Abstract
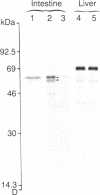
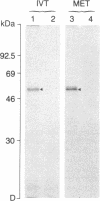
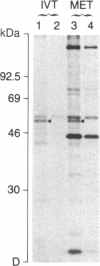
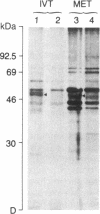
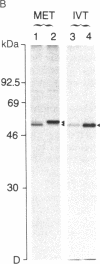
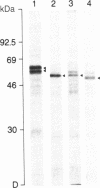
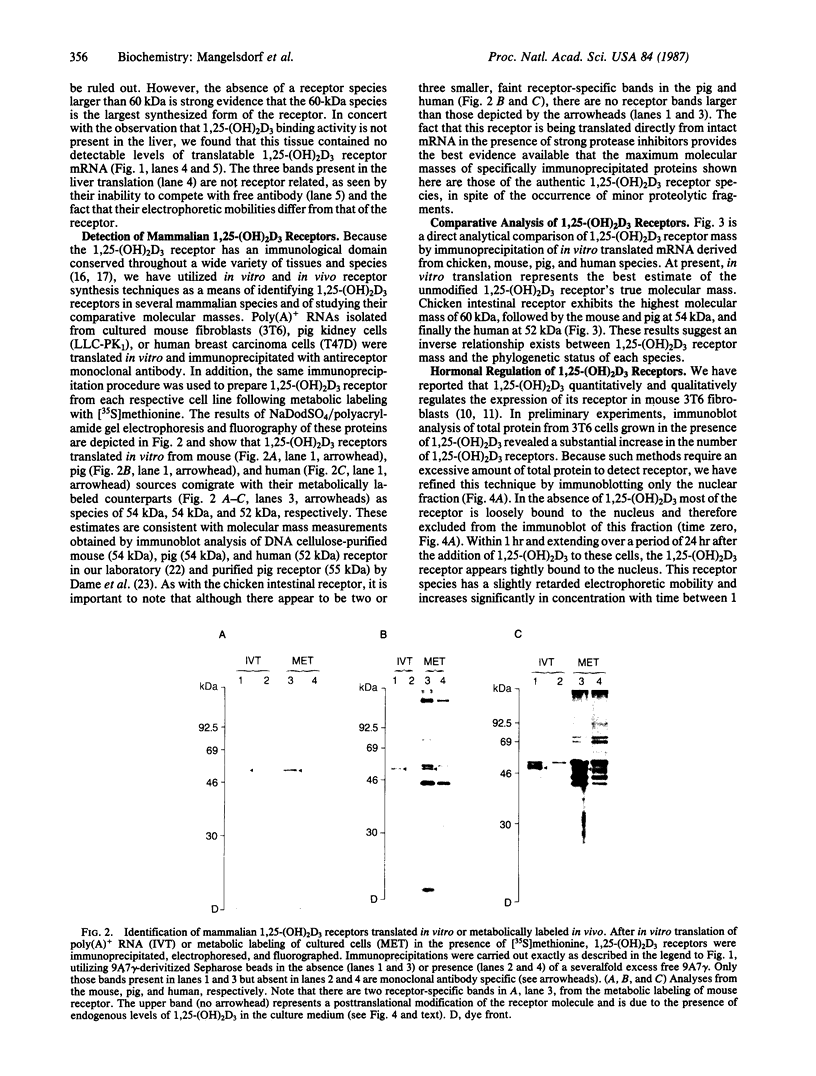
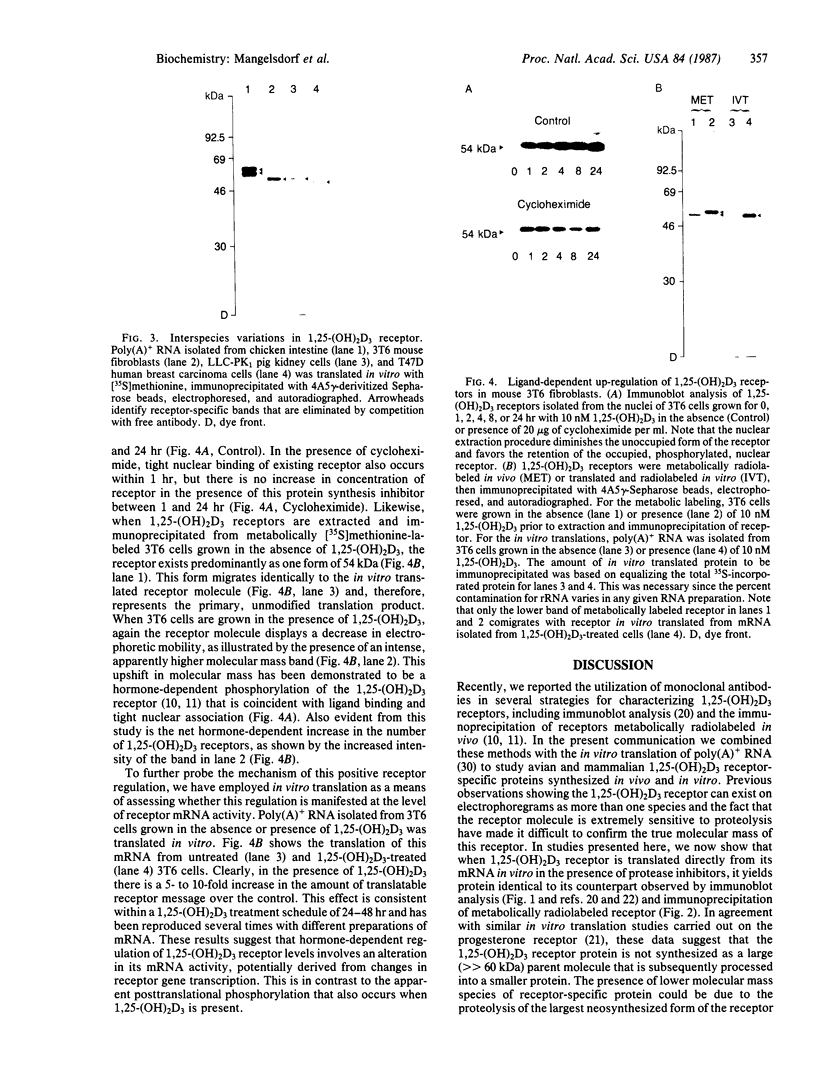
In vitro translation of cellular poly(A)+ RNA coupled with immunoprecipitation was developed as a technique for characterizing 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25-(OH)2D3] receptors and assessing receptor mRNA activity. Cell-free translation of poly(A)+ RNA isolated from chicken intestine revealed two immunoprecipitable forms of avian receptor at 60 kDa and 58 kDa. These two species were identical in electrophoretic mobility to those detected directly in intestinal cytosol by immunoblot analysis. Liver, a tissue devoid of 1,25-(OH)2D3 binding activity, contained no apparent translatable receptor mRNA. 1,25-(OH)2D3 receptors were also synthesized in vitro employing poly(A)+ RNA obtained from several cultured mammalian cell lines. Selective immunoprecipitation revealed a single form of receptor at 54 kDa in mouse fibroblasts (3T6) and pig kidney cells (LLC-PK1) and a 52-kDa species in human breast carcinoma (T47D). Each of these in vitro translated mammalian 1,25-(OH)2D3 receptors migrated identically with its cellular counterpart that was synthesized in vivo employing metabolic labeling of cell protein with [35S]methionine. In vitro translation of poly(A)+ RNA derived from mouse 3T6 cells treated with 1,25-(OH)2D3 for 24-48 hr disclosed a 5-fold increase in receptor mRNA activity over untreated control cells. These results are consistent with the conclusions that 1,25-(OH)2D3 receptors are protein species ranging from 52 to 60 kDa and that, though their functional and immunological domains have been evolutionarily conserved, an inverse relationship apparently exists between phylogenetic status and receptor mass. The data also support the hypothesis that the presence of 1,25-(OH)2D3 leads to a significant increase in receptor mRNA activity in 3T6 cells, indicative of receptor autoregulation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allegretto E. A., Pike J. W. Trypsin cleavage of chick 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors. Generation of discrete polypeptides which retain hormone but are unreactive to DNA and monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10139–10145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J., Horowitz Z. D., Copp R. P., McIntyre W. R., Pascual A., Samuels H. H. Photoaffinity labeling of thyroid hormone nuclear receptors. Influence of n-butyrate and analysis of the half-lives of the 57,000 and 47,000 molecular weight receptor forms. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12084–12091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E. M., Feldman D. Homologous up-regulation of the 1,25 (OH)2 vitamin D3 receptor in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):742–747. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E. M., Hirst M. A., Feldman D. Regulation of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors by vitamin D analogs in cultured mammalian cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):2203–2210. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-2203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame M. C., Pierce E. A., DeLuca H. F. Identification of the porcine intestinal 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels by renaturation and immunoblotting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7825–7829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M. R. Vitamin D receptors: nature and function. Annu Rev Nutr. 1986;6:527–562. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.06.070186.