Abstract
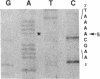
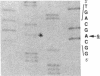
In five patients with hemophilia B and detectable Factor IX antigen, altered reactivity to a specific polyclonal antibody fraction or monoclonal anti-Factor IX antibodies was noted. Amplification of selected portions of their Factor IX genes by polymerase chain reaction allowed rapid identification of a single base transition in each of the five families tested. In a patient with severe hemophilia and an altered calcium binding domain, a G to A transition in exon II changed the codon for Glu-27 to Lys (Factor IXSeattle 3). Patients from two families with mild hemophilia with decreased reactivity to a MAb that binds to a site within the sequence coded for by exon IV had a G to A transition changing the codon for Gly-60 to Ser (Factor IXDurham). Two unrelated patients with moderately severe hemophilia lacked reactivity to another murine monoclonal anti-Factor IX which binds to an epitope in the amino-terminal half of the heavy chain of Factor IXa. In these patients, exon VIII contained a G to A transition changing Arg-248 to Gln (Factor IXSeattle 4).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. G., Steinberg M. H., Boxer L. A., Baehner R. L., Forget B. G., Tsistrakis G. A. The structure of hemoglobin Indianapolis [beta112(G14) arginine]. An unstable variant detectable only by isotopic labeling. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3479–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. K., Rees D. J., Rizza C., Brownlee G. G. Defective propeptide processing of blood clotting factor IX caused by mutation of arginine to glutamine at position -4. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski M., Furie B. C., Furie B. Distribution of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues in partially carboxylated human prothrombins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1624–1628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. L., Weinmann A. F., Thompson A. R. Calcium-specific immunoassays for factor IX: reduced levels of antigen in patients with vitamin K disorders. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Mar;107(3):269–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Scott C. R., Schoof J., Lovrien E. W., Kurachi K. Factor IXPortland: a nonsense mutation (CGA to TGA) resulting in hemophilia B. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):567–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Yoshitake S., Chance P. F., Bray G. L., Thompson A. R., Scott C. R., Kurachi K. An intragenic deletion of the factor IX gene in a family with hemophilia B. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2161–2164. doi: 10.1172/JCI112222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collawn J. F., Wallace C. J., Proudfoot A. E., Paterson Y. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of conformational changes in protein-engineered cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8625–8634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. M., Wilkinson A. J., Baron M., Pastore A., Tappin M. J., Campbell I. D., Gregory H., Sheard B. The solution structure of human epidermal growth factor. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):339–341. doi: 10.1038/327339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. M., McGraw R. A., Ware J. L., Roberts H. R., Stafford D. W. Factor IXAlabama: a point mutation in a clotting protein results in hemophilia B. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):140–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton P. H., Fowlkes D. M., Lord S. T., Reisner H. M. Hemophilia B Durham: a mutation in the first EGF-like domain of factor IX that is characterized by polymerase chain reaction. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1407–1411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diuguid D. L., Rabiet M. J., Furie B. C., Liebman H. A., Furie B. Molecular basis of hemophilia B: a defective enzyme due to an unprocessed propeptide is caused by a point mutation in the factor IX precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5803–5807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Bing D. H., Feldmann R. J., Robison D. J., Burnier J. P., Furie B. C. Computer-generated models of blood coagulation factor Xa, factor IXa, and thrombin based upon structural homology with other serine proteases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3875–3882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Jacobson R. J., Seligmann B. E., Metcalf J. A., McKay J. H., Sacher R. A., Malech H. L. A neutrophil membrane marker reveals two groups of chronic myelogenous leukemia and its absence may be a marker of disease progression. Blood. 1986 Aug;68(2):343–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes V. A., Le Bonniec B. F., Louie G. V., Brayer G. D., Thompson A. R., MacGillivray R. T. A moderate form of hemophilia B is caused by a novel mutation in the protease domain of factor IXVancouver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4689–4697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelione G. T., Wüthrich K., Nice E. C., Burgess A. W., Scheraga H. A. Solution structure of murine epidermal growth factor: determination of the polypeptide backbone chain-fold by nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5226–5230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella D., DeGraaf Mahoney S., Mattingly M., Roeder D., Timmons L., Fulcher C. A. Epitope mapping of human factor VIII inhibitor antibodies by deletion analysis of factor VIII fragments expressed in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6152–6156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. J., Ono K. Monoclonal antibodies to factor IX: characterization and use in immunoassays for factor IX. Thromb Res. 1984 Jan 15;33(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. J., Singaraju C., Smith L. F. Factor IX metal ion-dependent antigen assays for measurement of warfarin effect. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Mar;87(3):370–376. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.3.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. J., Thompson A. R., McMullen B. A., Frazier D., Lin S. W., Stafford D., Kisiel W., Thibodeau S. N., Chen S. H., Smith L. F. Carrier testing in hemophilia B with an immunoassay that distinguishes a prevalent factor IX dimorphism. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):1006–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer S. G., Pendurthi U. R., Kasper C. K., Bajaj S. P. Molecular defect in factor IXBm Lake Elsinore. Substitution of Ala390 by Val in the catalytic domain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10545–10548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. R. Factor IX antigen by radioimmunoassay. Abnormal factor IX protein in patients on warfarin therapy and with hemophilia B. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):900–910. doi: 10.1172/JCI108712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. R. Monoclonal antibody to an epitope on the heavy chain of factor IX missing in three hemophilia-B patients. Blood. 1983 Nov;62(5):1027–1034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J., Davis L., Frazier D., Bajaj S. P., Stafford D. W. Genetic defect responsible for the dysfunctional protein: factor IXLong Beach. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):820–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
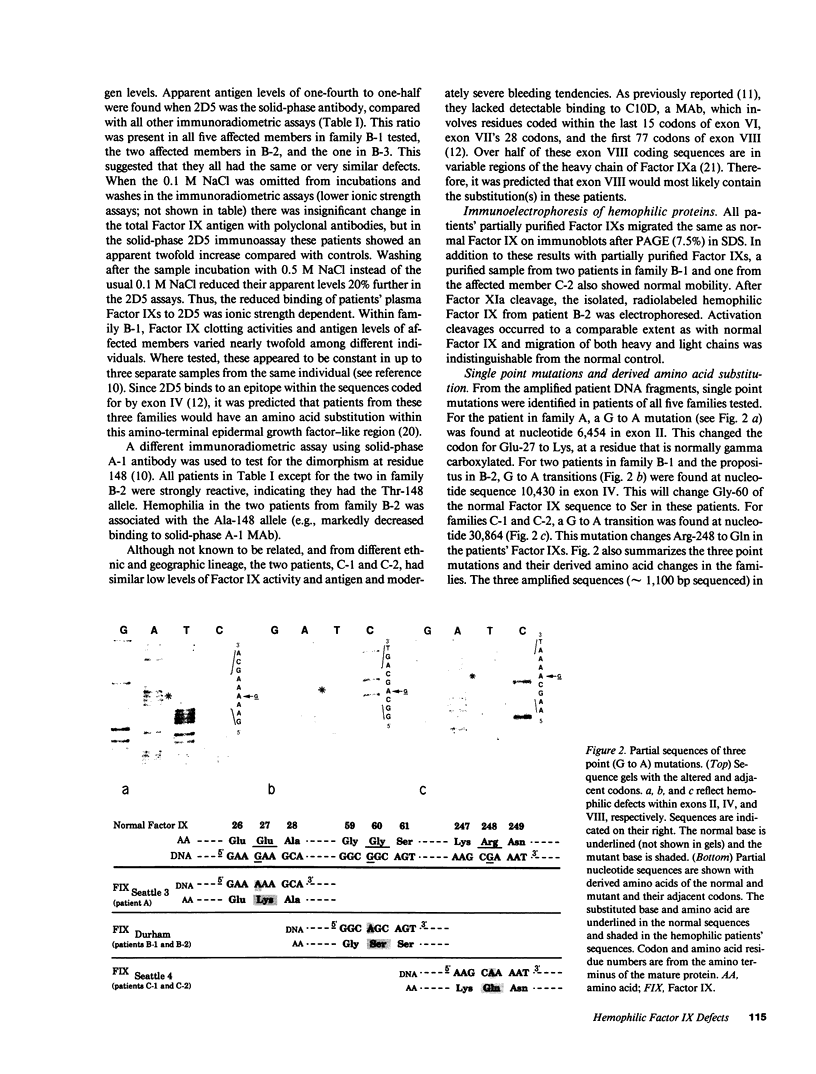
- Yoshitake S., Schach B. G., Foster D. C., Davie E. W., Kurachi K. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human factor IX (antihemophilic factor B). Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3736–3750. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Phillips D. G., Aronis S., Tsiftis G., Brown V. A., Antonarakis S. E. Recurrent mutations in haemophilia A give evidence for CpG mutation hotspots. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):380–382. doi: 10.1038/324380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]