Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Injury of the cerebellar vermis may occur in children with brain malignancies. Because the vermis is involved in motor and cognitive functioning, the goal of this prospective longitudinal study was to evaluate treatment-related changes in vermal volumes and neuropsychologic performance in children receiving brain radiation of the cerebellum.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Ten patients (mean age, 11.6 years) and 10 healthy children (mean age, 12.1 years) were examined. Lobar vermal volumes and performance on neuropsychologic tests evaluating motor, visual, verbal, attention, memory, and executive functions were assessed at baseline and at 6-month follow-up visits.
RESULTS:
At baseline, lower mean vermal volumes and impaired performance on visual-spatial and fine-motor tasks were detected in patients. At 6-month follow-up, further decrease in vermal volumes was detected only in patients with medulloblastoma, who received the largest radiation doses to the entire vermis. The volume decrease was not associated with reduction in neuropsychologic performance compared with baseline. At 6-month follow-up, data from all subjects revealed an association between smaller vermal volumes and slower fine-motor speed and lower visual-spatial skills.
CONCLUSIONS:
Reduced brain-tissue volumes following radiation have been reported previously in pediatric patients. In this study, lower vermal volumes were detected even earlier, before radiation treatment was initiated or completed. Six months postradiation, vermal volume decreases detected in patients with medulloblastoma were not accompanied by declines in already poor neuropsychologic performance. In addition to radiation, the presence of brain malignancies and preradiation treatment may be important factors affecting cerebellar vermis tissue.
The cerebellar vermis has been implicated in both motor functions and nonmotor behaviors. Lesions of the vermis or the posterior cerebellum may cause behavioral abnormalities (cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome), including impairment of executive function, difficulty with language production, visual-spatial disorganization, and impaired visual-spatial memory.1 The anterior vermis is involved in phonologic awareness and attention2 and appears vulnerable to perinatal hypoxic-ischemic injury.3 In a study of children prenatally exposed to alcohol, anterior vermal dysmorphology was negatively correlated with performance on verbal learning and memory tests.4 The presence of lesions in the posterior vermis may result in emotional lability and changes in affect.5 Incision of the vermis can lead to cerebellar mutism, which may develop into language and speech disorders and behavioral problems.6 The nature of the neuropsychologic deficits observed in patients with vermal (and cerebellar) lesions is suggestive of disruption of anatomic connections that link the cerebellum with the cerebral association areas and paralimbic regions.1
In children diagnosed with brain tumors, vermal injury may result from the presence of a tumor or from treatment, which may involve combinations of surgery, adjuvant chemotherapy, and radiation. Although the vermis typically receives the highest radiation doses in the treatment of posterior fossa tumors, it may also be included in the radiation field for tumors distant from the posterior fossa. Children treated with radiation can manifest a wide spectrum of neuropsychologic deficits, depending on the type and location of the tumor and subsequent treatment.7 The main risk factors for impairment in cognitive development include younger age at treatment, longer time after treatment completion, female sex, irradiated volume, and radiation dose.8 The most challenging long-term sequelae in patients treated with radiation are chronic neurocognitive effects—that is, declines in general intelligence, academic achievement, memory, attention, information-processing speed, concentration, visual-perceptual skills, and language.8 Recent studies in children treated for cerebellar tumors demonstrated that deficits in executive functions were pronounced in patients with tumors located in the vermis and dentate nucleus.9,10
Radiation and chemotherapy are associated with the reduction in volumes of normal-appearing white matter. White matter reduction was reported to contribute to deficits in attention, intelligence, and academic achievements.11,12 Cerebellar atrophy is also a negative prognostic factor for cognitive outcome from therapy.13
The objective of this prospective longitudinal study was to evaluate early-delayed effects of radiation treatment on the cerebellar vermis in children with brain tumors or ALL. The aims were to assess: 1) changes in anterior and posterior vermal volumes and related neuropsychologic performance, 2) the effect of radiation dose on changes in vermal volumes and neuropsychologic performance, and 3) the association between vermal volumes and neuropsychologic performance following radiation. We hypothesized that the following would occur 6 months after completion of radiation treatment: 1) vermal volumes and neuropsychologic performance in patients would be decreased, 2) the decrease in vermal volumes and neuropsychologic test scores would be more pronounced in children receiving higher radiation doses, and 3) performance on neuropsychologic tests considered to be associated with the cerebellar vermis function would be reduced in children with lower vermal volumes.
Materials and Methods
Ten pediatric patients (7 boys; mean age, 11.6 ± 4.0 years; 9 right-handed) treated with brain radiation were included in the study (Table). Ten healthy typically developing children (7 boys; mean age, 12.1 ± 3.4 years; 9 right-handed) composed the control group. The longitudinal study was designed to include ≤4 visits: baseline (before the start of radiation), 6-month, 15-month, and 27-month follow-ups (after completion of radiation).
