Abstract
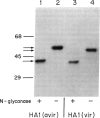
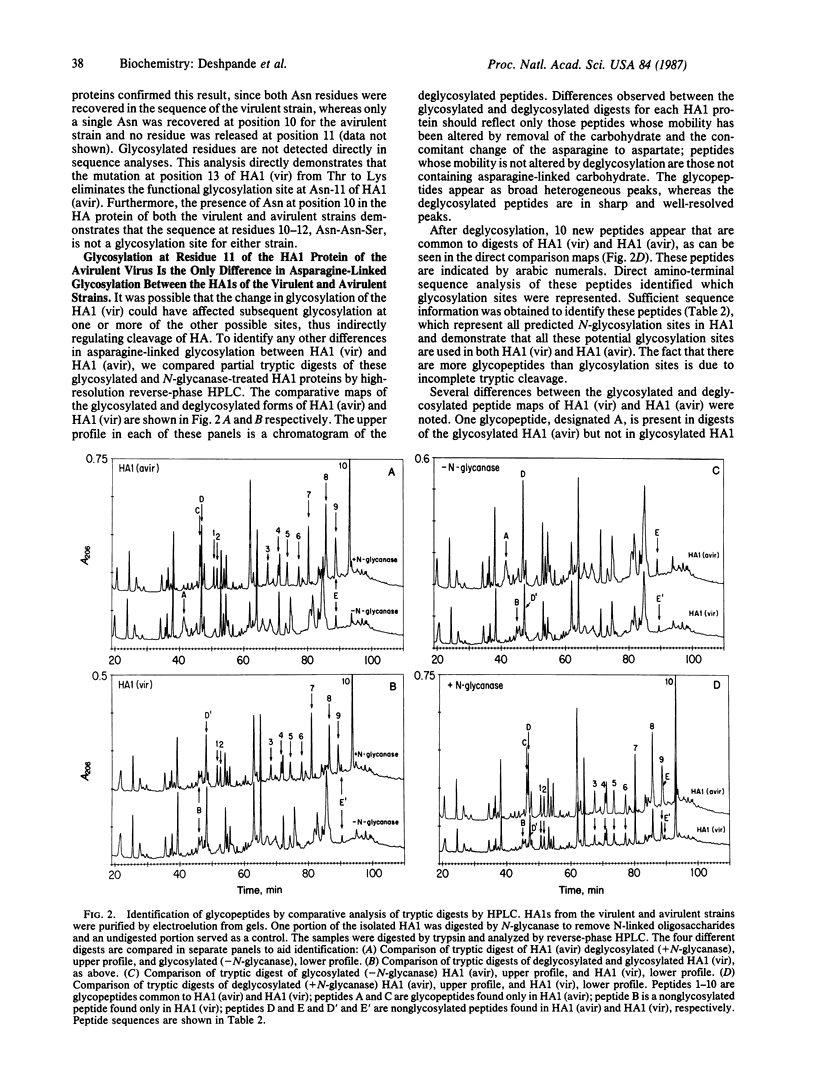
Based on nucleotide sequence analysis of the hemagglutinin (HA) gene from the virulent and avirulent A/chicken/Pennsylvania/83 influenza viruses, it was previously postulated that acquisition of virulence was associated with a point mutation that resulted in loss of a glycosylation site. Since there are two potential glycosylation sites in this region of the HA molecule and since all Asn-Xaa-Thr/Ser sequences in the HAs of different strains are not necessarily glycosylated, the question remained open as to whether either one of these sites was glycosylated. We now provide direct evidence that a site-specific glycosylation affects cleavage of the influenza virus HA and thus virulence. We have identified the glycosylation sites on the HA1 subunit from the virulent and avirulent strains by direct structural analysis of the isolated proteins. Our results show that the only difference in glycosylation between the HA1s of the virulent and avirulent strains is the lack of an asparagine-linked carbohydrate on the virulent HA1 polypeptide at residue 11. Further, we show that the HA1s of both the avirulent and virulent viruses are not glycosylated at one potential site, while all other sites contain carbohydrate. Amino acid sequence analysis of the HA1 of an avirulent revertant of the virulent strain confirmed these findings.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean W. J., Kawaoka Y., Wood J. M., Pearson J. E., Webster R. G. Characterization of virulent and avirulent A/chicken/Pennsylvania/83 influenza A viruses: potential role of defective interfering RNAs in nature. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):151–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.151-160.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Garten W., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of influenza virus hemagglutinins: primary structure of the connecting peptide between HA1 and HA2 determines proteolytic cleavability and pathogenicity of Avian influenza viruses. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Orlich M., Klenk H. D., Rott R. The structure of the hemagglutinin, a determinant for the pathogenicity of influenza viruses. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried V. A., Ando M. E., Bell A. J. Protein quantitation at the picomole level: an O-phthaldialdehyde-preTSK column-derivatization assay. Anal Biochem. 1985 Apr;146(1):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90426-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried V. A. Membrane biogenesis. Evidence that a soluble chimeric polypeptide can serve as a precursor of a mutant lac permease in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):244–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Linder D., Rott R., Klenk H. D. The cleavage site of the hemagglutinin of fowl plague virus. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90387-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. Glycosylation allows cell-surface transport of an anchored secretory protein. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Analysis of phenylthiohydantoins by ultrasensitive gradient high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:486–493. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Naeve C. W., Webster R. G. Is virulence of H5N2 influenza viruses in chickens associated with loss of carbohydrate from the hemagglutinin? Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):303–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Webster R. G. Evolution of the A/Chicken/Pennsylvania/83 (H5N2) influenza virus. Virology. 1985 Oct 15;146(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil W., Klenk H. D., Schwarz R. T. Carbohydrates of influenza virus. III. Nature of oligosaccharide-protein linkage in viral glycoproteins. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):253–256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.253-256.