Abstract
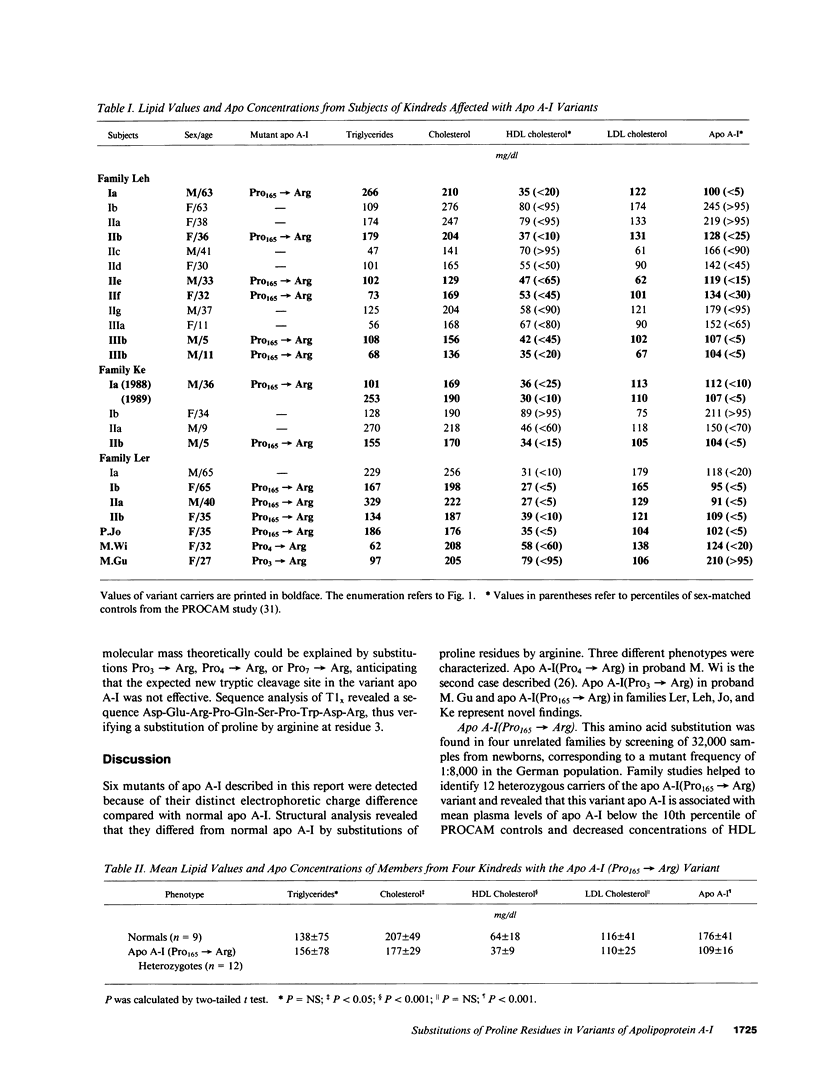
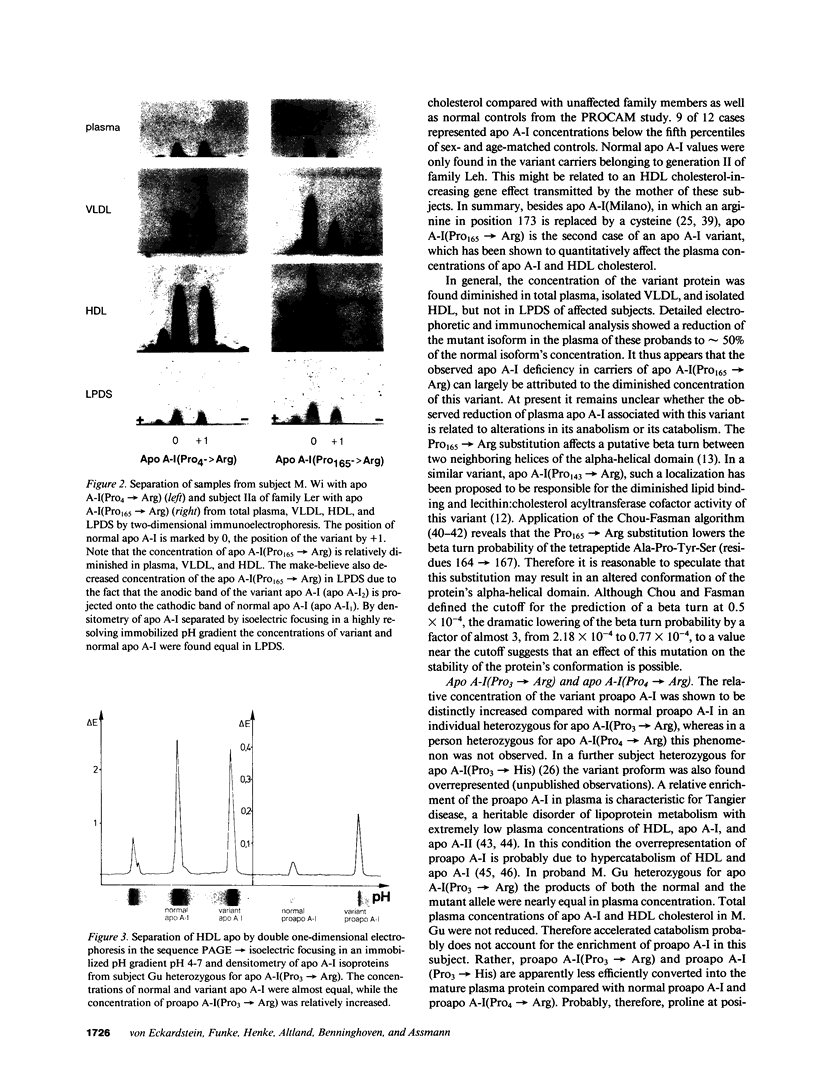
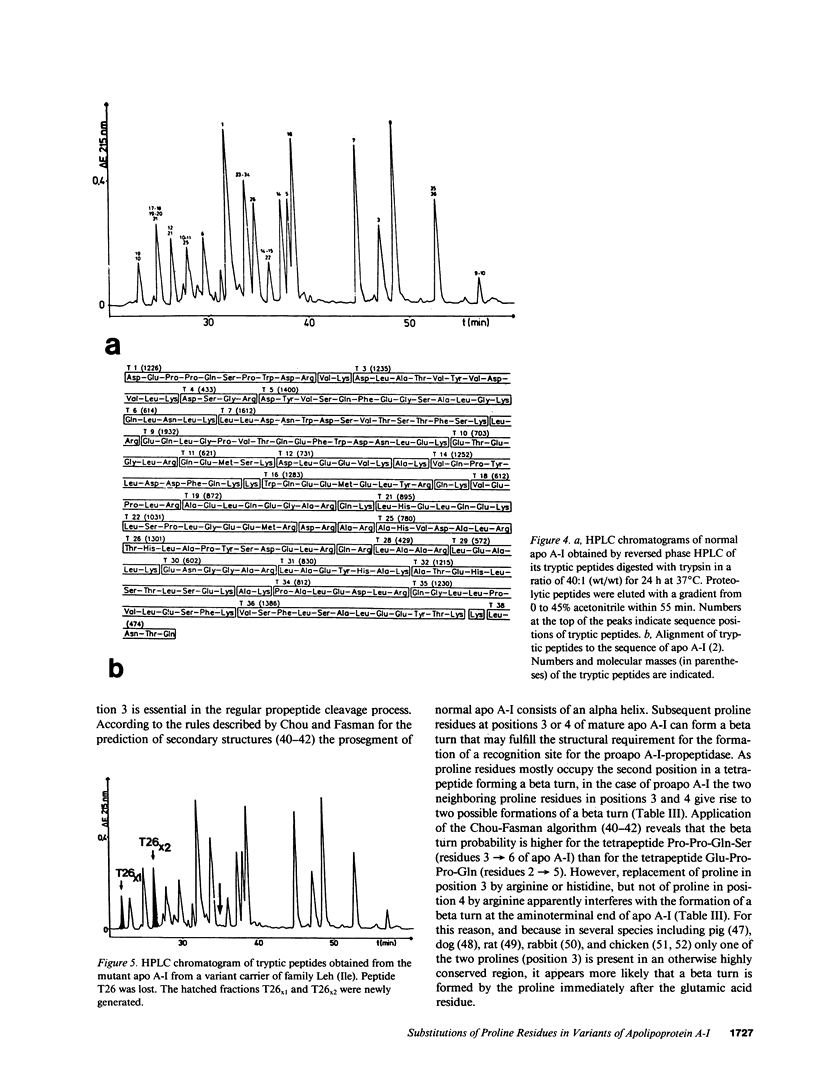
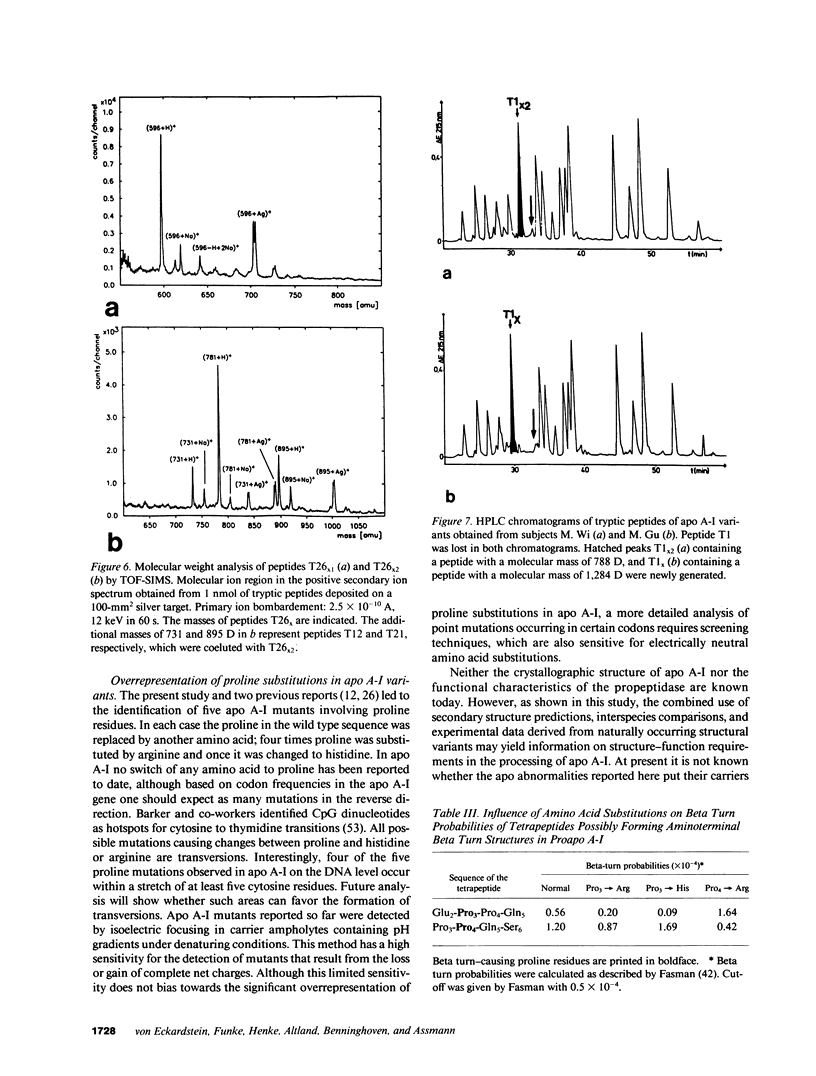
Six unrelated families with genetically determined structural variants of apo A-I were found in the course of an electrophoretic screening program for apo A-I variants in dried blood samples of newborns. The following structural variations were identified by the combined use of HPLC, time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (TOF-SIMS), and automated gas phase sequencing: Pro3----Arg (1x), Pro4----Arg (1x), and Pro165----Arg (4x). All variant carriers were heterozygous for their mutant of apo A-I. Subjects heterozygous for apo A-I(Pro165----Arg) (n = 12) were found to exhibit lower mean values for apo A-I (109 +/- 16 mg/dl) and HDL cholesterol (37 +/- 9 mg/dl) than unaffected family members (n = 9): 176 +/- 41 and 64 +/- 18 mg/dl, respectively (P less than 0.001). In 9 of 12 apo A-I(Pro165----Arg) variant carriers the concentrations of apo A-I were below the fifth percentile of sex-matched controls. By two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis as well as by densitometry the relative concentration of the variant apo A-I in heterozygous carriers of apo A-I(Pro165----Arg) was determined to account for only 30% of the total plasma apo A-I mass instead of the expected 50%. Thus, the observed apo A-I deficiency may be largely a consequence of the decreased concentration of the variant apo A-I. In the case of the apo A-I(Pro3----Arg) mutant, densitometry of HDL apolipoproteins demonstrated a distinctly increased concentration of the variant proapo A-I relative to normal proapo A-I. This phenomenon was not observed in the apo A-I(Pro4----Arg) mutant or in other mutants. This suggests that the interspecies conserved proline residue in position 3 of mature apo A-I is functionally important for the regular enzymatic conversion of proapo A-I to mature apo A-I.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anantharamaiah G. M., Jones J. L., Brouillette C. G., Schmidt C. F., Chung B. H., Hughes T. A., Bhown A. S., Segrest J. P. Studies of synthetic peptide analogs of the amphipathic helix. Structure of complexes with dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10248–10255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assmann G., Brewer H. B., Jr Lipid-protein interactions in high density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):989–993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avogaro P., Bon G. B., Cazzolato G., Quinci G. B. Are apolipoproteins better discriminators than lipids for atherosclerosis? Lancet. 