Abstract
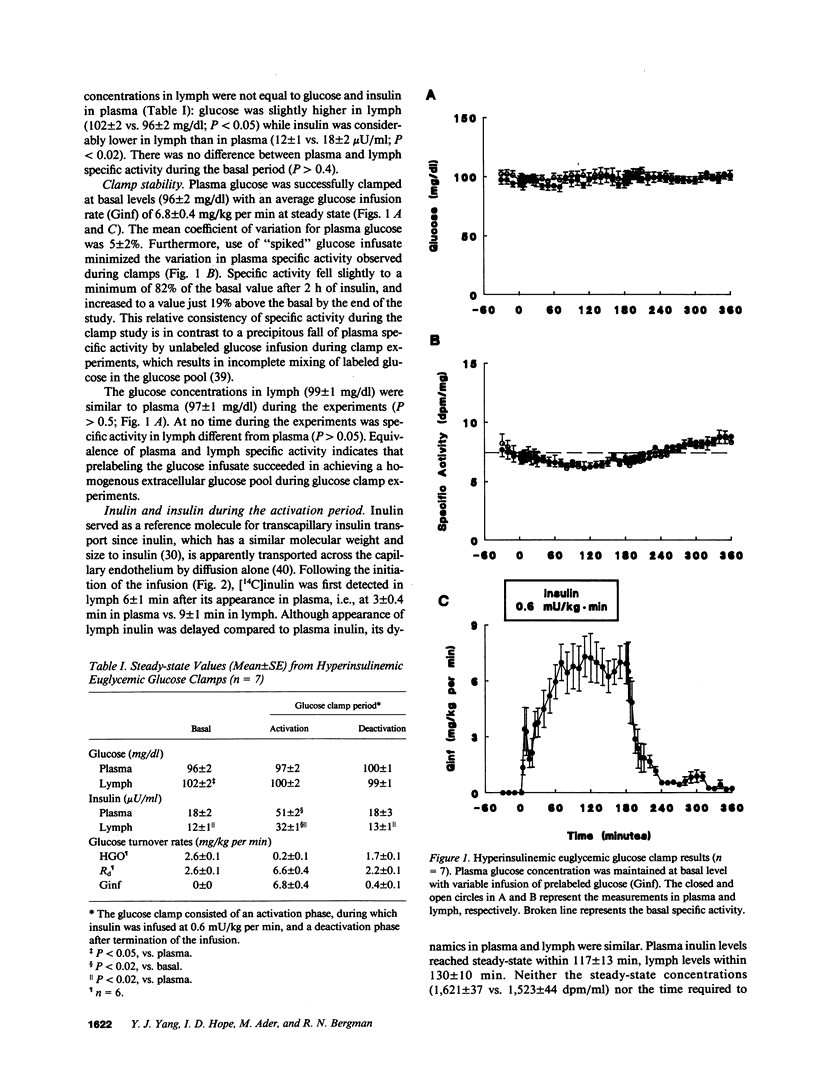
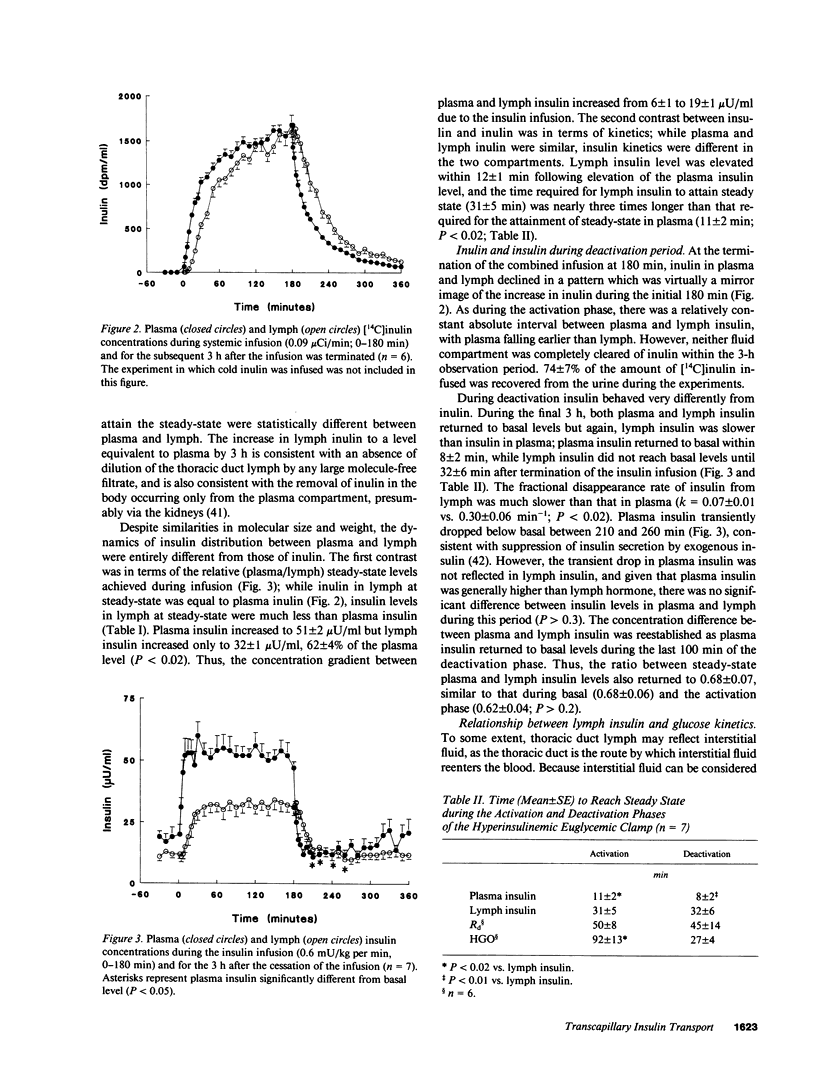
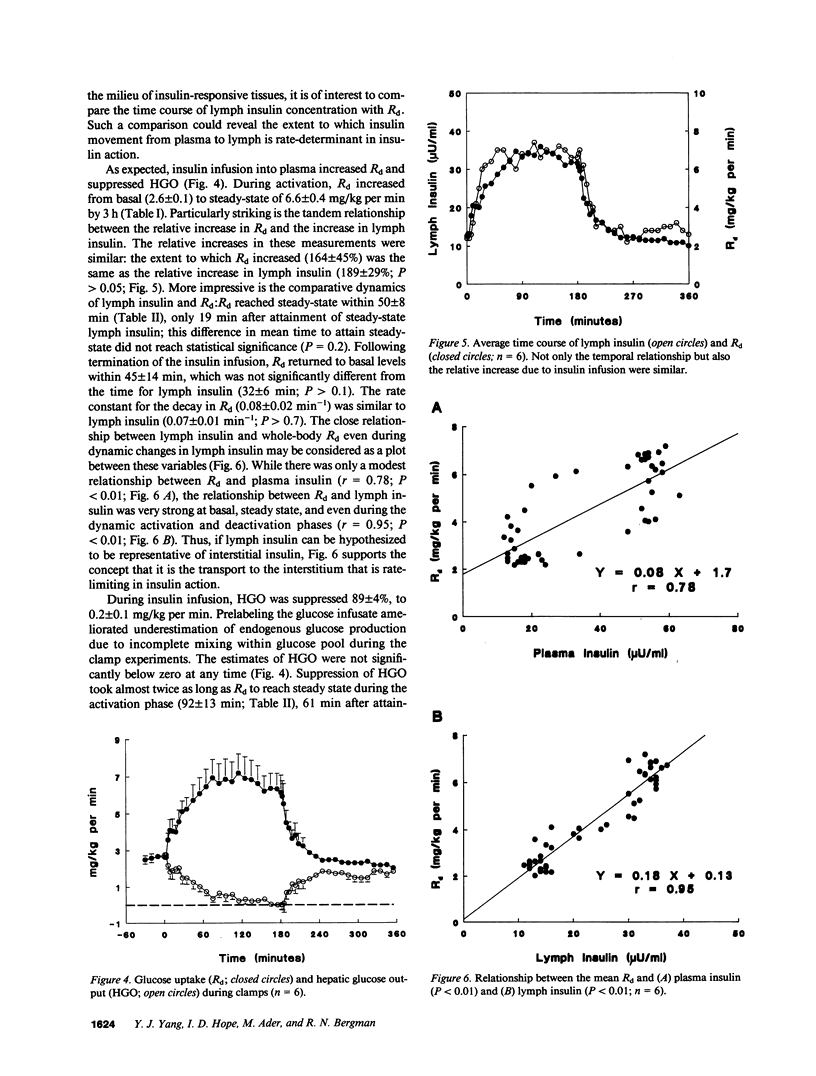
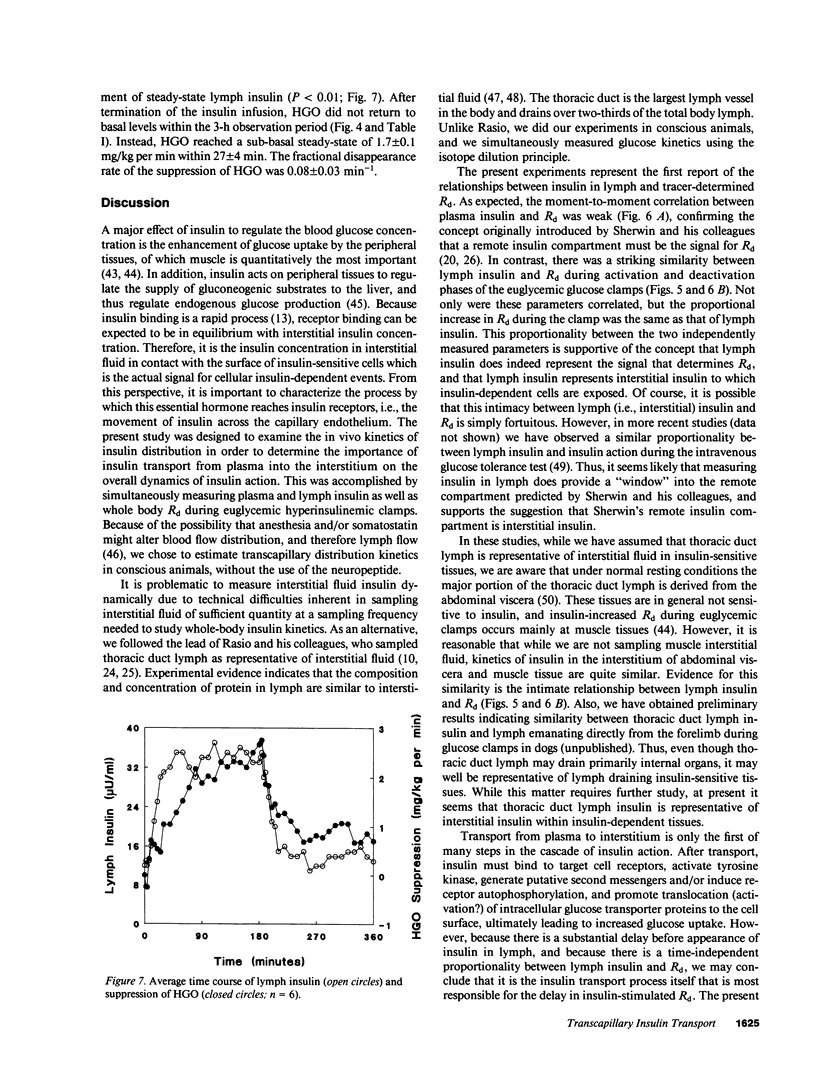
This study examined the relationship between transcapillary insulin transport and insulin action in vivo. During euglycemic clamps (n = 7) in normal conscious dogs we simultaneously measured plasma and thoracic duct lymph insulin and glucose utilization (Rd). Clamps consisted of an activation phase with constant insulin infusion (0.6 mU/kg per min) and a deactivation phase. [14C]Inulin was infused as a passively transported control substance. While [14C]inulin reached an equilibrium between plasma and lymph, steady-state (ss) plasma insulin was higher than lymph (P less than 0.05) and the ratio of 3:2 was maintained during basal, activation, and deactivation phases: 18 +/- 2 vs. 12 +/- 1, 51 +/- 2 vs. 32 +/- 1, and 18 +/- 3 vs. 13 +/- 1 microU/ml. In addition, it took longer for lymph insulin to reach ss than plasma insulin during activation and deactivation: 11 +/- 2 vs. 31 +/- 5 and 8 +/- 2 vs. 32 +/- 6 min (P less than 0.02). Rd increased from 2.6 +/- 0.1 to a ss of 6.6 +/- 0.4 mg/kg per min within 50 +/- 8 min. There was a remarkable similarity in the dynamics of insulin in lymph and Rd: the time to reach ss for Rd was not different from lymph insulin (P greater than 0.1), and the relative increases of the two measurements were similar, 164 +/- 45% and 189 +/- 29% (P greater than 0.05). While there was only a modest correlation (r = 0.78, P less than 0.01) between Rd and plasma insulin, the dynamic changes of lymph insulin and Rd showed a strong correlation (r = 0.95, P less than 0.01). The intimate relationship between lymph insulin and Rd suggests that the transcapillary insulin transport is primarily responsible for the delay in Rd. Thus, transcapillary transport may be rate limiting for insulin action, and if altered, it could be an important component of insulin resistance in obesity and diabetes mellitus.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar R. S., Boes M., Sandra A. Vascular transport of insulin to rat cardiac muscle. Central role of the capillary endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1225–1233. doi: 10.1172/JCI113439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Hoak J. C., Peacock M. L. Insulin receptors in human endothelial cells: identification and characterization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Sep;47(3):699–702. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-3-699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T. P., Olefsky J. M. Kinetic relationships between insulin receptor binding and effects on glucose transport in isolated rat adipocytes. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3475–3480. