Abstract
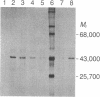
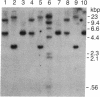
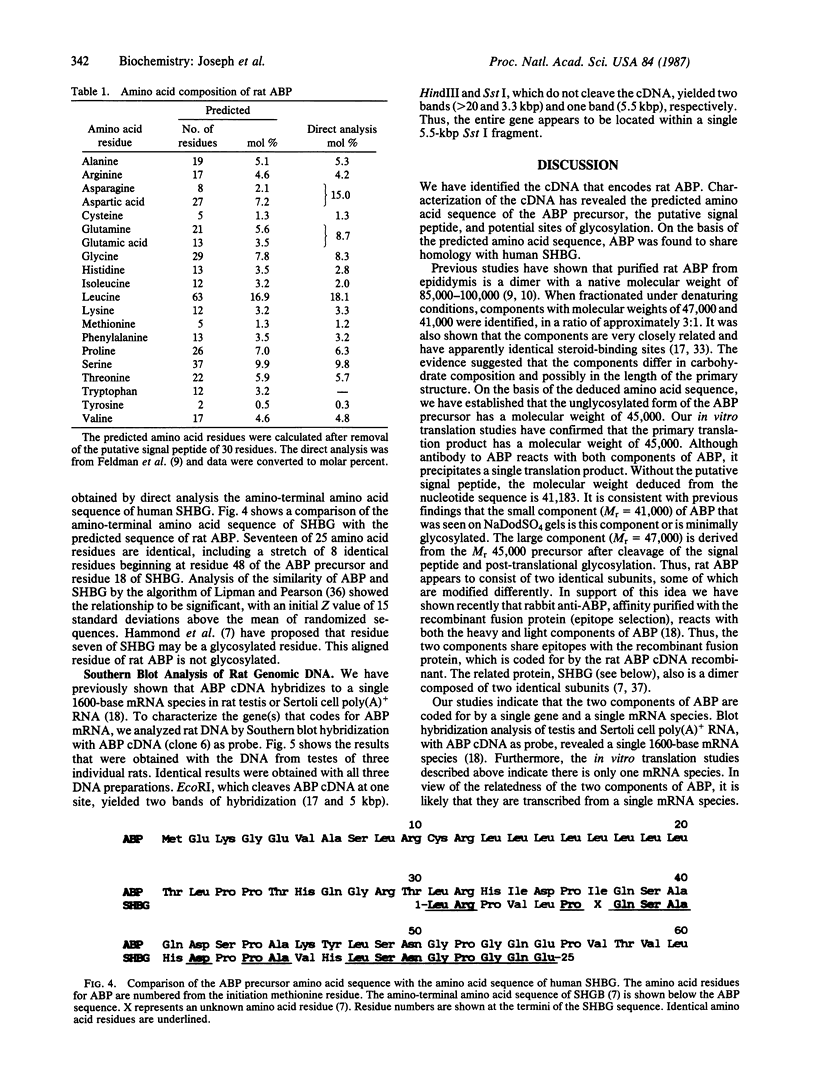
The cDNA for rat androgen-binding protein (ABP) was previously isolated from a bacteriophage lambda gt11 rat testis cDNA library and its identity was confirmed by epitope selection. Hybrid-arrested translation studies have now demonstrated the identity of the isolates. The nucleotide sequence of a near full-length cDNA encodes a 403-amino acid precursor (Mr = 44,539), which agrees in size with the cell-free translation product (Mr = 45,000) of ABP mRNA. Putative sites of N-glycosylation and signal peptide cleavage were identified. Comparison of the predicted amino acid sequence of rat ABP with the amino-terminal amino acid sequence of human sex hormone-binding globulin revealed that 17 of 25 residues are identical. On the basis of the predicted amino acid sequence the molecular weight of the primary translation product, lacking the signal peptide, was 41,183. Hybridization analyses indicated that the two subunits of ABP are coded for by a single gene and a single mRNA species. Our results suggest that ABP consists of two subunits with identical primary sequences and that differences in post-translational processing result in the production of 47,000 and 41,000 molecular weight monomers.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander D. C., Miller W. L. mRNA for ovine follicle-stimulating hormone beta-chain. An in vitro translational assay. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12628–12631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. Y., Musto N. A., Gunsalus G. L., Frick J., Bardin C. W. There are two forms of androgen binding protein in human testes. Comparison of their protomeric variants with serum testosterone-estradiol binding globulin. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5631–5640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzo B. J., Cooper T. G., Orgebin-Crist M. C. Androgen binding protein (ABP) in fluids collected from the rete testis and cauda epididymidis of sexually mature and immature rabbits and observations on morphological changes in the epididymis following ligation of the ductuli efferentes. Biol Reprod. 1977 Aug;17(1):64–77. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod17.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman M., Lea O. A., Petrusz P., Tres L. L., Kierszenbaum A. L., French F. S. Androgen-binding protein. Purification from rat epididymis, characterization, and immunocytochemical localization. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5170–5175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French F. S., Ritzén E. M. A high-affinity androgen-binding protein (ABP) in rat testis: evidence for secretion into efferent duct fluid and absorption by epididymis. Endocrinology. 1973 Jul;93(1):88–95. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-1-88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus G. L., Musto N. A., Bardin W. Immunoassay of androgen binding protein in blood: a new approach for study of the seminiferous tubule. Science. 1978 Apr 7;200(4337):65–66. doi: 10.1126/science.635573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. L., Robinson P. A., Sugino H., Ward D. N., Finne J. Physicochemical characteristics of human sex hormone binding globulin: evidence for two identical subunits. J Steroid Biochem. 1986 Apr;24(4):815–824. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(86)90442-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson V., Calandra R., Purvis K., Ritzen M., French F. S. Hormonal regulation of spermatogenesis. Vitam Horm. 1976;34:187–214. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson V., Reusch E., Trygstad O., Torgersen O., Ritzen E. M., French F. S. FSH stimulation of testicular androgen binding protein. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):56–58. doi: 10.1038/newbio246056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson V., Ritzen M. E., French F. S., Weddington S. C., Nayfeh S. N. Testicular androgen-binding protein (ABP): comparison of ABP in rabbit testis and epididymis with a similar androgen-binding protein (TeBG) in rabbit serum. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1975 Jul;3(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(75)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph D. R., Hall S. H., French F. S. Identification of complementary DNA clones that encode rat androgen binding protein. J Androl. 1985 Nov-Dec;6(6):392–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1939-4640.1985.tb03301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum A. L., Feldman M., Lea O., Spruill W. A., Tres L. L., Petrusz P., French F. S. Localization of androgen-binding protein in proliferating Sertoli cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5322–5326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrea F., Musto N. A., Gunsalus G. L., Mather J. P., Bardin C. W. Origin of the heavy and light protomers of androgen-binding protein from the rat testis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12566–12573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K., Dudock B. Characterization of a highly efficient protein synthesizing system derived from commercial wheat germ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1385–1397. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Fakunding J. L., Huckins C., Tindall D. J., Vitale R. Follicle-stimulating hormone, the Sertoli cell, and spermatogenesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1976;32:477–527. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571132-6.50027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musto N. A., Larrea F., Cheng S. L., Kotite N., Gunsalus G., Bardin C. W. Extracellular androgen-binding proteins: species comparison and structure-function relationships. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;383:343–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb23177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musto N. a., Gunsalus G. L., Bardin C. W. Purification and characterization of androgen binding protein from the rat epididymis. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2853–2860. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Kuff E. L. Structural gene identification and mapping by DNA-mRNA hybrid-arrested cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4370–4374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petra P. H., Kumar S., Hayes R., Ericsson L. H., Titani K. Molecular organization of the sex steroid-binding protein (SBP) of human plasma. J Steroid Biochem. 1986 Jan;24(1):45–49. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(86)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzen E. M., Boitani C., Parvinen M., French F. C., Feldman M. Stage-dependent secretion of ABP by rat seminiferous tubules. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Jan;25(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanborn B. M., Elkington J. S., Chowdhury M., Tcholakian R. K., Steinberger E. Hormonal influences on the level of testicular androgen binding activity: effect of FSH following hypophysectomy. Endocrinology. 1975 Feb;96(2):304–312. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-2-304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindall D. J., Hansson V., Sar M., Stumpf W. E., French F. S., Nayfeh S. N. Further studies on the accumulation and binding of androgen in rat epididymis. Endocrinology. 1974 Oct;95(4):1119–1128. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-4-1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]