1979 Apr 28;1(8122):901–903. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bojanovski D., Gregg R. E., Ghiselli G., Schaefer E. J., Light J. A., Brewer H. B., Jr Human apolipoprotein A-I isoprotein metabolism: proapoA-I conversion to mature apoA-I. J Lipid Res. 1985 Feb;26(2):185–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bojanovski D., Gregg R. E., Zech L. A., Meng M. S., Bishop C., Ronan R., Brewer H. B., Jr In vivo metabolism of proapolipoprotein A-I in Tangier disease. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1742–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI113266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Fairwell T., LaRue A., Ronan R., Houser A., Bronzert T. J. The amino acid sequence of human APOA-I, an apolipoprotein isolated from high density lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):623–630. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Studies of the proteins in human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5687–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. H., Anatharamaiah G. M., Brouillette C. G., Nishida T., Segrest J. P. Studies of synthetic peptide analogs of the amphipathic helix. Correlation of structure with function. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10256–10262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung H., Randolph A., Reardon I., Heinrikson R. L. The covalent structure of apolipoprotein A-I from canine high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2961–2967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Loof H., Rosseneu M., Brasseur R., Ruysschaert J. M. Functional differentiation of amphiphilic helices of the apolipoproteins by hydrophobic moment analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 5;911(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90268-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein C., Gordon J. I., Toscas K., Sims H. F., Strauss A. W., Scanu A. M. In vitro conversion of proapoprotein A-I to apoprotein A-I. Partial characterization of an extracellular enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11430–11433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H., Nestel P. J. Identification of apolipoproteins involved in the interaction of human high density lipoprotein3 with receptors on cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3570–3575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E. A protein cofactor of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90776-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima D., Yokoyama S., Kroon D. J., Kézdy F. J., Kaiser E. T. Chain length-function correlation of amphiphilic peptides. Synthesis and surface properties of a tetratetracontapeptide segment of apolipoprotein A-I. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10651–10657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon T., Castelli W. P., Hjortland M. C., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Am J Med. 1977 May;62(5):707–714. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90874-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. L., Oram J. F. Identification and characterization of a high density lipoprotein-binding protein in cell membranes by ligand blotting. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7439–7442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualandri V., Franceschini G., Sirtori C. R., Gianfranceschi G., Orsini G. B., Cerrone A., Menotti A. AIMilano apoprotein identification of the complete kindred and evidence of a dominant genetic transmission. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Nov;37(6):1083–1097. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs H. U., Assmann G., Greifendorf D., Benninghoven A. High performance liquid chromatography and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry: a new dimension in structural analysis of apolipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1986 Jun;27(6):613–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Isolation and characterization of the human apolipoprotein A-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim P. S., Baldwin R. L. Specific intermediates in the folding reactions of small proteins and the mechanism of protein folding. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:459–489. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H. Plasma lipoproteins: apolipoprotein structure and function. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1277–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T., Brewer H. B., Jr, Assmann G. Swine lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. Changes in the plasma lipoproteins and apoproteins induced by cholesterol feeding. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2817–2823. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Assmann G., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Human apolipoprotein A-I polymorphism. Identification of amino acid substitutions in three electrophoretic variants of the Münster-3 type. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3070–3076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Kladetzky R. G., Assmann G. One-step screening method for the polymorphism of apolipoproteins A-I, A-II, and A-IV. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):915–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. C., Dwulet F. E., Liepnieks J., Benson M. D. Variant apolipoprotein AI as a major constituent of a human hereditary amyloid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):762–768. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80909-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norum R. A., Lakier J. B., Goldstein S., Angel A., Goldberg R. B., Block W. D., Noffze D. K., Dolphin P. J., Edelglass J., Bogorad D. D. Familial deficiency of apolipoproteins A-I and C-III and precocious coronary-artery disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 24;306(25):1513–1519. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206243062503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajavashisth T. B., Dawson P. A., Williams D. L., Shackleford J. E., Lebherz H., Lusis A. J. Structure, evolution, and regulation of chicken apolipoprotein A-I. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7058–7065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Ogawa Y., Fielding C. J., Utermann G., Haas J., Steinmetz A., Menzel H. J., Assmann G. Abnormal lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase activation by a human apolipoprotein A-I variant in which a single lysine residue is deleted. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10063–10070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandkamp M., Tambyrajah B., Schriewer H., Assmann G. Simplified turbidimetric determination of apolipoproteins A-I, A-II and B using a microtitre method. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1988 Nov;26(11):685–688. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1988.26.11.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Ordovas J. M., Law S. W., Ghiselli G., Kashyap M. L., Srivastava L. S., Heaton W. H., Albers J. J., Connor W. E., Lindgren F. T. Familial apolipoprotein A-I and C-III deficiency, variant II. J Lipid Res. 1985 Sep;26(9):1089–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz G., Assmann G., Robenek H., Brennhausen B. Tangier disease: a disorder of intracellular membrane traffic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6305–6309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz G., Robenek H., Lohmann U., Assmann G. Interaction of high density lipoproteins with cholesteryl ester-laden macrophages: biochemical and morphological characterization of cell surface receptor binding, endocytosis and resecretion of high density lipoproteins by macrophages. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):613–622. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotte J. P., Oram J. F., Bierman E. L. Binding of high density lipoproteins to cell receptors promotes translocation of cholesterol from intracellular membranes to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):12904–12907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Bode C., Knyrim K. Serum apolipoprotein AI synthesis in rat hepatocytes and its secretion as proform. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Apr;364(4):439–445. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.1.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Haas J., Steinmetz A., Paetzold R., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein A-IGiessen (Pro143----Arg). A mutant that is defective in activating lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):325–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Bersot T. P., Mahley R. W., Franceschini G., Sirtori C. R. Apolipoprotein A-IMilano. Detection of normal A-I in affected subjects and evidence for a cysteine for arginine substitution in the variant A-I. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2508–2513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. Y., Yang T., Pownall H. J., Gotto A. M., Jr The primary structure of apolipoprotein A-I from rabbit high-density lipoprotein. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):427–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Fukushima D., Kupferberg J. P., Kézdy F. J., Kaiser E. T. The mechanism of activation of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase by apolipoprotein A-I and an amphiphilic peptide. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7333–7339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Karathanasis S. K., Keutmann H. T., Goldberger G., Breslow J. L. Intracellular and extracellular processing of human apolipoprotein A-I: secreted apolipoprotein A-I isoprotein 2 is a propeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2574–2578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Lees A. M., Lees R. S., Breslow J. L. Abnormal apoprotein A-I isoprotein composition in patients with Tangier disease. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4978–4986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]