Abstract
The high susceptibility of human immunoglobulin D to proteolytic degradation affects its biological function, metabolism, and immunoassay. High-pressure liquid chromatography was used to investigate the mechanism and rate of limited proteolytic cleavage of IgD and also to identify, isolate, and quantify the reaction products. Within 1 to 5 min, tryptic digestion of native IgD almost quantitatively yields a labile Fab fragment, a stable Fc fragment, and a highly charged peptide derived from the hinge region. A galactosamine-rich glycopeptide from the hinge region increases inversely as the Fab is largely degraded to a series of peptides within 1 hr. In contrast, the Fc and the high-charge peptide resist proteolysis for more than 24 hr. The initial sites of cleavage of IgD occur in the hinge region at exposed secondary structures predicted to be beta-turns. Concomitant with removal of the galactosamine-rich glycopeptide at its carboxyl terminus, the Fd fragment is rapidly and rather randomly degraded, but the light chain is somewhat more resistant than the Fd section of the delta heavy chain. This study of the rapid rate of proteolysis of IgD explains the rarity with which intact IgD is found in human sera. It also raises questions about immunoassay of IgD, which is usually measured with antisera against Fc. In vivo, proteolytic cleavage initiates the catabolism of circulating IgD and also affects the role and fate of IgD as an antigen receptor on the B-cell membrane.
Full text
PDF
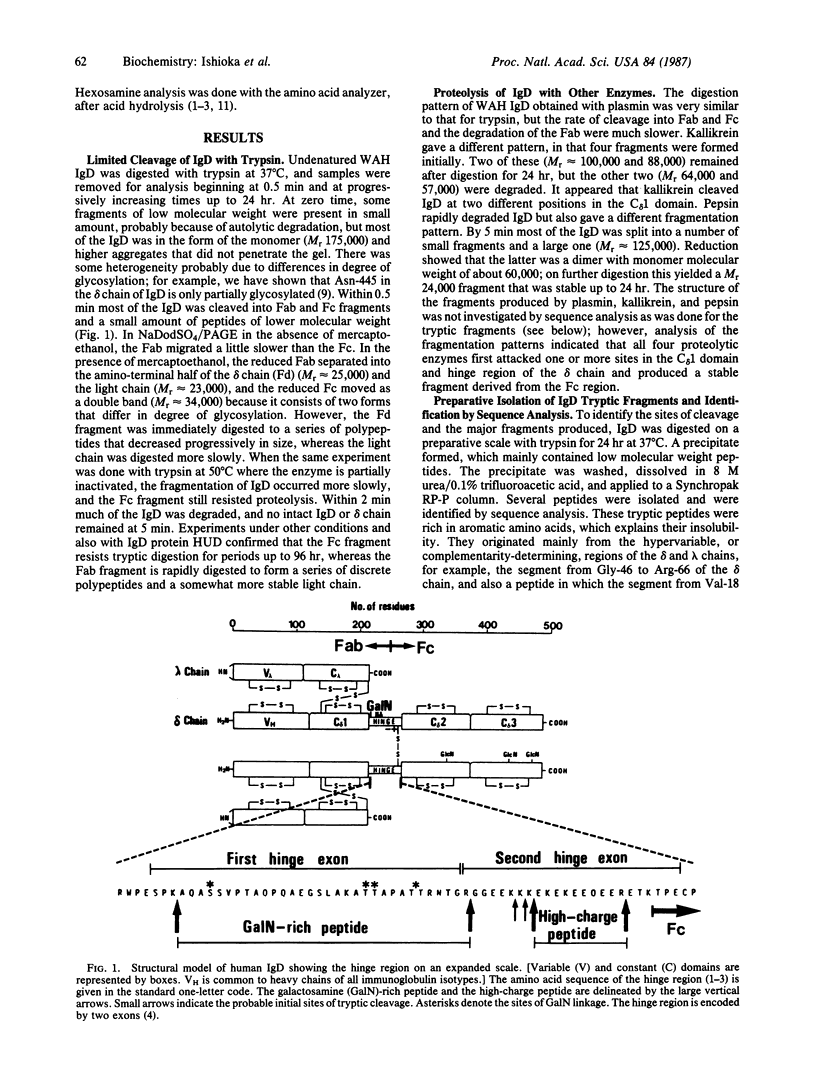
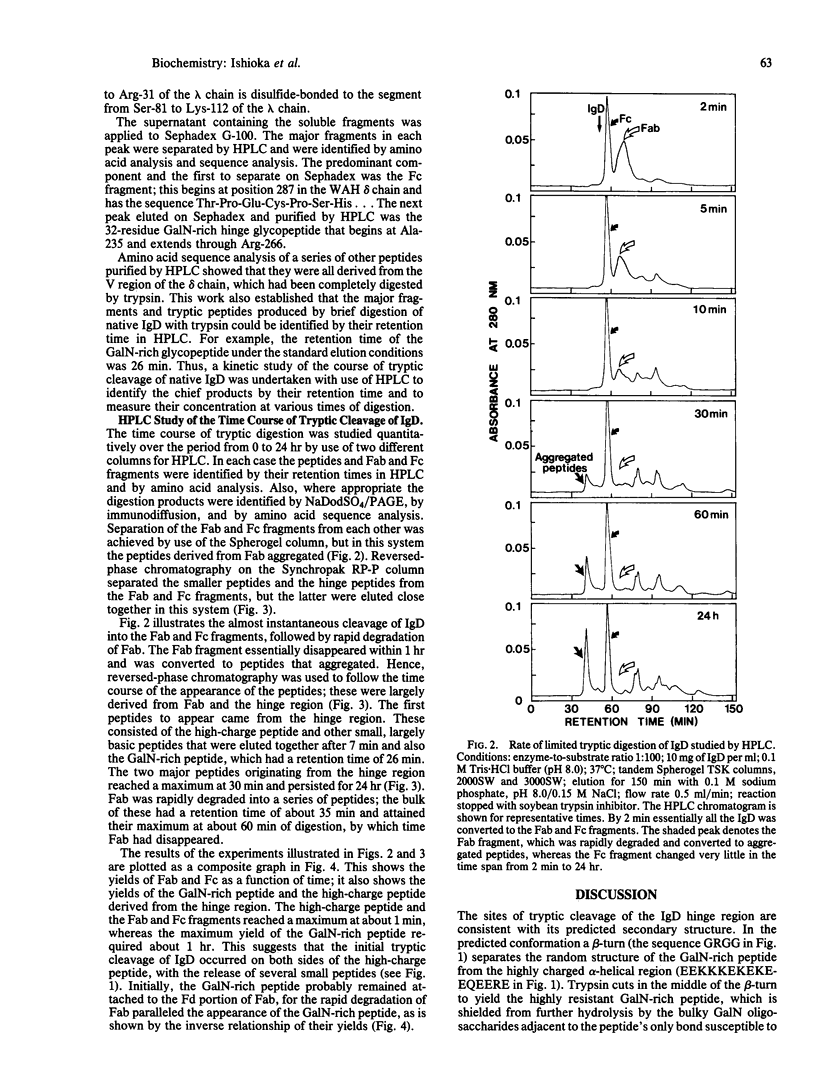
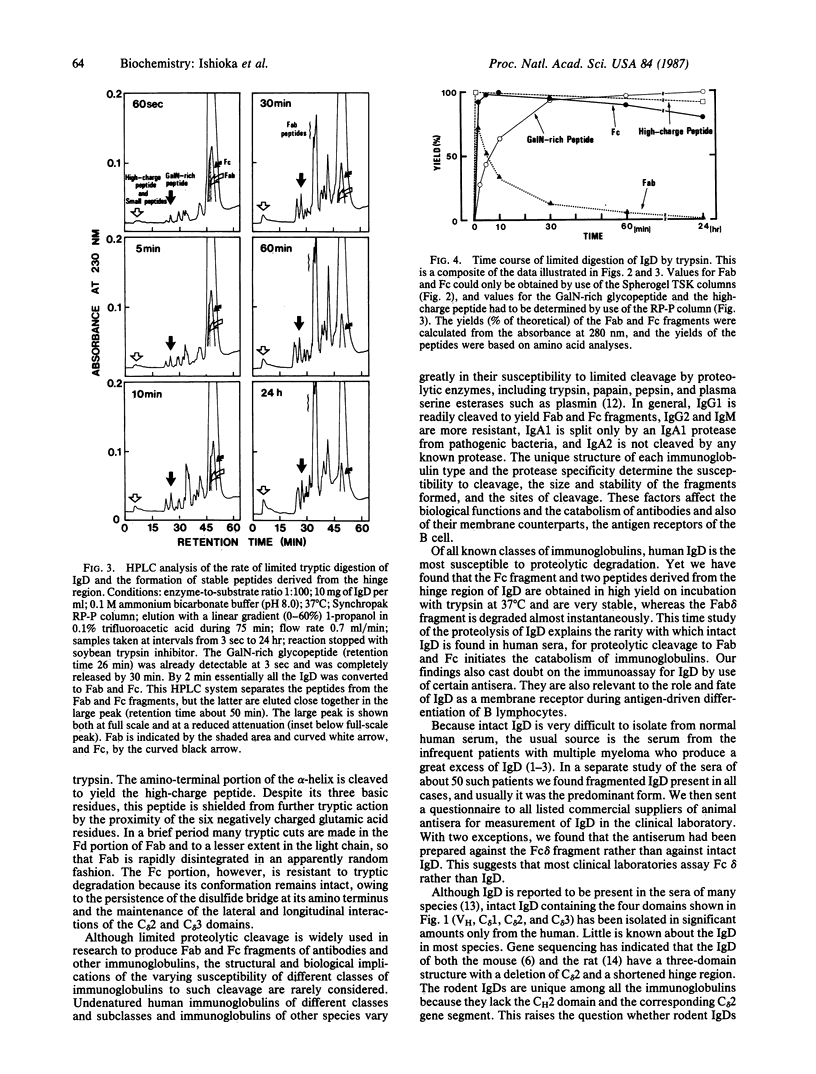

