Abstract
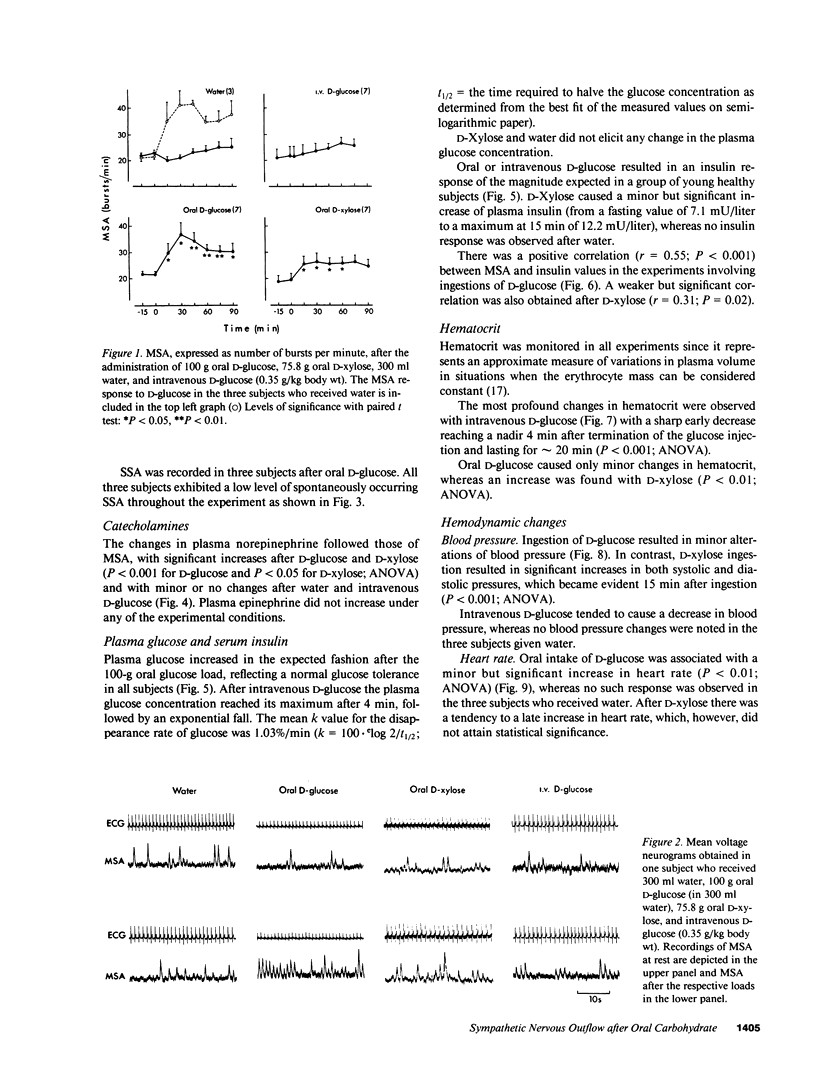
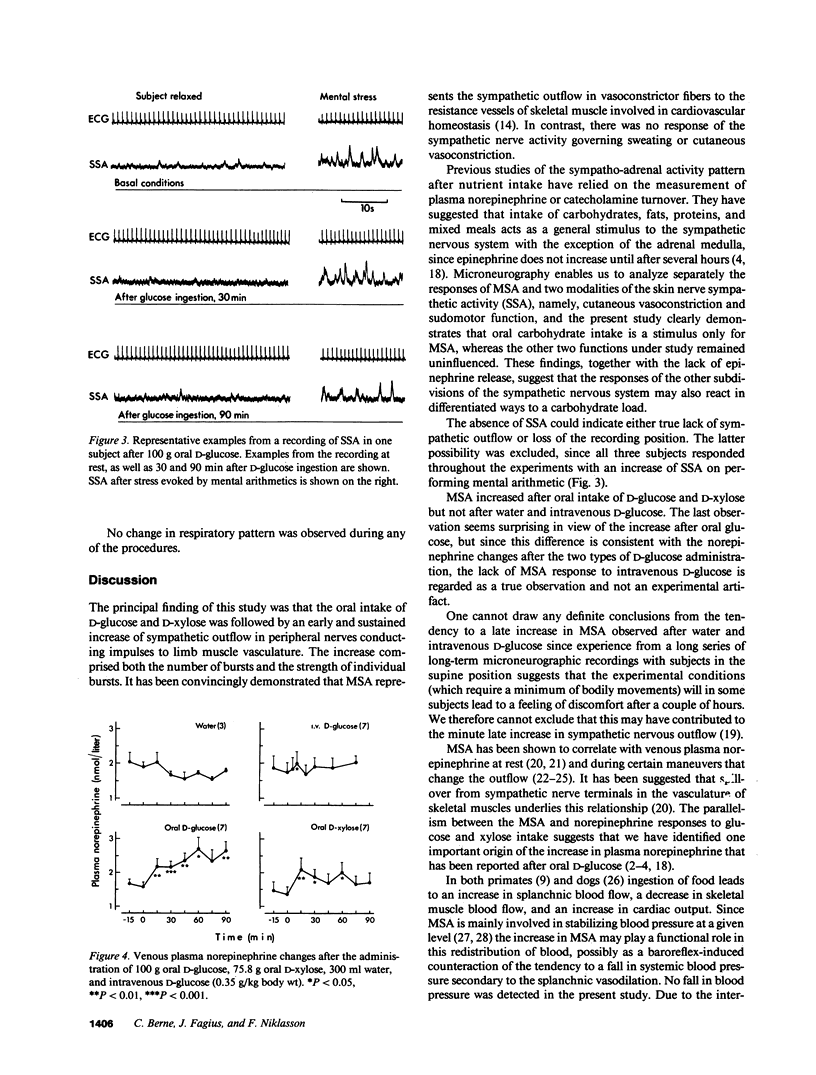
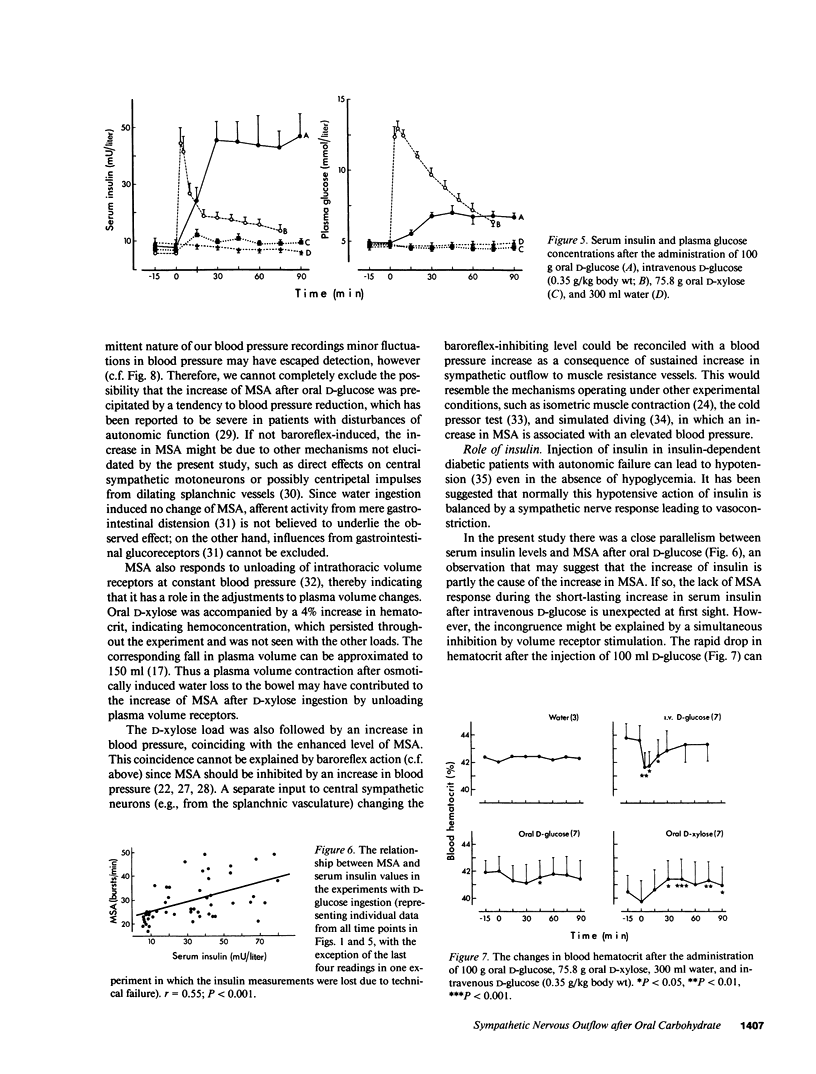
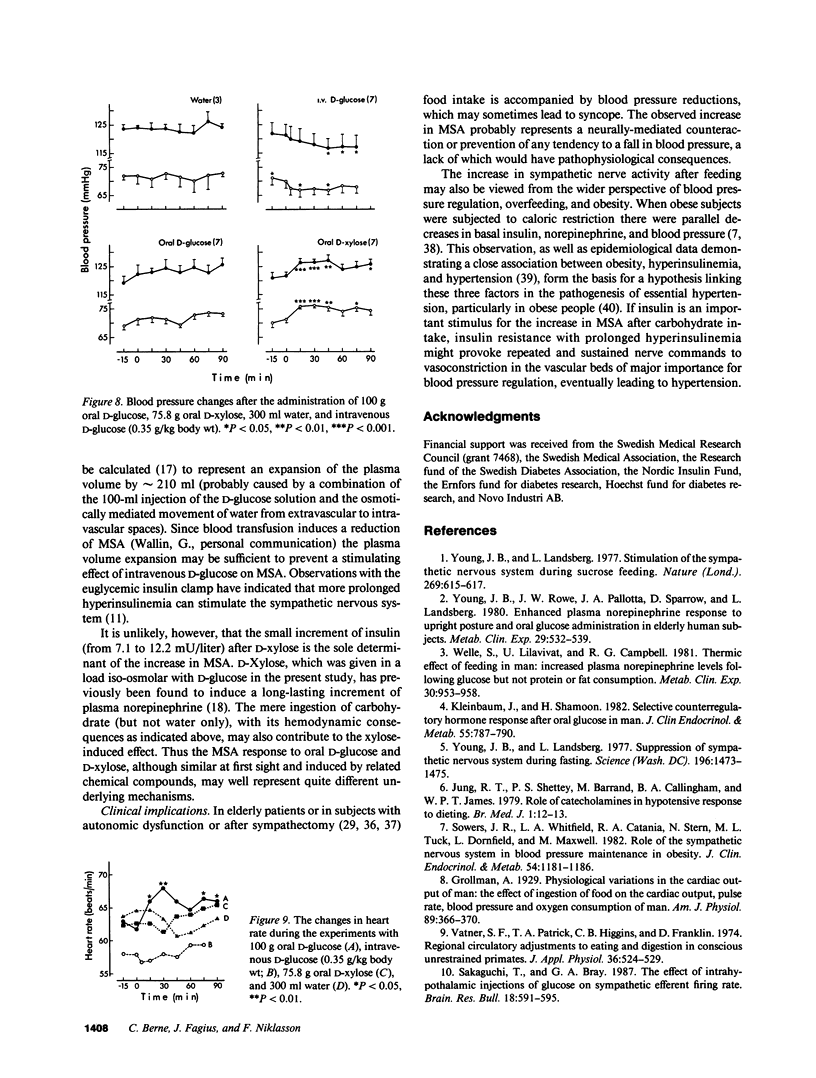
Microneurography was used to measure sympathetic outflow in human muscle nerves (MSA) for up to 90 min after the ingestion of 100 g D-glucose, 75.8 g D-xylose, intravenous D-glucose (0.35 g/kg), and 300 ml water. 19 healthy subjects were examined using a microelectrode positioned in the right peroneal nerve. MSA increased from 21 +/- 0.9 bursts/min at rest to 36.9 +/- 4.3 bursts/min 30 min after ingestion of D-glucose and from 18.9 +/- 2.9 to 26.3 +/- 3.4 bursts/min 30 min after D-xylose. The increase in MSA was already significant by 15 min. MSA had not returned to the basal level after 90 min. Neither intravenous D-glucose nor water intake enhanced MSA. MSA increased in parallel with plasma norepinephrine, and a significant correlation (r = 0.55; P less than 0.001) was observed between the plasma insulin concentration and MSA after D-glucose ingestion. In three subjects the outflow of sympathetic nerve activity to the skin was examined after oral D-glucose and no change was observed, emphasizing the differentiated nature of the sympathetic nerve response to carbohydrate. Multiple factors such as insulin alone, hemodynamic adjustment to splanchnic vasodilation, and gastrointestinal distension are probably involved in the increased muscle nerve sympathetic outflow after carbohydrate ingestion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. L. Vagal afferent innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Prog Brain Res. 1986;67:65–86. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62757-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Sundlöf G., Wallin G. Postural effects on muscle nerve sympathetic activity in man. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):399–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius W., Hagbarth K. E., Hongell A., Wallin B. G. Manoeuvres affecting sympathetic outflow in human skin nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Feb;84(2):177–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckberg D. L., Rea R. F., Andersson O. K., Hedner T., Pernow J., Lundberg J. M., Wallin B. G. Baroreflex modulation of sympathetic activity and sympathetic neurotransmitters in humans. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Jun;133(2):221–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagius J., Berne C. Changes of sympathetic nerve activity induced by 2-deoxy-D-glucose infusion in humans. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):E714–E720. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.6.E714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagius J., Sundlöf G. The diving response in man: effects on sympathetic activity in muscle and skin nerve fascicles. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:429–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fronek K., Stahlgren L. H. Systemic and regional hemodynamic changes during food intake and digestion in nonanesthetized dogs. Circ Res. 1968 Dec;23(6):687–692. doi: 10.1161/01.res.23.6.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth K. E., Vallbo A. B. Pulse and respiratory grouping of sympathetic impulses in human muscle-nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Sep-Oct;74(1):96–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb04218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung R. T., Shetty P. S., Barrand M., Callingham B. A., James W. P. Role of catecholamines in hypotensive response to dieting. Br Med J. 1979 Jan 6;1(6155):12–13. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6155.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinbaum J., Shamoon H. Selective counterregulatory hormone responses after oral glucose in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Oct;55(4):787–790. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-4-787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg L. Diet, obesity and hypertension: an hypothesis involving insulin, the sympathetic nervous system, and adaptive thermogenesis. Q J Med. 1986 Dec;61(236):1081–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsitz L. A., Nyquist R. P., Jr, Wei J. Y., Rowe J. W. Postprandial reduction in blood pressure in the elderly. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 14;309(2):81–83. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307143090205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modan M., Halkin H., Almog S., Lusky A., Eshkol A., Shefi M., Shitrit A., Fuchs Z. Hyperinsulinemia. A link between hypertension obesity and glucose intolerance. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):809–817. doi: 10.1172/JCI111776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mörlin C., Wallin B. G., Eriksson B. M. Muscle sympathetic activity and plasma noradrenaline in normotensive and hypertensive man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983;119(2):117–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. M., Watkins P. J. Provocation of postural hypotension by insulin in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes. 1976 Feb;25(2):90–95. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.2.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisin E., Frohlich E. D., Messerli F. H., Dreslinski G. R., Dunn F. G., Jones M. M., Batson H. M., Jr Cardiovascular changes after weight reduction in obesity hypertension. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):315–319. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Wade D., Robertson R. M. Postprandial alterations in cardiovascular hemodynamics in autonomic dysfunction states. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Dec;48(6):1048–1052. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. W., Young J. B., Minaker K. L., Stevens A. L., Pallotta J., Landsberg L. Effect of insulin and glucose infusions on sympathetic nervous system activity in normal man. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):219–225. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi T., Bray G. A. The effect of intrahypothalamic injections of glucose on sympathetic efferent firing rate. Brain Res Bull. 1987 May;18(5):591–595. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(87)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers J. R., Whitfield L. A., Catania R. A., Stern N., Tuck M. L., Dornfeld L., Maxwell M. Role of the sympathetic nervous system in blood pressure maintenance in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Jun;54(6):1181–1186. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-6-1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundlöf G., Wallin B. G. Effect of lower body negative pressure on human muscle nerve sympathetic activity. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:525–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundlöf G., Wallin B. G. Human muscle nerve sympathetic activity at rest. Relationship to blood pressure and age. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:621–637. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse T. F., Clutter W. E., Shah S. D., Miller J. P., Cryer P. E. Neuroendocrine responses to glucose ingestion in man. Specificity, temporal relationships, and quantitative aspects. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):270–277. doi: 10.1172/JCI110966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatner S. F., Patrick T. A., Higgins C. B., Franklin D. Regional circulatory adjustments to eating and digestion in conscious unrestrained primates. J Appl Physiol. 1974 May;36(5):524–529. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.5.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor R. G., Leimbach W. N., Jr, Seals D. R., Wallin B. G., Mark A. L. Effects of the cold pressor test on muscle sympathetic nerve activity in humans. Hypertension. 1987 May;9(5):429–436. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.5.