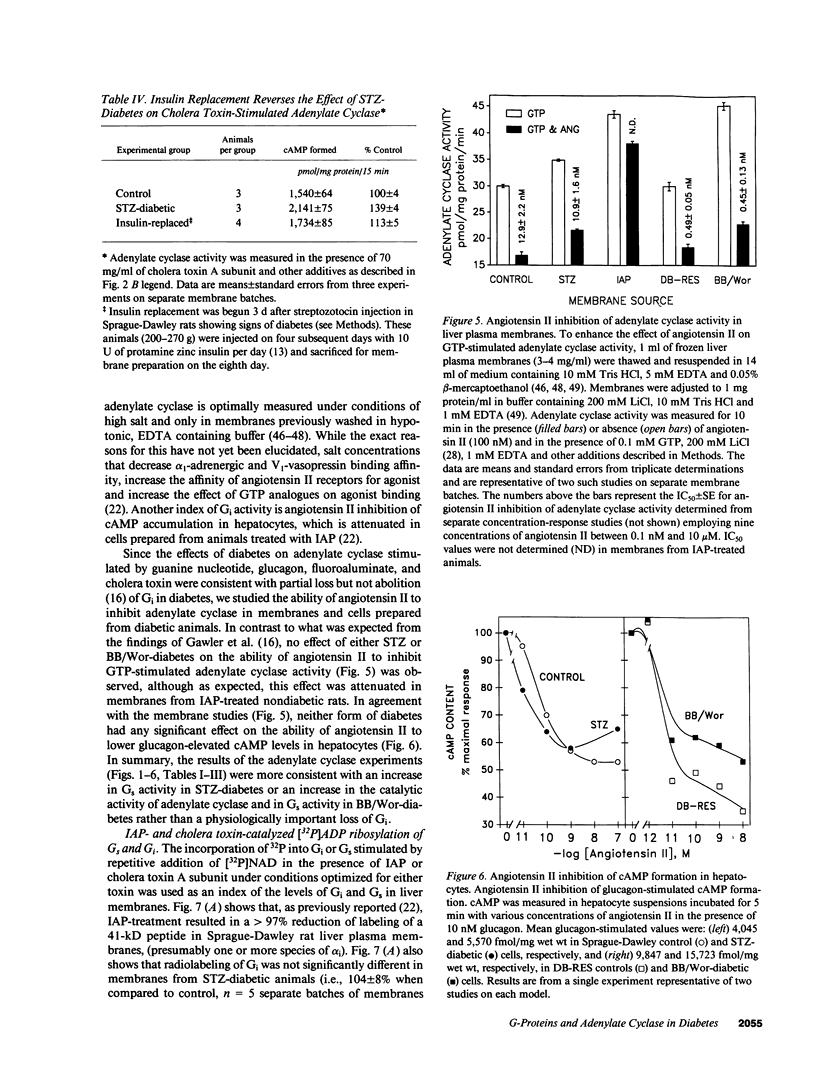
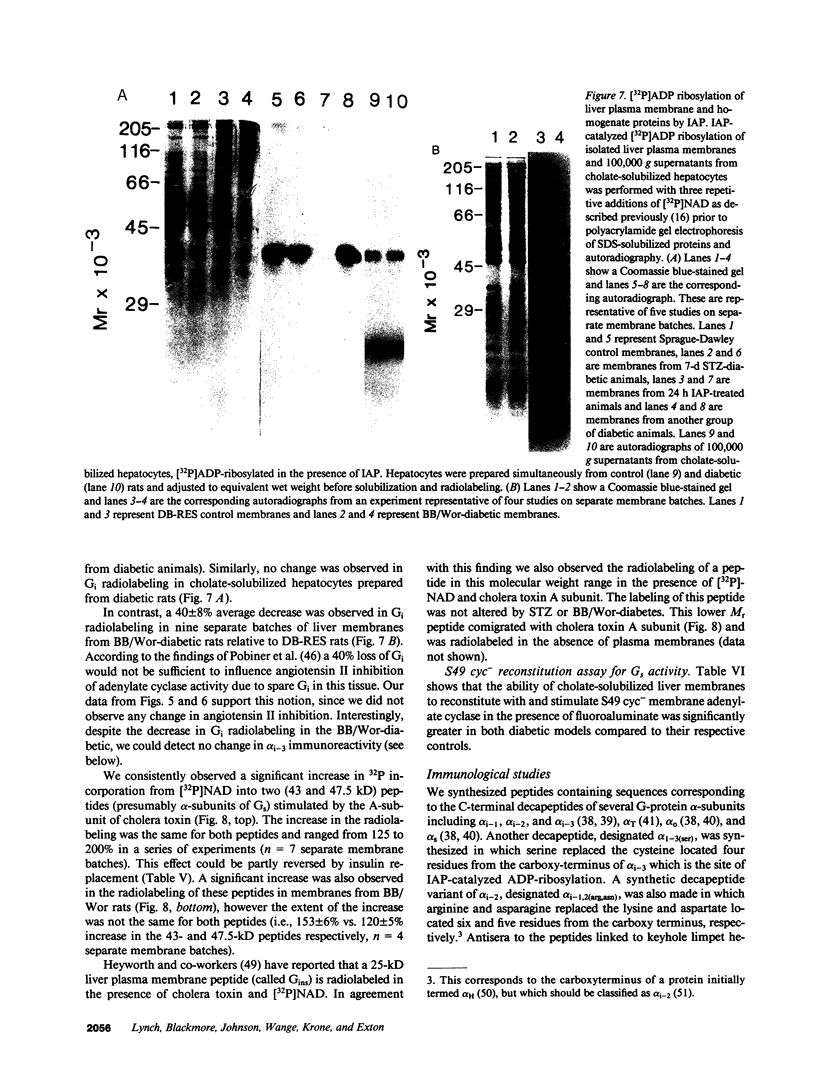
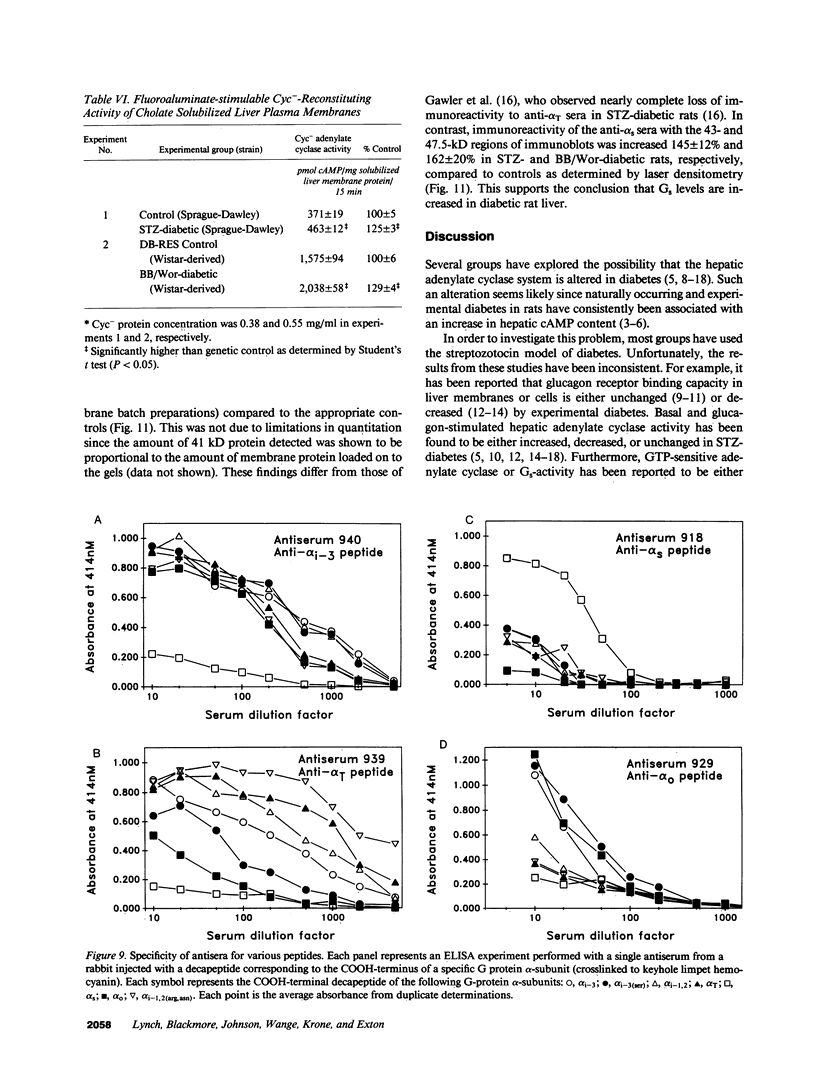
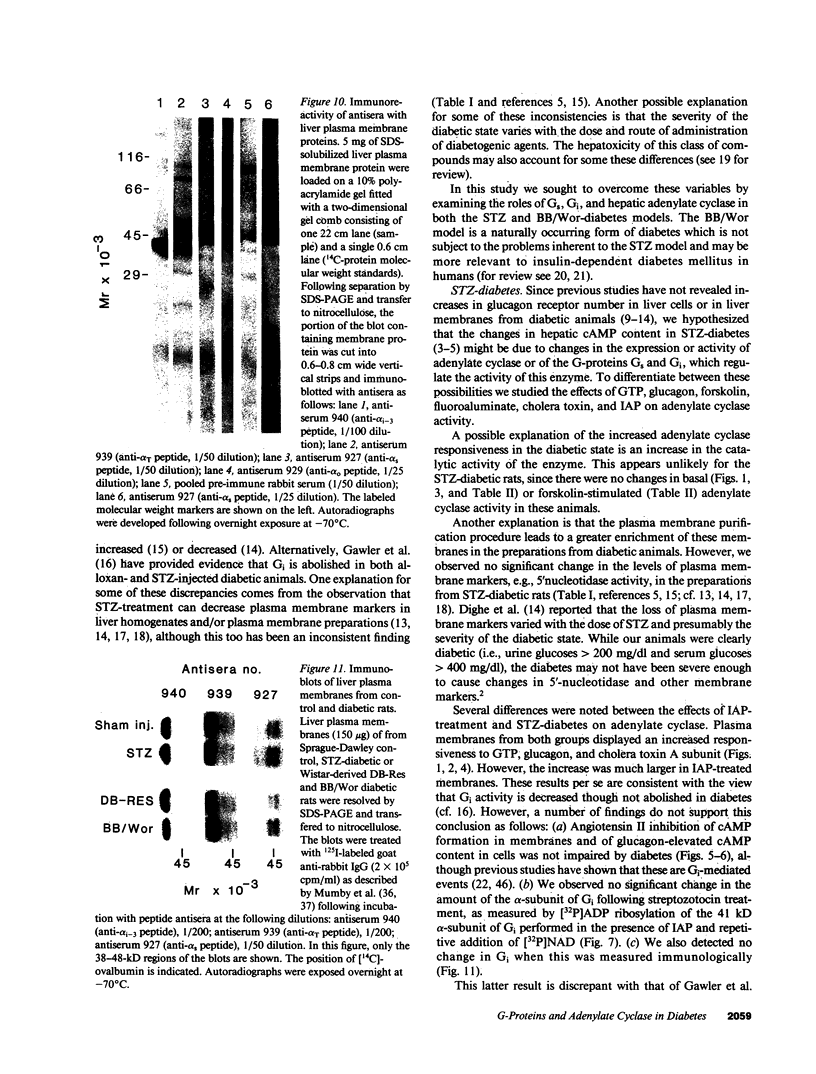
Adenylate cyclase in liver plasma membranes from streptozotocin-diabetic (STZ) or BB/Wor spontaneously diabetic rats showed increased responsiveness to GTP, glucagon, fluoroaluminate, and cholera toxin. Basal or forskolin-stimulated activity was unchanged in STZ rats, but increased in BB/Wor rats. No change in the alpha-subunit of Gi (alpha i) was observed in STZ or BB/Wor rats using pertussis toxin-stimulated [32P]ADP-ribosylation. Immunodetection using antibodies against the COOH-terminal decapeptides of alpha T and alpha i-3 showed no change in alpha i in STZ rats and a slight decrease in BB/Wor rats. Angiotensin II inhibition of hepatic adenylate cyclase was not altered in either diabetic rat. In both models of diabetes, Gs alpha-subunits were increased as measured by cholera toxin-stimulated [32P]-ADP-ribosylation of 43-47.5-kD peptides, reconstitution with membranes from S49 cyc- cells or immunoreactivity using antibodies against the COOH-terminal decapeptide of alpha s. These data indicate that STZ-diabetes increases hepatic Gs but does not change Gi or adenylate cyclase catalytic activity. In contrast, BB/Wor rats show increased hepatic Gs and adenylate cyclase. These changes could explain the increase in hepatic cAMP and related dysfunctions observed in diabetes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allgayer H., Bachmann W., Hepp K. D. Increased dose-response relationship of liver plasma membrane adenylate cyclase to glucagon stimulation in diabetic rats. A possible role of the guanyl nucleotide-binding regulatory protein. Diabetologia. 1982 Jun;22(6):464–467. doi: 10.1007/BF00282591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appel M. C., Like A. A., Rossini A. A., Carp D. B., Miller T. B., Jr Hepatic carbohydrate metabolism in the spontaneously diabetic Bio-Breeding Worcester rat. Am J Physiol. 1981 Feb;240(2):E83–E87. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.2.E83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann W., Böttger I., Allgayer H., Haslbeck M., Hepp K. D. Insulin-, Glucagonbindung und Adenylatzyklase-Aktivität von Leberplasmamembranen Streptozotocin-diabetischer Ratten. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1978;(84):1217–1220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhathena S. J., Voyles N. R., Smith S., Recant L. Decreased glucagon receptors in diabetic rat hepatocytes. Evidence for regulation of glucagon receptors by hyperglucagonemia. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1488–1497. doi: 10.1172/JCI109069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Assessment of effects of vasopressin, angiotensin II, and glucagon on Ca2+ fluxes and phosphorylase activity in liver. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:550–558. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanile C. P., Crane J. K., Peach M. J., Garrison J. C. The hepatic angiotensin II receptor. I. Characterization of the membrane-binding site and correlation with physiological response in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4951–4958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamras H., Fouchereau-Peron M., Rosselin G. The effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on the early steps of glucagon action in isolated rat liver cells. Diabetologia. 1980 Jul;19(1):74–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00258315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Pugh W., Blanchard S. G., McDermed J., Tam J. P. Antibody specific to the alpha subunit of the guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein Go: developmental appearance and immunocytochemical localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4929–4933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappel C. I., Chappel W. R. The discovery and development of the BB rat colony: an animal model of spontaneous diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1983 Jul;32(7 Suppl 1):8–10. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(83)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B., Kaplan S. A. Increased insulin binding by hepatic plasma membranes from diabetic rats: normalization by insulin therapy. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):22–30. doi: 10.1172/JCI108618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dighe R. R., Rojas F. J., Birnbaumer L., Garber A. J. Glucagon-stimulable adenylyl cyclase in rat liver. The impact of streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1013–1023. doi: 10.1172/JCI111286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Houslay M. D. Abolition of the expression of inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi activity in diabetes. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):229–232. doi: 10.1038/327229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg N. D., Dietz S. B., O'Toole A. G. Cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in mammalian tissues and urine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4458–4466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Malech H. L., Spiegel A. M. Antibodies directed against synthetic peptides distinguish between GTP-binding proteins in neutrophil and brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14683–14688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth C. M., Whetton A. D., Wong S., Martin B. R., Houslay M. D. Insulin inhibits the cholera-toxin-catalysed ribosylation of a Mr-25000 protein in rat liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):593–603. doi: 10.1042/bj2280593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff R. M., Axton J. M., Neer E. J. Physical and immunological characterization of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein purified from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10864–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff R. M., Axton J. M., Neer E. J. Physical and immunological characterization of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein purified from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10864–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelsson B., Tengrup I. Changes in adenylate cyclase and 5-nucleotidase activities in liver membranes from alloxan diabetic rats. Experientia. 1980 Feb 15;36(2):257–258. doi: 10.1007/BF01953768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nagata S., Nakamura S., Katada T., Ui M., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of cDNAs for alpha subunits of the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins Gs, Gi, and Go from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3776–3780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Toyama R., Kozasa T., Tsukamoto T., Matsuoka M., Kaziro Y. Presence of three distinct molecular species of Gi protein alpha subunit. Structure of rat cDNAs and human genomic DNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6656–6664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jard S., Cantau B., Jakobs K. H. Angiotensin II and alpha-adrenergic agonists inhibit rat liver adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2603–2606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Exton J. H., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W., Park C. R. Role of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the effects of insulin and anti-insulin serum on liver metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1031–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Goebel C. U., Hruby V. J., Bregman M. D., Trivedi D. Hyperglycemia of diabetic rats decreased by a glucagon receptor antagonist. Science. 1982 Feb 26;215(4536):1115–1116. doi: 10.1126/science.6278587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. Y., Ang S. L., Bloch D. B., Bloch K. D., Kawahara Y., Tolman C., Lee R., Seidman J. G., Neer E. J. Identification of cDNA encoding an additional alpha subunit of a human GTP-binding protein: expression of three alpha i subtypes in human tissues and cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4153–4157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand Y., Loten E. G., Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., Forgue M. E., Freychet P., Jeanrenaud B. Effect of fasting and streptozotocin in the obese-hyperglycemic (ob/ob) mouse. Apparent lack of a direct relationship between insulin binding and insulin effects. Diabetes. 1977 Jun;26(6):582–590. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.6.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Morbach L., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Alpha-subunits of Ns are released from the plasma membrane following cholera toxin activation. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 12;200(2):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Prpic V., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Effect of islet-activating pertussis toxin on the binding characteristics of Ca2+-mobilizing hormones and on agonist activation of phosphorylase in hepatocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;29(2):196–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Kahn R. A., Manning D. R., Gilman A. G. Antisera of designed specificity for subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):265–269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S., Pang I. H., Gilman A. G., Sternweis P. C. Chromatographic resolution and immunologic identification of the alpha 40 and alpha 41 subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2020–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhooda A. F., Like A. A., Chappel C. I., Murray F. T., Marliss E. B. The spontaneously diabetic Wistar rat. Metabolic and morphologic studies. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):100–112. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Exton J. H., Johnson R. A., Park C. R. Effects of glucagon on cyclic AMP and carbohydrate metabolism in livers from diabetic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):250–267. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pobiner B. F., Hewlett E. L., Garrison J. C. Role of Ni in coupling angiotensin receptors to inhibition of adenylate cyclase in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16200–16209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpić V., Green K. C., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Vasopressin-, angiotensin II-, and alpha 1-adrenergic-induced inhibition of Ca2+ transport by rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1382–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F. A., Mattera R., Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Field J. B., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D. ADP-ribosylation of membrane components by pertussis and cholera toxin. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:566–572. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich K. A., Codina J., Floyd G., Sekura R., Hildebrandt J. D., Iyengar R. Glucagon-induced heterologous desensitization of the MDCK cell adenylyl cyclase. Increases in the apparent levels of the inhibitory regulator (Ni). J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7893–7901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity: interactions of solubilized components with receptor-replete membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Resolution of some components of adenylate cyclase necessary for catalytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):6966–6969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Howlett A. C., Ferguson K. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity with resolved components of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6401–6412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Maguire M. E., Sturgill T. W., Biltonen R. L., Gilman A. G. Relationship between the beta-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5761–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y. Adenylate cyclase assay. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:35–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerheber R. D., Kuhn C. E., Hyslop P. A. Membrane structural/functional properties of adipocytes from normal and streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1984 Mar;33(3):258–265. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikant C. B., Freeman D., McCorkle K., Unger R. H. Binding and biologic activity of glucagon in liver cell membranes of chronically hyperglucagonemic rats. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7434–7438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11517–11526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Nukada T., Nishikawa Y., Sugimoto K., Suzuki H., Takahashi H., Noda M., Haga T., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of transducin and its relationship to ras proteins. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):242–245. doi: 10.1038/315242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Prpic V., Jiang H., Exton J. H. Hormone-stimulated polyphosphoinositide breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Orci L. Glucagon and the A cell: physiology and pathophysiology (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 25;304(26):1575–1580. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106253042604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eldik L. J., Ehrenfried B., Jensen R. A. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies with specificity for the S100 beta polypeptide of brain S100 fractions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6034–6038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B. Streptozocin: a review of its pharmacology, efficacy, and toxicity. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Mar;66(3):427–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Yamashita S., Yasuda H., Oka Y., Ogata E. A decreased response of cyclic adenosine monophosphate concentrations to glucagon in liver slices from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1980 Mar;29(3):188–192. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.3.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]