Abstract
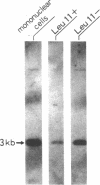
Lymphoproliferative disease of granular lymphocytes (LDGL) is a heterogeneous disorder and the pathogenesis is likely to be complex. Some patients with chronic active EBV (CAEBV) infection also have LDGL. To investigate the relationship between EBV infection and the pathogenesis of LDGL, we conducted a survey for EBV DNA sequences by Southern blot analysis of DNA obtained from the peripheral blood of seven patients with LDGL, including one with CAEBV infection. Interestingly, EBV DNA was detected in the sample from the patient with CAEBV infection, and in the samples from four other patients with CD3-LDGL. Moreover, a single band for the joined termini of the EBV genome was demonstrated in two samples, suggesting a clonal disorder of those LDGL. These findings strongly suggest that EBV may play a pathogenic role in some cases of LDGL.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andiman W., Gradoville L., Heston L., Neydorff R., Savage M. E., Kitchingman G., Shedd D., Miller G. Use of cloned probes to detect Epstein-Barr viral DNA in tissues of patients with neoplastic and lymphoproliferative diseases. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):967–977. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. A., Liu C. R., Wang Y. F., Garcia C. R. B-cell lymphoproliferation and lymphomagenesis are associated with clonotypic intracellular terminal regions of the Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):962–969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.962-969.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. C., Link S., Mawle A., Check I., Brynes R. K., Winton E. F. Heterogeneity of large granular lymphocyte proliferations: delineation of two major subtypes. Blood. 1986 Nov;68(5):1142–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco E., Kawa-Ha K., Doi S., Yumura K., Murata M., Ishihara S., Tawa A., Yabuuchi H. Remarkable depression of CD4+2H4+ T cells in severe chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Dec;26(6):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha-Kawa K., Yumura K., Hara J., Ishihara S., Yabuuchi H. Concomitant rearrangements of T-cell beta- and gamma-chain genes in childhood T-lineage leukemia/lymphoma. Leuk Res. 1987;11(8):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(87)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. E., Horwitz C. A. Epstein-Barr virus specific diagnostic tests in infectious mononucleosis. Hum Pathol. 1974 Sep;5(5):551–565. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura N., Kuramoto A., Kawa-Ha K., Fujii H., Takiguchi T. Negative association between the human T-cell leukaemia virus type I and large granular lymphocyte leukaemia in Japan. Lancet. 1988 Oct 22;2(8617):962–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92628-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara S., Tawa A., Yumura-Yagi K., Murata M., Hara J., Yabuuchi H., Hirai K., Kawa-Ha K. Clonal T-cell lymphoproliferation containing Epstein-Barr (EB) virus DNA in a patient with chronic active EB virus infection. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1989 Feb;80(2):99–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1989.tb02273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. F., Shurin S., Abramowsky C., Tubbs R. R., Sciotto C. G., Wahl R., Sands J., Gottman D., Katz B. Z., Sklar J. T-cell lymphomas containing Epstein-Barr viral DNA in patients with chronic Epstein-Barr virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 24;318(12):733–741. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803243181203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawa-Ha K., Franco E., Doi S., Yumura K., Ishihara S., Tawa A., Yabuuchi H. Successful treatment of chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection with recombinant interleukin-2. Lancet. 1987 Jan 17;1(8525):154–154. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91980-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuta H., Taguchi Y., Tomizawa K., Kojima K., Kawamura N., Ishizaka A., Sakiyama Y., Matsumoto S., Imai S., Kinoshita T. Epstein-Barr virus genome-positive T lymphocytes in a boy with chronic active EBV infection associated with Kawasaki-like disease. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):455–457. doi: 10.1038/333455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc M. P., Rabbitts T. H. Two tandemly organized human genes encoding the T-cell gamma constant-region sequences show multiple rearrangement in different T-cell types. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):464–466. doi: 10.1038/316464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Stashenko P., Hardy R., van Agthoven A., Terhorst C., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of a human B cell-specific antigen (B2) distinct from B1. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1941–1947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshimi K. Granular lymphocyte proliferative disorders: report of 12 cases and review of the literature. Leukemia. 1988 Oct;2(10):617–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfi F., De Rossi G., Semenzato G., Quinti I., Ranucci A., De Sanctis G., Lopez M., Gasparotto G., Aiuti F. Immunologic evaluation of T chronic lymphocyte leukemia cells: correlations among phenotype, functional activities, and morphology. Blood. 1982 Apr;59(4):688–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Flynn K. The structure of the termini of the Epstein-Barr virus as a marker of clonal cellular proliferation. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):883–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90803-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenzato G., Pandolfi F., Chisesi T., De Rossi G., Pizzolo G., Zambello R., Trentin L., Agostini C., Dini E., Vespignani M. The lymphoproliferative disease of granular lymphocytes. A heterogeneous disorder ranging from indolent to aggressive conditions. Cancer. 1987 Dec 15;60(12):2971–2978. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19871215)60:12<2971::aid-cncr2820601220>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi Y., Taguchi T., Ohta Y., Hirai K. Chromosomal localization of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome in Bloom's syndrome B-lymphoblastoid cell lines transformed with EBV. Chromosoma. 1985;93(2):157–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00293163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa S., Hatakeyama M., Shibano M., Taniguchi T., Kitani T. The expression of the p75 subunit of interleukin 2 receptor in Tac negative leukemic cells of two patients with large granular lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):1161–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa S., Tokumine Y., Ueda E., Waki K., Kanayama Y., Taniguchi N., Nakanishi T., Inoue R., Kitani T. Leu 11+ T gamma cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia with partially activated natural killer function and its further activation by recombinant IL2 in vitro. Blood. 1986 Oct;68(4):846–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Perussia B. Human natural killer cells: biologic and pathologic aspects. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):489–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Toothaker L. E., Smith J. A., Weis J. H., Fearon D. T. Structure of the human B lymphocyte receptor for C3d and the Epstein-Barr virus and relatedness to other members of the family of C3/C4 binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1047–1066. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi Y., Yoshikai Y., Leggett K., Clark S. P., Aleksander I., Mak T. W. A human T cell-specific cDNA clone encodes a protein having extensive homology to immunoglobulin chains. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):145–149. doi: 10.1038/308145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]