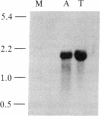
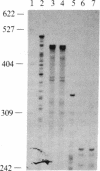
Abstract
P450c17 is the single enzyme mediating both 17 alpha-hydroxylase (steroid 17 alpha-monooxygenase, EC 1.14.99.9) and 17,20 lyase activities in the synthesis of steroid hormones. It has been suggested that different P450c17 isozymes mediate these activities in the adrenal gland and testis. We sequenced 423 of the 509 amino acids (83%) of the porcine adrenal enzyme; based on this partial sequence, a 128-fold degenerate 17-mer was synthesized and used to screen a porcine adrenal cDNA library. This yielded a 380-base cloned cDNA, which in turn was used to isolate several human adrenal cDNAs. The longest of these, lambda hac17-2, is 1754 base pairs long and includes the full-length coding region, the complete 3'-untranslated region, and 41 bases of the 5'-untranslated region. This cDNA encodes a protein of 508 amino acids having a predicted molecular weight of 57,379.82. High-stringency screening of a human testicular cDNA library yielded a partial clone containing 1303 identical bases. RNA gel blots and nuclease S1-protection experiments confirm that the adrenal and testicular P450c17 mRNAs are indistinguishable. These data indicate that the testis possesses a P450c17 identical to that in the adrenal. The human amino acid sequence is 66.7% homologous to the corresponding regions of the porcine sequence, and the human cDNA and amino acid sequences are 80.1 and 70.3% homologous, respectively, to bovine adrenal P450c17 cDNA. Both comparisons indicate that a central region comprising amino acid residues 160-268 is hypervariable among these species of P450c17. Comparison of the amino acid sequence of P450c17 with two other human steroidogenic cytochromes P450 show much greater homology with P450c21 (28.9%), another microsomal enzyme, than with P450scc (12.3%), a mitochondrial enzyme.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron J., Taylor W. E., Masters B. S. Immunochemical studies on electron transport chains involving cytochrome P-450. The role of the iron-sulfur protein, adrenodoxin, in mixed-function oxidation reactions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 May;150(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Structure of a bovine gene for P-450c21 (steroid 21-hydroxylase) defines a novel cytochrome P-450 gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Voutilainen R., Mohandas T. K., Miller W. L. Human cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc: cDNA cloning, assignment of the gene to chromosome 15, and expression in the placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8962–8966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHL E. V., BAHN R. C. Aberrant adrenal contical tissue near the testis in human infants. Am J Pathol. 1962 May;40:587–598. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebelsmann U., Zachmann M., Davajan V., Israel R., Mestman J. H., Mishell D. R. Male pseudohermaphroditism consistent with 17,20-desmolase deficiency. Gynecol Invest. 1976;7(3):138–156. doi: 10.1159/000301330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniu M., Ryan D. E., Levin W., Shively J. E. The primary structure of cytochrome P-450d purified from rat liver microsomes: prediction of helical regions and domain analysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Jan;244(1):323–337. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawke D. H., Harris D. C., Shively J. E. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. V. Design and performance of a novel gas-liquid-solid phase instrument. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jun;147(2):315–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Yoshioka H., Yamane M., Gotoh O., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes tandemly arranged in human chromosome: a pseudogene and a genuine gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2841–2845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami S., Ochi H., Kobayashi Y., Takemori S. Studies on the steroid hydroxylation system in adrenal cortex microsomes. Purification and characterization of cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid C-21 hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3386–3394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami S., Shinzawa K., Takemori S. Purification and some properties of cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylation and C17-C20 bond cleavage from guinea pig adrenal microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 15;109(3):916–921. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson K. J., Chung B. C., Urdea M. S., Miller W. L. Study of cholesterol side-chain cleavage (20,22 desmolase) deficiency causing congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia using bovine-sequence P450scc oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1296–1305. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson K. J., Picado-Leonard J., Chung B. C., Mohandas T. K., Miller W. L. Assignment of the gene for adrenal P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase) to human chromosome 10. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Sep;63(3):789–791. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-3-789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Coit D., Baxter J. D., Martial J. A. Cloning of bovine prolactin cDNA and evolutionary implications of its sequence. DNA. 1981;1(1):37–50. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 15;314(20):1321–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajin S., Shinoda M., Hall P. F. Purification and properties of 17 alpha-hydroxylase from microsomes of pig adrenal: a second C21 side-chain cleavage system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):512–517. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90336-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajin S., Shinoda M., Hall P. F. Purification and properties of 17 alpha-hydroxylase from microsomes of pig adrenal: a second C21 side-chain cleavage system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):512–517. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90336-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajin S., Shinoda M., Haniu M., Shively J. E., Hall P. F. C21 steroid side chain cleavage enzyme from porcine adrenal microsomes. Purification and characterization of the 17 alpha-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3971–3976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Miller W. L. Developmental expression of genes for the stereoidogenic enzymes P450scc (20,22-desmolase), P450c17 (17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase), and P450c21 (21-hydroxylase) in the human fetus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Nov;63(5):1145–1150. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-5-1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Tapanainen J., Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Hormonal regulation of P450scc (20,22-desmolase) and P450c17 (17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase) in cultured human granulosa cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jul;63(1):202–207. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-1-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Structure of human steroid 21-hydroxylase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachmann M., Völlmin J. A., Hamilton W., Prader A. Steroid 17,20-desmolase deficiency: a new cause of male pseudohermaphroditism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1972 Oct;1(4):369–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1972.tb00407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., John M. E., Okamura T., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Bovine adrenocortical cytochrome P-450(17 alpha). Regulation of gene expression by ACTH and elucidation of primary sequence. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2475–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]