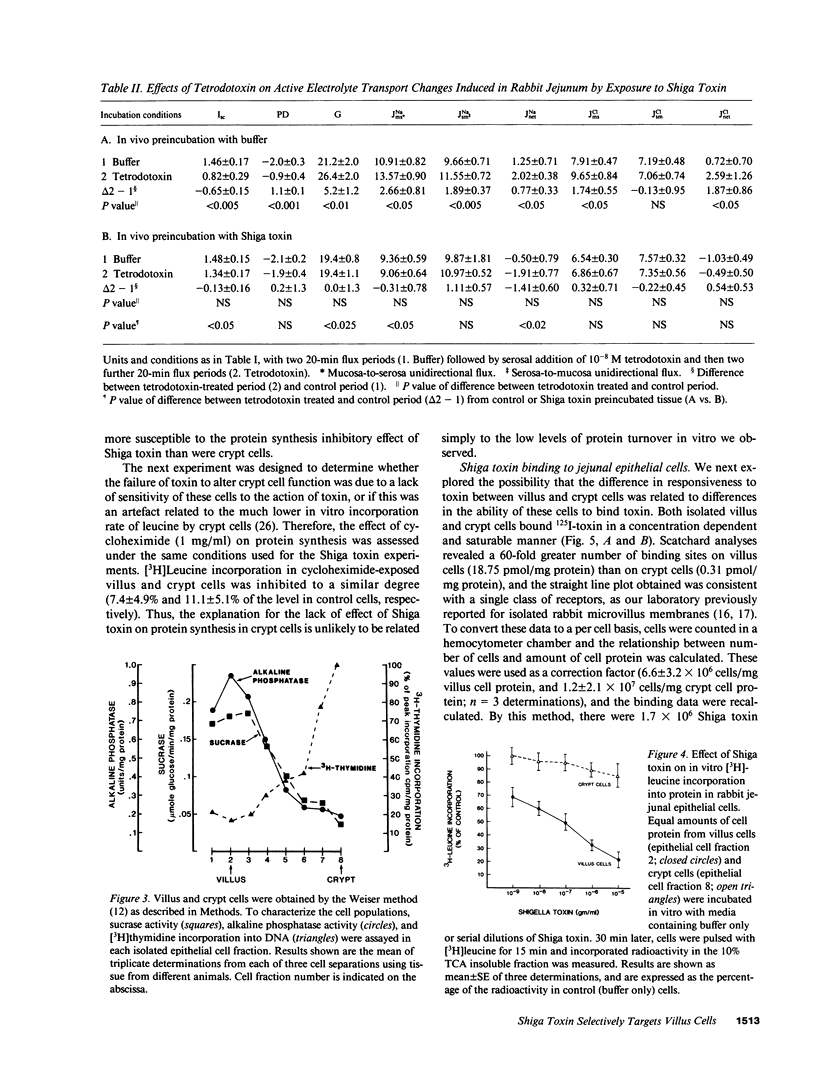
Abstract
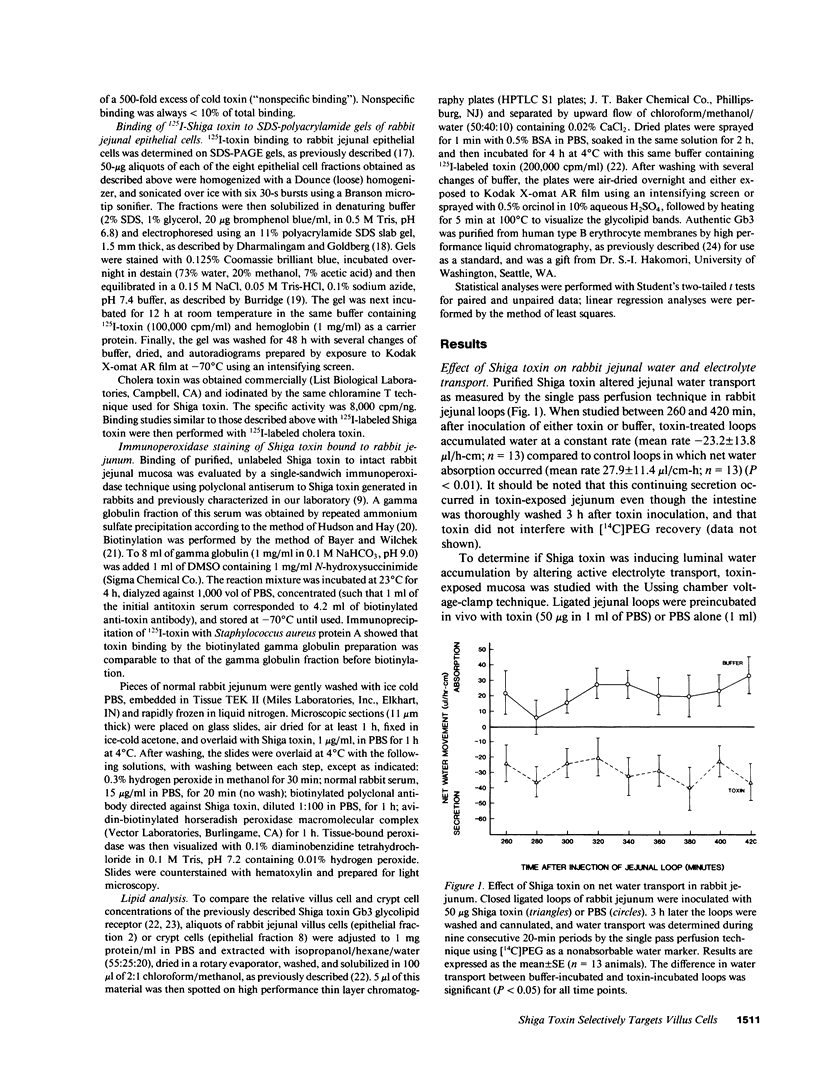
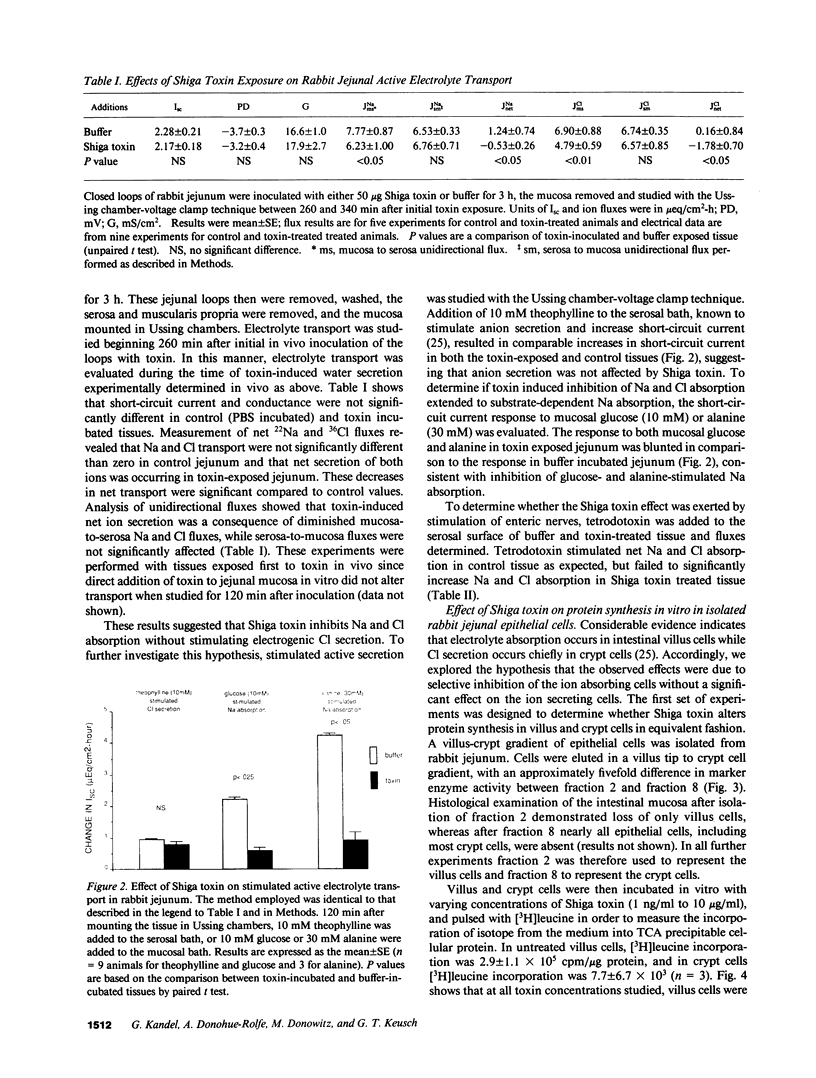
To examine the mechanism by which Shiga toxin alters intestinal water and electrolyte transport, ligated loops of rabbit jejunum were incubated in vivo with purified toxin and then studied in vivo by single pass perfusion and in vitro by the Ussing chamber voltage-clamp technique. Toxin exposure led to accumulation of water in the jejunal lumen, associated with decreased active basal NaCl absorption. Glucose- and alanine-stimulated Na absorption were also reduced, while toxin had no effect on either basal short-circuit current or the secretory response to theophylline. These observations suggest that Shiga toxin selectively inhibits NaCl absorption without significantly altering active anion secretion. To localize the cellular site of toxin action, populations of villus and crypt cells from rabbit jejunum were isolated and studied. Villus cells had a greater content of the glycolipid Shiga toxin receptor, Gb3, had more toxin binding sites than did crypt cells, and were much more sensitive than crypt cells to toxin-induced inhibition of protein synthesis. These experiments demonstrate that purified Shiga toxin inhibits jejunal fluid absorption without affecting active fluid secretion by a preferential effect on villus cells. The results suggest that this is due to the differential distribution of toxin receptors on villus compared to crypt cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpers D. H. Protein turnover in intestinal mucosal villus and crypt brush border membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):130–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. The use of the avidin-biotin complex as a tool in molecular biology. Methods Biochem Anal. 1980;26:1–45. doi: 10.1002/9780470110461.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Whiting D. S. Inhibition of small-intestinal sugar and amino acid transport by the enterotoxin of Shigella dysenteriae I. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):510–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.510-512.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K. Changes in cellular glycoproteins after transformation: identification of specific glycoproteins and antigens in sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4457–4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney A. N., Donowitz M. Prevention and reversal of cholera enterotoxin-induced intestinal secretion by methylprednisolone induction of Na+-K+-ATPase. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1590–1599. doi: 10.1172/JCI108429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney A. N., Gots R. E., Formal S. B., Giannella R. A. Activation of intestinal mucosal adenylate cyclase by Shigella dysenteriae I enterotoxin. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jun;70(6):1085–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley D. R., Magnani J. L., Fishman P. H. Interaction of cholera toxin with rat intestinal brush border membranes. Relative roles of gangliosides and galactoproteins as toxin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8724–8731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlqvist A. Assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmalingam K., Goldberg E. B. Restriction in vivo. III. General effects of glucosylation and restriction on phage T4 gene expression and replication. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Edson C., Thorley-Lawson D., Jacewicz M. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. IX. Simplified high yield purification of Shigella toxin and characterization of subunit composition and function by the use of subunit-specific monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1767–1781. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Asarkof N. Calcium dependence of basal electrolyte transport in rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):G28–G35. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.1.G28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Keusch G. T., Binder H. J. Effect of Shigella enterotoxin on electrolyte transport in rabbit ileum. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1230–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Yutsudo T., Takeda Y., Ogasawara T., Igarashi K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez A., Sninsky C. A., O'Brien A. D., Clench M. H., Mathias J. R. Purified Shigella enterotoxin does not alter intestinal motility. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):477–481. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.477-481.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Grady G. F., McIver J., Witkum P., Beckman B., Sharp G. W. Comparison of the effects of enterotoxins of Shigella dysenteriae and Vibrio cholerae on the adenylate cyclase system of the rabbit intestine. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):374–379. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs G., Mobassaleh M., Donohue-Rolfe A., Montgomery R. K., Grand R. J., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea: rabbit intestinal cell microvillus membrane binding site for Shigella toxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):372–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.372-377.