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor R. G., Seals D. R., Mark A. L. Differential control of heart rate and sympathetic nerve activity during dynamic exercise. Insight from intraneural recordings in humans. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):508–516. doi: 10.1172/JCI112841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., Fagius J. Peripheral sympathetic neural activity in conscious humans. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:565–576. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.003025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., Mörlin C., Hjemdahl P. Muscle sympathetic activity and venous plasma noradrenaline concentrations during static exercise in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Apr;129(4):489–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., Sundlöf G. A quantitative study of muscle nerve sympathetic activity in resting normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Hypertension. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):67–77. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.1.2.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., Sundlöf G., Eriksson B. M., Dominiak P., Grobecker H., Lindblad L. E. Plasma noradrenaline correlates to sympathetic muscle nerve activity in normotensive man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Jan;111(1):69–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welle S., Lilavivat U., Campbell R. G. Thermic effect of feeding in man: increased plasma norepinephrine levels following glucose but not protein or fat consumption. Metabolism. 1981 Oct;30(10):953–958. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90092-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. B., Landsberg L. Stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system during sucrose feeding. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):615–617. doi: 10.1038/269615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. B., Landsberg L. Suppression of sympathetic nervous system during fasting. Science. 1977 Jun 24;196(4297):1473–1475. doi: 10.1126/science.867049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. B., Rowe J. W., Pallotta J. A., Sparrow D., Landsberg L. Enhanced plasma norepinephrine response to upright posture and oral glucose administration in elderly human subjects. Metabolism. 1980 Jun;29(6):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Beaumont W., Strand J. C., Petrofsky J. S., Hipskind S. G., Greenleaf J. E. Changes in total plasma content of electrolytes and proteins with maximal exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Jan;34(1):102–106. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.34.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