Patient demographic and clinical information
| Patient No. | Sex | Age (yr) | Diagnosis | Tumor Location | Treatment Prior to RT (Time of Administration before RT, mo)a |
Radiation Dose (Gy) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior |
Posterior |
|||||||||
| Surgery | Chemotherapy | Steroids | I-V | VI-VII | VIII-X | |||||
| 1 | M | 5.5 | Pilocytic astrocytoma | Right frontal suprasellar/optic | Yes (42.7) | CaPt (35.0), TMZ (16.5) | No | 18.5 | 20.4 | 23.5 |
| 2b | F | 8.5 | Anaplastic medulloblastoma | Posterior fossa | Yes (5.8) | CsPt/VP-16/ CTX/VCR/MTX (5.2) | Dex (5.3) | 54.4 | 54.3 | 54.3 |
| 3 | F | 8.7 | Nonanaplastic medulloblastoma | Posterior fossa | Yes (1.1) | No | Dex (0.8) | 54.0 | 54.0 | 54.0 |
| 4b | M | 9.2 | Anaplastic medulloblastoma | Fourth ventricle | Yes (1.5) | No | Dex (1.5) | 54.5 | 54.5 | 54.5 |
| 5 | M | 10.2 | T-cell ALL | No tumor | No | T-cell IC (1.1) | Pred (0.7) | 18.3 | 18.3 | 18.3 |
| 6 | M | 11.8 | Nondiagnostic biopsy (astrocytoma or ependymoma) | Pineal | No (VP shunt) | No | No | 14.9 | 4.8 | 30.0 |
| 7 | M | 11.8 | Malignant glioneuronal tumor, otherwise unclassifiable | Left frontal | Yes (5.7) | No | No | 41.4 | 41.0 | 34.5 |
| 8 | M | 15.3 | Ependymoma | Left medial temporal lobe | Yes (0.9) | No | No | 36.7 | 36. 8 | 38.0 |
| 9b | M | 16.0 | Pontine glioma | Pons | No | No | Dex (2.0) | 50.6 | 24.7 | 33.1 |
| 10 | F | 18.6 | Germinoma | Suprasellar | Yes (4.1) | CsPt/VP-16/ CTX/VCR/(3.1) | HC (3.7) | 20.3 | 15.4 | 16.0 |
Note:—In all patients with medulloblastoma, the posterior vermis was affected by surgery. None of the patients were diagnosed with obstructive hydrocephalus; moderately enlarged ventricles were noted in patients 1 and 6. Postsurgical mutism was diagnosed in patient 3.
Time of administration before the start of radiation treatment is shown.
Patient died.
At baseline, all participants were free from psychiatric diagnoses on the basis of assessment with the Diagnostic Interview for Children and Adolescents, 4th ed. At follow-up assessments, no change in psychiatric status was reported for any of the participants. The study was approved by the institutional review board, and each family participating in the study signed a written informed consent.
High-resolution 3D spoiled gradient-recalled-echo T1-weighted images were acquired on a 1.5T scanner with 1.5-mm-section partitions. The vermis was measured according to a modified version of a previously published protocol14 by using the program Measure (P. Barta, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland). The midsagittal section and 1 section to the right and 1 to the left were identified. Separate regions of interest for lobules I-V, VI-VII, and VIII-X, drawn on all 3 sections of each dataset, were used for volume calculations. Reliability by using the ICC was determined by 2 B.A.-level raters, as follows: anterior vermis volume (ICC = 0.967), posterior vermis volume of lobules VI and VII (ICC = 0.946), and posterior vermis volumes lobules VIII, IX, and X (ICC = 0.940).
The following neuropsychologic tests used in the study provided a broad sampling of relevant neurobehavioral domains and included 2 tests recently linked to MR spectroscopic15 and volumetric measures16 in healthy children and adolescents:
Visual Matching (WJ-III Tests of Cognitive Ability), a measure of visual selective attention and processing speed.
Retrieval Fluency (WJ-III Tests of Cognitive Ability), a measure of rapid lexical retrieval and executive functioning.
Bead Memory (Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale, 4th ed), a test of visual-spatial working memory.
Developmental Test of Visual Perception, a visual discrimination test.
Purdue Pegboard Test, a test of fine-motor dexterity and speed.
CPT-II, a computerized measure of sustained attention, vigilance, and reaction time.
Statue (NEPSY-2, a developmental neuropsychologic assessment), a test designed to measure motor persistence and inhibition.
All available data are presented in the figures and were used in the main GLM analyses of vermal volumes and neuropsychologic test scores. For the present study, we focused on the baseline and 6-month follow-up visits. GLM multiple analysis of variance was used to evaluate the relationship between the volumes of vermis subregions (anterior vermis, lobules I-V; posterior vermis, lobules VI-VII; and posterior vermis, lobules VIII-X), age at the baseline visit (years), time since the baseline visit (years), and group (controls, patients). To control for differences in brain size, we divided volumes of the vermis subregions by total cranial gray and white matter volume obtained at the baseline visit [according to (vermal volume) * 1000 / (cranial volume at the baseline visit)], resulting in relative volumes. Two-sided t tests were applied post hoc to compare vermal volumes between patients and controls at individual time points. In these analyses, volumes of the posterior vermis, lobules VIII-X, in the 3 patients who had surgically removed tissue from this subregion were not included. The Fisher least significant difference method was used as a post hoc test to compare changes in relative vermal volumes among controls, patients without surgery, and patients with surgery.
Linear regression analyses were used to examine the relationship between changes in vermal volumes (in percentages) according to [(volume at 6-month follow-up − volume at baseline) * 100 / (volume at baseline)] and radiation doses.
