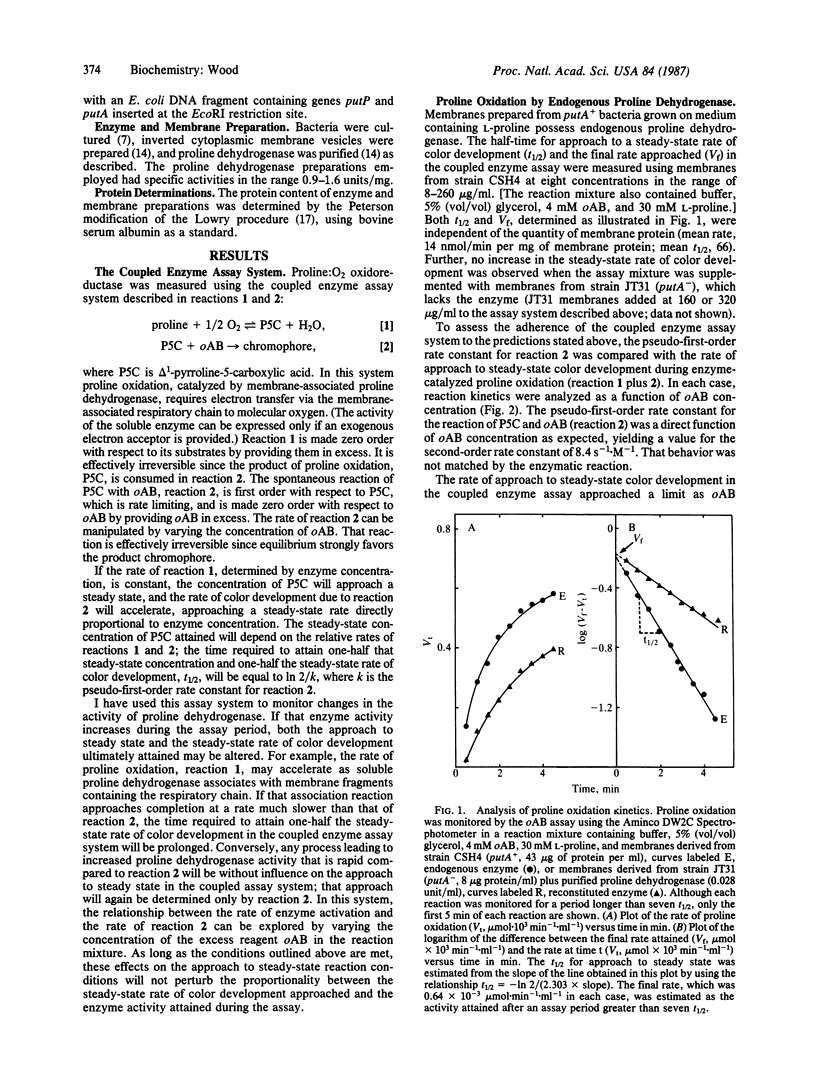
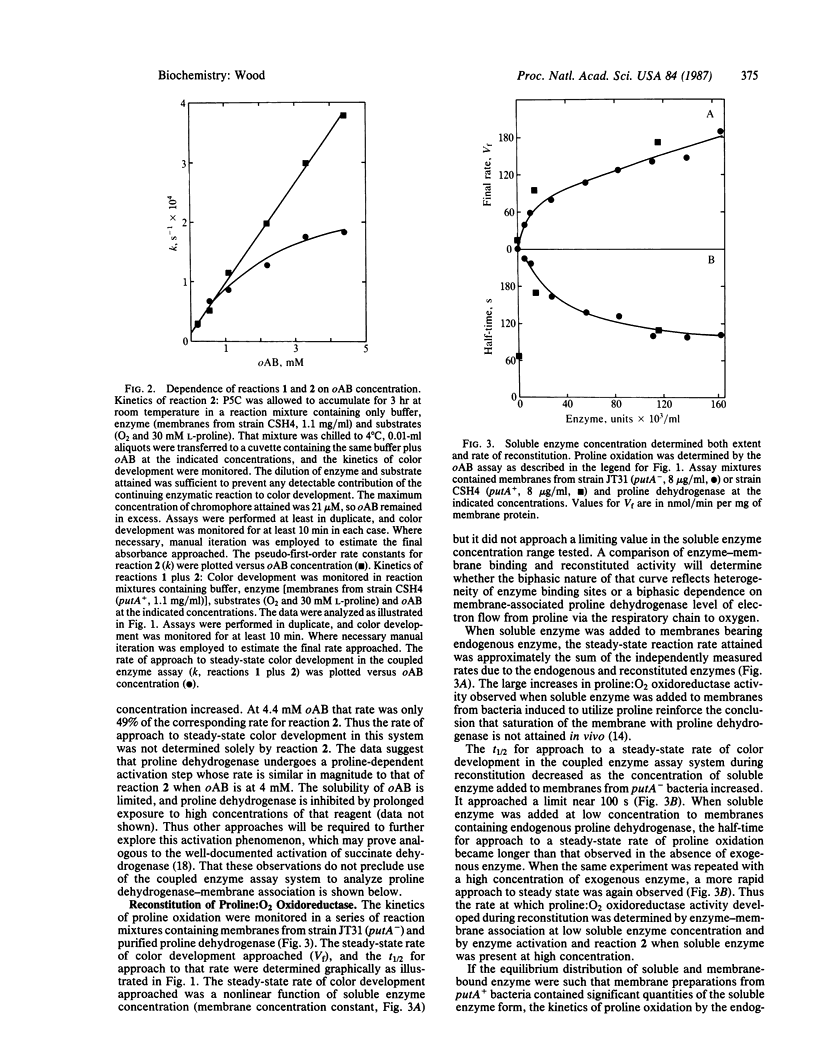
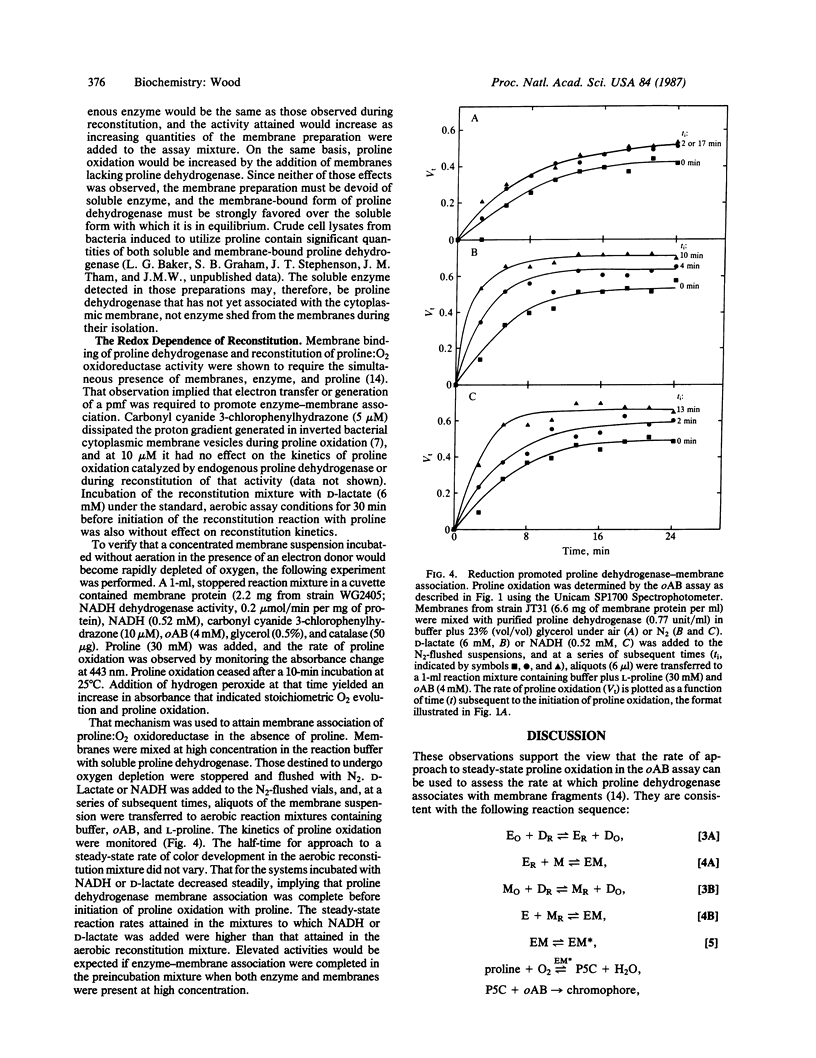
Abstract
The PutA protein, product of the Escherichia coli gene putA, has two functions essential for proline utilization and for the regulation of putP and putA expression: as the peripheral membrane flavoprotein, proline dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.99.8), it transfers electrons from proline to the respiratory chain, and, as a repressor, it controls expression of genes putP and putA in response to proline supply. Association of proline dehydrogenase with the membrane was shown to require the simultaneous presence of the soluble enzyme, membranes, and proline. The kinetics of that association, monitored by following proline oxidation in a coupled enzyme assay system, were not altered when the transmembrane proton gradient generated during proline oxidation was dissipated by a proton ionophore. However, D-lactate or NADH could replace proline as a promoter of proline dehydrogenase-membrane association under anaerobic reaction conditions. These data imply that reduction of proline dehydrogenase and/or a membrane constituent promotes enzyme-membrane association. A biochemical mechanism is suggested whereby the concentration of proline dehydrogenase associated with the respiratory chain would be determined by proline supply.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamson J. L., Baker L. G., Stephenson J. T., Wood J. M. Proline dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli K12. Properties of the membrane-associated enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;134(1):77–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Tsuchiya T., Yamane Y., Wood J. M., Wilson T. H. Na+ (Li+)-proline cotransport in Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1985;84(2):157–164. doi: 10.1007/BF01872213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Wilson