Abstract
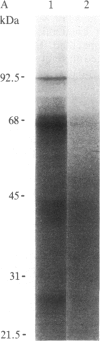
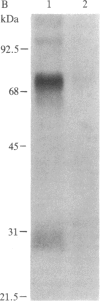
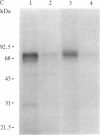
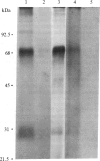
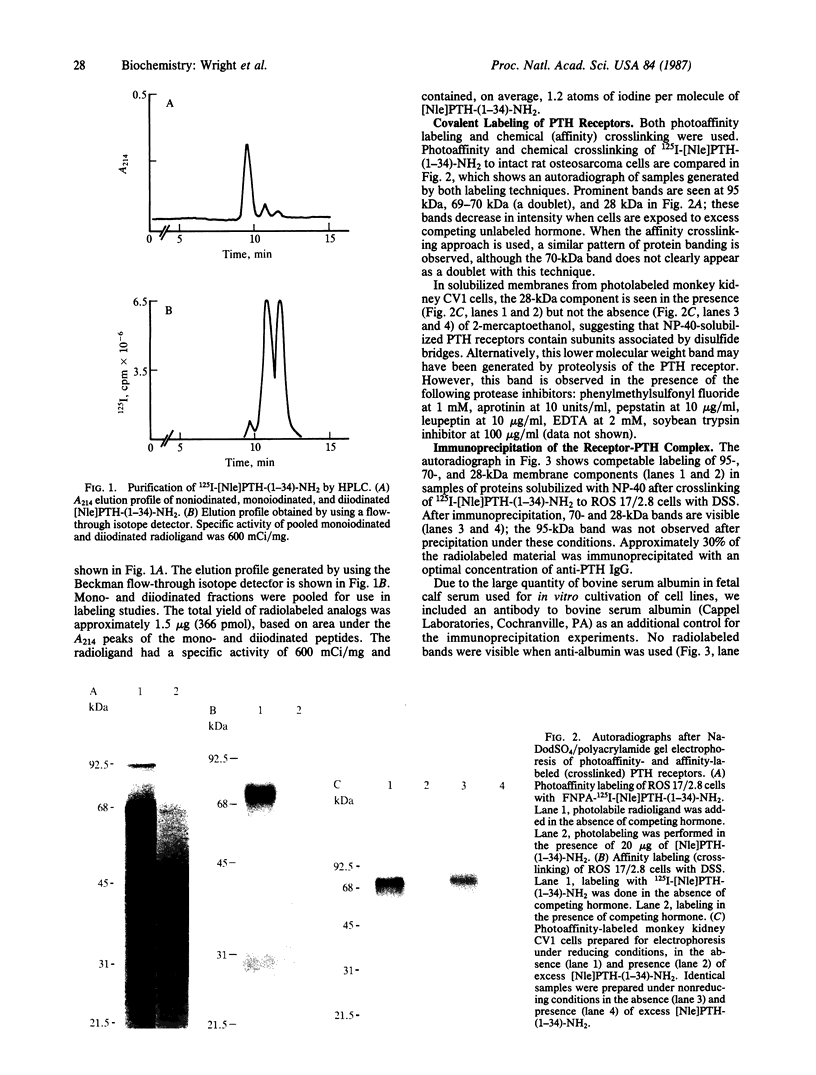
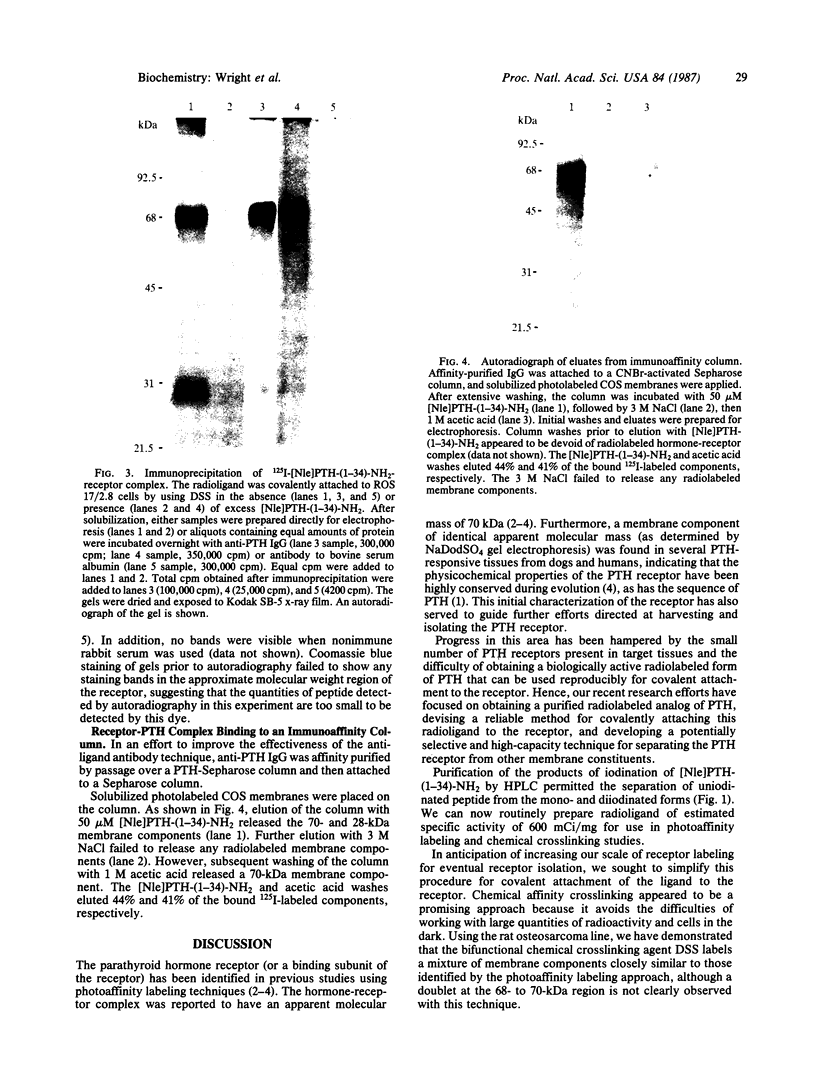
An 125I-labeled synthetic analog of bovine parathyroid hormone, [8-norleucine,18-norleucine,34-tyrosine]PTH-(1-34) amide ([Nle]PTH-(1-34)-NH2), purified by high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC), was employed to label the parathyroid hormone (PTH) receptor in cell lines derived from PTH target tissues: the ROS 17/2.8 rat osteosarcoma of bone and the CV1 and COS monkey kidney lines. After incubation of the radioligand with intact cultured cells, the hormone was covalently attached to receptors by using either a photoaffinity technique or chemical (affinity) cross-linking. In each case, covalent labeling was specific, as evidenced by a reduction of labeling when excess competing nonradioactive ligand was present. After covalent attachment of radioligand, membranes were prepared from the cells and solubilized in the nonionic detergent Nonidet P-40 or octyl glucoside. The soluble membrane fraction present in the supernatant of a 100,000 X g centrifugation was incubated with IgG prepared from anti-PTH antiserum generated to the amino-terminal region, residues 1-34, of PTH. The IgG-PTH-receptor complex was precipitated with staphylococcal protein A-Sepharose. Analysis of the immunoprecipitate on NaDod-SO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by autoradiography revealed the presence of a doublet of apparent molecular mass 69-70 kDa. Specifically labeled bands of approximate molecular mass 95 and 28 kDa were also observed. The anti-PTH IgG was affinity purified by passage over a PTH-Sepharose column and used to make an immunoaffinity column. The 70- and 28-kDa bands were also observed after labeled solubilized membrane preparations were allowed to bind to this column and then were eluted by using a [Nle]PTH-(1-34)-NH2-containing buffer or acetic acid. These studies suggest that the use of an anti-PTH antiserum that binds receptor-bound hormone is likely to be a useful step in the further physiochemical characterization and purification of the PTH receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltrera M. D., Potts J. T., Jr, Rosenblatt M. Identification of a renal receptor for parathyroid hormone by photoaffinity radiolabeling using a synthetic analogue. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10555–10559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Stadel J. M., Lefkowitz R. J. A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7108–7117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper M. W., Nissenson R. A., Winer J., Ramachandran J., Arnaud C. D. Photoaffinity labeling of the canine renal receptor for parathyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3714–3718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring S. R., Tyler G. A., Krane S. M., Potts J. T., Jr, Rosenblatt M. Photoaffinity labeling of parathyroid hormone receptors: comparison of receptors across species and target tissues and after desensitization to hormone. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 31;23(3):498–502. doi: 10.1021/bi00298a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich J., Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Purification of the adipocyte insulin receptor by immunoaffinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1732–1737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Stiles G. L. Mechanisms of membrane-receptor regulation. Biochemical, physiological, and clinical insights derived from studies of the adrenergic receptors. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 14;310(24):1570–1579. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406143102406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majeska R. J., Rodan S. B., Rodan G. A. Parathyroid hormone-responsive clonal cell lines from rat osteosarcoma. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1494–1503. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Zull J. E. Solubilization of a parathyroid hormone receptor from bovine kidney cortex plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80311-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metsikkö K., Rajaniemi H. Purification of luteinizing hormone receptor and its subunit structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 29;95(4):1730–1736. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissenson R. A., Mann E., Winer J., Teitelbaum A. P., Arnaud C. D. Solubilization of a guanine nucleotide-sensitive parathyroid hormone-receptor complex from canine renal cortex. Endocrinology. 1986 Mar;118(3):932–939. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-3-932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts J. T., Jr, Kronenberg H. M., Rosenblatt M. Parathyroid hormone: chemistry, biosynthesis, and mode of action. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:323–396. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60471-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Hart D. A., Holmes R. K., Holmes K. V., Eidels L. Immunoprecipitation and partial characterization of diphtheria toxin-binding glycoproteins from surface of guinea pig cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):685–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Burke T. R., Jr, Rice K. C., Jacobson A. E., Klee W. A. Purification of the opiate receptor of NG108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4974–4978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada H. G., Hass P. E., Sussman H. H. Transferrin receptor in human placental brush border membranes. Studies on the binding of transferrin to placental membrane vesicles and the identification of a placental brush border glycoprotein with high affinity for transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12629–12635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]