GLM analyses were also applied to compare neuropsychologic test scores between patients and controls; data from all visits were used in the main analyses. Age-corrected standard scores (Visual Matching, Retrieval Fluency, Bead Memory, Visual Perception, CPT-II mean reaction time), z scores (Purdue Pegboard, right, left, and both hands), and raw scores (Statue) were used. For neuropsychologic tests showing significant differences between patients and controls, correlation analysis was also applied to evaluate the relationship between total relative vermal volumes and neuropsychologic test scores at baseline and at 6-month follow-up.
To account for multiple comparisons in the limited sample size, we considered only results with both P < .05 and large effect sizes η2≥ 0.1417,18 as significant.
Results
Midsagittal images of the vermis are shown in Fig 1. The following number of subjects (n = number of patients/number of controls) completed the MR imaging and neuropsychologic evaluations at each visit: baseline (N = 10/10 for both MR imaging and NP), first follow-up (mean time since the baseline visit, 0.61/0.54 (patients/controls) years; n = 10/8 for MR imaging, 9/8 for NP), second follow-up (mean time since the baseline visit, 1.46/1.29 years; n = 6/8 for MR imaging, 6/7 for NP), and third follow-up (mean time since the baseline visit, 2.3/2.3 years; n = 3/3 for MR imaging, 6/7 for NP). In patients, the baseline examination was performed in 4 participants before the start of radiation (Table, patients 2, 3, 6, 10), as planned. Four patients completed the baseline examination within 11.5 days into radiation therapy, on average (patients 1, 4, 5, 7); and 2 patients were evaluated shortly after completion of radiation (7 days, patient 9; and 1 month, patient 8). The main reasons that some patients could not have been evaluated before the start of radiation included poor clinical condition of the patients and busy family schedules. In all subjects, neuropsychologic evaluations were completed within 3 months of the MR imaging examination (mean, 0.8 ± 1.2 months). There were no significant group differences in age at baseline (t test, P = .75) or at the 6-month follow-up (t test, P = .76).
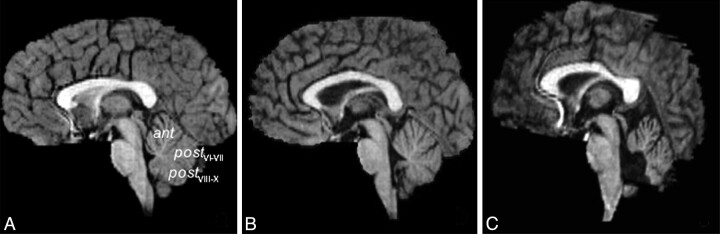
Fig 1.
T1-weighted midsagittal images obtained at baseline visit in an 8.6-year old healthy girl (A), a 10.2-year old boy with ALL (B), and an 8.5-year old girl diagnosed with medulloblastoma (C, surgical resection included the posterior vermis).
Volumes of vermal subregions (expressed relative to total cranial volumes at the baseline visit) in patients and controls are compared in Fig 2 . There was no significant difference in the total cranial gray and white matter volumes at the baseline between patients (1200.9 ± 118.5 cm3) and controls (1155.3 ± 180.8 cm3) (t test, P = .51). However, the main GLM analyses revealed significantly lower relative vermal volumes in patients compared with controls (anterior vermis; posterior vermis, lobules VI-VII; posterior vermis, lobules VIII-X; all, P < .0001 and η2> 0.39).
Fig 2.
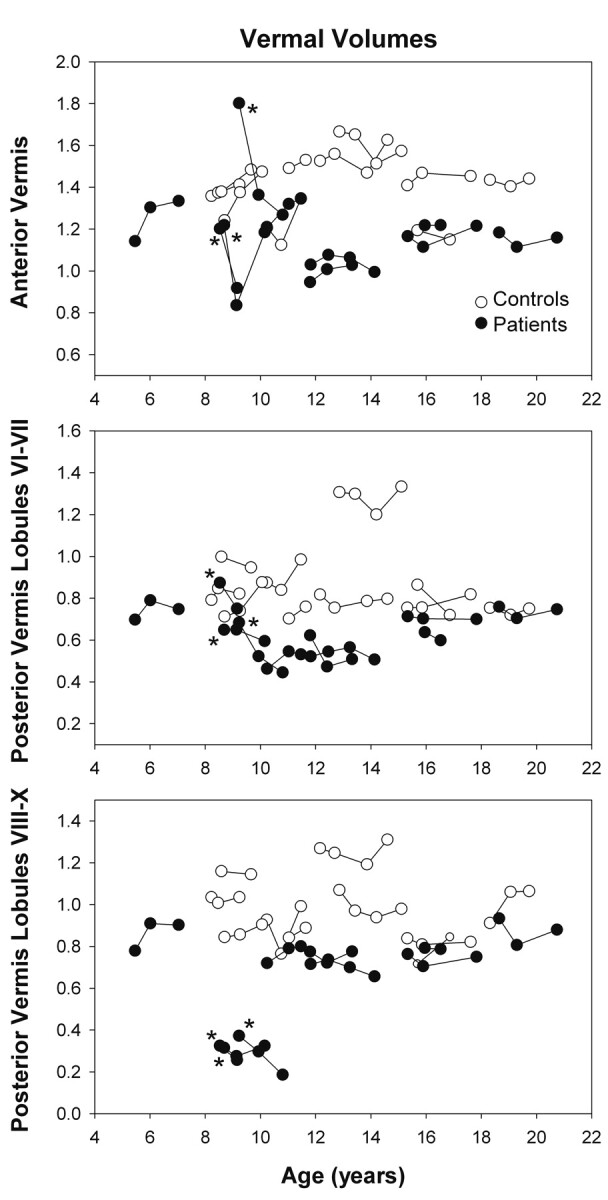
Relative lobar vermal volumes in healthy children and patients with brain malignancies. Patients tended to have lower relative vermal volumes even before the start of the radiation treatment. The volumes of the posterior vermis, lobules VIII-X, were the lowest in 3 patients with medulloblastoma treated by surgical resection, which involved removing parts of cerebellar tissue. The lines connect data from individual subjects; asterisks indicate patients with medulloblastoma.