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil W., Niemann H., Schwarz R. T., Klenk H. D. Carbohydrates of influenza virus. V. Oligosaccharides attached to individual glycosylation sites of the hemagglutinin of fowl plague virus. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Orlich M., Blödorn J. Activation of influenza A viruses by trypsin treatment. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):426–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Choppin P. W. Enhancement of the infectivity of influenza A and B viruses by proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Florkiewicz R. Z., Rose J. K. A single N-linked oligosaccharide at either of the two normal sites is sufficient for transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein to the cell surface. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3074–3083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Compans R. W. Effects of glucosamine, 2-deoxyglucose, and tunicamycin on glycosylation, sulfation, and assembly of influenza viral proteins. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):303–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Ueda M. Genes involved in the virulence of an avian influenza virus. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):304–313. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr, Elder J. H., Alexander S., Phelan A. W., Tarentino A. L. Demonstration of peptide:N-glycosidase F activity in endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F preparations. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10700–10704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronin C., Granier C., Caseti C., Bouchilloux S., Van Rietschoten J. Synthetic substrates for thyroid oligosaccharide transferase. Effects of peptide chain length and modifications in the Asn-Xaa-Thr-region. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):159–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R., Orlich M., Scholtissek C. Attenuation of pathogenicity of fowl plague virus by recombination with other influenza A viruses nonpathogenic for fowl: nonexculsive dependence of pathogenicity on hemagglutinin and neuraminidase of the virus. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):54–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.54-60.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R., Orlich M., Scholtissek C. Correlation of pathogenicity and gene constellation of influenza A viruses. III. Non-pathogenic recombinants derived from highly pathogenic parent strains. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):471–477. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Rott R., Orlich M., Harms E., Rohde W. Correlation of pathogenicity and gene constellation of an influenza A virus (fowl plague). I. Exchange of a single gene. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):74–80. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R. T., Rohrschneider J. M., Schmidt M. F. Suppression of glycoprotein formation of Semliki Forest, influenza, and avian sarcoma virus by tunicamycin. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):782–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.782-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K., Kaufman J., Gilbert W. Bacteria mature preproinsulin to proinsulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3988–3992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Kawaoka Y., Bean W. J., Jr Molecular changes in A/Chicken/Pennsylvania/83 (H5N2) influenza virus associated with acquisition of virulence. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90118-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):373–378. doi: 10.1038/289373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Ladner R. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. The structure and role of the carbohydrate moieties of influenza virus haemagglutinin. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Apr;11(Pt 2):145–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]