Abstract
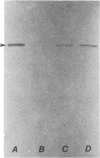
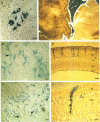
We describe a cell-lineage marking system applicable to the vertebrate nervous system. The basis of the technique is gene transfer using the retroviral vector system. We used Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase as a marker gene and demonstrate a high level of expression of this marker from the viral long terminal repeat promoter, with simultaneous expression of the Tn5 neo gene from the simian virus 40 early promoter. This expression has allowed us to detect individual infected cells histochemically. We applied this marking technique to the study of lineage relationships in the developing vertebrate nervous system, both in vivo and in culture. In the rat retina, we injected virus in vivo and histochemically identified clones of marked neural cells. In addition, we used this virus to infect cultures of rat cerebral cortex and have analyzed the clonal relationships of morphologically different neural cell types. The host range of the marking system extends to avian as well as mammalian species. Thus, this system should have broad applicability as a means of gene transfer and expression in the nervous system.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano T., Hamprecht B., Kemper W. High activity of choline acetyltransferase induced in neuroblastoma x glia hybrid cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Apr;85(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano T., Richelson E., Nirenberg M. Neurotransmitter synthesis by neuroblastoma clones (neuroblast differentiation-cell culture-choline acetyltransferase-acetylcholinesterase-tyrosine hydroxylase-axons-dendrites). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):258–263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augusti-Tocco G., Sato G. Establishment of functional clonal lines of neurons from mouse neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):311–315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braekevelt C. R., Hollenberg M. J. The development of the retina of the albino rat. Am J Anat. 1970 Mar;127(3):281–301. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001270305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C. High-efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells: generation of helper-free recombinant retrovirus with broad mammalian host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Shepherd B. M., Wensink P. C. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer from the Drosophila yolk protein 1 gene. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90560-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R. Retroviruses and embryogenesis: microinjection of Moloney leukemia virus into midgestation mouse embryos. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90399-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel C. B., Warga R. M. Tissue-specific cell lineages originate in the gastrula of the zebrafish. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):365–368. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4736.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Coffin J. M. Bacterial beta-galactosidase as a marker of Rous sarcoma virus gene expression and replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):281–290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Jensen F., Elder J., Dixon F. J., Lampert P. W. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with wild mouse virus. III. Role of input virus and MCF recombinants in disease. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):154–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. I., Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Hynes R. O. Cell-type-specific fibronectin subunits generated by alternative splicing. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12258–12265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Hynes R. O. Astrocytes in culture synthesize and secrete a variant form of fibronectin. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2205–2211. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02205.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puro D. G., Nirenberg M. On the specificity of synapse formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3544–3548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Abney E. R., Miller R. H. Two glial cell lineages diverge prenatally in rat optic nerve. Dev Biol. 1984 Nov;106(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Miller R. H., Noble M. A glial progenitor cell that develops in vitro into an astrocyte or an oligodendrocyte depending on culture medium. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):390–396. doi: 10.1038/303390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblat D. A., Sawyer R. T., Stent G. S. Cell lineage analysis by intracellular injection of a tracer enzyme. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1295–1298. doi: 10.1126/science.725606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]