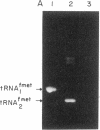
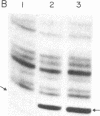
Abstract
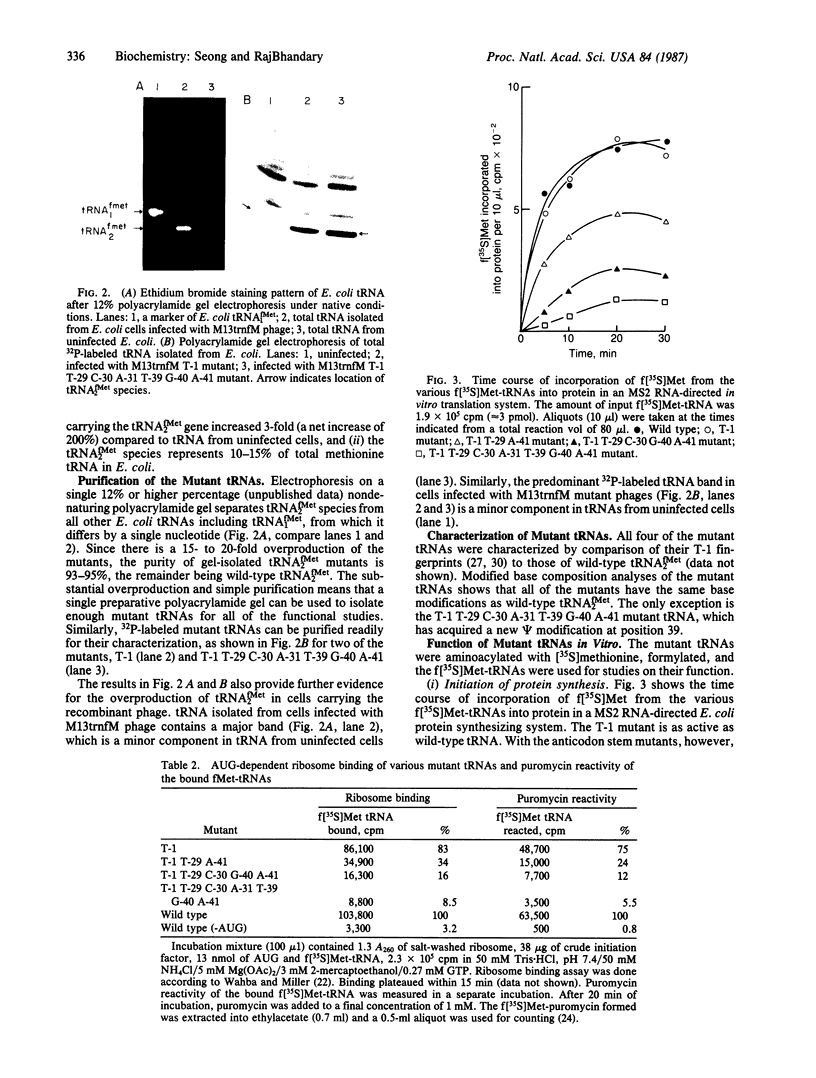
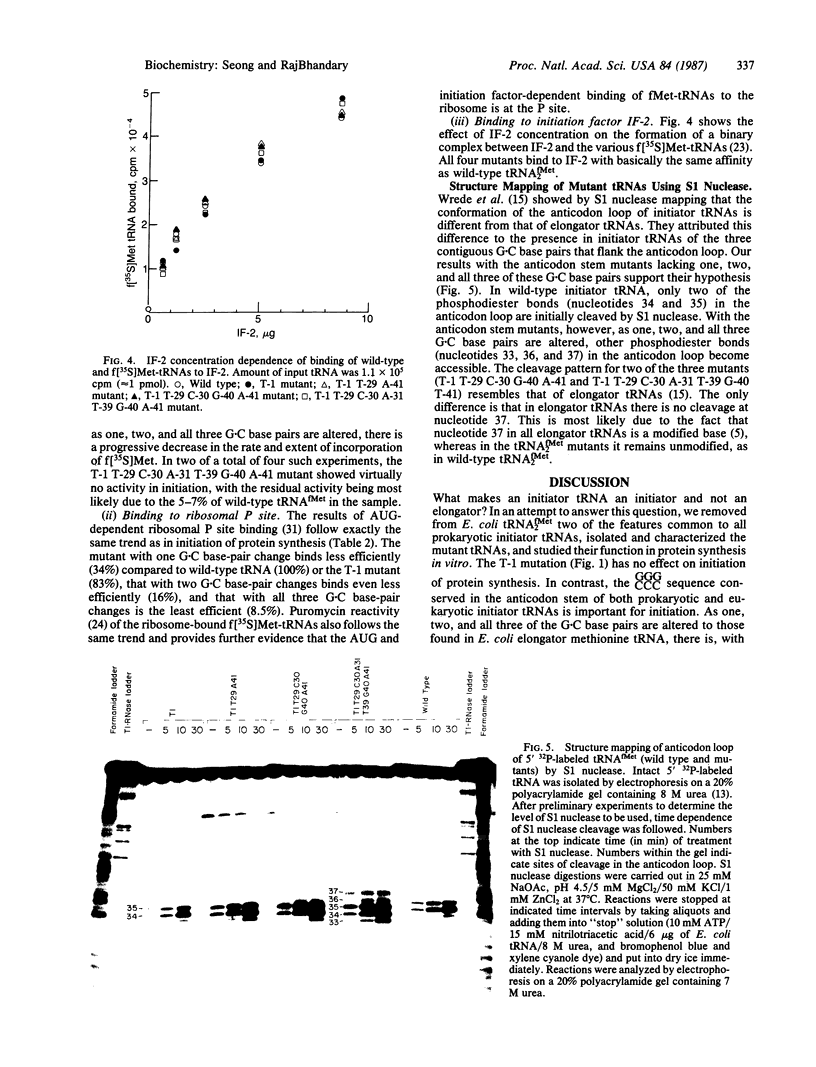
We have generated mutants of Escherichia coli formylmethionine initiator tRNA in which one, two, and all three G X C base pairs in the GGGCCC sequence in the anticodon stem are changed to those found in E. coli elongator methionine tRNA. Overproduction of the mutant tRNAs using M13 recombinants as an expression vector and development of a one-step purification scheme allowed us to purify, characterize, and analyze the function of the mutant tRNAs. After aminoacylation and formylation, the function of mutant formylmethionyl tRNAs was analyzed in an MS2 RNA-directed in vitro protein-synthesizing system, in AUG-dependent ribosomal P site binding, and in initiation factor binding. The mutant tRNAs show progressive loss of activity in initiation, the mutant with all three G X C base pairs substituted being the least active. The mutations affect binding to the ribosomal P site. None of the mutations affects binding to initiation factor 2. We also show that there is a progressive increase in accessibility of phosphodiester bonds in the anticodon loop of the three mutants to S1 nuclease, such that the cleavage pattern of the mutant with all three G X C base-pair changes resembles that of elongator tRNAs. These results are consistent with the notion that the contiguous G X C base pairs in the anticodon stem of initiator tRNAs impart on the anticodon loop a unique conformation, which may be important in targeting the initiator tRNA to the ribosomal P site during initiation of protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dickerman H. W., Steers E., Jr, Redfield B. G., Weissbach H. Methionyl soluble ribonucleic acid transformylase. I. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1522–1525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabkin H. J., RajBhandary U. L. Expression in vivo of a mutant human initiator tRNA gene in mammalian cells using a simian virus 40 vector. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5588–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabkin H. J., RajBhandary U. L. Site-specific mutagenesis on a human initiator methionine tRNA gene within a sequence conserved in all eukaryotic initiator tRNAs and studies of its effects on in vitro transcription. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5580–5587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K., Marcker K. A., Clark B. F., Cory S. Nucleotide sequence of N-formyl-methionyl-transfer RNA. Nature. 1968 Apr 20;218(5138):232–233. doi: 10.1038/218232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan B. Z., Weiss J. F., Kelmers A. D. Separation and comparison of primary structures of three formylmethionine tRNAs from E. coli K-12 MO. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):320–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman E., Gibel J. DNA sequesters endogenous mRNA during preparation of crude Escherichia coli extracts for protein synthesis; use of an S60 reduces the sequestered mRNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 1;224(1):134–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberg-Manago M., Gros F. Initiation mechanisms of protein syntehesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1977;20:209–284. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60474-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Kuroki K., Imamoto F. tRNAMetf2 gene in the leader region of the nusA operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):409–413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo I., Leineweber M., RajBhandary U. L. Site-specific mutagenesis on cloned DNAs: generation of a mutant of Escherichia coli tyrosine suppressor tRNA in which the sequence G-T-T-C corresponding to the universal G-T-pseudouracil-C sequence of tRNAs is changed to G-A-T-C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4753–4757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kössel H., RajBhandary U. L. Studies on polynucleotides. LXXXVI. Enzymic hydrolysis of N-acylaminoacyl-transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 14;35(3):539–560. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Bursztyn H. Initiation of protein synthesis II. A convenient assay for the ribosome-dependent synthesis of N-formyl-C14-methionylpuromycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 20;25(2):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo K. M., Jones S. S., Hackett N. R., Khorana H. G. Specific amino acid substitutions in bacterioopsin: Replacement of a restriction fragment in the structural gene by synthetic DNA fragments containing altered codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2285–2289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Secondary structure of bacteriophage f2 ribonucleic acid and the initiation of in vitro protein biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):689–702. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M., LEDER P. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. THE EFFECT OF TRINUCLEOTIDES UPON THE BINDING OF SRNA TO RIBOSOMES. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1399–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumbridge J. A., Deville F., Sacerdot C., Petersen H. U., Cenatiempo Y., Cozzone A., Grunberg-Manago M., Hershey J. W. Two translational initiation sites in the infB gene are used to express initiation factor IF2 alpha and IF2 beta in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):223–229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02339.