Abstract
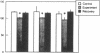
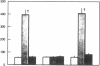
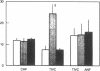
The current studies were designed to investigate the functional significance of elevated endogenous atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) in acute congestive heart failure (CHF). Integrated cardiorenal and endocrine function were measured in three models of acute low-output congestive heart failure with comparably reduced cardiac output (CO) and mean arterial pressure (MAP). Acute CHF was produced by rapid right ventricular pacing (group I, n = 5) which decreases CO and increases atrial pressures and plasma ANF. In group II, n = 5, thoracic inferior vena caval constriction (TIVCC) was produced to decrease venous return and CO but without increases in atrial pressure or plasma ANF. In group III, n = 5, TIVCC was performed and exogenous ANF infused to achieve plasma concentrations observed in acute CHF. In acute CHF with increases in endogenous ANF, sodium excretion (UNaV), renal blood flow (RBF), plasma renin activity (PRA), and plasma aldosterone (PA) were maintained despite decreases in CO and MAP. In contrast, TIVCC with similar reductions in CO and MAP but without increases in ANF resulted in decreases in UNaV and RBF and increases in PRA and PA. Exogenous administration of ANF in TIVCC to mimic levels in acute CHF prevented sodium retention, renal vasoconstriction, and activation of renin and aldosterone. These studies demonstrate that endogenous ANF serves as an important physiologic volume regulator in acute CHF to maintain sodium excretion and possibly participate in the suppression of activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system despite the stimulus of arterial hypotension.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnett J. C., Jr, Granger J. P., Opgenorth T. J. Effects of synthetic atrial natriuretic factor on renal function and renin release. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):F863–F866. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.5.F863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett J. C., Jr, Kao P. C., Hu D. C., Heser D. W., Heublein D., Granger J. P., Opgenorth T. J., Reeder G. S. Atrial natriuretic peptide elevation in congestive heart failure in the human. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1145–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.2935937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody R. J., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H., Kubo S. H., Covit A. B., Ryman K. S., Shaknovich A., Pondolfino K., Clark M., Camargo M. J. Atrial natriuretic factor in normal subjects and heart failure patients. Plasma levels and renal, hormonal, and hemodynamic responses to peptide infusion. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1362–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI112723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. O., PECHET M. M., BALL W. C., Jr, GOODKIND M. J. Increased aldosterone secretion in dogs with right-sided congestive heart failure and in dogs with thoracic inferior vena cava constriction. J Clin Invest. 1957 May;36(5):689–694. doi: 10.1172/JCI103470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz J. R. Release of natriuretic factor from rat heart-lung preparation by atrial distension. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 2):R1093–R1096. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.247.6.R1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding J., Thibault G., Gutkowska J., Garcia R., Karabatsos T., Jasmin G., Genest J., Cantin M. Cardiac and plasma atrial natriuretic factor in experimental congestive heart failure. Endocrinology. 1987 Jul;121(1):248–257. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-1-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards B. S., Ackermann D. M., Lee M. E., Reeder G. S., Wold L. E., Burnett J. C., Jr Identification of atrial natriuretic factor within ventricular tissue in hamsters and humans with congestive heart failure. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):82–86. doi: 10.1172/JCI113314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards B. S., Zimmerman R. S., Schwab T. R., Heublein D. M., Burnett J. C., Jr Atrial stretch, not pressure, is the principal determinant controlling the acute release of atrial natriuretic factor. Circ Res. 1988 Feb;62(2):191–195. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauer O. H., Henry J. P., Behn C. The regulation of extracellular fluid volume. Annu Rev Physiol. 1970;32:547–595. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.002555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald J. E., Sakata M., Michener M. L., Sides S. D., Needleman P. Is atriopeptin a physiological or pathophysiological substance? Studies in the autoimmune rat. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1036–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI113414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodsman G. P., Kohzuki M., Howes L. G., Sumithran E., Tsunoda K., Johnston C. I. Neurohumoral responses to chronic myocardial infarction in rats. Circulation. 1988 Aug;78(2):376–381. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.78.2.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maack T., Marion D. N., Camargo M. J., Kleinert H. D., Laragh J. H., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Atlas S. A. Effects of auriculin (atrial natriuretic factor) on blood pressure, renal function, and the renin-aldosterone system in dogs. Am J Med. 1984 Dec;77(6):1069–1075. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler C. H., Lee M. E., Thrasher T. N., Ramsay D. J. Increased right or left atrial pressure stimulates release of atrial natriuretic peptides in conscious dogs. Endocrinology. 1986 Nov;119(5):2396–2398. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-5-2396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J. B., Lattion A. L., Salzmann J. L., Cerol M. L., Philippe M., Camilleri J. P., Corvol P. Hormonal and cardiac effects of converting enzyme inhibition in rat myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 1988 Apr;62(4):641–650. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.4.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scriven T. A., Burnett J. C., Jr Effects of synthetic atrial natriuretic peptide on renal function and renin release in acute experimental heart failure. Circulation. 1985 Oct;72(4):892–897. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.4.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker Y., Sider R. S., Ostafin E. A., Grekin R. J. Plasma levels of immunoreactive atrial natriuretic factor in healthy subjects and in patients with edema. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1684–1687. doi: 10.1172/JCI112154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins L., Jr, Burton J. A., Haber E., Cant J. R., Smith F. W., Barger A. C. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in congestive failure in conscious dogs. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1606–1617. doi: 10.1172/JCI108431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. S., Schirger J. A., Edwards B. S., Schwab T. R., Heublein D. M., Burnett J. C., Jr Cardio-renal-endocrine dynamics during stepwise infusion of physiologic and pharmacologic concentrations of atrial natriuretic factor in the dog. Circ Res. 1987 Jul;61(1):63–69. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]