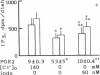Abstract
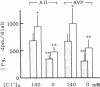
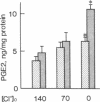
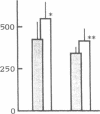
Our recent observation showed that angiotensin II (AII) and arginine vasopressin (AVP) stimulate Ca2+-activated Cl- conductance in mesangial cells. These data raise the possibility that mesangial cell function may be modulated by extracellular chloride concentration [( Cl-]o). The present study was undertaken to test this possibility using cultured rat mesangial cells. When the [Cl-]o was reduced to zero, the percentage of mesangial cells showing contraction responding to AII and AVP was decreased from 72 +/- 9 to 33 +/- 10% and from 60 +/- 4 to 24 +/- 11%, respectively. Ca2+ transients induced by AII and AVP, measured in mesangial cells loaded with Ca2+-sensitive photoprotein aequorin, were attenuated as [Cl-]o decreased. Also, when [Cl-]o decreased, inositol trisphosphate (IP3) levels of mesangial cells were suppressed, both in the presence and absence of AII or AVP. PGE2 production by mesangial cells increased when [Cl-]o decreased and the effects of ambient Cl- deprivation could be restored by addition of indomethacin to the Cl- -free medium. Moreover, PGE2 decreased mesangial cell contractility, Ca2+ transients, and IP3 production in response to AII and AVP. These data suggest that the decrease in [Cl-]o attenuates mesangial cell contraction by suppressing IP3 production and thus Ca2+ transients in response to AII and AVP through enhanced PGE2 production.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. G., Blinks J. R., Prendergast F. G. Aequorin luminescence: relation of light emission to calcium concentration--a calcium-independent component. Science. 1977 Mar 11;195(4282):996–998. doi: 10.1126/science.841325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardaillou N., Hagege J., Nivez M. P., Ardaillou R., Schlondorff D. Vasoconstrictor-evoked prostaglandin synthesis in cultured human mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F240–F246. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausiello D. A., Kreisberg J. I., Roy C., Karnovsky M. J. Contraction of cultured rat glomerular cells of apparent mesangial origin after stimulation with angiotensin II and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):754–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI109723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V., Skorecki K. L., Kreisberg J. I., Cheung J. Y. Vasopressin increases cytosolic free calcium concentration in glomerular mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 2):F94–102. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.1.F94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foidart J., Sraer J., Delarue F., Mahieu P., Ardaillou R. Evidence for mesangial glomerular receptors for angiotensin II linked to mesangial cell contractility. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 1;121(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80375-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassid A., Pidikiti N., Gamero D. Effects of vasoactive peptides on cytosolic calcium in cultured mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 2):F1018–F1028. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.6.F1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Ferguson K. M., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of hormone-sensitive GTP-dependent regulatory proteins by chloride. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3597–3602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I. Direct analysis of the effector mechanism of the tubuloglomerular feedback system. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):F447–F455. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.5.F447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima I., Ogata E. Direct demonstration of adrenocorticotropin-induced changes in cytoplasmic free calcium with aequorin in adrenal glomerulosa cell. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9832–9838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Karnovsky M. J. Glomerular cells in culture. Kidney Int. 1983 Mar;23(3):439–447. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Karnovsky M. J., Levine L. Prostaglandin production by homogeneous cultures of rat glomerular epithelial and mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1982 Oct;22(4):355–359. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Petersen O. H. Voltage clamp study of stimulant-evoked currents in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Sep;399(1):54–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00652522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mené P., Dunn M. J. Contractile effects of TxA2 and endoperoxide analogues on cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 2):F1029–F1035. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.6.F1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Vascular smooth muscle: the first recorded Ca2+ transients. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):75–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00584972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda T., Yamashita N., Kurokawa K. Angiotensin II and vasopressin stimulate calcium-activated chloride conductance in rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1443–1448. doi: 10.1172/JCI112734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson B. E., Sakai T., Marsh D. J. Juxtaglomerular interstitial hypertonicity in Amphiuma: tubular origin-TGF signal. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):F445–F449. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.3.F445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Bauer C. Pertussis toxin abolishes angiotensin II-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis and prostaglandin synthesis in rat renal mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):289–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2360289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J. Tumour promotor 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate inhibits angiotensin II-induced inositol phosphate production and cytosolic Ca2+ rise in rat renal mesangial cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 28;203(2):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80755-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangachari P. K., Triggle C. R., Daniel E. E. Chloride removal selectively inhibits phasic contractions of guinea pig ileal longitudinal smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Dec;60(12):1741–1744. doi: 10.1139/y82-258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt L. A., Dunn M. J. Prostaglandin synthesis by rat glomerular mesangial cells in culture. Effects of angiotensin II and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1756–1764. doi: 10.1172/JCI110931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlondorff D., Satriano J. A., Hagege J., Perez J., Baud L. Effect of platelet-activating factor and serum-treated zymosan on prostaglandin E2 synthesis, arachidonic acid release, and contraction of cultured rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1172/JCI111309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnermann J., Ploth D. W., Hermle M. Activation of tubulo-glomerular feedback by chloride transport. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Apr 6;362(3):229–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00581175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin S., Fujiwara Y., Wada A., Takama T., Orita Y., Kamada T., Tagawa K. Angiotensin II-induced increase in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in cultured rat mesangial cells: evidence by refined high performance liquid chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 15;142(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner R., Schiller A., Kaissling B., Kriz W. Gap junctional coupling between the JGA and the glomerular tuft. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Jan 17;186(2):279–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00225537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Cell growth factors. Bicarbonate and pHi response. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):601–601. doi: 10.1038/337601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Kreisberg J. I. Agonist-induced isotonic contraction of cultured mesangial cells after multiple passage. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 1):C48–C55. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.1.C48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]