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON W. D., SACKNER M. A. SIMPLIFICATION OF THE ANTHRONE METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF INULIN IN CLEARANCE STUDIES. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Aug;62:351–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1000–1007. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dernovsek K. D., Bar R. S., Ginsberg B. H., Lioubin M. N. Rapid transport of biologically intact insulin through cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Apr;58(4):761–763. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-4-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doberne L., Greenfield M. S., Schulz B., Reaven G. M. Enhanced glucose utilization during prolonged glucose clamp studies. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):829–835. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C. Insulin degradation: mechanisms, products, and significance. Endocr Rev. 1988 Aug;9(3):319–345. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-3-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki O., Kono T. Effects of temperature on basal and insulin-stimulated glucose transport activities in fat cells. Further support for the translocation hypothesis of insulin action. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14306–14310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegood D. T., Bergman R. N. Optimal segments: a method for smoothing tracer data to calculate metabolic fluxes. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):E472–E479. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.5.E472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegood D. T., Bergman R. N., Vranic M. Estimation of endogenous glucose production during hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic glucose clamps. Comparison of unlabeled and labeled exogenous glucose infusates. Diabetes. 1987 Aug;36(8):914–924. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegood D. T., Pacini G., Bergman R. N. The insulin sensitivity index. Correlation in dogs between values determined from the intravenous glucose tolerance test and the euglycemic glucose clamp. Diabetes. 1984 Apr;33(4):362–368. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.4.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank B. W., Kern F., Jr Intestinal and liver lymph and lymphatics. Gastroenterology. 1968 Sep;55(3):408–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Sonne O. Binding and receptor-mediated degradation of insulin in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7857–7863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimditch G. K., Barnard R. J., Kaplan S. A., Sternlicht E. Insulin binding and glucose transport in rat skeletal muscle sarcolemmal vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1985 Oct;249(4 Pt 1):E398–E408. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.249.4.E398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Tobin J. D., Sherwin R. S., Watkins P., Andres R., Berman M. Insulin control of glucose metabolism in man: a new kinetic analysis. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1057–1066. doi: 10.1172/JCI108006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Kraegen E. W. Heterogeneity of insulin action in individual muscles in vivo: euglycemic clamp studies in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E567–E574. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jialal I., King G. L., Buchwald S., Kahn C. R., Crettaz M. Processing of insulin by bovine endothelial cells in culture. Internalization without degradation. Diabetes. 1984 Aug;33(8):794–800. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.8.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Zarnowski M. J., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transport systems in the isolated rat adipose cell. Time course, reversal, insulin concentration dependency, and relationship to glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4772–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Blithe D. L., Kahn C. R. Tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity is associated with the purified insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2137–2141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Goodman A. D., Buzney S., Moses A., Kahn C. R. Receptors and growth-promoting effects of insulin and insulinlike growth factors on cells from bovine retinal capillaries and aorta. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):1028–1036. doi: 10.1172/JCI111764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Johnson S. M., Jialal I. Processing and transport of insulin by vascular endothelial cells. Effects of sulfonylureas on insulin receptors. Am J Med. 1985 Sep 20;79(3B):43–47. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(85)80006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Johnson S. M. Receptor-mediated transport of insulin across endothelial cells. Science. 1985 Mar 29;227(4694):1583–1586. doi: 10.1126/science.3883490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Burstein P., Insel J., Scarlett J. A., Olefsky J. M. Receptor and postreceptor defects contribute to the insulin resistance in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):957–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI110350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Insel J., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in human obesity: evidence for receptor and postreceptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1272–1284. doi: 10.1172/JCI109790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Robinson F. W., Blevins T. L., Ezaki O. Evidence that translocation of the glucose transport activity is the major mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10942–10947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. R., Olefsky J. M. The trafficking and processing of insulin and insulin receptors in cultured rat hepatocytes. Endocrinology. 