At the baseline visit, the volume of the anterior vermis, lobules I-V, was 13% lower (P = .051, η2 = 0.20), the volume of lobules VI-VII was 23% lower (P = .01, η2 = 0.32), and the volume of lobules VIII-X was 33% lower (P = .002, η2 = 0.41) in patients (n = 10) compared with controls, all with large effect sizes. In the patients who did not have surgery of the posterior vermis, the volume of lobules VIII-X was 19% lower (P = .02, η2 = 0.31; n = 7) compared with controls, also showing a large effect size.
Across all participants, the main GLM analysis did not detect significant changes in relative volumes of vermal subregions between baseline and 6-month follow-up for either controls or patients. However, a significant decrease in relative anterior and posterior (lobules VIII-X) vermal volumes was observed in the 3 patients with medulloblastoma (Table, patients 2–4) at the 6-month follow-up compared with controls and patients without surgery (Fig 2; anterior vermis: P < .001, η2 = 0.79; posterior vermis, lobules VIII-X: P = .035, η2 = 0.35). While the relative anterior vermal volume in controls and patients with diagnoses other than medulloblastoma remained stable at the 6-month follow-up (mean volume changes <4% in both groups), in the 3 patients with medulloblastoma, the relative anterior volume decreased by 26 ± 4% on average (both, P < .001, η2>0.84). A decrease in the relative volume of the posterior vermis, lobules VIII-X, was also detected in the patients with medulloblastoma (−18.1 ± 4.7%) compared with other patients (0.1 ± 10.6%) and controls (−1.4 ± 10.0%) (both, P < .025, η2>0.45). The differences in relative-volume changes of the posterior vermis, lobules VI-VII, in controls (0.3 ± 5.6%), patients with medulloblastoma (−12.5 ± 12.0%), and patients with diagnoses other than medulloblastoma (−0.5 ± 14.1%) were not significant. While the volume of the posterior vermis, lobules VI-VII, decreased by >10% in 2 patients with medulloblastoma (Table, patients 2 and 4), no changes were observed in the third patient (patient 3).
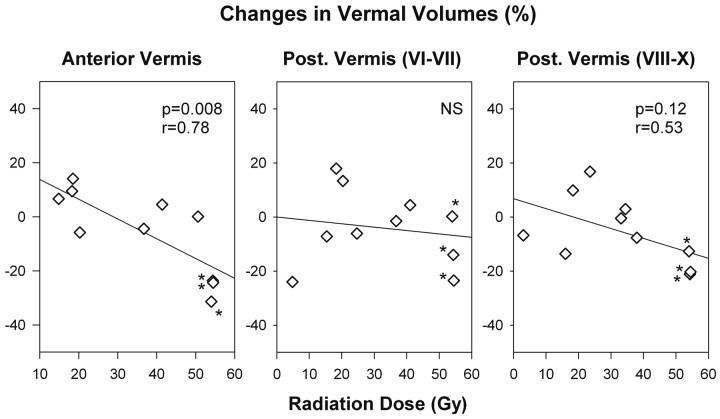
The more pronounced volume changes in the patients with medulloblastoma appeared to be associated with high posterior fossa radiation doses (>50 Gy). Linear regression analyses indicated an association between changes in anterior and posterior vermal volumes and radiation doses (anterior vermis: r = 0.78, P = .008; posterior vermis, lobules VIII-X: r = 0.53, P = .12) (Fig 3). No significant relationship between changes in relative volume and radiation doses was detected for the posterior vermis, lobules VI-VII.
Fig 3.
Relationship between percentage changes in relative lobar vermal volumes and corresponding radiation doses. Results of linear regression analyses are shown. The decrease in anterior and posterior vermal volumes was the highest in the patients with medulloblastoma (labeled with asterisks) who were treated with the highest radiation doses to the vermis (in addition to surgery and chemotherapy).
Across all participants, patients had lower scores on processing speed (Visual Matching) and motor speed (Purdue Pegboard, both hands) (main GLM analyses: P = .015, η2 = 0.093, and P = .001, η2 = 0.18, respectively) (Fig 4 ). The Purdue Pegboard right-hand and left-hand scores also tended to be lower in patients (main GLM analyses: P = .059, η2 = 0.059 and P = .071, η2 = 0.054, respectively) (Fig 4). No significant group differences were observed on any of the other neuropsychologic measures (Retrieval Fluency, Bead Memory, Visual Perception, CPT-II, and Statue).
Fig 4.
