Abstract
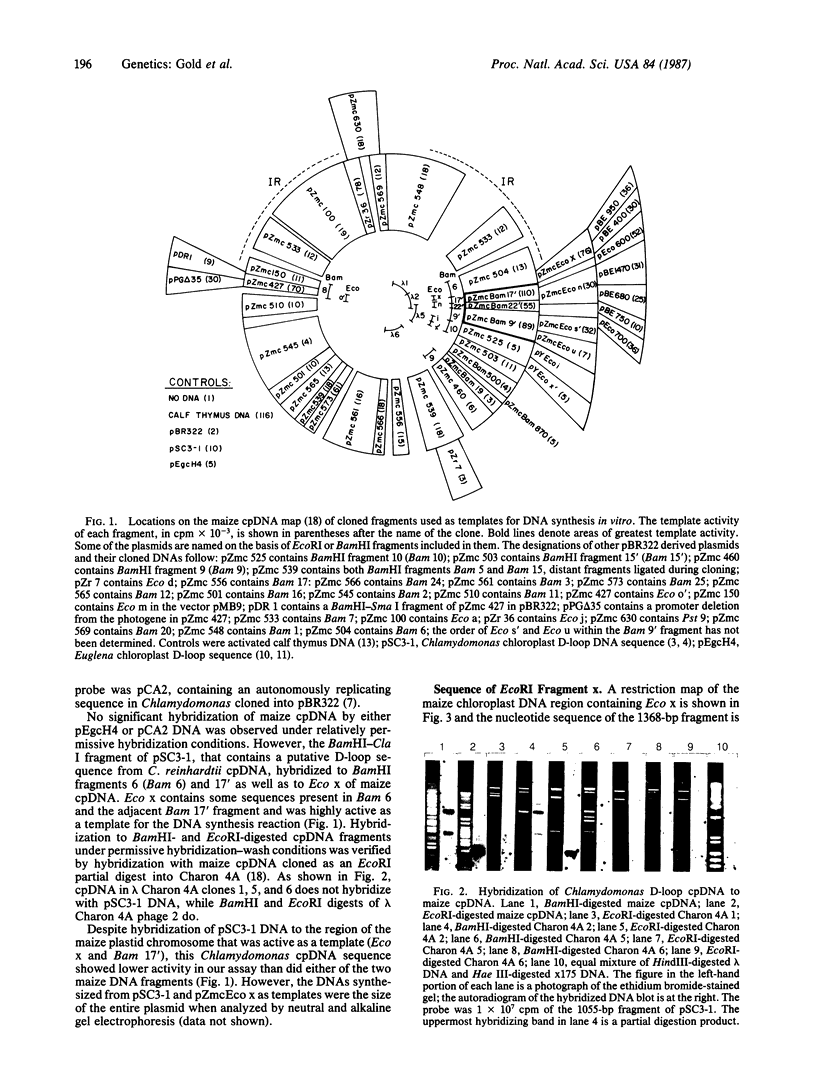
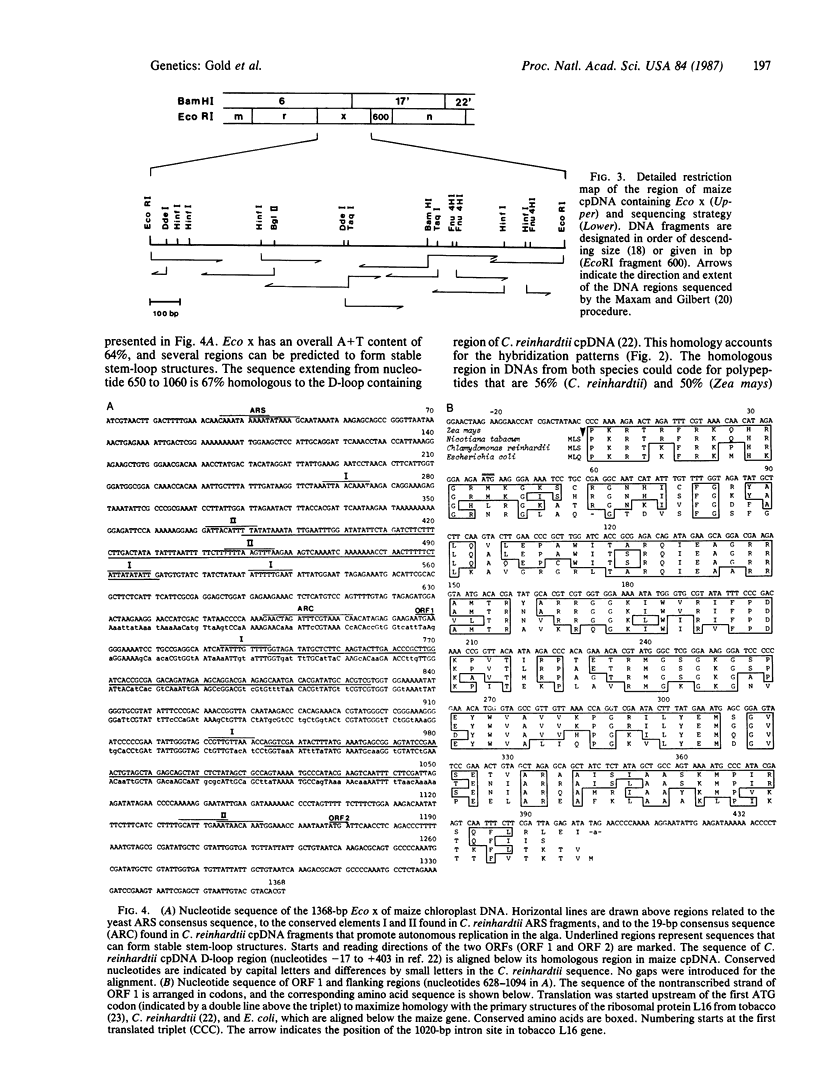
Maize chloroplast DNA sequences representing 94% of the chromosome have been surveyed for their activity as autonomously replicating sequences in yeast and as templates for DNA synthesis in vitro by a partially purified chloroplast DNA polymerase. A maize chloroplast DNA region extending over about 9 kilobase pairs is especially active as a template for the DNA synthesis reaction. Fragments from within this region are much more active than DNA from elsewhere in the chromosome and 50- to 100-fold more active than DNA of the cloning vector pBR322. The smallest of the strongly active subfragments that we have studied, the 1368-base-pair EcoRI fragment x, has been sequenced and found to contain the coding region of chloroplast ribosomal protein L16. EcoRI fragment x shows sequence homology with a portion of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast chromosome that forms a displacement loop [Wang, X.-M., Chang, C.H., Waddell, J. & Wu, M. (1984) Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 3857-3872]. Maize chloroplast DNA fragments that permit autonomous replication of DNA in yeast are not active as templates for DNA synthesis in the in vitro assay. The template active region we have identified may represent one of the origins of replication of maize chloroplast DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R. D., Tewari K. K. Chloroplast DNA from higher plants replicates by both the Cairns and the rolling circle mechanism. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):708–711. doi: 10.1038/256708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. Presence of displacement loops in the covalently closed circular chloroplast deoxyribonucleic acid from higher plants. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8840–8847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKown R. L., Tewari K. K. Purification and properties of a pea chloroplast DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2354–2358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posno M., van Vliet A., Groot G. S. The gene for Spirodela oligorhiza chloroplast ribosomal protein homologous to E. coli ribosomal protein L16 is split by a large intron near its 5' end: structure and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3181–3195. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D., van Dillewijn J., Rahire M. Construction and characterization of autonomously replicating plasmids in the green unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):925–931. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Thomas M., Kelly J., Selker E., Davis R. W. Eukaryotic DNA segments capable of autonomous replication in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4559–4563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Sugita M., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Genes for the eight ribosomal proteins are clustered on the chloroplast genome of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum): similarity to the S10 and spc operons of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6030–6034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallet J. M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Localization and sequence analysis of chloroplast DNA sequences of Chlamydomonas reinhardii that promote autonomous replication in yeast. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):415–421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01822.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell J., Wang X. M., Wu M. Electron microscopic localization of the chloroplast DNA replicative origins in Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3843–3856. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. M., Chang C. H., Waddell J., Wu M. Cloning and delimiting one chloroplast DNA replicative origin of Chlamydomonas. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3857–3872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Lou J. K., Chang D. Y., Chang C. H., Nie Z. Q. Structure and function of a chloroplast DNA replication origin of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6761–6765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Weissbach A. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in isolated chloroplasts and chloroplast extracts of maize. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3334–3343. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]