1987 Dec;121(6):2075–2086. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-6-2075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljenquist J. E., Horwitz D. L., Jennings A. S., Chiasson J. L., Keller U., Rubenstein A. H. Inhibition of insulin secretion by exogenous insulin in normal man as demonstrated by C-peptide assay. Diabetes. 1978 May;27(5):563–570. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.5.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillioja S., Bogardus C. Obesity and insulin resistance: lessons learned from the Pima Indians. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1988 Aug;4(5):517–540. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610040508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillioja S., Young A. A., Culter C. L., Ivy J. L., Abbott W. G., Zawadzki J. K., Yki-Järvinen H., Christin L., Secomb T. W., Bogardus C. Skeletal muscle capillary density and fiber type are possible determinants of in vivo insulin resistance in man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):415–424. doi: 10.1172/JCI113088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S. Degradative processing of internalized insulin in isolated adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13517–13523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Sagara H., Usukura N., Yoshimitsu K., Imamura T., Seta T., Yanase E., Kawato M., Hiraiwa Y., Sakato S. Effect of somatostatin on the flow rate and triglyceride levels of thoracic duct lymph in normal and vagotomized dogs. Diabetes. 1981 May;30(5):440–445. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.5.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. LIlly lecture 1980. Insulin resistance and insulin action. An in vitro and in vivo perspective. Diabetes. 1981 Feb;30(2):148–162. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.2.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. The insulin receptor: its role in insulin resistance of obesity and diabetes. Diabetes. 1976 Dec;25(12):1154–1162. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.12.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paaske W. P., Sejrsen P. Transcapillary exchange of 14C-inulin by free diffusion in channels of fused vesicles. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Aug;100(4):437–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb05968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacini G., Bergman R. N. PACBERG: an adaptive program for controlling the blood sugar. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Feb-Apr;16(1-2):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock M. L., Bar R. S., Goldsmith J. Interactions of insulin with bovine endothelium. Metabolism. 