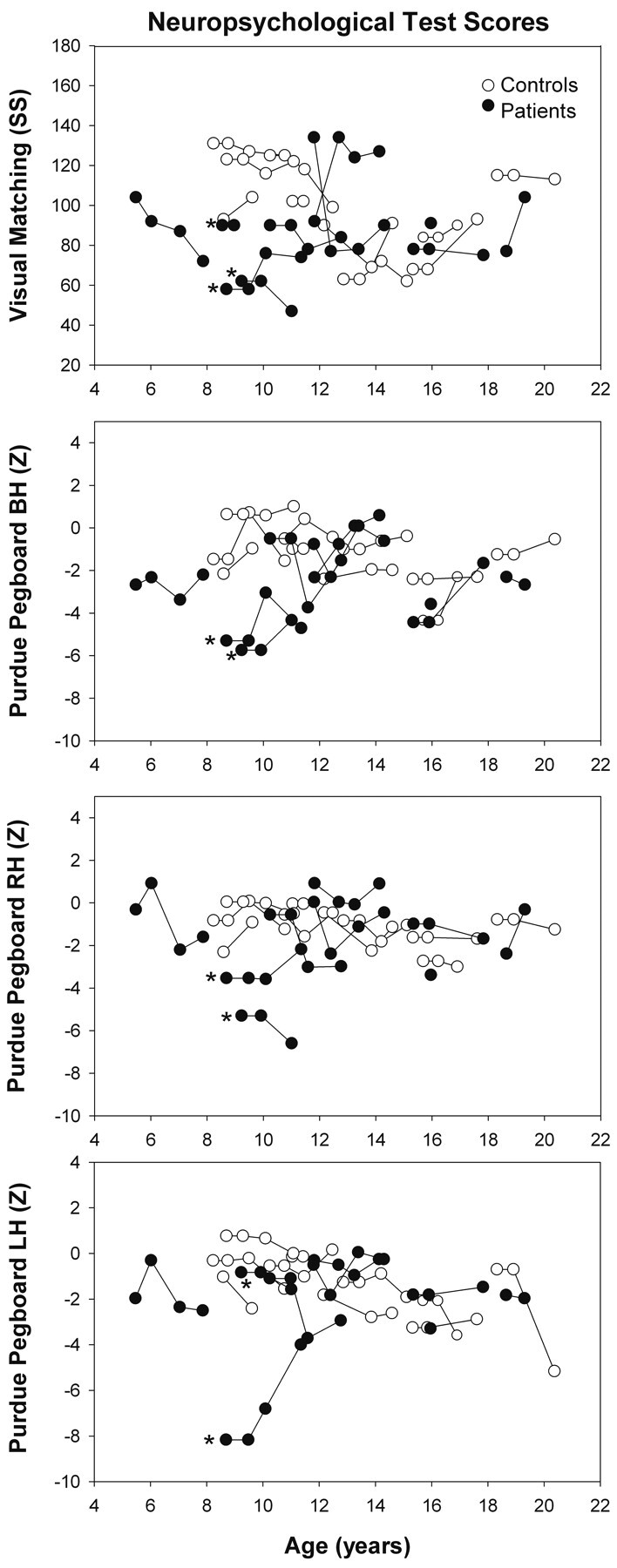
Standard scores of the WJ-III Visual Matching test and z scores of the Purdue Pegboard both hands, right hand, and left hand tests in healthy children and patients with brain malignancies. Low test scores in patients indicate impairment in visual selective attention, processing speed, and manipulative dexterity. The lines connect data from individual subjects. Asterisks indicate patients with medulloblastoma.
No significant changes in any of the neuropsychologic measures between baseline and 6-month follow-up were detected in either controls or patients. Of all participants, the lowest Visual Matching and Purdue Pegboard, both hands, scores in the entire sample were observed in 2 patients with medulloblastoma (patients 3 and 4, Table; the Purdue Pegboard was not completed by patient 2 with medulloblastoma) at the first 2 visits, with no changes in test scores observed between these 2 visits.
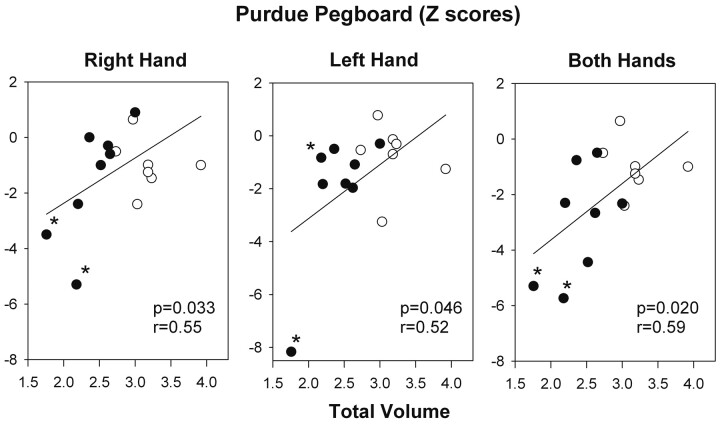
In pooled data from both groups, there was a significant relationship between total vermal volumes and motor speed (Purdue Pegboard) at 6-month follow-up, such that worse (slower) performance was associated with lower total relative vermal volumes (right hand: r = 0.55, P = .033; left hand: r = 0.52, P = .046; both hands: r = 0.59, P = .020) (Fig 5). However, there was no significant association between total vermal volumes and processing speed (Visual Matching) either at baseline or 6-month follow-up.
Fig 5.
