Abstract
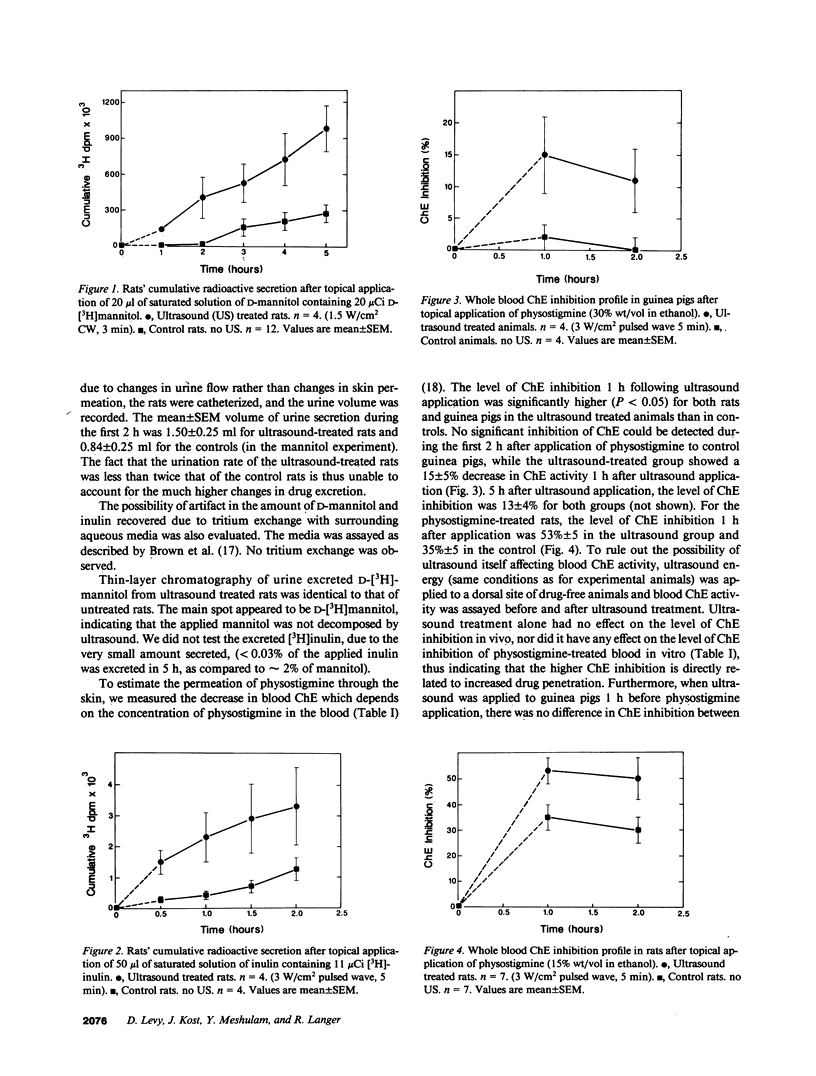
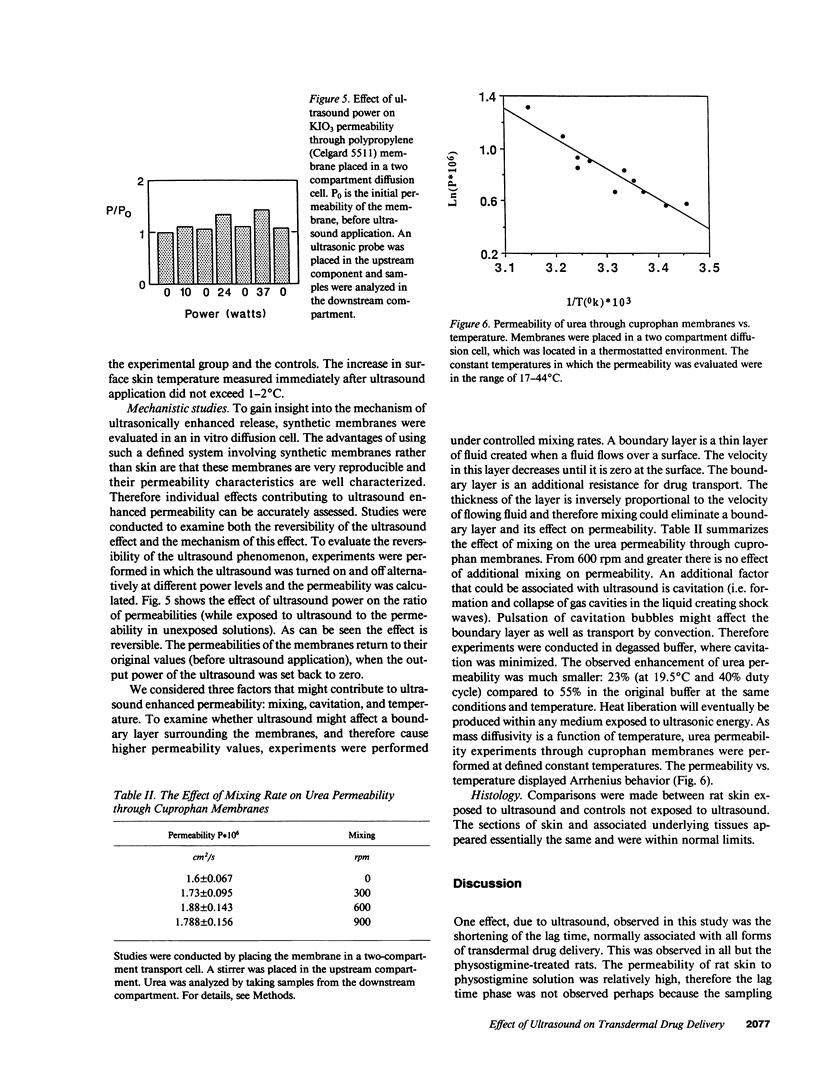
The effect of therapeutic range ultrasound (1 MHz) on skin permeation of D-mannitol, a highly polar sugar alcohol, inulin, a high molecular weight polysaccharide and physostigmine, a lipophilic anticholinesterase drug was studied in rats and guinea pigs. D-Mannitol and inulin are totally and rapidly excreted, once they have penetrated through the skin into the blood stream, permitting direct in vivo monitoring. For evaluating skin penetration of physostigmine the decrease of whole blood cholinesterase was measured. Ultrasound nearly completely eliminated the lag time usually associated with transdermal delivery of drugs. 3-5 min of ultrasound irradiation (1.5 W/cm2 continuous wave or 3 W/cm2 pulsed wave) increased the transdermal permeation of inulin and mannitol in rats by 5-20-fold within 1-2 h following ultrasound application. Ultrasound treatment also significantly increased (P less than 0.05) the inhibition of cholinesterase during the first hour after application in both physostigmine treated rats and guinea pigs: while in control guinea pigs no significant inhibition of cholinesterase could be detected during the first 2 h after application of physostigmine, the ultrasound treated group showed a 15 +/- 5% (mean +/- SEM) decrease in blood cholinesterase 1 h after ultrasound application. For physostigmine-treated rats the level of cholinesterase inhibition 1 h after ultrasound application was 53 +/- 5% in the ultrasound-treated group and 35 +/- 5% in the controls.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndts D., Arndts K. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of transdermally administered clonidine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;26(1):79–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00546713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. R., Wei C. L., Langer R. In vivo and in vitro release of macromolecules from polymeric drug delivery systems. J Pharm Sci. 1983 Oct;72(10):1181–1185. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600721019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L., Langer R. Transdermal delivery of drugs. Annu Rev Med. 1988;39:221–229. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.39.020188.001253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTMAN Y., GOTTSCHALK C. W., LASSITER W. E. MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF INULIN ABSORPTION IN THE RAT KIDNEY. Science. 1965 Feb 12;147(3659):753–754. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3659.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. D., Russell R. L. A rapid, simple radiometric assay for cholinesterase, suitable for multiple determinations. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kari B. Control of blood glucose levels in alloxan-diabetic rabbits by iontophoresis of insulin. Diabetes. 1986 Feb;35(2):217–221. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH W. H., FINGERHUT B., MILLER H. AUTOMATED AND MANUAL DIRECT METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF BLOOD UREA. Clin Chem. 1965 Jun;11:624–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maibach H. I., Feldmann R. J. The effect of DMSO on percutaneous penetration of hydrocortisone and testosterone in man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Mar 15;141(1):423–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb34906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElnay J. C., Matthews M. P., Harland R., McCafferty D. F. The effect of ultrasound on the percutaneous absorption of lignocaine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;20(4):421–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1985.tb05089.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price N. M., Schmitt L. G., McGuire J., Shaw J. E., Trobough G. Transdermal scopolamine in the prevention of motion sickness at sea. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Mar;29(3):414–419. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thal L. J., Fuld P. A., Masur D. M., Sharpless N. S., Davies P. Oral physostigmine and lecithin improve memory in Alzheimer's disease. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1983;19(3):454–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Haar G. R., Daniels S. Evidence for ultrasonically induced cavitation in vivo. Phys Med Biol. 1981 Nov;26(6):1145–1149. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/26/6/013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