1982 Jan;31(1):52–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager R., Wallace P., Olefsky J. M. In vivo kinetics of insulin action on peripheral glucose disposal and hepatic glucose output in normal and obese subjects. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):472–481. doi: 10.1172/JCI112599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Measurement and validation of nonsteady turnover rates with applications to the inulin and glucose systems. Fed Proc. 1974 Jul;33(7):1855–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasio E. A., Hampers C. L., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Diffusion of glucose, insulin, inulin, and Evans blue protein into thoracic duct lymph of man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jun;46(6):903–910. doi: 10.1172/JCI105596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasio E. A., Hill G. J., 2nd, Soeldner J. S., Herrera M. G. Effect of pancreatectomy on glucose tolerance and extracellular fluid insulin in the dog. Diabetes. 1967 Aug;16(8):551–556. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.8.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasio E. A., Mack E., Egdahl R. H., Herrera M. G. Passage of insulin and inulin across vascular membranes in the dog. Diabetes. 1968 Nov;17(11):668–672. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.11.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Bernstein R., Davis B., Olefsky J. M. Nonketotic diabetes mellitus: insulin deficiency or insulin resistance? Am J Med. 1976 Jan;60(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutili G., Arfors K. E. Protein concentration in interstitial and lymphatic fluids from the subcutaneous tissue. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Jan;99(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb10345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., WALL J. S., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):15–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Kramer K. J., Tobin J. D., Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Berman M., Andres R. A model of the kinetics of insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1481–1492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtmauer L. A., Rosen O. M. Phosphorylation of exogenous substrates by the insulin receptor-associated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6682–6685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela G., Woods L. L., Brace R. A. Thoracic duct lymph flow in pregnant sheep and response to blood volume expansion. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 2):R1095–R1098. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.6.R1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