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz M., Clausen H., Nudelman E., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. XI. Isolation of a shigella toxin-binding glycolipid from rabbit jejunum and HeLa cells and its identification as globotriaosylceramide. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz M., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. VIII. Evidence for a translocation step in the cytotoxic action of Shiga toxin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Nov;148(5):844–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.5.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keenan K. P., Sharpnack D. D., Collins H., Formal S. B., O'Brien A. D. Morphologic evaluation of the effects of Shiga toxin and E coli Shiga-like toxin on the rabbit intestine. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):69–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Donohue-Rolfe A., Jacewicz M. Shigella toxin and the pathogenesis of shigellosis. Ciba Found Symp. 1985;112:193–214. doi: 10.1002/9780470720936.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Grady G. F., Mata L. J., McIver J. The pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. I. Enterotoxin production by Shigella dysenteriae I. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1212–1218. doi: 10.1172/JCI106915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Grady G. F., Takeuchi A., Sprinz H. The pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. II. Enterotoxin-induced acute enteritis in the rabbit ileum. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):92–95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Gershon E., Schooley R. T., Henderson A. Effects of cycloheximide on the response of intestinal mucosa to cholera enterotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1376–1383. doi: 10.1172/JCI107310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo F. C., Peterson J. W., Houston C. W., Molina N. C. Pathogenesis of experimental salmonellosis: inhibition of protein synthesis by cytotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):93–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.93-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentze M. J., Colony P. C., Trier J. S. Glucocorticoid receptors in isolated intestinal epithelial cells in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 1):G58–G65. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.1.G58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Brown J. E., Strömberg N., Westling-Ryd M., Schultz J. E., Karlsson K. A. Identification of the carbohydrate receptor for Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1779–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias J. R., Carlson G. M., Martin J. L., Shields R. P., Formal S. Shigella dysenteriae I enterotoxin: proposed role in pathogenesis of shigellosis. Am J Physiol. 1980 Nov;239(5):G382–G386. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.239.5.G382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobassaleh M., Donohue-Rolfe A., Jacewicz M., Grand R. J., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea: evidence for a developmentally regulated glycolipid receptor for shigella toxin involved in the fluid secretory response of rabbit small intestine. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1023–1031. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobassaleh M., Gross S. K., McCluer R. H., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Quantitation of the rabbit intestinal glycolipid receptor for Shiga toxin. Further evidence for the developmental regulation of globotriaosylceramide in microvillus membranes. Gastroenterology. 1989 Aug;97(2):384–391. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita A., Tsao D., Kim Y. S. Identification of cholera toxin binding glycoproteins in rat intestinal microvillus membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2549–2553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudelman E., Kannagi R., Hakomori S., Parsons M., Lipinski M., Wiels J., Fellous M., Tursz T. A glycolipid antigen associated with Burkitt lymphoma defined by a monoclonal antibody. Science. 1983 Apr 29;220(4596):509–511. doi: 10.1126/science.6836295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisbig R., Olsnes S., Eiklid K. The cytotoxic activity of Shigella toxin. Evidence for catalytic inactivation of the 60 S ribosomal subunit. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8739–8744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Brown J. E., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Endocytosis from coated pits of Shiga toxin: a glycolipid-binding protein from Shigella dysenteriae 1. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1331–1343. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S. E., Banwell J. G., Yardley J. H., Keusch G. T., Hendrix T. R. Comparison of secretory and histological effects of shigella and cholera enterotoxins in rabbit jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1975 Feb;68(2):309–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Intestinal epithelial cell surface membrane glycoprotein synthesis. I. An indicator of cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]