Relationship between z scores of the Purdue Pegboard Tests and total relative vermal volumes at the 6-month follow-up visit. Results of linear regression analyses are presented. Low vermal volumes in patients with medulloblastoma (labeled with asterisks) were associated with poor performance on the Purdue Pegboard Tests. Filled circles indicate patients; open circles indicate controls.
Discussion
The present prospective longitudinal study reports lower relative volumes of anterior and posterior vermal subregions in patients diagnosed with brain malignancies and treated with combinations of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. While there was no overall difference in total cranial volumes between patients and age-matched controls at the baseline evaluation (completed in 8 patients before or early in the course of radiation therapy and in 2 patients shortly after radiation treatment), lower relative vermal volumes were detected in patients. At baseline, impaired performance on tests of processing speed and motor speed presumed to be associated with cerebellar function was also observed in patients; these deficits remained unchanged 6 months postradiation. Pathologic changes associated with the presence of malignancy or early initial clinical interventions (surgery, chemotherapy, and administration of steroids) may contribute to the observed reductions in vermal volumes and affect neuropsychologic performance.
By 6 months postradiation, further decrease in vermal volumes was detected only in patients with medulloblastoma. In patients with medulloblastoma, the decrease in vermal volumes was not associated with a corresponding decrease in processing-speed performance, perhaps because these patients were already performing near the floor of the tests at baseline. Across participants, however, there was a significant association between motor speed and vermal volumes observed at 6-month follow-up, indicating the sensitivity of measures of fine-motor speed to vermal anatomy.
The impact of treatment for childhood brain tumors and ALL on gray and white matter volumes has been studied previously. In survivors of medulloblastoma treated with surgery, radiation, and with or without chemotherapy, reductions in volumes of normal-appearing white matter were detected compared with age-matched patients with low-grade posterior fossa astrocytoma treated only with surgery.19 Longitudinal studies in patients with medulloblastoma demonstrated a decline in the volume of normal-appearing white matter with time after tumor resection and radiation treatment; the volume decline was faster in patients receiving higher radiation doses.20,21
Radiation treatment also affects gray matter. In medulloblastoma survivors, hippocampal volumes decreased during a period of 2–3 years after diagnosis, followed by an increase in volume.22 The volume reduction was explained by the proximity of posterior hippocampal regions to brain regions receiving the highest radiation doses. Thinning of posterior regions of the cerebral cortex was detected in children treated for medulloblastoma who were examined at a mean interval of 2.8 years after diagnosis.23 The posterior regions showing lower cortical thickness in patients with medulloblastoma were not cerebral regions receiving the highest radiation doses but cortical regions in which normal age-related thinning is typically observed. While undergoing developmental changes, these regions may be more susceptible to treatment effects.23
In contrast to most previous reports, patients in this longitudinal study were assessed earlier in the course of therapy, contemporaneously with a control group of healthy children. The results suggest that significant reductions in vermal volumes may be detected as early as at the initial stages of treatment, even before early-delayed effects of radiation are typically manifest (6–12 weeks postradiation).24 Six months after completion of radiation, significant declines in vermal volumes were detected only in patients with medulloblastoma, though 3 other patients (Table, patients 7, 8, and 9) were also treated with high radiation doses (≥35 Gy) to the vermis. Literature findings23 and our data indicate that the radiation dose may be only one of the factors associated with reductions in vermal volumes in children with brain malignancies. In this study, the presence of medulloblastoma, affecting the cerebellar midline structures, appears to have the most prominent effect.
In children with cerebellar lesions, impairment in visual-spatial organization, executive function for planning and programming, and reduced information-processing speed have been reported.25,26 Studies of childhood cerebellar disorders revealed deficits in attention, processing speed, visuospatial functions, and language.13 Impairment in executive functions was also noted in children treated for posterior fossa medulloblastoma and astrocytoma.10 The frontal-like deficits in executive functions were more severe in patients with medulloblastoma, particularly those who had a tumor localized in the vermis. Patients with astrocytoma presented with slight-to-moderate deficits in executive functions and reduced speed of processing. More severe impairment in the medulloblastoma group was explained by the tumor type and additional treatment (patients with medulloblastoma received chemotherapy and radiation in addition to surgery, which was the only treatment in the patients with astrocytoma).
A larger study including 61 children with malignant posterior fossa tumors examined the relationship between neurologic deficits, neuropsychologic deficits, and anatomic damage. The degree of impairment in neurologic and neuropsychologic functions (fine-motor speed) was related to the severity of injury to the dentate and inferior vermis; cerebellar deficits were smaller in patients with an intact vermis or dentate.9 Consistent with the literature findings on the role of the cerebellum in higher cognitive functions, impaired performance was detected on the Visual Matching test, a measure of visual attention and processing speed, and on the Purdue Pegboard Tests, which evaluate manual dexterity and motor speed. In agreement with the recent studies,9,10 the deficits detected in this study were most pronounced in children with a posterior fossa tumor involving the vermis. However, neuropsychologic impairment was also detected in children with brain tumors in the supratentorial regions, indicating impairment of skills dependent on frontal-cerebellar connections.
