Abstract
To investigate the functional sites on a protein and the prediction of binding sites (residues)in proteins, it is often required to identify the binding site residues at different distance threshold from protein three dimensional (3D)structures. For the study of a particular protein chain and its interaction with the ligand in complex form, researchers have to parse the output of different available tools or databases for finding binding-site residues. Here we have developed a tool for calculating amino acid contact distances in proteins at different distance threshold from the 3D-structure of the protein. For an input of protein 3D-structure, ContPro can quickly find all binding-site residues in the protein by calculating distances and also allows researchers to select the different distance threshold, protein chain and ligand of interest. Additionally, it can also parse the protein model (in case of multi model protein coordinate file)and the sequence of selected protein chain in Fasta format from the input 3D-structure. The developed tool will be useful for the identification and analysis of binding sites of proteins from 3D-structure at different distance thresholds.
Availability
It can be accessed at: http://procarb.org/contpro/
Background
The function of proteins depends on their interaction with other molecules like proteins, DNA, RNA, carbohydrates and other ligands [1]. Therefore, identifying amino acid contacts is important for understanding the biological processes. In order to understand the mechanism of these interactions it is important to calculate the amino acid contacts at different distance thresholds [2–4]. Binding site residues of proteins can also be identified from pictorial databases [6], visualization tools like Ligplot [7], or many other web servers developed earlier [1, 5], but this becomes overwhelmingly imposing when a large set of proteins have to be analyzed. With the help of ContPro (Figure 1), user can identify a binding residue by selecting a protein chain and ligand of interest and retrieve the results in the form of different output files. Additionally, it can also parse the multi model PDB file, sequence of selected protein chain from the 3Dstructure of protein and gives the atomic details of contacts including distance as compared with the previous developed tools for calculating binding-site residue from PDB structures [1,5,9]. Protein Data Bank (PDB)is repository of for 3D structures of biological macromolecules which contains coordinates of its atoms [8], and by using these coordinates of two atoms, one can compute the distance between them.
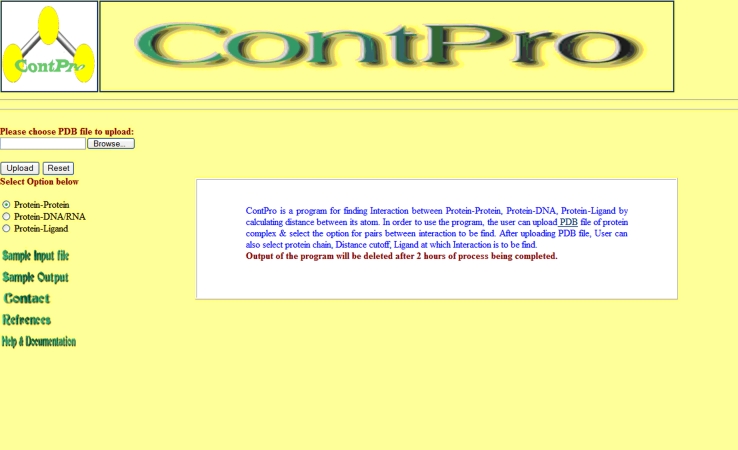
Figure 1.
Screen shot of ContPro Home page. From this home page user can upload PDB file.
Methodology
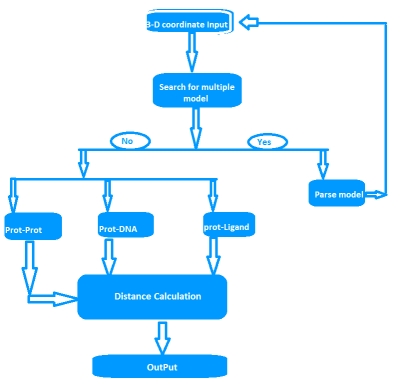
A residue is defined as a binding residue if the distance between atoms of the interacting partner is less than a certain distance cutoff [1,9]. Upon uploading the protein 3D-structure file of interest and option selected for interacting partners by user, ContPro searches the PDB file for the protein chains, DNA chain and the number of protein models (if multi model protein). If more than one model is present, ContPro gives option to select and parse the desired model present in the uploaded PDB file. Distance threshold in angstroms, protein chain and ligand of interest can also be selected by the user. Then ContPro calculates the distance between selected protein chain residue atoms and interacting partner atoms, and when this distance falls below or equal to the selected distance threshold, this residue is considered as binding residue. The overall methodology is illustrated in figure (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Flow chart of ContPro, where overall methodology is illustrated
Web interface
Web interface of current version of ContPro was developed using HTML and CGI-PERL scripting language. Help & Documentation, Sample Input file, Sample output file are provided at the ContPro web site.
Program input
The input to the Contpro is a protein 3D coordinate file like PDB, modeled protein or a docked complex file. The user can select between proteinprotein, protein-DNA and protein-ligand interaction type as well as protein chain, ligand, distance threshold, model number if structure has more than one model after uploading file.
Program output
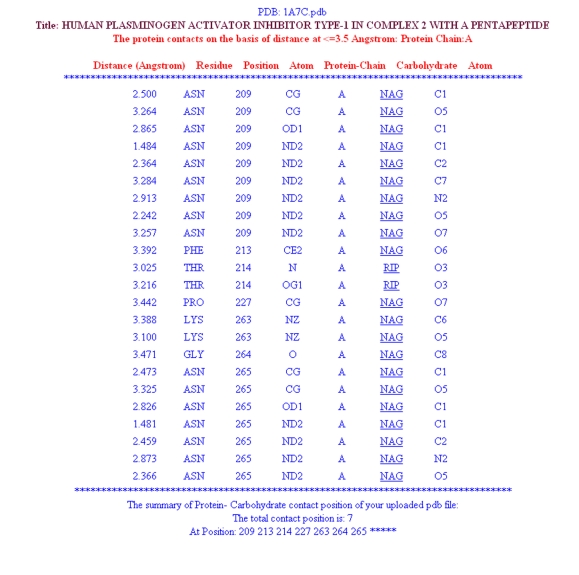
At the top of the program's result page (Figure 3), the uploaded file name and distance threshold selected for the calculations are displayed. The calculated distance between the two atoms, its residue, protein chain and the interacting atoms is displayed in a tabular form (Figure 3). The page summary section at the end has three downloadable output files. These three downloadable files are:-
the protein sequence file in the Fasta format which was extracted from the structure of selected protein chain,
result.txt for details about contact and
Con.txt which has three column data.
First column has residue in one letter code of selected protein chain, second column has chain name of protein and third column has 0 or 1 where is 0 indicates non binding and 1 indicates binding to respective residue.
Figure 3.
Screen shot of ContPro result page
Conclusion
The developed tool will be useful for the identification and analysis of binding sites of protein from 3D-structure at different distance threshold.
Acknowledgments
The financial support under Project “Biomedical Informatics Centre of ICMR” is gratefully acknowledged.
Footnotes
Citation:Firoz et al, Bioinformation 5(2): 55-57 (2010)
References
- 1.Jing H, Changhuian Y. BMC Struct Biol. 2009;9:52. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-9-52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Malik A, Ahmad S. BMC Struct Biol. 2007;7:1. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-7-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Liu T, Altman RB. BMC Struct Biol. 2009;9:7. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-9-72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kumar M, et al. Proteins: Struct Func Bioinform. 2007;71:189. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mancini AL, et al. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:2145. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Laskowski RA, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:221. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wallace CA, et al. Protein Eng Design Selec. 1995;8:127. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Berman H, et al. Nucleic Acid Research. 2007;35:D301. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sobolev V, et al. Bioinformatics. 1999;15:327. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/15.4.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]