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Weinberger C., Ong E. S., Cerelli G., Oro A., Lebo R., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):635–641. doi: 10.1038/318635a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker W., Siebert P. D., King M. W., Stucki P., Dugaiczyk A., Norman A. W. Molecular cloning of a vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein mRNA sequence from chick intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loosfelt H., Logeat F., Vu Hai M. T., Milgrom E. The rabbit progesterone receptor. Evidence for a single steroid-binding subunit and characterization of receptor mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14196–14202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Koeffler H. P., Donaldson C. A., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced differentiation in a human promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL-60): receptor-mediated maturation to macrophage-like cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):391–398. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNutt K. W., Haussler M. R. Nutritional effectiveness of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in preventing rickets in chicks. J Nutr. 1973 May;103(5):681–689. doi: 10.1093/jn/103.5.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike J. W., Donaldson C. A., Marion S. L., Haussler M. R. Development of hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibodies to the chicken intestinal 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7719–7723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike J. W., Haussler M. R. Association of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 with cultured 3T6 mouse fibroblasts. Cellular uptake and receptor-mediated migration to the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8554–8560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike J. W., Haussler M. R. Purification of chicken intestinal receptor for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike J. W. Intracellular receptors mediate the biologic action of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Nutr Rev. 1985 Jun;43(6):161–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1985.tb02406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike J. W., Marion S. L., Donaldson C. A., Haussler M. R. Serum and monoclonal antibodies against the chick intestinal receptor for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Generation by a preparation enriched in a 64,000-dalton protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1289–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike J. W. Monoclonal antibodies to chick intestinal receptors for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Interaction and effects of binding on receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1167–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike J. W., Sleator N. M. Hormone-dependent phosphorylation of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor in mouse fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):378–385. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91813-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Baukol S. A. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 increases synthesis of the vitamin K-dependent bone protein by osteosarcoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11660–11663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai D., Gorski J. Reversible denaturation of the estrogen receptor and estimation of polypeptide chain molecular weight. Endocrinology. 1984 Dec;115(6):2379–2383. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-6-2379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert P., Hunziker W., Norman A. W. Cell-free translation analysis of the vitamin D-dependent calcium binding protein mRNA activity present in total RNA and polysomal extracts from chick intestine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Dec;219(2):286–296. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]