Preradiation treatment (surgery and chemotherapy) and pathologic changes may contribute to neurocognitive impairment observed at the baseline visit. In agreement with our results, cognitive impairment was reported in children with low-grade cerebellar tumors27 and extracerebellar tumors28 treated only with surgery and evaluated within 1 year thereafter. In children diagnosed with ALL and treated with chemotherapy, impaired performance on measures of perceptual and motor timing was detected ≥5 years postdiagnosis.29 The observed deficits were similar to the neuropsychologic impairment seen in patients with cerebellar-frontal abnormalities.29 Most of the patients in this study (7 of 10) were treated with surgery, and 4 patients received chemotherapy before the start of radiation treatment. The reported findings of abnormal neuropsychologic scores are thus consistent with reports in the literature. A positive relationship between the vermal volumes and motor speed (Purdue Pegboard) was detected at the 6-month follow-up visit, after completion of radiation therapy, but not at the baseline visit. This may possibly be due to a wider range of present medical problems early in the therapy. It may also be possible that early in the course of the disease, due to the presence of malignancy and initial interventions, brain connectivity may be altered, resulting in changed performance.
At 6 months postradiation, neuropsychologic performance may be affected by both clinical condition and possible compensatory mechanisms, which may develop with time. However, a larger study is needed to provide a definite explanation. No deficits in verbal working memory were detected in the patient group, in contrast to findings of a previous study in patients with cerebellar damage.30 This may be, however, due to a relatively short follow-up for the long-term cognitive impairments to manifest.8
The cerebellum continues to develop into late adolescence, a finding that has implications for how age of diagnosis and cerebellar maturation (before diagnosis) may relate to the symptom onset and developmental changes in phenotypic markers for patients, especially because the cerebellum appears to be sensitive to environmental variables.31 The presence of cerebellar-frontal and cerebellar-parietal functional connectivity in the human brain was first demonstrated in a functional connectivity MR imaging study.32 Areas of functional coherence in the cerebellum included the anterior and posterior vermis. There is also evidence to suggest that the cortex, subcortical white matter, and cerebellum share a pattern of reciprocal influence. For example, white matter injury in premature infants is followed by marked reduction in cortical gray matter at term.33 Early unilateral cerebral injury in premature infants is associated with a significantly decreased volume of the contralateral cerebellar hemisphere; conversely, early unilateral cerebellar injury is associated with a decrease in contralateral supratentorial brain volume.34 These findings suggest an early “crossed-trophic effect” between cerebral and subcortical structures, such that early injury to white matter impairs not only the cerebral cortical development but also the development of cerebellum, and vice versa. Thus, the cerebellum may be vulnerable in patients before implementation of radiation therapy, even when lesions and surgery do not directly affect the cerebellum itself.
The prospective longitudinal design, inclusion of a carefully screened control group, and the evaluation of the relationship between volume and neuropsychologic deficits are advantages of this study; however, there are several limitations. The main limitations (which are characteristic for many studies including children treated with brain radiation) include a small number of patients and missing data (missed or not yet completed visits at the time of data evaluation, 3 deceased patients). Inclusion of different diagnoses resulted in an inhomogeneous group of patients; however, it permitted an evaluation of the relationship between volume changes and radiation doses. Because total vermal volumes were evaluated, whether lower vermal volumes are the result of reductions in gray or white matter cannot be assessed. In future studies, segmentation of gray and white matter of the vermis and cerebellar hemispheres may be applied to evaluate the impairment of cerebellocerebral connections.
Conclusions
While we hypothesized that reduced vermal volumes and impaired neuropsychologic performance would be detected postradiation, volumetric and neuropsychologic deficits were observed earlier in the course of treatment. Radiation treatment contributed to decreases in vermal volumes, while neuropsychologic performance remained stable 6 months postradiation. The presence of brain malignancies and the effects of initial surgery, chemotherapy, and steroid administration appear to be important clinical factors affecting morbidity.
Acknowledgment
We thank Firouzeh Tannazi, PhD, for her assistance in evaluating radiation doses.
Abbreviations
- ALL
acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Ant
anterior vermis, lobules I-V
- BH
both hands
- CaPt
carboplatin
- CPT-II
Conner Continuous Performance Test-II
- CsPt
cisplatin
- CTX
cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan)
- DEX
dexamethasone
- GLM
generalized linear model
- HC
hydrocortisone
- IC
(T-cell) induction chemotherapy
- ICC
intraclass correlation coefficient
- LH
left hand
- MTX
methotrexate
- η2
eta-squared
- NP
neuropsychologic evaluation
- NS
nonsignificant relationship
- Post.
posterior
- Pred
prednisone
- postVI-VII
posterior vermis, lobules VI-VII
- postVIII-X
posterior vermis, lobules VIII-X
- RH
right hand
- RT
radiation therapy
- SS
standard scores
- TMZ
temozolomide
- WJ-III
Woodcock-Johnson III
- VCR
vincristine
- VP
ventriculoperitoneal
- VP-16
etoposide
Footnotes
This work was supported by R01 NS04285, P30HD024061–16, HD-24061 (Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Research Center) and Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Institute for Clinical and Translational Research, an NIH/National Center for Research Resources Clinical and Translational Science Awards Program, UL1-RR025005.