T. H. Solubilization and functional reconstitution of the proline transport system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2599–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dendinger S., Brill W. J. Regulation of proline degradation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):144–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.144-152.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham S. B., Stephenson J. T., Wood J. M. Proline dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli K12. Reconstitution of a functional membrane association. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2656–2661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Olsiewski P. J., Walsh C., Kaczorowski G. J., Bhaduri A., Kaback H. R. Simultaneous reconstitution of Escherichia coli membrane vesicles with D-lactate and D-amino acid dehydrogenases. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4590–4596. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. F., Henning U. Limiting availability of binding sites for dehydrogenases on the cell membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):925–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Roth J. R. Regulation of proline utilization in Salmonella typhimurium: characterization of put::Mu d(Ap, lac) operon fusions. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):561–568. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.561-568.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Roth J. Enzymatic properties of the purified putA protein from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9762–9766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Roth J. Purification of the putA gene product. A bifunctional membrane-bound protein from Salmonella typhimurium responsible for the two-step oxidation of proline to glutamate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9755–9761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Roth J. Regulation of the genes for proline utilization in Salmonella typhimurium: autogenous repression by the putA gene product. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 5;148(1):21–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratzkin B., Grabnar M., Roth J. Regulation of the major proline permease gene of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):737–743. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.737-743.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratzkin B., Roth J. Cluster of genes controlling proline degradation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):744–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.744-754.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpulla R. C., Soffer R. L. Membrane-bound proline dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. Solubilization, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5997–6001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M. Genetics of L-proline utilization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):895–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.895-901.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M., Zadworny D. Amplification of the put genes and identification of the put gene products in Escherichia coli K12. Can J Biochem. 1980 Oct;58(10):787–796. doi: 10.1139/o80-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M., Zadworny D. Characterization of an inducible porter required for L-proline catabolism by Escherichia coli K12. Can J Biochem. 1979 Oct;57(10):1191–1199. doi: 10.1139/o79-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M., Zadworny D., Lohmeier E., Weiner J. H. Hybrid plasmids complement a putP mutation in Escherichia coli K12. Can J Biochem. 1979 Nov;57(11):1328–1330. doi: 10.1139/o79-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



