Abstract
Antibodies to aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (anti-Jo-1, anti-PL-7, anti-PL-12) have been found in the serum of some patients with polymyositis (PM). Patients with these antibodies have an unusually high rate of interstitial lung disease (ILD) in association with their PM. Two patients (K.J. and B.T.) with severe ILD and PM were found to have antibodies to a cytoplasmic antigen, but tests to determine whether the antigen was an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase were negative, including tests of KJ serum for inhibitory effects on the 20 synthetases. KJ immunoprecipitates did not contain tRNA, in contrast to antisynthetase sera. When IgG samples were added to a reticulocyte in vitro translation system at a concentration of 0.3 mg/ml, KJ IgG inhibited globin mRNA translation by 98%, while anti-Jo-1 IgG inhibited 62% and normal IgG had little effect. Thus, both anti-KJ and the antisynthetases are directed at antigens that are involved in translation and protein synthesis, and both are associated with the syndrome of lung disease and PM. This syndrome may be associated with antibodies to translation-related proteins in general, which may have implications for the link of PM and enteroviruses, which are mRNA viruses.
Full text
PDF






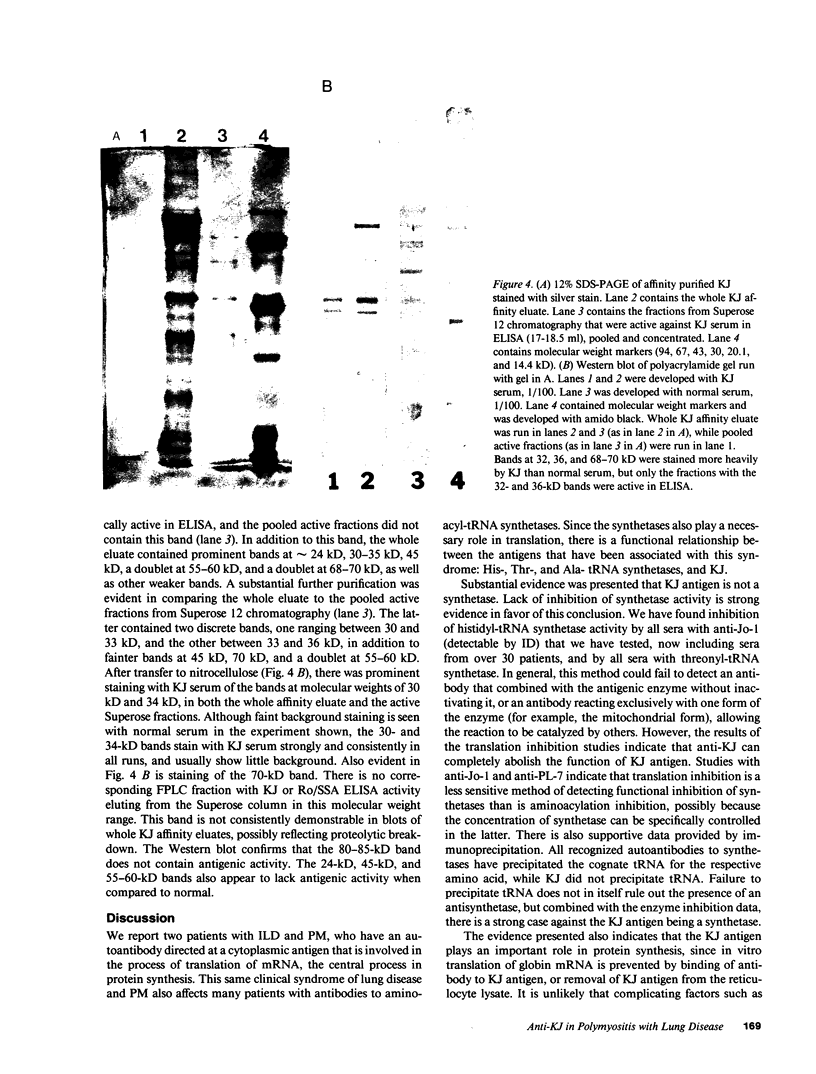



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. G., Kole R. Alu RNA transcribed in vitro binds the 68-kDa subunit of the signal recognition particle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2908–2912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Hirsch T. J., Bias W. B., Nishikai M., Reichlin M. The Jo-1 antibody system in myositis: relationships to clinical features and HLA. J Rheumatol. 1981 Nov-Dec;8(6):925–930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Morgan S. H., Chapman J., Bunn C. C., Mathews M. B., Turner-Warwick M., Hughes G. R. Anti-Jo-1 antibody: a marker for myositis with interstitial lung disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Jul 21;289(6438):151–152. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6438.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas T., Miller F. W., Takagaki Y., Plotz P. H. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection and quantitation of anti-Jo-1 antibody in human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 16;98(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohan A., Peter J. B., Bowman R. L., Pearson C. M. Computer-assisted analysis of 153 patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Jul;56(4):255–286. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197707000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohan A., Peter J. B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 20;292(8):403–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502202920807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles N. E., Dubowitz V., Sewry C. A., Archard L. C. Dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and Coxsackie-B-virus infection. Lancet. 1987 May 2;1(8540):1004–1007. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn C. C., Bernstein R. M., Mathews M. B. Autoantibodies against alanyl-tRNA synthetase and tRNAAla coexist and are associated with myositis. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1281–1291. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen M. L., Pachman L. M., Schneiderman R., Patel D. C., Friedman J. M. Prevalence of Coxsackie B virus antibodies in patients with juvenile dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Nov;29(11):1365–1370. doi: 10.1002/art.1780291109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Dang C. V. Higher eukaryotic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in physiologic and pathologic states. Mol Cell Biochem. 1986 Aug;71(2):107–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00214769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denman A. M. Inflammatory disorders of muscle. Aetiology. Clin Rheum Dis. 1984 Apr;10(1):9–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K. B., Parnassa A. P., Foster C. L. Lupus autoantibodies target ribosomal P proteins. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):459–471. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman M. S., Nakamura M., Mimori T., Gelpi C., Hardin J. A. Detection of antibodies to small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins using unlabeled cell extracts. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Dec;28(12):1356–1361. doi: 10.1002/art.1780281207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenni A. L., Joshi S., Chapeville F. tRNA-like structures in the genomes of RNA viruses. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1982;27:85–104. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60598-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg M. C., Feldman D., Stevens M. B., Arnett F. C., Reichlin M. Antibody to Jo-1 in polymyositis/dermatomyositis: association with interstitial pulmonary disease. J Rheumatol. 1984 Oct;11(5):663–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastaglia F. L., Ojeda V. J. Inflammatory myopathies: Part 2. Ann Neurol. 1985 Apr;17(4):317–323. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M. Myositis autoantibody inhibits histidyl-tRNA synthetase: a model for autoimmunity. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):177–179. doi: 10.1038/304177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Reichlin M., Hughes G. R., Bernstein R. M. Anti-threonyl-tRNA synthetase, a second myositis-related autoantibody. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):420–434. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldave K., Sadnik I. Preparation of derived and native ribosomal subunits from rat liver. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:402–410. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikai M., Reichlin M. Heterogeneity of precipitating antibodies in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Characterization of the Jo-1 antibody system. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Aug;23(8):881–888. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Mimori T., Mukai R., Kashiwagi H., Hardin J. A. Characterization of human autoantibodies that selectively precipitate the 7SL RNA component of the signal recognition particle. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3219–3223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Mukai R., Harada F., Kabashima T., Nakao Y., Yamane K., Ohshima Y., Sakamoto K., Itoh M., Kashiwagi H. Isolation of a novel antibody, which precipitates ribonucleoprotein complex containing threonine tRNA from a patient with polymyositis. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 15;139(3):425–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. M. Editorial: Myopathy with viral-like structures. N Engl J Med. 1975 Mar 20;292(12):641–641. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197503202921212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. L., Hancher C. W., Weiss J. F., Holladay D. W., Kelmers A. D. Preparation of crude transfer RNA and chromatographic purification of five transfer RNAs from calf liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;294(2):236–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotz P. H. Autoantibodies are anti-idiotype antibodies to antiviral antibodies. Lancet. 1983 Oct 8;2(8354):824–826. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H., Nigam S. K., Blobel G. Human autoantibodies reactive with the signal-recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9507–9511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M., Arnett F. C., Jr Multiplicity of antibodies in myositis sera. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Oct;27(10):1150–1156. doi: 10.1002/art.1780271011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M., Maddison P. J., Targoff I., Bunch T., Arnett F., Sharp G., Treadwell E., Tan E. M. Antibodies to a nuclear/nucleolar antigen in patients with polymyositis overlap syndromes. J Clin Immunol. 1984 Jan;4(1):40–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00915286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon R., Littauer U. Z. Enzymatic acylation of histidine to mengovirus RNA. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):32–34. doi: 10.1038/249032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strongwater S. L., Dorovini-Zis K., Ball R. D., Schnitzer T. J. A murine model of polymyositis induced by coxsackievirus B1 (Tucson strain). Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Apr;27(4):433–442. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targoff I. N., Arnett F. C., Reichlin M. Antibody to threonyl-transfer RNA synthetase in myositis sera. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Apr;31(4):515–524. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targoff I. N. Laboratory manifestations of polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Clin Dermatol. 1988 Apr-Jun;6(2):76–92. doi: 10.1016/0738-081x(88)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targoff I. N., Reichlin M. Measurement of antibody to Jo-1 by ELISA and comparison to enzyme inhibitory activity. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2874–2882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targoff I. N., Reichlin M. The association between Mi-2 antibodies and dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Jul;28(7):796–803. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treadwell E. L., Alspaugh M. A., Wolfe J. F., Sharp G. C. Clinical relevance of PM-1 antibody and physiochemical characterization of PM-1 antigen. J Rheumatol. 1984 Oct;11(5):658–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables P. J., Mumford P. A., Maini R. N. Antibodies to nuclear antigens in polymyositis: relationship to autoimmune 'overlap syndromes' and carcinoma. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Jun;40(3):217–223. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.3.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. J., Tymms K. E., Webb J., Jeffrey P. D. Improved detection of anti-Jo-1 antibody, a marker for myositis, using purified histidyl-tRNA synthetase. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Feb 11;96(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasicek C. A., Reichlin M., Montes M., Raghu G. Polymyositis and interstitial lung disease in a patient with anti-Jo1 prototype. Am J Med. 1984 Mar;76(3):538–544. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90677-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward W. R., Ivey J. L., Herbert E. Protein synthesis with rabbit reticulocyte preparations. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:724–731. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata H., Harley J. B., Reichlin M. Molecular properties of the Ro/SSA antigen and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of antibody. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):625–633. doi: 10.1172/JCI111460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D. C., Dang C. V., Arnett F. C. Rat liver histidyl-tRNA synthetase. Purification and inhibition by the myositis-specific anti-Jo-1 autoantibody. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 16;120(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91407-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Akizuki M., Mimori T., Yamagata H., Inada S., Homma M. The precipitating antibody to an acidic nuclear protein antigen, the Jo-1, in connective tissue diseases. A marker for a subset of polymyositis with interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 May;26(5):604–611. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]