References
- 1. Schmahmann JD, Sherman JC. The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain 1998;121(pt 4):561–79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Kibby MY, Fancher JB, Markanen R, et al. A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging analysis of the cerebellar deficit hypothesis of dyslexia. J Child Neurol 2008;23:368–80 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Connolly DJ, Widjaja E, Griffiths PD. Involvement of the anterior lobe of the cerebellar vermis in perinatal profound hypoxia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2007;28:16–19 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. O'Hare ED, Kan E, Yoshii J, et al. Mapping cerebellar vermal morphology and cognitive correlates in prenatal alcohol exposure. Neuroreport 2005;16:1285–90 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Stoodley CJ, Schmahmann JD. Functional topography in the human cerebellum: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage 2009;44:489–501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Wells EM, Walsh KS, Khademian ZP, et al. The cerebellar mutism syndrome and its relation to cerebellar cognitive function and the cerebellar cognitive affective disorder. Dev Disabil Res Rev 2008;14:221–28 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Stargatt R, Rosenfeld JV, Maixner W, et al. Multiple factors contribute to neuropsychologic outcome in children with posterior fossa tumors. Dev Neuropsychol 2007;32:729–48 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Butler RW, Haser JK. Neurocognitive effects of treatment for childhood cancer. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 2006;12:184–91 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Puget S, Boddaert N, Viguier D, et al. Injuries to inferior vermis and dentate nuclei predict poor neurological and neuropsychologic outcome in children with malignant posterior fossa tumors. Cancer 2009;115:1338–47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Vaquero E, Gomez CM, Quintero EA, et al. Differential prefrontal-like deficit in children after cerebellar astrocytoma and medulloblastoma tumor. Behav Brain Funct 2008;4:18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Reddick WE, Shan ZY, Glass JO, et al. Smaller white-matter volumes are associated with larger deficits in attention and learning among long-term survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 2006;106:941–49 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Mulhern RK, Reddick WE, Palmer SL, et al. Neurocognitive deficits in medulloblastoma survivors and white matter loss. Ann Neurol 1999;46:834–41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Steinlin M. Cerebellar disorders in childhood: cognitive problems. Cerebellum 2008;7:607–10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Mostofsky SH, Mazzocco MM, Aakalu G, et al. Decreased cerebellar posterior vermis size in fragile X syndrome: correlation with neurocognitive performance. Neurology 1998;50:121–30 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Ozturk A, Degaonkar M, Matson MA, et al. Proton MR spectroscopy correlates of frontal lobe function in healthy children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30:1308–14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Wells CT, Mahone EM, Matson MA, et al. Relationship of temporal lobe volumes to neuropsychologic test performance in healthy children. Brain Cogn 2008;68:171–79 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum Associates; 1988 [Google Scholar]
- 18. Olejnik S, Algina J. Generalized eta and omega squared statistics: measures of effect size for some common research designs. Psychol Methods 2003;8:434–47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Mulhern RK, Merchant TE, Gajjar A, et al. Late neurocognitive sequelae in survivors of brain tumours in childhood. Lancet Oncol 2004;5:399–408 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Palmer SL, Reddick WE, Glass JO, et al. Decline in corpus callosum volume among pediatric patients with medulloblastoma: longitudinal MR imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23:1088–94 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Reddick WE, Russell JM, Glass JO, et al. Subtle white matter volume differences in children treated for medulloblastoma with conventional or reduced dose craniospinal irradiation. Magn Reson Imaging 2000;18:787–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Nagel BJ, Palmer SL, Reddick WE, et al. Abnormal hippocampal development in children with medulloblastoma treated with risk-adapted irradiation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25:1575–82 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Liu AK, Marcus KJ, Fischl B, et al. Changes in cerebral cortex of children treated for medulloblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;68:992–98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Kim JH, Brown SL, Jenrow KA, et al. Mechanisms of radiation-induced brain toxicity and implications for future clinical trials. J Neurooncol 2008;87:279–86 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Botez-Marquard T, Bard C, Leveille J, et al. A severe frontal-parietal lobe syndrome following cerebellar damage. Eur J Neurol 2001;8:347–53 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Botez-Marquard T, Leveille J, Botez MI. Neuropsychologic functioning in unilateral cerebellar damage. Can J Neurol Sci 1994;21:353–57 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Beebe DW, Ris MD, Armstrong FD, et al. Cognitive and adaptive outcome in low-grade pediatric cerebellar astrocytomas: evidence of diminished cognitive and adaptive functioning in National Collaborative Research Studies (CCG 9891/POG 9130). J Clin Oncol 2005;23:5198–204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Ris MD, Beebe DW, Armstrong FD, et al. Cognitive and adaptive outcome in extracerebellar low-grade brain tumors in children: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:4765–70 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Mahone EM, Prahme MC, Ruble K, et al. Motor and perceptual timing deficits among survivors of childhood leukemia. J Pediatr Psychol 2007;32:918–25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Ravizza SM, McCormick CA, Schlerf JE, et al. Cerebellar damage produces selective deficits in verbal working memory. Brain 2006;129:306–20 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Fassbender C, Schweitzer JB. Is there evidence for neural compensation in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder? A review of the functional neuroimaging literature. Clin Psychol Rev 2006;26:445–65 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Allen G, McColl R, Barnard H, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebellar-prefrontal and cerebellar-parietal functional connectivity. Neuroimage 2005;28:39–48 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Inder TE, Huppi PS, Warfield S, et al. Periventricular white matter injury in the premature infant is followed by reduced cerebral cortical gray matter volume at term. Ann Neurol 1999;46:755–60 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Limperopoulos C, Soul JS, Haidar H, et al. Impaired trophic interactions between the cerebellum and the cerebrum among preterm infants. Pediatrics 2005;116:844–50 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]