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly R. M., RajBhandary U. L. A single mutation in loop IV of Escherichia coli SuIII tRNA blocks processing at both 5'- and 3'-ends of the precursor tRNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2928–2935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., RajBhandary U. L. Transfer RNA: molecular structure, sequence, and properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:805–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H., Pelka H., Sundari R. M. Structural requirements for recognition of Escherichia coli initiator and non-initiator transfer ribonucleic acids by bacterial T factor. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7102–7110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H., Pelka H. The structural basis for the resistance of Escherichia coli formylmethionyl transfer ribonucleic acid to cleavage by Escherichia coli peptidyl transfer ribonucleic acid hydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):542–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spremulli L. L., Agris P. F., Brown G. M., Rajbhandary U. L. Escherichia coli formylmethionine tRNA: methylation of specific guanine and adenine residues catalyzed by HeLa cells tRNA methylases and the effect of these methylations on its biological properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 May;162(1):22–37. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Moll J., Meissner F., Hartmann T. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13 (Suppl):r1–49. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundari R. M., Pelka H., Schulman L. H. Structural requirements of Escherichia coli formylmethionyl transfer ribonucleic acid for ribosome binding and initiation of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3941–3944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Hofstad G. A., Voorma H. O., Bosch L. Formation of a preribosomal binary complex consisting of fMet-tRNA and IF-2 and its interaction with the ribosome. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:215–224. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahba A. J., Miller M. J. Chain initiation factors from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:3–18. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo N. H., Roe B. A., Rich A. Three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli initiator tRNAfMet. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):346–351. doi: 10.1038/286346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Woo N. H., Rich A. Initiator tRNAs have a unique anticodon loop conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3289–3293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurst R. M., Vournakis J. N., Maxam A. M. Structure mapping of 5'-32P-labeled RNA with S1 nuclease. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4493–4499. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]