Abstract
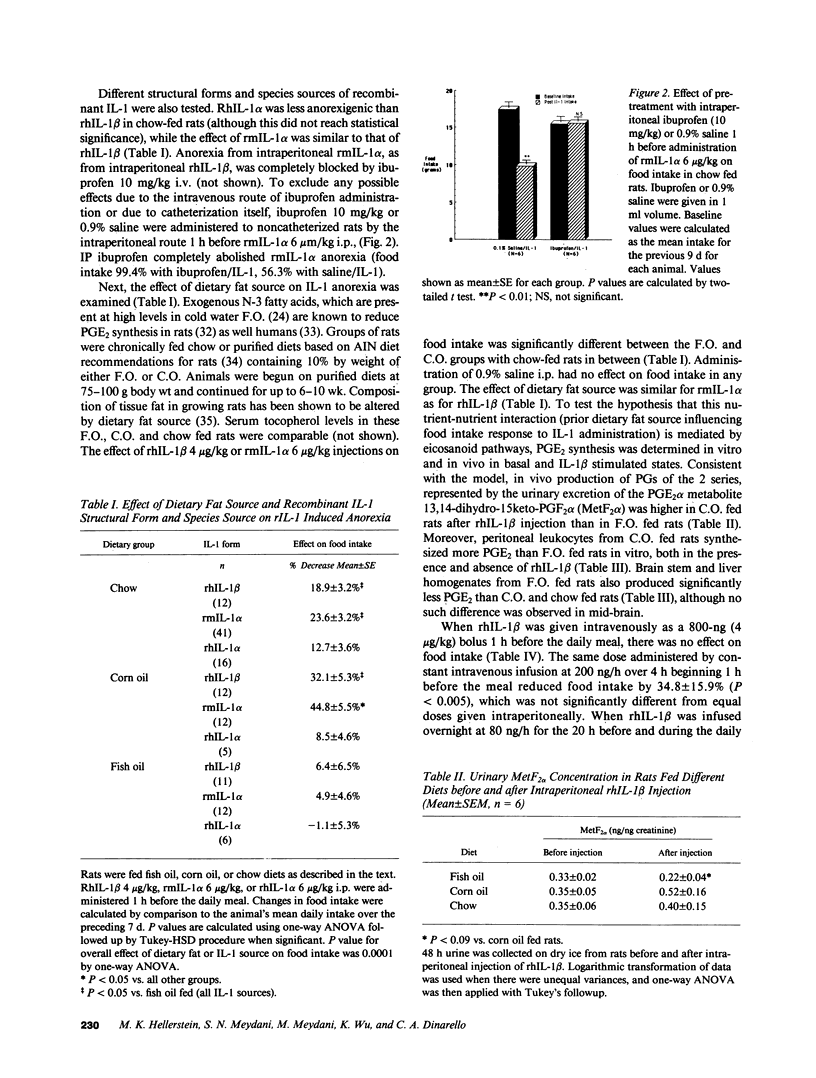
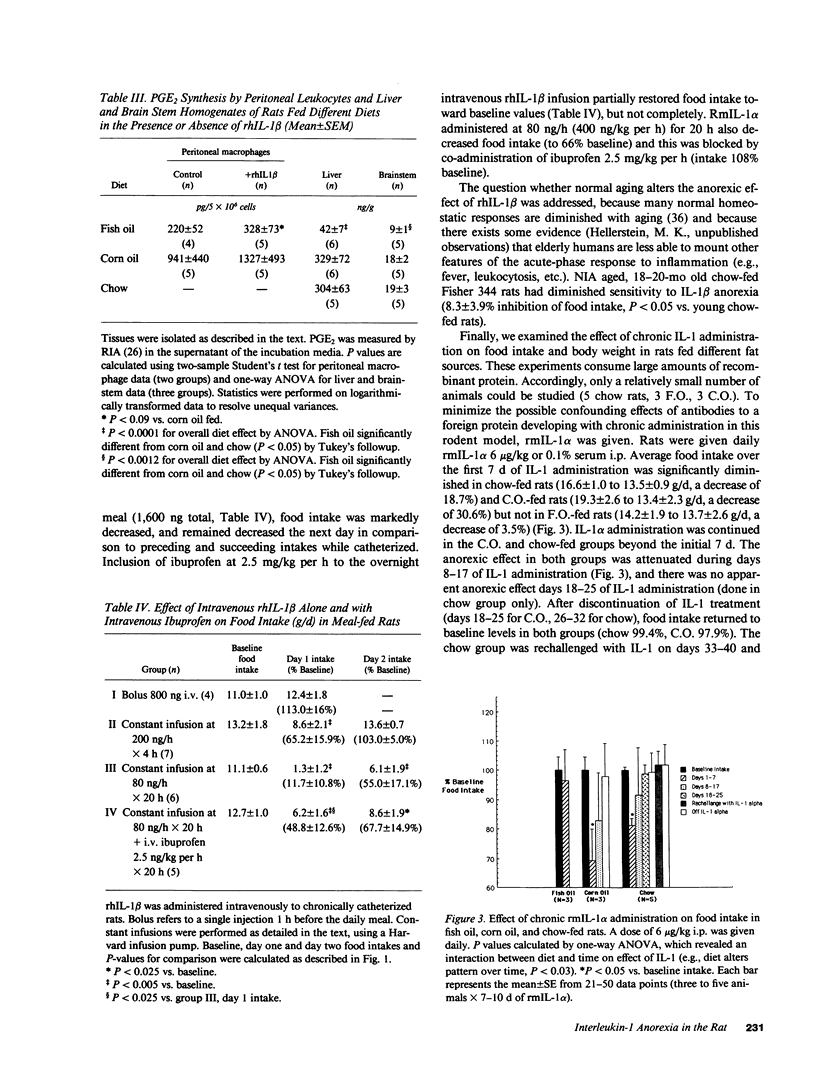
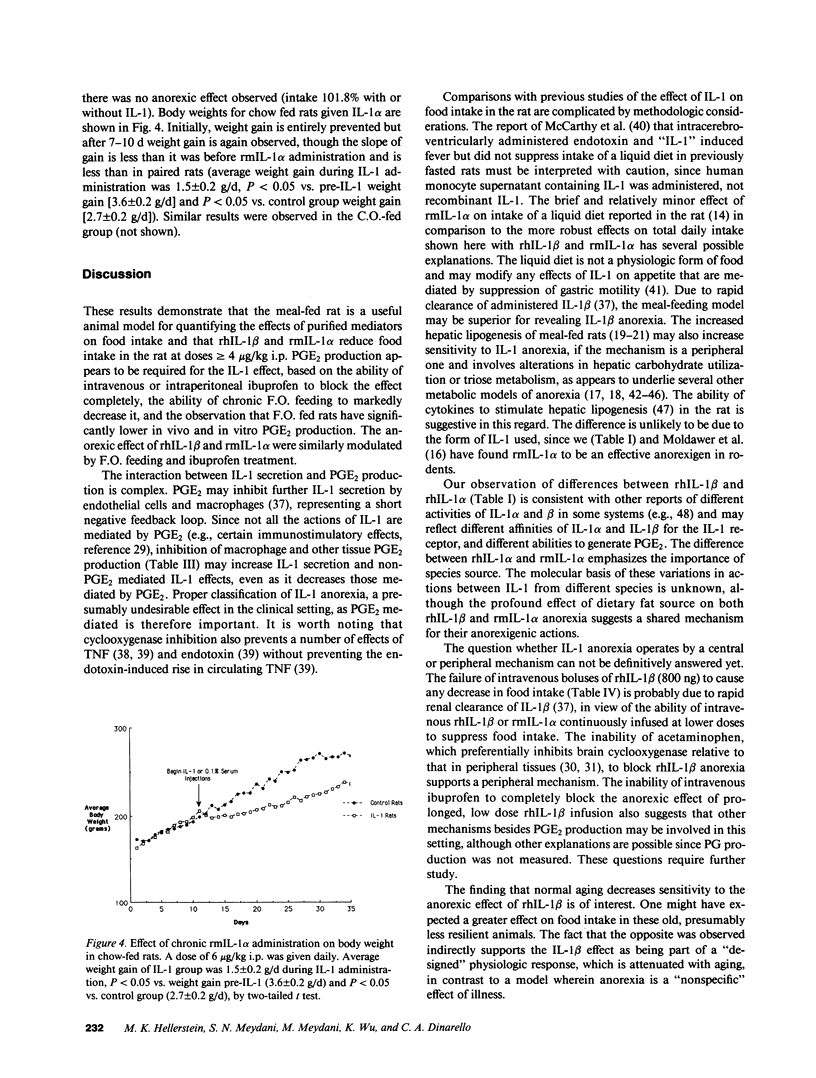
The anorexia associated with acute and chronic inflammatory or infectious conditions is poorly understood. Our objectives were to explore the anorexigenic effects of interleukin-1 (IL-1) in the rat. Recombinant human (rh) IL-1 beta, murine (rm) IL-1 alpha and to a lesser extent rhIL-1 alpha significantly reduced food intake at greater than or equal to 4.0 micrograms/kg i.p. but not at lower doses, in young (200-250 g) meal-fed rats on chow diets. The anorexic effect appears to be mediated by prostaglandins since pretreatment with ibuprofen completely blocked it, and a fish oil based diet abolished it, in comparison to corn oil or chow diets. Fish oil feeding also decreased basal and IL-1 stimulated prostaglandin E2 production by tissues in vitro (liver, brain, peritoneal macrophages) and in the whole body. Constant intravenous infusions of lower doses of IL-1 also diminished food intake, though intravenous boluses did not (reflecting rapid renal clearance). Chronic daily administration of IL-1 caused persistent inhibition of food intake for 7-17 d in chow and corn oil fed rats, but had no effect in fish oil fed rats. There was an attenuation of the effect (tachyphylaxis) after 7 d in corn oil and chow fed rats, but slowed weight gain and lower final weights were observed after 17-32 d of daily IL-1. Old (18-20 mo Fisher 344) rats showed less sensitivity to IL-1 induced anorexia. In conclusion, IL-1 is anorexigenic in the rat, but this is influenced by the structural form of IL-1, the route and chronicity of administration, the source of dietary fat, and the age of the animal. The ability of prior fat intake to influence the anorexic response to IL-1 represents a novel nutrient-nutrient interaction with potential therapeutic implications.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baile C. A., Zinn W. M., Mayer J. Effects of lactate and other metabolites on food intake of monkeys. Am J Physiol. 1970 Dec;219(6):1606–1613. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.6.1606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel W. R. Impact of infection on nutritional status: definition of the problem and objectives of the Workshop. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 Aug;30(8):1206–1210. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.8.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel W. R. Metabolic response to infection. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:9–20. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.000301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathcart E. S., Leslie C. A., Meydani S. N., Hayes K. C. A fish oil diet retards experimental amyloidosis, modulates lymphocyte function, and decreases macrophage arachidonate metabolism in mice. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1850–1854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlebowski R. T. Significance of altered nutritional status in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Nutr Cancer. 1985;7(1-2):85–91. doi: 10.1080/01635588509513843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Mier J. W., Bernheim H. A., LoPreste G., Lynn D. L., Love R. N., Webb A. C., Auron P. E., Reuben R. C. Multiple biological activities of human recombinant interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1734–1739. doi: 10.1172/JCI112495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Ikejima T., Warner S. J., Orencole S. F., Lonnemann G., Cannon J. G., Libby P. Interleukin 1 induces interleukin 1. I. Induction of circulating interleukin 1 in rabbits in vivo and in human mononuclear cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1902–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:153–205. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Marnoy S. O., Rosenwasser L. J. Role of arachidonate metabolism in the immunoregulatory function of human leukocytic pyrogen/lymphocyte-activating factor/interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):890–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Gustilo K., Baeder W., Freundlich B. Synergistic stimulation of fibroblast prostaglandin production by recombinant interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3812–3816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres S., Ghorbani R., Kelley V. E., Georgilis K., Lonnemann G., van der Meer J. W., Cannon J. G., Rogers T. S., Klempner M. S., Weber P. C. The effect of dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by mononuclear cells. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 2;320(5):265–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902023200501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Grunfeld C. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates hepatic lipogenesis in the rat in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):184–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI113046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase in brain explains the anti-pyretic activity of paracetamol (4-acetamidophenol). Nature. 1972 Dec 15;240(5381):410–411. doi: 10.1038/240410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerstein M. K., Greenblatt D. J., Munro H. N. Glycoconjugates as noninvasive probes of intrahepatic metabolism: pathways of glucose entry into compartmentalized hepatic UDP-glucose pools during glycogen accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7044–7048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman-Goetz L., Kluger M. J. Protein deficiency: its effects on body temperature in health and disease states. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jul;32(7):1423–1427. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.7.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler D. P., Wang J., Pierson R. N. Body composition studies in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Dec;42(6):1255–1265. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/42.6.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer J. M., Jubiz W., Michalek A., Rynes R. I., Bartholomew L. E., Bigaouette J., Timchalk M., Beeler D., Lininger L. Fish-oil fatty acid supplementation in active rheumatoid arthritis. A double-blinded, controlled, crossover study. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Apr;106(4):497–503. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-4-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhans W., Damaske U., Scharrer E. Different metabolites might reduce food intake by the mitochondrial generation of reducing equivalents. Appetite. 1985 Jun;6(2):143–152. doi: 10.1016/s0195-6663(85)80035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen K. Creatinine assay by a reaction-kinetic principle. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Oct;41:209–217. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Hoover R. L., Williams J. D., Sperling R. I., Ravalese J., 3rd, Spur B. W., Robinson D. R., Corey E. J., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Effect of dietary enrichment with eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on in vitro neutrophil and monocyte leukotriene generation and neutrophil function. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 9;312(19):1217–1224. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505093121903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveille G. A. The long-term effects of meal-eating on lipogenesis, enzyme activity, and longevity in the rat. J Nutr. 1972 Apr;102(4):549–556. doi: 10.1093/jn/102.4.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin M. D. The regulation of ACTH secretion by IL-1. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):452–454. doi: 10.1126/science.2821618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. O., Kluger M. J., Vander A. J. Effect of centrally administered interleukin-1 and endotoxin on food intake of fasted rats. Physiol Behav. 1986;36(4):745–749. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(86)90363-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. O., Kluger M. J., Vander A. J. Suppression of food intake during infection: is interleukin-1 involved? Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Dec;42(6):1179–1182. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/42.6.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meydani S. N., Dupont J. Effect of zinc deficiency on prostaglandin synthesis in different organs of the rat. J Nutr. 1982 Jun;112(6):1098–1104. doi: 10.1093/jn/112.6.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meydani S. N., Shapiro A. C., Meydani M., Macauley J. B., Blumberg J. B. Effect of age and dietary fat (fish, corn and coconut oils) on tocopherol status of C57BL/6Nia mice. Lipids. 1987 May;22(5):345–350. doi: 10.1007/BF02534004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldawer L. L., Andersson C., Gelin J., Lundholm K. G. Regulation of food intake and hepatic protein synthesis by recombinant-derived cytokines. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 1):G450–G456. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.3.G450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Burrowes C. E., Cybulsky M. I., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation and a Shwartzman-like reaction induced by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Synergistic action of the cytokines in the induction of inflammation and microvascular injury. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):463–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld H. A., Pace J. A., White F. E. The effect of bacterial infections on ketone concentrations in rat liver and blood and on free fatty acid concentrations in rat blood. Metabolism. 1976 Aug;25(8):877–884. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Ikejima T., Connolly R. J., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits. Synergism with tumor necrosis factor and the effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1162–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI113431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Defeo-Jones D., Boyer M., Martinez D., Kiefer D., Vuocolo G., Wolfe A., Socher S. H. Tumors secreting human TNF/cachectin induce cachexia in mice. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. S., Peters P. M., McCabe J., Crase D., Hansen S., Chen A. B., Liggitt D. Development of partial tolerance to the gastrointestinal effects of high doses of recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rodents. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1587–1596. doi: 10.1172/JCI113245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. S. Rapid extraction of oxygenated metabolites of arachidonic acid from biological samples using octadecylsilyl silica. Prostaglandins. 1980 Nov;20(5):947–957. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(80)90144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prickett J. D., Trentham D. E., Robinson D. R. Dietary fish oil augments the induction of arthritis in rats immunized with type II collagen. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):725–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A. An intestinal disease produced experimentally by a prostaglandin deficiency. Gastroenterology. 1975 Oct;69(4):1045–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A. Cytoprotection by prostaglandins. Gastroenterology. 1979 Oct;77(4 Pt 1):761–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russek M. Current status of the hepatostatic theory of food intake control. Appetite. 1981 Jun;2(2):137–143. doi: 10.1016/s0195-6663(81)80007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwadda D., Mugerwa R. D., Sewankambo N. K., Lwegaba A., Carswell J. W., Kirya G. B., Bayley A. C., Downing R. G., Tedder R. S., Clayden S. A. Slim disease: a new disease in Uganda and its association with HTLV-III infection. Lancet. 1985 Oct 19;2(8460):849–852. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(85)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan A. C., Gruen R. K. Mechanisms of appetite modulation by drugs. Fed Proc. 1985 Jan;44(1 Pt 1):139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan A. C., Triscari J., Hamilton J. G., Miller O. N. Effect of (-)-hydroxycitrate upon the accumulation of lipid in the rat. II. Appetite. Lipids. 1974 Feb;9(2):129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF02532137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN J., TEPPERMAN H. M. Effects of antecedent food intake pattern on hepatic lipogenesis. Am J Physiol. 1958 Apr;193(1):55–64. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theologides A. Anorexins, asthenins, and cachectins in cancer. Am J Med. 1986 Oct;81(4):696–698. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90558-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theologides A. Cancer cachexia. Cancer. 1979 May;43(5 Suppl):2004–2012. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197905)43:5+<2004::aid-cncr2820430708>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Wei H., Manogue K. R., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Kuo G. C., Beutler B., Cotran R. S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1211–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tredget E. E., Yu Y. M., Zhong S., Burini R., Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Dinarello C. A., Young V. R., Burke J. F. Role of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor on energy metabolism in rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):E760–E768. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.6.E760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Itallie T. B., Smith N. S., Quartermain D. P. Short-term and long-term components in the regulation of food intake: evidence for a modulatory role of carbohydrate status. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 May;30(5):742–757. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.5.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