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blattner F. R., Tucker P. W. The molecular biology of immunoglobulin D. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):417–422. doi: 10.1038/307417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devare S. G., Reddy E. P., Law J. D., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Nucleotide sequence of the simian sarcoma virus genome: demonstration that its acquired cellular sequences encode the transforming gene product p28sis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Ellis J., Svec P., Schlesinger D. H., Nussenzweig V. Identification and chemical synthesis of a tandemly repeated immunogenic region of Plasmodium knowlesi circumsporozoite protein. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):29–33. doi: 10.1038/305029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishioka N., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Amino acid sequence of human plasma alpha 1B-glycoprotein: homology to the immunoglobulin supergene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2363–2367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie G. A., Martin L. N. Structure and function of serum and membrane immunoglobulin D (IgD). Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1978;7:1–49. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0779-3_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. C., Putnam F. W. Structural studies of human IgD: isolation by a two-step purification procedure and characterization by chemical and enzymatic fragmentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6572–6576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam F. W., Takahashi N., Tetaert D., Debuire B., Lin L. C. Amino acid sequence of the first constant region domain and the hinge region of the delta heavy chain of human IgD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6168–6172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam F. W., Takahashi N., Tetaert D., Lin L. C., Debuire B. The last of the immunoglobulins: complete amino acid sequence of human IgD. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;399:41–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sire J., Auffray C., Jordan B. R. Rat immunoglobulin delta heavy chain gene: nucleotide sequence derived from cloned cDNA. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Ishioka N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Automated tandem high-performance liquid chromatographic system for separation of extremely complex peptide mixtures. J Chromatogr. 1985 Jun 19;326:407–418. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)87466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Ortel T. L., Lozier J. N., Ishioka N., Putnam F. W. Purification of glycopeptides of human plasma proteins by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 28;317:11–26. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)91643-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Tetaert D., Debuire B., Lin L. C., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of the delta heavy chain of human immunoglobulin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Takahashi N., Tetaert D., Putnam F. W. Complete covalent structure of a human immunoglobulin D: sequence of the lambda light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele C. J., Owens J. D., Finkelman F. D., Mushinski J. F. Mouse IgD half molecules with shortened IgD heavy chain result from alterations within C delta locus. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1251–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. B., Shen A. L., Word C. J., Tucker P. W., Blattner F. R. Human immunoglobulin D: genomic sequence of the delta heavy chain. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):733–737. doi: 10.1126/science.3922054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




